What is a concrete production business?
Modern realities are such that a business based on the production and sale of concrete is among the most profitable ways of making a profit.
Given the dynamics of the construction industry (especially in large cities with large populations), the demand for this material continues to grow. The demand for this building material will always remain high. And its largest buyer is companies specializing in the construction industry. If you are interested in investing in this area, then the most correct decision to purchase a mini concrete plant would be at the very beginning of the construction intensification season.
As a rule, such a period is the month of May. This must be done because by the end of the season (that is, by November), you will be able to start promoting your business and make a good profit.
Hiring workers for a concrete plant
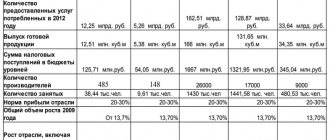
In order to open a concrete plant, it is necessary to hire about 49 people on staff. These will include:
- 4 drivers;
- 9 working storage areas for aggregates;
- 9 concrete mixing shop workers;
- 10 support service workers;
- 12 workers for the cement warehouse;
- 5 workers in the administration.
For a small concrete plant in the first stages of opening, it is not worth hiring a separate accountant and lawyer. Their salary will be an additional expense that will be difficult to cover with the initial volumes of concrete sales. In this case, it is better to use the services of third-party companies.
Studying the competitive environment between mini-factories
Before moving forward, it is worth drawing up a business plan for the development of a concrete production plant. You need to understand with whom and how you have to compete, and decide on a pricing policy. The main target consumer is developers, they will absorb up to 90-95% of your production volume (these figures are obtained based on market analysis data). The difference in the coefficient between the growth rate of the construction sector and the production of concrete is 0.9 units.
However, it is necessary to understand that a mini concrete production plant has certain specifics, in the form of geographic localization on the ground. The technology is such that it is possible to sell concrete profitably only within a radius of up to 50 kilometers from the location of the plant. Therefore, first of all, you have to assess the level of competition in the area where production development is planned. The current practice gives a real understanding that it will not be possible to win in the competition with the help of dumping in the price level of products alone.
Having studied the issue, you should understand that the vast majority of factories produce approximately the same brand of concrete mixtures and their characteristics are almost the same. Production and manufacturing technologies are well known, and anyone can master them. The company's sales volume depends only on how great the demand is in the area where your plant is located.
Serious competition can come from entrepreneurs engaged in the production and sale of construction products, using which the need to use concrete can be avoided. Problems will arise if, not far from your concrete production plant, there is an enterprise whose specialization is concentrated in the production of building structures and reinforced concrete profiles.
The ticket to the future, in which you can make systematic profits and grow your company, will be agreements with target consumers. It is important that these transactions have a long-term basis. Only in this way will you have the strength to withstand the competition.
Registering a business and choosing a tax system
In the business plan being developed, it is imperative to include the issue of registering a legal entity, in our case it will be a Limited Liability Company (LLC). This step is important for several reasons. The first is that in case of any unforeseen situations, the LLC is responsible only with its authorized capital. Secondly, any company or organization will agree to work with an organization of a similar form of ownership.
To organize and conduct the production in question, the OKVED code is determined: 26.63. The production of ready-mixed concrete requires the following standards (they must comply with established GOSTs):
- “Concrete. Methods for determining frost resistance" (10060.0-95);
- “Concrete. Squad selection rules" (27006-86);
- “Concrete. Rules for controlling compressive strength for monolithic structures" (18105 – 86).
- “Concrete mixtures. Test methods" (10181-2000);
- “The concrete is heavy and fine-grained. Technical conditions" (26633-91);
Let's move on to choosing a taxation system; in generally accepted practice, this is the general taxation system, the simplified tax system for annual revenues of less than 60 million rubles. To maintain accounting records for an enterprise, it is necessary to hire an accountant. The taxation system of the enterprise under consideration is the simplified tax system “income-expenses” 7%.
Characteristic features of mini production
The sale of concrete mixtures is accompanied by a characteristic problem - solving difficulties with organizing the delivery of products to their destination. Concrete has certain properties that require it to be transported to its destination at a strictly defined time. If you linger longer than the technology allows, the composition may harden. The composition is delivered to the construction site in specialized vehicles called “concrete mixers.”
An alternative option is to produce finished molds on site. After hardening, these forms are transported to the building site. But the most advantageous option is production right on the construction site. This is precisely the reason that requires some geographical localization of production.
Raw materials used for production
Modern technology for the production of concrete solutions requires the following components:
- One of the main components of mixtures is water. It must be of high quality and clean, and not contain foreign matter. The volume of its supply is determined by the technologist.
- Ballast mixture, also called general mixture. This is a kind of porridge of sand and gravel. The most suitable proportion of components is three parts gravel to one part sand;
- Crushed stone - crushed gravel is used as this component (the most suitable, extracted from rocks), its standard diameter is about 5 mm. Addition of slags is allowed.
- Sand. It must meet the requirements of GOST 8736-93, where the diameter of sand grains is no more than half a millimeter.
- Cement. The main component of the mixture. This is a loose powder mass of a grayish tint. During the production process of the mixture, the powder crystallizes after adding liquid.
Depending on the required brand of concrete, the proportions between the main components differ. For example, to produce grade 100 concrete we need 1 kg. cement grade 400, 4.1 kg. sand, 6.1 kg. crushed stone and water
| Concrete grade | proportions cement: sand: crushed stone | |
| cement grade 400 | cement grade 500 | |
| 100 | 1,0 : 4,1 : 6,1 | 1,0 : 5,3 : 7,1 |
| 150 | 1,0 : 3,2 : 5,0 | 1,0 : 4,0 : 5,8 |
| 200 | 1,0 : 2,5 : 4,2 | 1,0 : 3,2 : 4,9 |
| 250 | 1,0 : 1,9 : 3,4 | 1,0 : 2,4 : 3,9 |
| 300 | 1,0 : 1,7 : 3,2 | 1,0 : 2,2 : 3,7 |
| 400 | 1,0 : 1,1 : 2,4 | 1,0 : 1,4 : 2,8 |
| 450 | 1,0 : 1,0 : 2,2 | 1,0 : 1,2 : 2,5 |
We will also give the consumption of materials per cubic meter of concrete.
| Concrete grade | Cement brand | Water-cement ratio | Filler grain size, mm | Water volume, l/m3 concrete | Cement weight kg/m3 concrete | Sand weight kg/m3 concrete | Weight of crushed stone/gravel, kg/m3 of concrete |
| M100 | M300 | 0,75 | Gravel 10 | 205 | 273 | 1092 | 1092 |
| 0,8 | Crushed stone 10 | 205 | 275 | 1100 | 1100 | ||
| 0,75 | Graphy 20 | 220 | 253 | 1012 | 1012 | ||
| 0,8 | Crushed stone 20 | 190 | 256 | 1024 | 1024 | ||
| M200 | M400 | 0,63 | Gravel 10 | 205 | 325 | 1300 | 1300 |
| 0,68 | Crushed stone 10 | 220 | 324 | 1296 | 1296 | ||
| 0,63 | Gravel 20 | 190 | 302 | 1208 | 1208 | ||
| 0,68 | Crushed stone 20 | 205 | 302 | 1208 | 1208 | ||
| M250 | M500 | 0,64 | Gravel 10 | 205 | 320 | 1280 | 1280 |
| 0,69 | Crushed stone 10 | 220 | 319 | 1276 | 1276 | ||
| 0,64 | Gravel 20 | 190 | 297 | 1188 | 1188 | ||
| 0,69 | Crushed stone 20 | 205 | 297 | 1188 | 1188 |
Equipment for the production of
Despite the fact that the technology for producing building mixtures is simple, special production lines are usually installed that are fully automated. They allow you to strictly adhere to the established recipe. This line includes the following units (cost - thousand rubles):
- The cabin where the control panel is located (100).
- Dispensers separately for water and separately for cement (150).
- Plate conveyor (50).
- Rail loader (80).
- Return exit conveyor (95).
- Lift (50).
- Reducer (100).
- Belt conveyor with a capacity of 50 m3/hour (90).
- Basic concrete aggregate dispenser (320).
- Dispenser for ready-mixed concrete aggregates (260).
- Auger (135).
- Basic concrete mixer (46.5).
- Facial concrete mixer (43.3).
- Silo for 60 tons 40 m3 (477.9).
About 2 million rubles will have to be allocated for the purchase of equipment.
Staff
For smooth production and business operations at the plant, the following minimum number of workers is required.
| Job title | Qty | Salary | Salary | Total | |
| Human | rub/month | rub/shift | Payroll | ||
| RBU operator | 1 | 30000 | 1363,6364 | 30000 | |
| Loader driver | 1 | 30000 | 1363,6364 | 30000 | |
| Repairman | 1 | 30000 | 1363,6364 | 30000 | |
| Dispatcher | 1 | 20000 | 909,09091 | 20000 | |
| Technologist | 1 | 10000 | 454,54545 | 10000 | |
| Director of operations | 1 | 40000 | 1818,1818 | 40000 | |
| Director | 1 | 20000 | 666,66667 | 20000 | |
| TOTAL | 7 | 180000 | 7272,7273 | 180000 | |
Let's make a table showing the costs of the wage fund.
| Total | Total | Total | |
| 1 year | 2 year | 3 year | |
| RBU operator | 210000 | 210000 | 210000 |
| Loader driver | 210000 | 210000 | 210000 |
| Repairman | 210000 | 210000 | 210000 |
| Dispatcher | 140000 | 140000 | 140000 |
| Technologist | 70000 | 70000 | 70000 |
| Director of operations | 280000 | 280000 | 280000 |
| Director | 220000 | 240000 | 240000 |
| TOTAL PAYROLL | 1340000 | 1360000 | 1360000 |
And on payroll taxes.
| Total | Total | Total | |
| 1 year | 2 year | 3 year | |
| RBU operator | 63000 | 63000 | 63000 |
| Loader driver | 63000 | 63000 | 63000 |
| Repairman | 63000 | 63000 | 63000 |
| Dispatcher | 42000 | 42000 | 42000 |
| Technologist | 21000 | 21000 | 21000 |
| Director of operations | 84000 | 84000 | 84000 |
| Director | 66000 | 72000 | 72000 |
| TOTAL PAYROLL | 402000 | 408000 | 408000 |
It was decided to engage an accounting company under a contract for accounting services.
The amount of financial costs for the purchase of raw materials for concrete
The most popular brand of concrete, the safest to start working with, is the M 250 and M 350 grades.
Cost calculation depends on the selected production technology. In our business plan, we made a calculation based on the M 250 grade, so based on the consumption of materials per 1 m3 of ready-made concrete, the following figures will be obtained:
- M 250: crushed stone – 1280 kg, cement – 320 kg, sand – 1280 kg, water – 205 liters
Materials are purchased from officially operating quarries in the city of Yekaterinburg and nearby cities that have the necessary certificates and strength test reports for their material, etc., the cost of the material includes delivery to our territory
The volume of material consumption per 1 m3 of the finished product will be 2000 rubles, water costs will be included in utility costs, because We do not purchase water, but get it from a well.
There are other associated costs - staff salaries, costs for work clothes and equipment for work, diesel fuel for the loader, payment for electricity and site rental. If all this is taken into account, then the production cost will increase to 2,250 rubles per 1 m3 of finished concrete. The next section of the business plan provides a detailed table of variable and fixed costs.
Calculation of the cost of concrete production
Characteristics such as strength, frost resistance, ductility, etc. can be improved with special additives.
When carrying out construction work, the cost of concrete plays an important role. The contractor either buys ready-made mortar from organizations that sell dry and liquid concrete, or produces it himself directly on the construction site using a concrete plant of one type or another (all-terrain self-loading batching unit , mobile or stationary concrete plant). Concrete production requires a careful assessment of profitability.
In the first case, calculating the cost is quite simple; just look at the supplier’s price list, select the desired brand of concrete and add the cost of delivery to the site. If the customer does not have his own transport for delivery, then its price will depend on several factors, in particular, on the place where the finished product needs to be delivered, on the quantity of concrete ordered, as well as on the form in which it must be delivered to the site - dry or ready. Most often, delivery is carried out by a mixer or a regular truck.
In the second case, calculating the cost of concrete production seems to be a little more difficult, but the obvious difference in the final figures will undoubtedly show the benefits of making the concrete mixture yourself and will be worth the effort. Cost influences the choice of the most efficient and economical method of concrete production.
To simplify the calculation of the profitability of concrete production as much as possible, we have prepared a special table, thanks to which you can find out the cost of producing 1 m³ of concrete mixture using the three main models of Carmix mobile concrete plants (you need to use the table corresponding to the concrete mixer model). The mobile RBU CARMIX 2.5 TT produces up to 80 m³ per shift (up to 10 m³ per hour), CARMIX 3.5 TT - up to 105 m³ (up to 15 m³ per hour), CARMIX 5.5 XL - 130 m³ and more (up to 22 m³ per hour).
All that is needed for the calculations in the table is to enter the cost of one ton of crushed stone (the fraction for making concrete with a CARMIX mixer should vary from 5 to 10 mm), sand and cement in your region. The cost of fuel, maintenance and operator wages can be left unchanged (we took into account the average figures for Russia) or you can also enter your own data for a more accurate calculation:
Such a calculation makes it easy to assess the profitability of producing concrete using a self-loading concrete mixer CARMIX: it is not only profitable, but also effective in terms of the self-sufficiency of this equipment.
It should be noted that significant cost savings when producing concrete on your own are not least due to the absence of costs for transporting the finished mixture. Bring the inert materials to the site - CARMIX will do the rest for you!
We have prepared a calculation of the cost of producing concrete using a self-loading mixer CARMIX in several regions of our country: the Far East, Siberia, the Urals and Crimea. First, we will provide data on current prices for inert materials (rubles per ton) in the corresponding cities, then - calculations of the cost of concrete produced by three Carmix models, obtained using the table.
| REGIONS | ||||||
| Far Eastern Federal District | Ural federal district | Siberian Federal District | Crimean Federal District | |||
| Kamchatka region, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | Sakhalin region, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | Sverdlovsk region, Ekaterinburg | Krasnoyarsk region, Krasnoyarsk | Irkutsk region, Irkutsk | Republic of Crimea, Simferopol | |
| crushed stone | 900 | 1000 | 980 | 760 | 605 | 800 |
| sand | 500 | 500 | 1400 | 970 | 530 | 1650 |
| cement | 4500 | 4500 | 2600 | 3700 | 3750 | 5600 |
| COST, rub | ||||||
| Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | Ekaterinburg | Krasnoyarsk | Irkutsk | Simferopol | |
| CARMIX 2.5TT | 2734,83 | 2842,83 | 3279,15 | 2728,38 | 2225,57 | 3855,45 |
| CARMIX 3.5TT | 2713,98 | 2821,98 | 3258,09 | 2707,52 | 2204,92 | 3833,69 |
| CARMIX 5.5 XL | 2715,15 | 2823,15 | 3259,73 | 2709,03 | 2206,30 | 3834,88 |
The CARMIX mini-concrete plant helps save money and resources, and provides productivity sufficient for the construction of small and medium-sized facilities. Thanks to mobility, there are no costs for transporting ready-made concrete to the unloading site, and compactness and maneuverability ensure complete autonomy on the construction site.
You can find the table on the main page of the site by clicking on the CALCULATION OF CONCRETE COST button.