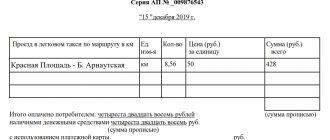
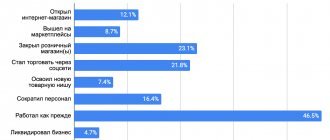
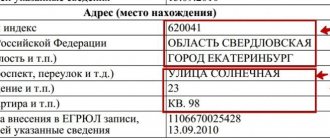
alternative liquidation” appeared in the Russian Federation.
».
This concept denotes the termination of a company’s activities, a formal, conditionally legal withdrawal of a legal entity from its obligations to creditors. Let's consider methods of alternative liquidation and their consequences.
The first method is “reorganization”. During reorganization through merger or accession, the company will be deleted from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but as a result a legal successor will appear. After the reorganization, all responsibilities of the company, including those not fulfilled and not identified before, are transferred to the newly formed legal entity.
For example, an LLC has large debts and cannot pay off all creditors, but does not want to give away its own. The owner of the company first withdraws all assets, usually through fictitious transactions. Then the founders and directors, the place of registration of the organization and the name are changed. After these machinations, a reorganization is announced in the form of annexation, and sometimes merger.
As a result, the debtor legal entity ceases its activities and disappears. All his responsibilities are transferred to another organization. As a result of all this paperwork, documents confirming the debt disappear. Alternative liquidation completed successfully.
Despite this, the disadvantage of alternative liquidation is that the legal entity remains. And there is a high probability of verification of the successor. Checking the successor also means auditing the activities of the predecessor company. Who will be responsible for its work? Of course, the one who managed it or owned it before the “reorganization”. Consequently, the former management and owners may be brought to criminal and subsidiary liability.
The second way is to change participants and management, which actually means its sale. The company will simply be re-registered to a third party. The renewed company has a new extract from the state register and can fully function. The cost of such services depends on how problematic the organization is and how active the regulatory authorities will show interest in it.
After re-registration, the company continues to operate, so third parties can make claims against it, try to collect debts, etc. However, the founders are not liable for the obligations of the organization, except in case of emergency. If the bankruptcy of a legal entity is caused by the actions of the owners, they may be held subsidiary liable for the obligations of the legal entity (Clause 3 of Article 56 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). And also, if any claims arise regarding the “old cases,” the new organization will continue to function, and proceedings will be conducted with the previous owners and management.
The third way is to stop using the company. In accordance with Art. 64.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 21.1 and clauses 7 - 8 art. 22 of the Federal Law “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs”, the procedure for excluding an inactive legal entity from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities means that the company has actually ceased its activities.
A decision to exclude from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities can be made if the following circumstances exist simultaneously: 1) the legal entity has not submitted tax reports over the past 12 months; 2) did not carry out transactions on at least one of her accounts. If a company has several accounts, then there should be no transactions on any of them (clause 1 of the information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 17, 2006 N 100).
In order to get rid of the company, the owner only needs to withdraw assets in advance, fire all staff and wait about 1.5 - 2 years. The registrar, having made a decision to exclude from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, informs the owner of the company, creditors and other interested parties about this, indicating the address and publishing it in the State Registration Bulletin. Interested parties may submit an application within 3 months from the date of publication of the registrar's decision to block the administrative procedure for terminating the activities of the counterparty. (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service ZSO dated February 20, 2013 in case No. A81-921/2012). The risk of impossibility of collecting debts as a result of the company’s exclusion from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities lies with its creditor (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service ZSO dated 06.08.2014 in case No. A03-13327/2013). Therefore, we can say that if creditors did not have time to declare themselves after the debtor was excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, then they do not have the right to recognize the debt (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 11, 2012 N 03-03-06/1/649 and dated November 8, 2012 N 03 -03-06/1/577). But interested parties can appeal the decision to exclude them from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities within one year from the day they learned or should have learned of a violation of their rights.
Each of the methods of alternative liquidation can attract the attention of Federal Tax Service employees and trigger a tax audit. The result of such checks may be the emergence of civil claims by creditors, the need to pay penalties and fines for administrative and tax penalties.
However, it is not uncommon to initiate criminal cases against former leaders. For example, under Article 177 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for malicious evasion of repayment of accounts payable, under Article 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for tax evasion, or under Article 173 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for illegal entrepreneurship. In addition, alternative liquidation may fall under such a crime
, as Art. 173.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation for the formation (creation, reorganization) of a legal entity through dummies and Art. 173.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for criminal liability for the illegal use of documents aimed at the formation (creation, reorganization) of a fictitious legal entity.
Therefore, it can be said that in case of fictitious closure of companies by incorporation/merger or simply re-registration to a third party, the owner bears responsibility for failure to fulfill obligations to creditors, failure to pay taxes, and even criminal liability.
According to S. Kleimenov, alternative liquidation is a lottery or even fraud, in which the legal entity is not liquidated, and the likelihood of negative consequences increases. However, the choice is up to the owner to formally liquidate the company or alternative liquidation. Liquidation by “white” methods in accordance with the law is a lengthy and expensive procedure, but it guarantees peace of mind in the future.
Alternative liquidation of an LLC is a procedure in which a legal entity is abolished with a minimum of costs and tax audits. This technology is quite in demand, as it reduces the time for carrying out all operations. It does not involve significant costs, like a standard procedure. There is no need to undergo many inspections by government agencies, which is important if a legal entity has debt and other controversial issues.
There are two main ways of alternative abolition: through a change of general director and reorganization. In the second case, the company ceases to exist, whereas if key persons change, it can continue to operate.
Is it possible to just quit the company?
When leaving a company, there are 3 options for the development of events.
- A company without debts When a company has signs of an inactive organization, the tax office excludes it from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. The general director is included in the register of unscrupulous entrepreneurs, so for 3 years he will not be able to be a participant or head of commercial organizations.
- A company with tax debts The tax office, after excluding the company from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities for 3 years, can hold the participants to subsidiary liability, that is, the debts will still be collected from you.
- A company with debts to counterparties. Here everything depends on the activity and mood of the creditors, so a variety of options are possible, from judicial collections to the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings.
Sale of company shares and change of director
The founders' shares are sold, the general director is replaced. A formal purchase and sale agreement is drawn up.
As a result, the company record remains in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but with new founders and a general director.
Simplified procedure
- We are preparing a package of documents for registration of the purchase and sale of shares
- we are preparing documents for changing the general director
- the transaction for the purchase and sale of shares is drawn up by a notary (about 10 days)
- we submit documents on the change of general director to the tax office
- we receive documents confirming successful registration of changes
The period for completing and registering the purchase and sale of shares and the simultaneous change of director is about 14 days.
Alternative liquidation through change of ownership and reorganization
The desire to avoid scrutiny, publicity, or the desire to quickly get rid of the business after being elected to a position incompatible with business or leaving for government service has led to the fact that business leaders also resort to alternative liquidation and its variations:
- Change of CEO and change of owner. The period for such separation from the business is calculated from 15 days. In this case, the organization continues to function, but its general director and founder change. At best, a change of ownership occurs through a sale. By resorting to this method, the business manager expects that responsibility is transferred to other persons. Contrary to the misconception that this method makes it possible to avoid wide publicity due to the absence of the need for publication, we note that there is an obligation to publish. It is established by clause 4 of Art. 6 of the LLC Law. Systematic failure to comply with a requirement is a consequence of the lack of a legally established sanction. If, as a result of such a “sale,” the organization ceases its activities, then it is subsequently excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities at the initiative of the tax authority, and this is a successful option for ending the fate of the organization.
- Reorganization by merger. The period for such termination of the company’s existence is from 6 months. In this case, the organization is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but it has a legal successor. By resorting to this method, business management expects that responsibility also passes to other persons. This method does not guarantee that verification can be avoided (see paragraph 10 of Article 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Demand creates supply. Since there is demand, the market responds with an abundance of offers for alternative liquidation. Sellers of such services do not give any guarantees, do not think much about documentation, and in some cases openly hold back when advising on the benefits of alternative liquidation. As a result of turning to such businessmen, the debts and problems of the first persons do not disappear, but for creditors the procedure for holding them accountable becomes more expensive and takes longer. The rise in cost of the collection procedure actually eliminates some of the creditors. If the creditor is principled or if the amount of debt is large, then responsibility cannot be avoided.
Entry of a new participant through an increase in authorized capital and change of director
This method of alternative liquidation is quite similar to the method of selling shares. A prerequisite is that the charter should not prohibit the withdrawal of a participant from the LLC.
Procedure
- A new participant enters the LLC, contributing his share and thereby increasing the authorized capital.
- Old participants leave the LLC
- The CEO is changing
- As a result, the company will remain in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but it will have a new composition of founders and a general director.
The re-registration period is about 14 days
- We are preparing a package of documents for introducing a new participant into the LLC
- state registration procedure
- We are preparing a package of documents for the withdrawal of an old participant from the LLC
- state registration procedure
- At the same time, we are carrying out the procedure for registering a change of general director
Change of leadership
This method involves selling the company to a third party. The old owners will no longer be involved in it and will no longer be responsible for current affairs. However, they can always be contacted with questions regarding previous activities.
At the same time, new participants first join the company, are appointed to management positions, and old ones leave it, about which changes are made to the company’s charter. In addition, the previous founder can be removed by other participants based on a court decision.
Replacement of some of the founders and general director
With this type of alternative liquidation, not all founders leave the LLC. The general director changes, and some of the founders sell their shares to third parties or leave the company.
Simplified procedure
- we are preparing documents for the sale of LLC shares to new participants (third parties)
- registration of changes with the tax office
- we prepare documents for the withdrawal of participants from the LLC
- registration of changes with the tax office
- At the same time, the procedure for changing the general director takes place
Please note that when selling LLC shares to third parties, notarized registration of the agreement and the permission of the spouse are not required. The duration of the procedure is about 14 days.
As a result, the company remains in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but with a new general director and a partially updated composition of founders.
What is the best way to close a company?
Let's consider how an alternative liquidation of an LLC can be carried out. In this case, there will definitely not be a tax audit, the whole process will take much less time and will cost much less. As a result, the enterprise will continue to function, but completely different people will be at the helm, or it will cease to exist. Thus, the founders will “retire” with a clear conscience.
The procedure can be implemented in different ways. One of them involves the replacement of all the main persons of the company, and in other cases there is a reorganization in the form of the merger of one organization with another or a merger when another legal entity arises.
However, you should not think that everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. Tax authorities are showing increased interest in such companies. Therefore, if, for example, the activity continues, the company may soon face a tax audit, which will be carried out with special care. The risk of this event may be somewhat reduced if the affiliated organization is located in another region.
So, there are 2 ways to carry out alternative liquidation. They differ mainly in that if the management changes, the company will continue to operate. At the same time, during reorganization, it ceases to exist, and another organization becomes the legal successor.
Taking the company offshore
Offshore is a territory in which economic activity has significant benefits for non-residents of the country. These countries and territories are included in a special list of the Federal Tax Service and do not provide exchange of tax information.
Until recently, offshore companies included the UK, Latvia, Cyprus, Hong Kong, Seychelles, Belize, and the Virgin Islands.
On January 1, 2020, Hong Kong, the Virgin Islands, Congo, and South Korea officially ceased to be considered offshore in Russia. On January 1, the Convention for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and the Prevention of Tax Evasion between Russia and Brazil also comes into force.
Depending on the legislation, offshore companies may not have the right to conduct economic activities on the territory of the state.
When registering on the territory of the Russian Federation, the company’s activities must be completely transparent; when registering offshore, the owners and conduct of the business remain confidential.
Usually, to register a company offshore, you need to pay state fees. duty, rent office space and hire employees to conduct activities. You can also simply buy an offshore company.
Risks of alternative liquidation
Criminal Code of the Russian Federation N 63-FZ (as amended on February 19, 2018)
ILLEGAL FORMATION (CREATION, REORGANIZATION) OF A LEGAL ENTITY ARTICLE 173.1.
- Formation (creation, reorganization) of a legal entity through nominees, as well as submission to the body carrying out state registration of legal entities, resulting in the entry into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities of information about nominees, is punishable by a fine in the amount of one hundred thousand to three hundred thousand rubles or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of seven months to one year, or forced labor for a term of up to three years, or imprisonment for the same period.
- The same acts committed:
a) by a person using his official position;
b) by a group of persons by prior conspiracy, –
shall be punishable by a fine in the amount of three hundred thousand to five hundred thousand rubles, or in the amount of the wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of one to three years, or by compulsory labor for a term of one hundred eighty to two hundred forty hours, or by imprisonment for a term of up to five years. .
Civil Code of the Russian Federation (part one)” dated November 30, 1994 N 51-FZ (as amended on December 29, 2017)
Article 53.1. Responsibility of a person authorized to act on behalf of a legal entity, members of collegial bodies of a legal entity and persons determining the actions of a legal entity
- A person who, by virtue of the law, another legal act or the constituent document of a legal entity, is authorized to act on its behalf (clause 3 of Article 53), is obliged to compensate, at the request of the legal entity, its founders (participants) acting in the interests of the legal entity, losses caused by his fault to the legal entity.
A person who, by virtue of the law, another legal act or the constituent document of a legal entity, is authorized to act on its behalf, shall be liable if it is proven that in the exercise of his rights and performance of his duties he acted in bad faith or unreasonably, including if his actions ( inaction) did not correspond to the usual conditions of civil turnover or normal business risk.
- The responsibility provided for in paragraph 1 of this article is also borne by members of the collegial bodies of a legal entity, with the exception of those of them who voted against the decision that caused losses to the legal entity, or, acting in good faith, did not take part in the voting.
- A person who has the actual ability to determine the actions of a legal entity, including the ability to give instructions to persons named in paragraphs 1 and 2 of this article, is obliged to act in the interests of the legal entity reasonably and in good faith and is responsible for losses caused to the legal entity through his fault.
- In case of joint infliction of losses to a legal entity, the persons specified in paragraphs 1 – 3 of this article are obliged to compensate the losses jointly and severally.
- An agreement to eliminate or limit the liability of persons specified in paragraphs 1 and 2 of this article for committing unfair actions, and in a public company for committing unfair and unreasonable actions (paragraph 3 of Article 53) is void.
An agreement to eliminate or limit the liability of the person specified in paragraph 3 of this article is void.
For questions regarding bringing former founders and managers of an organization to subsidiary liability, consult a lawyer by phone
0
0
0
0
Reorganization of a legal entity
Reorganization of a legal entity can be carried out in various ways. However, in any case, the procedure involves the termination of the company’s existence in its current format.
It becomes the property of the receiving company. Reorganization is carried out in two ways:
- Merger
. Involves the abolition of the previous legal entity. All rights to the company are transferred to the new LLC. To do this, you will need to register a new person in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. The procedure will take about a week. Before completing the procedure, the liquidated company is required to go through certain legislative processes. These include notifying creditors of the transaction. It is necessary to send them special notifications confirming their receipt, and also publish the news about the abolition in the State Registration Bulletin. A merger is carried out, after which a certificate of termination of the activities of the legal entity is provided. A certificate of registration of the legal successor is also issued. All LLC tax liabilities must be paid by the new owners. - Joining
. It looks like a merger, but the mechanisms differ in the following way: upon merger, all companies complete their work except the one to which the rights to all other abolished LLCs will be transferred. Among the advantages of the event, it can be noted that there is no need to obtain a certificate of absence of debt from the Pension Fund. This simplifies the process and makes it faster. After the procedure is completed, you can receive a certificate confirming its confirmation, as well as the termination of the activities of the remaining companies.
The merger involves the dissolution of the former LLC.
Let's consider the advantages of reorganization:
- The legal entity is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- There is no need to collect a lot of documents;
- The event will take about three months.
Among the disadvantages of the procedure are:
- If creditors present their demands, it will be impossible to carry out the reorganization. First you need to fulfill all the necessary requirements;
- Increased risk of subsidiary liability of previous owners.
These are the most common methods and are an alternative to the standard procedure. Their choice depends on the preferred timing of the event, as well as on the organization’s debts.