What is "cession"
Assignment is the transfer (assignment) of rights to claim debt. Currently, the most understandable example of assignment is the transfer of the right to collect receivables or a loan issued to a legal entity or individual by a bank to a collection agency.
Also, the concept of “cession” is used in Russia to refer to an agreement for the transfer of rights and obligations within the framework of shared construction from one shareholder to another (occurs with the consent of the developer). However, due to the fact that in this case not only rights and obligations are transferred, in the strict sense it is impossible to call such an agreement “assignment”.
The concept of “cession” is used in Russia to refer to an agreement for the transfer of rights and obligations within the framework of shared construction from one shareholder to another.
Legislative regulation of assignment in Russia
The basis of the Russian legislative framework in the field of assignment agreements is Chapter 24 of the Civil Code “Change of persons in an obligation”, Articles 155 and 279 of the Tax Code. Letters from the Ministry of Finance and clarifications from the Supreme Court are devoted to certain regulatory parameters.
The activities of collection agencies are regulated by Federal Law 230-FZ, dedicated to the protection of the rights and interests of individuals when returning overdue debts and carrying out the activities of microfinance organizations.
Please note that in January 2020, changes were made to this law that significantly reduced the rights of collectors.
Parties to the process of transfer of foreclosure rights
In simple terms, assignment is the transfer of rights to claim debt repayment. Now let's look at which parties are involved in this process and what rights they are endowed with, that is, who are the assignor and assignee?
- The assignor is the original owner of the rights to the debt. This role is most often played by banks and credit organizations that provide loans to legal entities and individuals. In problematic situations, when debt repayment is delayed, these organizations, as a rule, trying to avoid losses, transfer the right to collect debt to a “profile” organization. Russian legislation gives banks and credit organizations such a right, therefore the transfer of rights to claim the repayment of loans is completely legitimate if the requirements of the law are met. The main requirement is the transfer of rights to return only the debt, but not associated expenses, for example, moral damage. Please note that the amount of debt includes interest and penalties. However, the loan is transferred exclusively in the form in which it is described in the agreement. Changing the terms of the loan - adding additional fines, interest, changing the rate - is strictly prohibited.
- Assignee is the recipient of the rights to claim repayment of the debt. Banks and collection agencies most often act in this capacity. An assignee is a third party who was not initially involved in the conclusion of the agreement between the borrower and the creditors. The new owner of the rights to repay the loan has the same powers as the original one - no less, but no more. For example, if the original agreement provided for the option of repaying the debt by transferring property, the assignee also receives the right to do so. Conversely, if there is no option to repay the loan through the sale of property, the assignee does not have the right to demand repayment of the debt in this way.
- Debtor is a legal entity or individual who has a problem debt (overdue loan).
The new owner of the rights to repay the loan has the same powers as the original
Assignor, assignee and debtor - features of an assignment agreement
- Financial. The right is confirmed exclusively by a signed agreement and accompanying documents, which indicate the exact remaining amount that should be returned.
- Property. The volume of documentation here is much larger, and each unit will require a separate document that will confirm ownership of the property.
In any case, during the conclusion of a tripartite agreement, it is very important to inform the third party, in relation to whom all rights and obligations apply. Often, persons sign all formalities in the presence of the “debtor,” because in this case he is automatically considered notified and a whole series of formalities that must be resolved in the coming days can be avoided.
: April 03, 2016
The relationship between the assignor and the assignee of the debtor can arise in a wide variety of cases, but they always come down to drawing up the appropriate agreement. There are quite a few peculiarities of office work in this case, however, only in exceptional cases is the debtor notified.
A similar agreement is used in the financial sector in quite a number of areas, because often the creditor does not have the ability to collect the required amount on his own.
Most civil legal relations between two entities become the basis for the emergence of obligations of one to the other. There are quite a few types of contracts for their execution. Each specific case may differ radically in the following features:
- The parties can be represented by individuals (PEs) or legal entities (LEs).
- The type of agreement depends solely on the need that arises - loan, purchase and sale, lease, etc.
- Obligations assumed: transfer of financial resources, property, provision of services, etc.
The contract itself is considered concluded immediately after it is signed by both parties. During the drafting process, you need to indicate absolutely all the conditions, because both parties during the validity of the agreement will have to adhere to all the nuances that are indicated here. Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for recognizing the fulfillment of conditions.
During the interaction, a situation may arise in which one of the parties is no longer interested in further cooperation.
For example, the debtor does not repay the loan on time, or even has serious arrears. Here the bank simply wants to return the money assigned to it as quickly as possible.
It is on this basis that the transfer of powers occurs from one organization (assignor) to another (assignee).
An assignment agreement is a transfer of the right to claim under a contract.
- Assignor. A company that transfers its rights and obligations to the debtor
- Debtor. The party who owes a debt or obligation to a partner.
- Assignee. A company that assumes the right to claim obligations in relation to the second party. Read here the procedure for collecting loan debt.
In the process of concluding a transaction, it is imperative to consider all the features of the interaction of the debtor with the assignor, because only in this case will it be possible to achieve optimal results and fully clarify the legal framework within which the assignee will operate.
When drawing up an agreement on the assignment of property rights, it is required to use generally accepted literature. This approach ensures uniformity of all terms and also significantly simplifies office work in the future.
Cession – from Latin means “assignment” or “transfer”. If we consider the assignment agreement, then there are several fundamental factors:
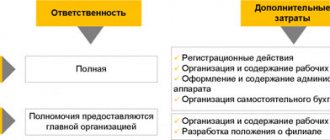
- The concession is complete. After the conclusion of the contract, all rights and obligations of the assignor are transferred to the assignee, while this should not affect the debtor for the worse.
- Benefit. The transfer of rights implies compensation, which is most often expressed in financial terms, although legal aspects are often indicated.
In the process of concluding an assignment agreement, it is necessary to take into account that it is the assignor who assumes most of the formal responsibilities, because he needs to confirm the legality of the requirements presented to the debtor. And after that, also provide the assignee with all the documents that will confirm the rights to any property transferred.
The compensation that the assignor receives from the assignee depends on many factors. Thus, one of the most important conditions is the complexity of debt collection.
If the debtor maliciously evades his obligations or occasionally disappears from sight, then the amount of compensation increases significantly, because
It is important to understand that such an approach is beneficial not only to the assignor, but also to the assignee, and together with them will help the debtor get out of an unpleasant situation.
There are many types of agreements that can be concluded under a wide variety of conditions - divorce, enterprise reorganization, failure to complete a transaction, and many others. With all the diversity, there are also the most popular among all:
- Between YL. It is most common during the reorganization of an enterprise, and in this case only the name of the debtor changes. During the transaction process, stamps will be required on both sides.
- Between FL. Such agreements do not need to be notarized, but all details must be included - passport numbers, full name, amount, terms and method of return. Most often, such relationships arise when dividing property, transferring children's debts to parents or vice versa, and providing support in obtaining a loan.
- Transfer from legal entity to individual entrepreneur. The most common case is the bankruptcy of an enterprise, in which all responsibilities of the legal entity are transferred in full to the director personally. The agreement is sealed on one side and signed on the other. Read more about the concept of bankruptcy here.
The assignor assumes most of the formal responsibilities.
When concluding contracts, all parties must adhere to a number of conditions:
- Openness. It is necessary to indicate all the required details, including signatures and seals for legal entities, as well as passport data from individuals.
- Conditions. All conditions for the transfer of rights must be clearly reflected in the contract, because only in this case can each party be completely confident in their legal security.
- Price. Indicated when the contract is for a fee. If it is free of charge, then this will also need to be indicated.
- Documentation. A complete list of documentation that was provided to confirm ownership of the property, as well as all additional formalities, is indicated.
- The agreement that started it all. It must certainly be available, and its data must be transferred to the newly compiled one.
- Date of. This specifies the precise moment at which rights and obligations are transferred from one party to the other. Most often, this moment is the signing of the contract, although the time of transfer of all necessary accompanying documents is often used.
There are a number of factors that make the conclusion of such agreements impossible. Among them are the payment of alimony and compensation for material damage incurred as a result of harm to health or life.
In addition, it should be remembered that such a transaction cannot contradict the law or other legal acts.
Declaring insolvency can be made much easier by a bankruptcy lawyer. In difficult cases, it is better to seek help from a specialist at the very beginning of the process. Credit organizations often transfer the rights to collect debt to third parties, that is, they enter into an assignment agreement. Find out more about where to get protection from creditors here. You should not delay contacting specialists.
The assignor and assignee are equally interested in ensuring that the debtor fulfills its obligations by legal means. Most often, the methods of claim and possible sanctions are prescribed in the text of the contract itself, although it is often necessary to refer to the current legislation.
In the process of concluding an agreement, only two parties often participate, and the third party is notified of the transfer of rights only after signing. This is due to the fact that this action will not bring any legal changes to the latter, and the party to whom compensation will be sent can be absolutely anyone.
If the debtor was not notified and sent the funds to the assignor at the address indicated in the original agreement, then the obligations are considered fulfilled to the assignee. All further disputes should no longer affect the rights and freedoms of the debtor, and all imposed sanctions should be declared unlawful and immediately cancelled.
Civil legal relations between two entities are often the reason on which one of the parties to such relations may have obligations towards the other.
Despite the fact that the legal nature of such relations will be quite similar, their specific conditions and circumstances may differ significantly: for example, the parties may be individuals or legal entities, the agreement concluded between them may be a loan, lease or other type of agreement, and the obligation assumed by one of the parties in accordance with it may consist of the transfer of an item or value, the provision of services, the performance of any work or other actions.
Moreover, in all of these cases, it is a written document signed by both parties between whom the agreement is concluded that confirms the fact that both parties agree with the rights and obligations that such a document imposes on them. It is assumed that all specific conditions for fulfilling obligations under the contract and the procedure for recognizing them as fulfilled are also fully reflected in the document signed by the parties.
Attention!
However, subsequently the borrower repeatedly violated the terms and conditions specified in the agreement. In this regard, the banking institution was no longer interested in having a long-term financial relationship with this borrower.
Types of assignment agreements
In legal practice, there are several options for assignment agreements:
- Paid. In this case, the assignor pays the second creditor to buy out the debt, and then compensates for losses by repaying the loan by the debtor.
- Free. There is no payment for such assignment of debt.
- Paid - the assignor pays collectors for the assignment.
- Free - the assignee works under a free agreement.
- Trilateral. The debtor participates in signing the agreement.
- By court decision or writ of execution.
What debts are transferred under an assignment agreement?
Not all types of debt can be transferred by assignment. The most common ones include:
- overdue loans, credits, advances;
- bills and other securities;
- accounts receivable for any material goods - goods and products.
The Civil Code provides for only one significant limitation on the transfer of debt to a third party (Article 388) - the transfer limitation is the essential importance of the identity of the creditor for the debtor. Thus, debts based on the identities of the creditor and the borrower (for example, between close relatives) cannot be transferred.
Legislative framework applied when registering a cession
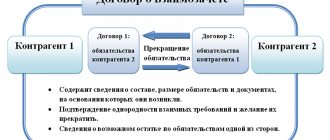
Whatever transaction is regulated by the assignment agreement, three parties always take part in it: the assignor, the assignee and the debtor. At the same time, the legislation regulates the rights of each of the participants in this “triangle”. They are established, in particular, by Art. 388 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to it, such an assignment of the right of claim is allowed only in situations where it does not contradict the current legislation. Claims for obligations that are personal in nature cannot be transferred, for example:
- payment of alimony;
- compensation for damage caused (for example, damage to life or health);
- compensation for moral damage.
The original agreement between the creditor and the debtor may contain a clause prohibiting the conclusion of an assignment agreement and the transfer of debt to another person. However, if it is nevertheless concluded, it cannot be considered void. It will be legal, paradoxically as it may seem. However, in this case, the assignor will be liable to the debtor for violation of the terms of the contract.
If several creditors took part in the initial credit transaction, then the assignment of debt can only be carried out with the consent of other creditors.
The assignment of a claim must be in writing. The right of claim passes to the new creditor immediately upon signing the assignment agreement, unless the agreement or law provides otherwise.
The assignor has the obligation to transfer to the assignee everything that was received from the debtor on account of the assigned claim. For example, in our case, he will have to transfer part of the repaid debt. But here again there is a caveat: unless otherwise provided in the agreement.
In this case, the old creditor is responsible to the new creditor for the validity of the transferred right. However, he will not be liable if the debtor ultimately fails to fulfill his obligations to the assignee. However, the situation changes radically if the assignor vouches for the borrower.
If the assignor violates his obligations, he will be obliged to return everything that was transferred under the assignment agreement and compensate for the damage caused.
Is the assignor obligated to notify the debtor of the transfer of rights of collection?
Now that we have understood the basic concepts and active parties, let’s take a closer look at their rights and responsibilities. To begin with, is the assignor—the original creditor—obligated to notify the debtor of the transfer of rights to collect the debt?
To fully answer this question you need to know two nuances:
- The assignor is not required to obtain the borrower's consent to assign the debt. He may enter into a contract with a third party without the approval of the debtor.
- The assignor must notify the borrower in writing of the conclusion of an assignment agreement with a third party. However, in practice, creditors often neglect this responsibility.
Notification of the transfer of the right of collection to a third party will avoid confusion in the processing of payments and document flow. After all, if the borrower is not informed about the need to pay the debt to the new creditor (using new payment details), he will create another debt.
The only exception to this rule is the situation when the possibility and conditions for transferring debt are directly stated in the contract. However, remember that even in the absence of notification, the assignment agreement will be considered legitimate.
Notification of the transfer of the right of collection to a third party will avoid confusion in the processing of payments and document flow.
Assignment agreement, features of the agreement between the assignor, assignee and debtor
Important!
After the conclusion of the contract, both parties are interested in ensuring that the conditions are fully observed. But over time, even this interest can change. For example, if the borrower repeatedly violates the terms described in the original document.
To know who the assignor and assignee are, you must first find out what an assignment agreement is - this is the process of transferring debt from one creditor to another. In this case, the debtor has no right to participate in the procedure. The participants and, accordingly, the main persons are the assignor (creditor) and the assignee (new creditor), to whom the debtor must pay the due amount. All transfer of debt occurs in accordance with the law. Let's take a closer look at this process and the people involved in it.
The assignor is the party who transfers all rights to another person or entity. In different cases, the meaning of these two sides has different meanings. If the matter concerns the bank and financial transactions, then he, as the sole main creditor, is obliged to cede the right to the loan. An example is when a bank gives all rights to collect finances to a collection agency.
What is the benefit of the parties
For the assignor, the main benefit is the ability to partially or fully compensate for losses. There are two options here - when the debt is completely purchased by a third party or transferred free of charge for collection, but then receives reimbursement of the debt minus interest.
There are several options for making a profit for the assignee:
- compensation for transfer of debt;
- the opportunity to receive material benefits if the loan was in kind.
In most cases, only overdue debts with losses, the prospects for recovery of which are unclear, are transferred by assignment. In this case, it is more profitable for the creditor to transfer the rights to it to another organization with compensation than to seek repayment of the loan and losses on their own.
What is the difference between assignment and assignment
People new to the financial sector are unlikely to be able to distinguish an assignment contract from an assignment agreement. These types of agreements have minimal differences from each other. According to the assignment contract, the party acting as the assignor transfers to the assignee only the right to demand repayment of the outstanding loan.
As an example, consider an agreement for the assignment of rights to lease a property. This form of agreement cannot be regarded as the object of an assignment contract. This fact is explained by the fact that the lease agreement implies the establishment of a certain tariff according to which the rented premises are paid.
However, when the assignor and assignee enter into an agreement for the assignment of rights under securities, the concluded contract receives the status of an assignment agreement. In this case, the new owner of the rights acquires the opportunity to receive dividend payments. It should be noted here that obtaining such rights does not impose any obligations on this participant in legal relations.
How conflict situations between creditors are resolved
Let's look at the situation when the assignee did not pay the assignor under the assignment agreement. How is such a conflict situation resolved? Firstly, all conditions for the transfer of debt, including material remuneration of the parties, are clearly indicated in the agreement.
Secondly, failure by the assignee to fulfill its obligations towards the assignor in a timely manner may give rise to legal proceedings. Thirdly, the transfer of the right to claim debt is in any case unconditional, that is, Russian legislation does not provide for the possibility of returning rights to the original owner.
Therefore, if the assignment agreement is signed, but the assignee does not fulfill its obligations to collect and return funds, the original creditor must collect the overdue debt not from the borrower, but from a third party. The concluded assignment deprives him of the right to appeal to the debtor.
In what form should an assignment agreement be concluded?
A unified form of debt assignment agreement has not currently been developed. The parties have the right to conclude it in a free form, taking into account certain mandatory requirements:
- Indication of the date of the agreement.
- Full name of the parties entering into the agreement.
- Subject of the transaction. This could be financial debt, products, real estate. The subject of the agreement should be described in as much detail as possible.
- Mutual rights and obligations of the assignor and assignee.
- Conditions for transferring rights to claim debt - price, interest, and so on.
- Liability for failure to fulfill obligations.
- Details of the parties, including payment details, in the form of a table.
- Signatures of responsible persons with transcript.
A unified form of debt assignment agreement has not currently been developed.
Who are the assignor and assignee?
The parties involved in this agreement are called assignors and assignees. The participant in the transaction who assigns the right of claim under the contract is the assignor, and the receiving party is the assignee. The document certifying the assignment of rights is called title. The ability to collect debt passes from one creditor to another. Actually, the debtor does not participate in this at all (with the exception of tripartite assignment agreements, which we mentioned above), the legal act is completed without him, and he learns about everything, as a rule, after the conclusion of the transaction. There is an assignment of debt. Initially, when determining contractual obligations, the borrower has obligations to the assignor, and after the assignment of rights - to the assignee. The relations arising as a result of the conclusion of these agreements are regulated by Russian legislation in sufficient detail.
When can a contract be invalidated?
In most cases, the debtor does not participate in the signing of this agreement and is faced with the fact of a change of creditor. Many are dissatisfied with this change and go to court with a demand to declare the assignment invalid.
Russian judicial practice shows that the majority of such claims are unsatisfied , especially if, from the point of view of legislation and paperwork, the contract was drawn up correctly. Please note that even the presence in the original agreement of a ban on the sale of debt is often not a restriction. Therefore, there is practically no chance of challenging the assignment agreement in court.