What is the tariff rate
People cannot receive the same compensation for their work. The amount to be paid as salary depends on:
- qualification level of personnel;
- difficulties of the labor functions assigned to the employee;
- quantitative characteristics of work;
- conditions of employment;
- time allocated for completing work, etc.
Differentiation of wages according to the degree of expression of these points is carried out within the framework of the tariff system of labor remuneration. Its key element is the tariff rate as the main component of wages.
Tariff rate is a documented amount of financial remuneration for achieving a labor standard of varying degrees of difficulty by an employee of a certain qualification for a given unit of time. This is the “backbone”, the minimum component of the payment for labor, on the basis of which the amount received by employees “in hand” is based.
REFERENCE! An employee cannot receive an amount less than the tariff rate under any circumstances if all functional duties are performed in full - this is the minimum guaranteed by law.
Not part of the tariff rate:
- compensation;
- incentive payments;
- social charges.
Question: The organization is planning organizational changes (personnel changes, staff reductions, changes in wage conditions, etc.). In what cases will it be necessary to make changes to the staffing table and how often do they need to be made? Is it enough to reflect only the tariff rate (salary) in the employment contract, and stipulate incentive payments in the collective agreement? View answer
Estimated time of tariff rate
The time period for which the tariff rate is calculated can be any period convenient for the employer:
- hour;
- day;
- month.
hourly tariff rates if the enterprise operates a shift schedule, which stipulates the mode of summarized recording of working hours, as well as when hourly employees work.
Daily tariff rates are applied when work has the status of a daily wage, while the number of working hours in each such day is the same, but differs from the usual norm established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Monthly tariff rates are valid subject to constant observance of normal working hours: a stable schedule, fixed days off. In such conditions, the employee will “close” the month regardless of how many hours he actually worked: having worked the monthly norm, he earns his salary.
How to indicate salary and tariff rate in an employment contract ?
Tasks “Tariff system of remuneration”
⇐ PreviousPage 32 of 39Next ⇒There is a mathematical relationship between the individual elements of the tariff system, with the help of which it is possible to determine the values of others from the values of some elements, as well as calculate their average indicators. The latter can be used for integrated planning of the wage fund (average tariff coefficient), analysis of the use of the qualification composition of workers (average tariff category of workers and works), etc.
Determination of the average tariff coefficient
Problem 8.3.4.1
Initial data and problem statement
The average tariff category is 4.5.
Determine the average tariff coefficient of employees.
Guidelines
If the number of workers (or the complexity of their work) is unknown, and only their average rank is known, then the average coefficient can be determined using the following formulas:
= Km + (Kb - Km) * ( - Rm) or = Kb-(K6 -Km).(R6 - ),
where Km, Kb are tariff coefficients corresponding to the smaller and larger of two adjacent digits, between which the value of the middle digit is located;
— average tariff category;
Rm, Rb - respectively, the smaller and larger of two adjacent tariff categories, between which lies the value of the known average tariff category.
Solution
1) = 1,36 + (1,51 — 1,36) • (4,5 — 4) = 1,435;
2) = 1,51 -(1,51 — 1,36) • (5,0 -4,5)= 1.435.
Answer:
1,435.
Problem 8.3.4.2
Initial data and problem statement
Work is performed under normal 40-hour workweek conditions. The average hourly tariff rate is 5 rubles. Determine the average tariff coefficient of employees.
Guidelines
If the average tariff rate is known, then the average tariff coefficient ( ) is determined by the formula
where C1 are the hourly tariff rates of the first and middle tariff categories (or monthly tariff rates), respectively.
Tariff coefficients corresponding to the categories of work.
are established by the Unified Tariff Schedule.
Table 8.7
UNIFIED TARIFF SCHEDULE FOR WAGES OF WORKERS IN THE BUDGETARY SECTOR
| Indicators | Tariff categories | ||||||||
| Tariff coefficients | 1,0 | 1,11 | 1,23 | 1,36 | 1,51 | 1,67 | 1,84 | 2,02 | 2,22 |
| Indicators | Tariff categories | ||||||||
| Tariff coefficients | 2,44 | 2,68 | 2,89 | 3,12 | 3,36 | 3.62 | 3.9 | 4,2 | 4,5 |
Note.
Established since 2001 by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On increasing tariff rates (salaries) of the Unified tariff schedule for remuneration of employees of public sector organizations” dated November 6, 2001 No. 775 and dated October 2, 2003 No. 609.
Hourly tariff rates are calculated based on monthly tariff rates and working time balances. The latter are published annually in official statistics[5].
Solution
Based on the balance of working hours and the minimum wage level, we determine the hourly wage rate of the 1st category:
C1 = 600/ 166 = 3.614; K = 5/3.614 = 1.38.
Answer.
1,38.
Determination of the average tariff category
Problem 8.3.4.3
Initial data and problem statement
Of the 296 employees of the organization, 50 have the 2nd category, 100 - the 3rd, 15 - the 4th, 10 - the 5th, 2 - the 6th, the rest are charged the 1st category.
Determine the average tariff category.
Guidelines
If the distribution of workers by qualification category is known, then the average tariff coefficient is determined, and on its basis - the average tariff category ( ) using the formulas:
= Rm+[( - Km)/(Kb - Km)] or = R6 -[(K6 - )/(Kb - Km)].
Solution
The average tariff coefficient will be 1.14 based on the calculation:
K = (1.11 • 50 + 1.23 • 100 + 1.36 • 15+ 1.51 • 10 + 1.67 • 2 + 1.0 • 119) / 296;
the average tariff category is 2.203, since the average coefficient is between the coefficients corresponding to the 2nd and 3rd categories:
= 2 + [(1.14 - 1.11)/(1.23 - 1.11)] = 2.25 or = 3-[(1.23 - 1.14)/(1.23 - 1, 11)] = 2.25.
Answer.
2,25.
Problem 8.3.4.4
Initial data and problem statement
With a total labor intensity of the product of 400 standard hours, 100 standard hours are for work of the 2nd and 3rd categories, 150 standard hours are for work of the 4th category, and 50 standard hours are for work of the 5th category.
Determine the average tariff category of work.
Guidelines and solution
If the labor intensity of the work is known, then the calculation of the average tariff category ( ) is carried out in the following order using the formulas given earlier.
1. The average tariff coefficient for work is determined:
= (100- 1,11 + 100- 1,23+ 150- 1,36 + 50- 1,51)/400= 1,28.
2. The average tariff category of work is determined if the average coefficient is between the coefficients corresponding to the 3rd and 4th categories (1.23 < 1.28 > 1.36). Then
= 3 + [(1,28- 1,23)/( 1,36-1,23)| = 3,38;
= 4 — [(1.36 — 1,28)/(1,36- 1,23)] = 3,38. Answer.
3,38.
Problem 8.3.4.5
⇐ Previous32Next ⇒
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use Google search on the site:
Tariff Rate Functions
The use of a tariff payment system for calculating remuneration in monetary form for the performance of labor functions has a number of advantages over other forms of payment.
The tariff rate as a unit of payroll calculation performs a number of important functions:
- makes wages and maintenance commensurate;
- divides the minimum part of payment depending on the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of labor;
- organizes labor incentives in the prescribed conditions (for example, in hazardous production, with significant work experience, overwork, etc.);
- helps to adequately calculate payment for different labor organization systems and work schedules.
NOTE! The main principle of applying tariff rates is equal remuneration for an equal amount of work.
8.4. Additional payments and allowances
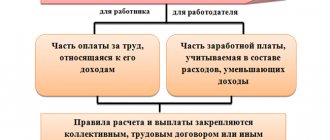
Labor legislation provides for the establishment of additional payments and allowances for employees of a compensatory and incentive nature.
Compensatory additional payments are related to working conditions and conditions. These include additional payments for work at night, in difficult and hazardous working conditions, on rest days, and overtime. The specific amount of additional payments is determined independently by the enterprise and is paid within the limits of available funds, but not lower than those provided for by law. The types, procedure for establishing and amounts of compensatory additional payments are fixed in the collective agreement.
Overtime work is paid for the first two hours at least one and a half times the rate, and for subsequent hours at least double the rate.
Work on holidays is paid at least double the rate, and for piece workers at no less than double the rate, and for hourly workers at the rate of at least double the hourly or daily rate.
Additional payments for working conditions are made at workplaces where work is performed, provided for by the industry list of jobs with heavy and harmful, especially difficult and especially harmful working conditions, and are accrued to workers only for the duration of their actual employment in these places. For workers engaged in work with difficult and harmful working conditions, the specific amount of additional payments is established on the basis of certification of workplaces and an assessment of actual working conditions.
Night work is also paid at a higher rate because it is more tiring. Night working hours are considered to be from 10 pm to 6 am. The duration of working time on a night shift is reduced by 1 hour, and during shift work, for example in continuous production, the duration of night work is equal to day work. A night shift is considered to be one in which at least 50% of the working time is spent at night. Additional payments for night shift work are established for workers, employees, specialists, foremen and managers of production facilities, sections, workshops and other departments.
The types, procedure for establishing and amounts of additional incentive payments are determined independently by the enterprise and are fixed in the collective agreement. These include: additional payments for professional excellence, for high achievements in work, for completing particularly important tasks, etc.
Keywords
Tariff system, tariff rate, tariff schedule, qualification category, tariff-qualification reference book, additional payments and salary supplements.
Control questions
1. Reveal the essence of wages in a market economy.
2. What functions does wages perform?
3. Basic principles of wage organization.
4. What is meant by the organization of wages, what are its main elements?
5. What is meant by the tariff system? List the main elements of the tariff system.
6. Tariff rates, their purpose.
7. Tariff schedules, their construction and purpose.
Get full text
8. Describe the procedure for paying additional payments and salary supplements.
Forms and systems of wages are the third element of the organization of remuneration and determine the procedure for calculating wages. With their help, the connection between wages and its quantitative and qualitative results is carried out.
There are two forms of remuneration: time-based and piece-rate.
How is the tariff rate calculated?
IMPORTANT! A sample employment contract indicating the size of the tariff rate from ConsultantPlus is available here
The unit rate with which all other categories are correlated is the tariff rate of category 1 - it determines the amount due to an unqualified employee for his work during a specified time period.
The remaining categories are arranged depending on the increasing complexity of the work and the qualifications required for it ( tariff categories ), or according to the level of professional training of employees (qualification categories). The complex of all categories leaves the tariff schedule of the enterprise. In it, each subsequent rank is several times larger than the unit rate (that is, 1 rank) - this indicator reflects the tariff coefficient .
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The minimum wage is set by the state, and all other elements of the tariff schedule are adopted separately for each organization and are enshrined in the relevant local acts. The exception is labor in organizations financed from the state budget, where accruals occur according to the Unified Tariff Schedule (UTS).
Knowing the tariff coefficient and the size of the unit rate, you can always calculate the amount of payment due to a specific employee according to the tariff.
An example of tariff calculation for the UTS
A teacher with an academic degree of Candidate of Philosophical Sciences and the title of Associate Professor is hired at the Faculty of Philosophy of a State University. He was accepted to the position of Associate Professor of the Department of Cultural Studies and appointed curator of the student group. According to the Unified Tariff Schedule, the billing period of which is equal to a month, his qualification corresponds to the 15th category. Let's calculate his salary.
The minimum payment under the UTS, corresponding to category 1, is equal to the minimum wage. It must be multiplied by the tariff coefficient for the 15th category of the tariff schedule, namely 3.036.
A bill regulating the procedure and amount of bonuses due to teaching staff is currently under consideration. For our example, we will use data from this bill.
To calculate the tariff you need:
- Multiply the inter-grade coefficient and the minimum wage
- Add assistant professor position (+ 40%)
- Add the required allowances for having an academic degree (for example + 8,000 rubles), as well as a supervisory surcharge (for example, + 3,000 rubles).
Example of tariff calculation for hourly rate
If an employee works according to a system of summarized working hours, then his tariff rate will depend on the hourly rate for a given year - it will be shown by the production calendar, as well as the monthly tariff rate established at the enterprise.
1 way. You can divide the monthly rate by working hours into the rate indicator. For example, for a worker of a certain qualification, a tariff of 25,000 rubles is set. per month. In this case, the established standard working time per month is 150 hours. Thus, the hourly wage rate for such a worker will be 25,000 / 150 = 166.6 rubles.
Method 2. If you need to calculate the average hourly rate for the current year, you first need to determine the average monthly hourly rate. To do this, divide the corresponding annual indicator of the production calendar by 12 (the number of months). After this, we reduce the worker’s average monthly tariff rate established by the tariff schedule by the resulting number of times. For example, the annual norm is 1900 hours. Let's take the same monthly rate as for the previous example - 25,000 rubles. Let's calculate the average amount this worker earned per hour during a given year: 25,000 / (1900 /12) = 157.9 rubles.
Calculation of the average tariff category of workers
The average tariff category of main production workers is calculated using the formula:
| (12) |
where Р1, Р2, …, Р6 – tariff categories of the main production workers;
Cho1, Cho2, . , Cho6 – number of main workers of the corresponding categories, people;
Cho – total number of main production workers, people.
The average tariff category of auxiliary workers is determined by the formula:
| (13) |
where Chv1, Chv2, …, Chv6 – the number of auxiliary workers of the corresponding categories, people;
Chv – the total number of auxiliary workers.
2.7 Calculation of the annual wage fund and average wages at the site
The annual wage fund of workers is determined for each category separately. The following systems are used to calculate PPP salaries:
— piecework bonus for main production workers;
— time-based bonus for auxiliary production workers;
— system of official salaries for specialists and employees.
Calculation of the wage fund of main production workers
The initial data for the calculation are the average tariff category, the average tariff coefficient, the average hourly tariff rate of the main production workers and the annual labor intensity of the site.
Hourly tariff rates are taken from the tariff schedule of METROVAGONMASH OJSC (Table 9).
Table 9 – Extract from the tariff schedule of OJSC “METROVAGONMASH”
| Tariff categories | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. |
| Tariff coefficients | 1,0 | 1,13 | 1,28 | 1,44 | 1,63 | 1,84 |
| Hourly tariff rates: for piece workers | 73,18 | 82,69 | 93,67 | 105,38 | 119,28 | 134,65 |
| for temporary workers | 40,20 | 45,43 | 51,46 | 57,89 | 65,53 | 73,97 |
The average hourly wage rate for key production workers is determined in accordance with their average wage grade.
If the average category of workers is expressed as an integer, then the average hourly tariff rate is not calculated, but is taken to be equal to the hourly tariff rate of this category according to Table 9.
Because The average category of workers is expressed as a fraction, then the average tariff coefficient is determined by calculating:
where is the tariff coefficient corresponding to the smaller of two adjacent categories of the tariff schedule, between which the average tariff category is located;
- tariff coefficient corresponding to the larger of two adjacent categories, between which the average tariff category is located;
— average wage category of workers;
- the smaller of two adjacent categories of the tariff schedule, between which there is an average tariff category.
Thus, for main production workers the average tariff coefficient will be equal to: 1.38
We similarly calculate the average tariff coefficient for auxiliary workers.1.33
After calculating the average hourly wage rate, the annual wage fund of workers is determined.
The wage fund represents the total cost of paying workers for the year
The procedure for calculating the annual wage fund of main production workers is as follows:
a) the tariff wage fund for workers is determined, rub.
where is the total annual labor intensity of the site, hours, f. (1);
— average hourly tariff rate, rub./hour.
b) the basic wage fund of workers is calculated in rubles (for hours worked), which includes the tariff wage fund, bonuses according to the current bonus system, additional payments for work in the evening and at night, on weekends and holidays, for unfavorable working conditions , additional payments to foremen who are not exempt from their main work, etc.:
where P
– bonuses, rub.;
D
– additional payments, rub.;
Np
– standard bonuses established according to the current bonus system, % (accept 80%);
Nd
– standard additional payments, % (accept 15%).
c) an additional wage fund for workers is calculated, including remuneration for time not worked in production (payment for regular and additional vacations, preferential hours for teenagers, performance of government duties, remuneration for long service, etc.):
where Ndop is the standard additional salary, % (accept 11%);
d) the total wage fund of workers is determined, rub., which is the sum of the basic and additional wages
(20)
The calculation of the annual wage fund ends with the determination of the average monthly wage of workers.
Average monthly salary of main production workers, rub. calculated by the formula:
Calculation of the annual wage fund and average wages of auxiliary workers
The initial data for the calculation are the average tariff category, the average tariff coefficient and the average hourly tariff rate of auxiliary workers, as well as the actual annual working time of one worker.
Hourly tariff rates are taken from Table 9 for time workers.
The average tariff coefficient and the average hourly tariff rate of auxiliary workers are calculated using formulas similar to the calculation formulas for main production workers f. (16).
The annual wage fund for auxiliary workers is determined by the formula:
where is the average hourly wage rate for auxiliary workers, rubles/hour.
The annual basic, additional and general wage funds, as well as the average monthly wages of auxiliary workers are calculated using formulas similar to the calculation formulas for main production workers f. (15)-f.(21).
N
The additional payment standard is 15%, the bonus standard is 40%.
c) an additional wage fund for workers is calculated, including remuneration for time not worked in production (payment for regular and additional vacations, preferential hours for teenagers, performance of government duties, remuneration for long service, etc.):
where Ndop is the standard additional salary, % (accept 11%);
d) the total wage fund of workers is determined, which is the sum of the basic and additional wages
The calculation of the annual wage fund ends with the determination of the average monthly wage of workers.
Average monthly salary of auxiliary workers, rub. is calculated similarly to formula (f.22):
Tariff salary construction system
The limiter on the size of the tariff rate is the amount of the minimum wage established at the state level. The totality of tariff categories constitutes a tariff schedule, structured by positions and professions.
To distinguish between different types of work in the tariff system, qualification categories are used, which characterize the level of compliance of an employee with a certain position. The tariff coefficient sets the percentage ratio between the stages of the entire system. In other words, it shows how much the rate of a certain category differs from the tariff of the first category. In turn, the tariff rate of the first category is a kind of starting point for any salary.
The tariff schedule differentiates the scale of salary ratios, taking into account the qualifications of the worker. Modern legislation allows you to set the number of categories and tariff coefficients depending on the specifics of a particular production. At the same time, in the public sector, the salary tariff system is established centrally and is called the Unified Rate System.
Minimum wage and tariff schedule
Tariff rate is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for fulfilling a standard of work of a certain complexity (qualification) per unit of time (hour, day, month) without taking into account compensation, incentives and social payments. The tariff rate of the first category determines the minimum wage for unskilled labor per unit of time.
This system is most convenient when taking into account the shift nature of work. If the company until recently used a different remuneration system, then the manager is obliged to inform all employees about the changes that have occurred a month before the introduction of the new regime. When calculating wages by the hour, you must adhere to the rule of a forty-hour work week. In the event of a reduction in the total number of hours, the norm is fixed by an additional agreement to the employment contract and the written consent of the employee. Otherwise, such a change in the labor regime may give rise to legal proceedings.
07 Feb 2020 juristsib 521
Share this post
- Related Posts
- How to leave a mother at the request of a child if the child lives with other relatives
- Is Income Tax Deducted From The Salary Of A Working Veteran Of Labor Or Not?
- Payment Usn 6 Percent 2020 Sample
- The cost of hot water per cubic meter according to the meter in 2020 Perm
The role of the tariff scale in determining workers' wages
- the salary for the lowest category cannot be less than the legal minimum wage;
- the work of workers of the same position and qualifications should be paid equally;
- salary reduction is unacceptable;
- fixed salaries and rates are set taking into account membership in a professional qualified group;
- all salaries, rates, allowances and bonuses are included in the staffing table.
We recommend reading: List of documents when selling an apartment in 2020 through the MFC
According to the norm of Article 143 of the Labor Code, an employee’s payment must be proportionate to his efficiency. That is, the higher the rank or qualification of an employee, the more expensive his work. And the category directly depends on the type of work. All types of work inherent in a particular category (by profession) are listed in the ETKS.
The first category tariff rate is being increased in Belarus
As a result, the increase in estimated wages in October 2020 compared to August 2020 will be: associate professor of an educational institution - Br72.1, or 11.3%; teacher with 1 qualification category - Br64.7, or 12.7%; assistant teacher - Br55.1, or 15.7%; a surgical doctor with the highest qualification category - Br128.6, or 19.3%; operating room nurse with 1 qualification category - Br63.7, or 14.1%; pharmacist with 1 qualification category - Br178.4, or 46.4%; pharmacist with 1 qualification category - Br98.8, or 26.7%. The adoption of the resolution will make it possible in 2020 to ensure that the ratio of average wages in the public sector and in the republic as a whole for the fourth quarter is achieved at a level of no less than 80%, as well as to increase the average wage of teaching staff by 13.5% (the ratio will be 88%), doctors - by 19.1% (ratio - 144%).
Alexander Lukashenko agreed on a draft resolution of the Council of Ministers “On establishing the size of the first-class tariff rate and increasing wages for certain categories of workers.” The document was prepared to increase the level of wages for public sector workers and provide material support for certain categories of workers.
We recommend reading: Maternity capital for 3 children in 2020 in Chuvashia
How to calculate the tariff rate knowing the salary
Let's figure out how to find out the tariff rate, the formula is as follows:
TC = TC of a 1st category specialist x increasing coefficient
Knowing the salary, you can use two calculation methods:
- using the standard labor hours per month;
- in a year.
The formula will look like this: vehicle (hour) x hours worked per month = salary.
Salary/number of working hours per month = hourly vehicle
The outcome that such a vehicle determines will differ in different months, since they may have different numbers of hours worked. For example, in April there will be 160 of them, while in August – 184.
For example: salary = 25,000. Vehicle in April = 25,000 / 160 = 156.25 rubles, in August = 25,000 / 184 = 135.87 rubles.
Norm of working hours per year (NRCH)/12 months = average monthly norm of working hours (SMNRCH). The employee's salary is divided into it
NRChG with a 40-hour work week - 1970 hours; SMNRCH – 164.16 hours per month. To better understand the features of the procedure under consideration, you can find sample calculations. For example: salary = 25,000. Vehicle = 25,000 / 164.16 = 152.29 rubles.
Calculate the tariff rate of an employee of the 9th category
The calculation can be made using the same formula as for worker 1. Only the coefficient will differ, since the calculation takes into account his higher qualification skills.
Tariff schedule by category for 2020-2020
From December 1, 2008, the Unified Tariff Schedule was replaced by a slightly different method of tariffication of public sector salaries. This happened after the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the introduction of new remuneration systems for employees of federal budgetary, autonomous and government institutions” dated August 5, 2008 No. 583 came into force.
Recently, along with the term “tariff system”, another term has been used – “grading system”. This is a kind of analogue that has managed to establish itself abroad. Grading, like the tariff system, involves building a hierarchical structure of positions depending on their complexity. Although there are differences: grading involves the use of more criteria, such as independence, communication skills, cost of error, etc.