* The calculations use average data for Russia
700,000 ₽ Minimum starting capital
300% Profitability
3,800,000 ₽ Profit for the year
3 years Payback
Growing flowers in greenhouses is a profitable and profitable business, which, however, requires considerable investment. Thanks to the advent of new technologies, such very whimsical flowers as roses can be grown in protected soil in almost any region of our country.
If you want your business growing roses for sale to be successful, you need to start by drawing up a detailed business plan. It seems that the algorithm for constructing it is extremely simple. All you need is a greenhouse with the ability to regulate temperature and light levels, fertile soil, fertilizers, special preparations for treating plants against insect pests, roses themselves and free time to care for flowers. In fact, there are many nuances in this matter, ignorance of which can lead to significant material losses.
What varieties of roses are suitable for growing?
Obviously, the goal of growing roses in a greenhouse as a business is primarily to obtain the maximum number of quality buds. Therefore, the farmer needs to study the characteristics of various crop varieties in order to choose among them the most suitable for indoor soil. All of them are divided into several varieties:
- Polyanthaceae. They form massive clusters of dozens of small flowers in white, yellow, red or pink. The bushes grow up to 60 cm in height, but the stems themselves are short, so it is difficult to sell roses individually;
- Miniature. They are distinguished by bushes up to 40 cm high and small inflorescences that densely cover the plants. Suitable for growing as ornamental plants - for example, in pots on balconies or along paths in the garden;
- Hybrid tea. Plants familiar to everyone with long stems and dense inflorescences, presented in all flower stalls. They cannot be considered unpretentious, but these varieties are of great commercial importance;
- Teahouses. They have dense single inflorescences on short stems. The common range is standard and combined colors. They have a rich aroma and are usually sold in large bouquets;
- Peony-shaped. They have dense bell-shaped inflorescences with dozens of petals. Each shoot usually opens several buds, which is why peony roses are used for lush wedding bouquets;
- Floribunda. They are distinguished by lush and large multi-petal inflorescences of various shades. The bushes grow up to 1–1.2 m in height. They occupy an intermediate place between polyanthas and hybrid teas, and are often odorless;
- Grandiflora. The result of crossing floribunda with hybrid tea roses, bred no more than forty years ago. They have shoots up to 2 m high and huge lush inflorescences of white, yellow, red or pink shades.
To grow roses in a greenhouse all year round, breeders have created dozens of different varieties of almost all varieties. Here are the most interesting of them:
- Abracadabra. Hybrid tea rose 60 cm high with variegated striped or spotted burgundy-yellow flowers;
- Black Baccara. Hybrid tea rose up to 80 cm high with huge velvety dark cherry, almost black flowers. Has few thorns;
- Carina. Hybrid tea rose up to 110 cm high with delicate creamy pink flowers. It has a strong aroma and dark leaves;
- Casanova. Hybrid tea rose up to 90 cm high with large golden or pink-golden flowers;
- Lolita. Hybrid tea rose up to 100 cm high. It has cream-colored petals with a red or pink base and edges. Has a strong odor;
- Memoire. Snow-white hybrid tea rose with flowers 10–12 cm in size. In hot weather it turns pinkish. Plant height - up to 120 cm;
- Rose Gaujard. Hybrid tea rose 100 cm high. Distinguished by white petals with a pink or cherry base and edges;
- Pat Austin. A peony rose of copper-orange color, up to 105 cm high. The inflorescences are large, cup-shaped, up to 12 cm in diameter. The smell is similar to rose oil;
- Carte Blanche. Floribunda rose with large cream or white flowers. The bush reaches a height of 100–110 cm;
- Niccolo Paganini. Bright red or scarlet floribunda with velvet flowers 8–10 cm in diameter. The plant reaches a height of 110–120 cm;
- Queen Elizabeth. Floribunda is a rich pink color with dark green leaves and shoots up to 100 cm high;
- Scarlet Gem. A miniature rose with a bush up to 40 cm high, densely strewn with bright red flowers with a diameter of 3–5 cm.
Realization of colors
The easiest way is to find wholesale buyers who will pick up flowers directly after cutting several times a week, but it is not always possible to find such wholesalers, so gardeners use other sales methods:
- creating your own points of sale in markets and public places;
- online store or groups on social networks with delivery functions;
- a small shop right in the greenhouse.
The combination of these methods will allow you to find regular customers and make your business profitable and your profits stable.
Income from the sale of roses
Note! If sales volumes are small, it is advisable to cut roses to order - this way the flowers will be fresher and last longer.
Growing roses in a greenhouse is a profitable business, especially if demand is stable and the climate is suitable. Even from a small greenhouse you can get a decent annual profit and recoup the initial costs. In just a few years, you can achieve an increase in turnover and transform your hobby into a small business.
Ways to grow roses
Comparing growing roses in open ground with planting them in a greenhouse, it should be noted that under the protection of polycarbonate, the farmer gets more opportunities to control the microclimate, prevent the influence of weather conditions and increase crop yields. You can place bushes in the greenhouse space in different ways:
- On the beds. For planting plants, a nutrient substrate is prepared, which is poured in the form of ridges a meter wide, 70–80 cm high. On each of them, with a row spacing of 25–30 cm, four to five rows of bushes are placed;
- In pots. This technology is suitable for growing roses at home - in a room, on a balcony. Miniature varieties are planted in plastic boxes or containers 30–40 cm high, filled with drainage expanded clay and substrate;
- On hydroponics. Suitable for saving space in large greenhouse complexes. The bushes are germinated in seedling cubes and placed on mats made of coconut fiber or stone wool, inside which a nutrient liquid circulates;
- On the rootstock. This method of growing roses involves grafting onto ordinary rosehip bushes that have a powerful root system and strong stems. First, they are planted in pots and then transferred to closed ground.
How much can you earn from growing roses?
The flower business has always been considered extremely profitable . By growing roses in a large greenhouse, you can sell up to 100 thousand flowers a year.
Such a business can bring the entrepreneur a net profit of 250 thousand rubles per month (subject to the purchase of high-quality planting material and compliance with flower growing technology).
The success of such an undertaking depends on how quickly the entrepreneur can find regular buyers of roses.
As a rule, with the low wholesale cost of flowers (40 rubles per piece), problems with finding distribution channels do not arise.
How to prepare the soil for roses?
One of the main features of growing roses in a greenhouse is the need to use the same soil for several years, which is replaced only when the plantation is completely renovated. It is logical to assume that ordinary land is not suitable for such purposes. Therefore, the farmer needs to take care of saturating the soil with nutrients. How to prepare a place for planting rose bushes:
- The easiest way to purchase soil is ready-made. But if desired, it can be made from a mixture of 50% garden soil, 35% last year’s manure and 15% sand;
- The finished substrate is thoroughly mixed, adding 20 g of potassium nitrate, 30 g of superphosphate and 400 g of wood ash per cubic meter;
- The result should be a mixture with an acidity pH of 5.5–6.5 and a mass density of about 1200–1400 kg/m³;
- After marking the beds in this place, the soil is removed to a depth of 50–60 cm. A drainage layer of crushed stone is installed at the bottom and pipes are laid to drain water;
- Then the pits are filled with substrate so that the beds rise 20 cm above the adjacent paths;
- The soil is thoroughly watered to settle it, after which the missing layer is added. After a week, it is loosened and holes are prepared for bushes.
Planting and care: step-by-step instructions
Growing roses in a greenhouse requires regular care; only in this case will you get abundant flowering and, as a result, profit. It is necessary to follow all the specified stages of caring for bushes, ensuring the best conditions.
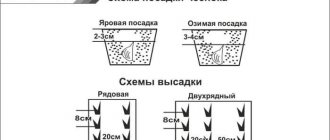
Step 1. Planting seedlings. Pre-treated planting material is planted in prepared soil heated to 12°C with a planting density of 15-20 plants per 1 m2. Planting pattern – 30x30 cm or 25x40 cm.
Planting density of cuttings
When planting, it is important not to bury the seedlings - the grafting site should be at ground level. If planted too high, the roots will dry out and the seedling will die. If deepened too much, the roots will begin to rot, and the plant will take a long time to take root. Even if a buried rose takes root well, it will begin to sprout from the rootstock.
Planting seedlings
The soil around the planted bushes is lightly pressed and watered abundantly from a sprinkler without a diffuser or from a hose with medium pressure. This will help compact the soil around the roots.
Watering a seedling
Step 2. Rooting of seedlings. The temperature in the greenhouse is set at 10°C, the soil temperature should be 12°C. Rooting is indicated by the massive growth of young shoots. After rooting, the temperature is increased to 20-22°C during the day and 15-17°C at night. The maximum permissible temperature is 27°C.
Rooted roses begin to grow actively
Step 3. Watering the bushes. Roses need plenty of watering. If the greenhouse is equipped with a drip irrigation system, it is necessary to ensure that the soil is constantly moderately moist.
When manually watering, you must adhere to the following schedule:
- February, March – 3-5 times a week;
- from April to August – daily, in hot weather up to 5 times a day;
- from August to November – 2-4 times a week.
Watering roses from a watering can
The volume of watering should be such that the soil is well moistened to a depth of 50-70 cm. After 2-3 days, the soil around the bushes is carefully loosened.
Drip watering of roses in a greenhouse
Step 4. Mulching. To reduce the amount of watering and create good conditions for aeration of the roots, the soil around the bushes is mulched with peat, rotted manure or humus. Mulched soil is less susceptible to fluctuations in temperature and humidity.
Mulching roses with humus
Step 5. Maintaining air humidity. The greenhouse should have a constant humidity of 70%. When humidity decreases, plants open and shed buds faster, and a favorable environment is created for roses to be attacked by spider mites.
Rose affected by spider mites
Higher humidity promotes the development of fungal diseases.
Powdery mildew on roses
Step 6. Fertilizer. Fertilizing is carried out once every 10-14 days with organic or mineral fertilizers. Roses respond well to the application of a 1:10 solution of mullein with the addition of potassium and phosphorus fertilizers. You can use complex mineral fertilizers for roses. Experienced gardeners recommend combining organic watering with foliar fertilizing with macro- and microelements. Starting from August, organic matter and mineral nitrogen fertilizers are not used.
Fertilizer for roses
Prices for fertilizers for roses
fertilizer for roses
Step 7. Lighting. Roses need lighting in the winter and autumn months, as well as shading in the spring and summer. Daylight hours for most varieties should be 18-19 hours. The illumination standard is 15,000 lux. Such illumination can be achieved by installing DNAT and DNAZ lamps with a power of 400 W at the rate of 1 lamp for every 3-4 m2 of greenhouse area. When using lamps for illumination, you can reduce their number to 1 lamp per 8-10 m2. When placing lamps, you need to make sure that the light falls on the leaves and buds, and not on the soil.
Greenhouse lighting
Step 8. Ventilation. Access to fresh air is necessary for active photosynthesis, shoot development and flowering. Ventilate the greenhouse daily using vents or a forced ventilation system. In this case, it is necessary to avoid strong drafts and overcooling of the soil.
Ventilation of the greenhouse
Step 9. Preventive treatments against diseases and pests. In order to prevent diseases and the appearance of pests, roses are periodically treated with fungicides and contact insecticides.
Pest treatment
Step 10. Forming a bush. In the process of caring for bushes, it is necessary to promptly remove side shoots growing below the grafting site, as well as weak growth that creates excessive thickening of the bush.
Pruning flowering rose bushes
Step 11. Flowering and cutting. When buds appear, reduce the daytime temperature to 18-20 degrees. Flowers are cut in the phase of slightly blossoming buds in the morning with a special pruner at an angle of 35-45 degrees. Flowers are placed in a bucket of warm water with the addition of a disinfectant solution, and then put in a cool place for 20-24 hours before transportation. When cutting, it is important to leave a sufficient number of leaves on the bush for active photosynthesis and further growth of shoots.
Cutting roses
Step 12. Rest phase. Roses, like any plants, need rest. It is combined with the darkest and coldest period. In early November, watering is reduced and then stopped. Reduce the temperature in the greenhouse to 2-3 degrees. Cut off the last flowers and buds.
Pruning roses for the winter
In early January, the bushes are pruned, leaving 3-4 stems with 4-5 buds, and on weak bushes - 2-3 shoots with 2-3 buds. The bushes are kept at low temperatures above zero and without additional lighting until February. After this, you can begin a new forcing cycle.
Video - Technology for growing roses in a greenhouse
Growing flowers in a greenhouse as a business
To run a flower business, you need to take care of having the necessary permits. You can become an individual entrepreneur or cheat a little and take advantage of the advantages of being the owner of a personal plot.
How to choose rose seedlings?
When the greenhouse soil is ready, you need to think about how to obtain planting material. The most suitable option is selected taking into account how much time, effort and money the farmer plans to allocate for these purposes:
- From cuttings. To grow roses from cuttings at home in the summer, cut out an area with one or two buds from a strong shoot. The segment is treated with a stimulant and germinated in a pot, after which it is transplanted into the ground;
- From seeds. To grow roses from seeds at home, the plant is allowed to bloom, after which the seeds are extracted from the fruit. They are soaked and placed in the refrigerator, and as they germinate, they are planted in peat cups;
- From seedlings. This method is recommended for beginners or farmers who want to save time. If you are planning to open a business growing roses, it is better to purchase seedlings not at the market, but at gardening centers or nurseries.
Preference should be given to two-year or three-year-old seedlings: as a rule, they are already quite viable plants. Unfortunately, sellers are usually interested in selling planting material at any cost, so a beginner should figure out how to distinguish a good seedling from a bad one:
- The plant must have at least three strong shoots with smooth elastic bark without wrinkled areas or dark spots;
- To check, the bark at the top of the shoot needs to be scratched a little. A good seedling will have light wood, and the damaged area will be moist with sap;
- The buds should be closed or slightly hatched. If they open and white feeding threads appear on the roots, the plant has already woken up;
- At the site where the varietal rose is grafted onto the rootstock and near the root collar there should be clean bark, without signs of peeling or rotting;
- The strong seedling has a developed root system. If short stumps remain instead, such a plant will not produce a productive bush;
- The roots should have dark brown bark and light wood underneath. When cut, juice should also be released from them;
- For seedlings with a closed root system, the packaging and transport soil should not be too wet or too dry.
Purchase and preparation of seedlings for planting
Beginning flower growers are recommended to purchase ready-made rooted seedlings. It is better to purchase them at a nursery or garden center - this way you will receive a guarantee of varietal compliance and health of the planting material.
Seedlings can be rooted, grown from rooted cuttings, and grafted onto less demanding rootstocks. The latter are unpretentious, but bloom less profusely. Grafted seedlings are sold at least three years old: it takes two years to grow the rootstock, and another year to develop the grafted plant. Healthy grafted seedlings should have at least two or three strong shoots with buds.
Rose seedlings with closed root system
The root system of seedlings can be closed (ZKS), in pots, or open (OKS). Both seedlings are suitable for growing, but when purchasing planting material with OCS, you must carefully inspect it.
Rose seedlings with open root system
Signs of healthy planting material:
- living, flexible stems 20-30 cm high with 3-4 green buds;
- absence of stains, cracks, wrinkled bark;
- living and elastic roots.
For transportation, seedlings with OCS are packaged: the root system is wrapped in a damp cloth or placed in a bag with damp moss or peat. Plants with ZKS are not removed from the pots, watered well and packed in boxes.
Rose seedlings packed for storage and transportation
Before planting, seedlings can be stored for a short time at a temperature of +4-6°C; for long-term storage, a temperature of +2-3°C is required. A day before planting, the seedlings are removed from the packaging and the roots are examined. If there are dried roots, planting material is immersed in cool water for 12-24 hours.
Soaking seedlings in water
Immediately before planting, all seedlings with ACS are treated with a solution of copper sulfate, foundation or other antifungal and antibacterial drug. The roots are completely immersed in the solution for 10 minutes, then rinsed with cold water.
Weak shoots are removed, 1-2 stems with 3-4 buds are left on each plant. The sections are treated with an antibacterial drug and dried. For better germination of buds, seedlings are treated with a stimulant, placed in boxes with damp peat and covered with film. Keep on racks in a greenhouse at a temperature of 18°C until sprouts 2-3 cm long appear from the buds.
Rose seedling
Prices for rose seedlings of different varieties
rose seedlings
How to plant roses?
When picking up seedlings from the store, you should remember that they are in an unfamiliar environment. Therefore, before planting, rose bushes need to be helped to get out of the state of shock by carrying out some preparatory measures:
- Plants with ZKS are removed from the packaging and freed from peat. The roots are straightened, removing dried and damaged shoots;
- The day before planting, the roots are disinfected for 10–15 minutes in a solution of copper sulfate, after which they are soaked for 16–20 hours in water with the addition of a growth stimulator;
- Weakened shoots are cut off, leaving 2–3 stems on the seedling with several buds on each. The sections are disinfected and dried.
The most common way to grow roses in a greenhouse is to plant bushes on ridges. How to perform this operation:
- A week before planting, they begin to warm up the greenhouse so that the soil temperature at a depth of 5–6 cm reaches 11–13°C;
- In meter-wide beds, holes of sufficient size are dug every 30–35 cm with a row spacing of 25 cm. The planting density is 8–12 pcs/m²;
- The seedlings are placed in the holes so that the grafting point is at soil level. The roots are straightened and covered with soil, periodically compacting it;
- Stronger plants are placed in the center, and weaker ones are placed at the edges. The bed is made slightly convex by adding more soil to the middle;
- After the operation is completed, the bush is watered abundantly to ensure that the soil around the roots settles.
Equipment and materials
To grow roses throughout the year in different climatic zones, different types of greenhouses are used.
- With a wooden frame the most inexpensive option. The frame is covered with plastic film. The advantage of a greenhouse is its lightness, ease of construction, and low cost. The negative aspects are the fragility of the frame, fragility and very poor thermal insulation of the structure. Entrepreneurs do not recommend using it in cold regions.
- A glass greenhouse will be more expensive, but it is more reliable than a wooden one.
- Galvanized polycarbonate is a modern version of a stainless greenhouse with thermal insulation. Polycarbonate diffuses sunlight, is durable, strong and easy to process.
Entrepreneurs most often install on their plots the simplest structure in the form of a rectangle from 10 m to 15 m long, 4-5 m wide. To uniformly heat the interior of the greenhouse, a pitched roof . The north side should be made higher than the south and covered with opaque material. On one square place you can place from 10 to 30 roses , depending on the variety. For industrial production, specialized greenhouses with a reinforced frame and a large volume of air are used.
There are several ways to grow roses.
- In containers and pots
This method is used by amateurs to grow flowers at home, on a windowsill, terrace, or balcony. It is convenient to swap flowers . The thickness of the container walls is from 2 cm to 2.5 cm, the height is at least 40 cm. If you use a plastic container, then it is advisable to place it in a large container , fill the voids with foam plastic, and fill the bottom with expanded clay. The plant needs to be watered and fed once every two weeks.
- Hydroponics
To grow the plant, mineral wool , preferably coconut soil with good drainage properties. Watering and feeding roses is done directly under the plant itself. Thanks to the water-aeration balance in the root zone, the quality of flowers increases . The method is used on an industrial scale when growing plants.
How to care for roses?
Growing and caring for roses is a rather complex process. These plants are considered to be quite delicate: if left unattended for several days, you can lose a significant part of the harvest. In a word, the farmer will not be left without work:
1. Plants require temperature regulation depending on the growing season. An entrepreneur must follow this algorithm:
- Immediately after planting, set the temperature to 10°C at night and 12–14°C during the day;
- After the buds open, the air is heated to 15°C;
- When leaves appear, the temperature is increased to 18°C;
- At the stage of bush formation, maintain 22°C;
- After the buds appear, the air is cooled to 18°C during the day and 16°C at night;
- After cutting, shoot growth is stimulated by increasing to 22°C;
- In summer, do not allow the greenhouse to warm up above 25–30°C.
2. Humidity in the greenhouse is maintained at 65–75%. It is regulated by ventilation or spraying water mist using fans;
3. Although photosynthesis begins at 2000 lux, in winter the beds are illuminated with an intensity of 6000–8000 lux for 18 hours a day;
4. On hot summer days, to reduce the temperature and protect plants from sunlight, the greenhouse is curtained with a special translucent material;
5. To moisten the soil to a depth of 50–60 cm, intensive watering is carried out. In this case, they adhere to a certain schedule:
- From November to March - every 10 days;
- From March to May and from September to November - every 7 days;
- From May to September - every 4 days.
6. A day after each watering, the soil in the beds is loosened to break the crust and facilitate the penetration of air to the roots;
7. The greenhouse is regularly ventilated. In summer, the windows are simply opened, and in winter, air is pumped through fans with preheating on heat exchangers;
8. To prevent the evaporation of moisture from the soil surface, the area around the plants is mulched with peat, straw or sawdust;
9. Bushes are fed monthly. The technology for growing roses in a greenhouse includes the addition of 40 g/m² superphosphate, 15 g/m² nitrate and 15 g/m² potassium;
10. After collecting the flowers, the plants are pruned, leaving 3-4 strong shoots on the bush. Each second-order sprout is also shortened so that 2–3 buds remain on them;
11. In December and January, roses have a rest. The bushes are pruned, watering is stopped, and the temperature in the greenhouse is reduced to 2–3°C.
How to grow flowers for sale in a greenhouse - a detailed business plan
Roses remain in high demand among buyers all year round.
The first flowers can be cut a month after planting. The profitability of a flower growing enterprise is extremely high and in ideal conditions reaches 300%. Taking into account force majeure and various circumstances, the average return is 70%. In favorable conditions, rose bushes produce an excellent harvest, reaching 10 kg of green mass per 1 sq. m every year. The cost of constructing one greenhouse structure will be approximately 650–700 thousand rubles. Of these, 500 thousand rubles. will be spent on the installation and arrangement of greenhouse support systems, and the remainder of the amount will be spent on the purchase of seedlings, chemicals and fertilizers, equipment, and materials. Current expenses will include payment for heating, lighting, and water supply.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CRmBg7qry_k
Thus, these expenses will amount to at least 55 thousand rubles. One way or another, the annual profit can approach the amount of 3.8 million rubles. if total expenses during the year amount to 80 thousand rubles. The annual income from the sale of roses reaches 3.5 million rubles. To start a business, you need to allow at least two months (installation of greenhouse structures, rooting of seedlings). Profits will begin to flow six months after launch. The payback period for such enterprises is approximately 9 months.
If we talk about greenhouse complexes, the ratio of profit and costs will be different. If we consider ideal conditions, then when growing roses throughout the year without interruptions, the yield of the bushes in the second year of work will reach 200 flowers with a shoot length of at least 80 cm per 1 sq. m. For the purchase of 300 thousand.
rose seedlings will require about 48 million rubles. About 14 million rubles will be spent on fertilizers and 50 thousand mineral wool or coconut mats. Projects of this scale pay for themselves within 3–5 years, and the payback period depends on what varieties of roses were purchased, in which region the greenhouses were set up, what the cost of using electricity, water supply and some other factors are.
When starting your own business, you don’t need to draw up a business plan. Especially if the entrepreneur has experience working in a similar structure, or even better, in organizing a similar business. It is entirely possible not to draw up a business plan if you are going to grow roses on a small scale without attracting outside investment and have definitely decided on a reliable way to sell the finished product. But when building a highly profitable and dynamically developing business, careful planning will help you avoid many nuances and problems.
A competently and efficiently drawn up business plan will have a positive impact on the outcome of contacting creditors and investors, will help determine immediate and far-reaching goals, investment amounts at various stages of project development, the sales market, payback periods and profitability of the chosen business. For a novice entrepreneur who does not have sufficient experience and knowledge in the field of business planning and is not confident in his competence, it is better to contact a specialist to draw up such a plan.
Rare businesses are able to show a profitability of 300%, but growing flowers for sale falls into this category. You will have to work a lot, especially if resources for starting are limited, and it is not possible to afford to hire employees.
A competent business plan will solve problems with preparation and help you get off to an active start. With just five stages of planning, your products will be destined for success.
If the land for the greenhouse is state-owned or registered under a lease agreement, it is wiser to submit documents to open an individual entrepreneur.
The stages of opening a private enterprise are as follows:
- filing an application for registration of an individual entrepreneur or legal entity with government authorities;
- selection of OKVED code. In our case, this is 01.12.2 – gardening and flower growing;
- choice of taxation system - for agricultural producers this figure will be 6% of profit.
You may need to clarify exactly what types of flowers you will grow.
Seedlings and seeds are purchased from January to May. Experienced flower growers germinate seedlings on their own, experimenting with new varieties and developing their own selections.
Wholesale suppliers are ready to offer favorable conditions, but retail purchases for testing are also possible. Hybrid varieties that are able to tolerate low temperatures and are resistant to pests are popular. Store the seeds in a cool place for no more than a year, otherwise the crop may not germinate. Look for seed material on the Internet or at agricultural industry shows.
After purchasing seedlings and seeds, we proceed to the construction and arrangement of the greenhouse. Depending on the plot of land and the scale of the greenhouse, we create a project for the future structure. Standard dimensions will be 20 m long and 5 m wide. The height in the southern and northern parts will be different - 1.8 m and 2.5 m, respectively.
The installation process looks like this:
- Laying strip foundation.
- Installation of a metal frame.
- Sheathing with polycarbonate sheets.
- Installation of a pitched roof.
The structure is placed along the coordinate from east to west, and the northern part is mounted from opaque durable raw materials. Designate ventilation points to prevent mold growth in excessively humid environments. Experienced gardeners recommend sheathing the frame with polycarbonate from the inside to create an air gap that will enhance the thermal insulation effect.
To save money at the initial stage, soil is taken from meadows or forest edges. In early spring, the layer of soil with vegetation is cut off and rolled up. Afterwards, the soil is stored in an expanded form on the site under a polyethylene cover.
In several stages, the ground is irrigated, then covered again with film to heat and destroy weed spores and pest larvae. Only after such preparation is the soil transferred to the greenhouse.
Another option is hydroponics. In this case, the soil is replaced by nutrient liquid. The greenhouse itself will resemble indoor flowerpots in production quantities.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Varieties and technology for growing leeks
Drawing up a business plan should not be neglected - if you do not plan your expenses correctly, you may ultimately suffer significant financial damage.
A rose growing business requires the following:
- a greenhouse, necessarily equipped with equipment for controlling temperature, lighting and heating levels;
- soil with high fertility rates;
- quality fertilizers;
- preparations intended to protect flowers from insect pests;
- roses of the same or different varieties;
- caring for roses and working in the greenhouse according to a specific schedule.
If you are implementing a business idea for the first time, it will take a lot of time to write down its description and design the activities of the future company. These processes involve studying the market, assessing the cost and revenue side, describing the technology and the intricacies of working with personnel, as well as many other issues and nuances. A business plan that describes the company’s activities in growing flowers for sale will allow you to remove most of them.
It is ideal for both beginners and experienced businessmen. This is due to its versatility and applicability to any commercial areas, logic and structure of presentation, as well as a developed system of analytics and financial and economic calculations.
Diseases and pests of roses
Unfortunately, when breeding many spectacular varieties, breeders had to sacrifice the unpretentiousness of plants for the sake of beauty. Therefore, roses often suffer from fungal and viral diseases, which are well known to farmers in businesses such as raspberry growing. You can fight them by spraying plants with systemic fungicides, sulfur preparations and Bordeaux mixture:
- Powdery mildew. Covers leaves, young shoots and buds with a white coating, which causes their gradual death;
- Rust. Appears on the stems as an orange dusty mass. The growth of the bushes stops, the leaves and stems dry out;
- Tracheomycosis. It affects roots, growing in their vascular system. The shoots become brown and brittle and begin to rot;
- Root cancer. It looks like ugly bumpy growths of different sizes. Infected plants stop growing and die;
- Stems cancer. Covers the bark of the shoots with depressed brown spots, in place of which deep ulcers subsequently form;
- Downy mildew. Appears on the leaves in the form of yellow dry spots. Fluffy mycelium is visible on the underside of the plate. Leaves curl and fall off;
- Septoria. Covers the leaves with small cream spots with a brown border. As the disease progresses, the leaf blades die;
- Phyllosticosis. On roses it appears as dark brown or red spots that cover the leaves. The affected parts of the bush dry out;
- Cercospora blight. It appears on the leaves as small gray spots with a wide brown border. Then they cover the entire surface of the leaf blade and cause its death.
There is a widespread belief that in greenhouses there is no need to fear the invasion of insects that damage plants during the process of growing roses in the open ground and caring for them. But experience shows that various pests often appear in closed ground, which should be destroyed with insecticides and acaricides:
- Slobbery pennies. Coleoptera fly 5–12 mm long. Has green wings with a black stripe. Adults and larvae feed on leaf sap;
- Rose aphid. Scarlet insect 1–2 mm long. Forms colonies on leaves and buds, as a result of which they dry out and fall off;
- Spider mite. An insect 0.5 mm long with a red or green body. It feeds on the juice of leaves and young shoots;
- Rose leafhopper. Light green coleopterous fly 3–4 mm long. The larvae eat rose leaves, leaving light marks in the form of stripes and dots;
- Rose sawfly. A family of eight different insects with a brown body 8–10 mm long. The larvae gnaw holes in the shoots and develop there;
- Roseate borer. Bronze-green beetle 6–8 mm long. Its larvae feed on leaves and stems, leaving behind thickenings - galls;
- Gall midge. A mosquito-like fly 2–3 mm long with a brown body. Penetrates shoots and feeds on sap. In these places, spherical growths form;
- Leaf roller. A family of three butterfly species with brown spotted wings. Caterpillars eat young leaves and shoots.
Optimal varieties for growing
There are a lot of rose varieties, but not all of them can grow in a greenhouse; some are intended for growing in open ground. This should be taken into account when choosing seedlings.
The right plant variety is selected not only by its buds, but also by what diseases it is resistant to, especially powdery mildew and various pests.
The most common ones for greenhouses are Floribunda and Grandiflora; tea roses are also perfect for greenhouse propagation, which can be used to decorate ready-made bouquets.
Among the varieties that are not afraid of pests, you can choose Rose Gojard and Queen Elizabeth.
Hybrid varieties have a high survival rate, and they can also come in different shades, giving the gardener the opportunity to create new varieties. These roses include Carina, Baccara, Casanova, Pascali.
There are varieties that were created specifically for cultivation in a greenhouse and they are miniature - these are Little Flirt with a red-yellow color, Skarlet Gem, which has an orange tint, and Beauty Secret - with a rich red color.
Now new varieties are being developed that can grow well and create full buds under full artificial light; they are created specifically for greenhouses.
When choosing varieties, do not forget about how they will grow, whether it will be possible to graft them, or whether the bushes will have an independent root system.
On grafted bushes the number of buds is smaller, but they have strong stems, and on their own root system the flowering is most abundant, but the stems may be slightly thinner. And when using grafting, you can create additional income from the sale of seedlings.
How to cut and store roses?
When organizing business processes, an entrepreneur must know how long a rose grows in a greenhouse. The first full-fledged buds will appear within a month and a half after planting, and in the future the bush will produce new flowers every 5–7 weeks. During the harvesting process, you need to follow some rules:
- Roses are cut until they fully bloom and the buds remain dense. In order not to deprive the plant of leaves, no more than 30% of the flowers are collected at a time;
- The operation is carried out in the early morning or evening, when the concentration of water and sugar in the shoots reaches its maximum. This way roses last longer;
- For cutting, use a sharp knife or pruning shears, treated with a disinfectant solution to prevent infection;
- The collected roses are placed in the refrigerator and cooled to 6–8°C so that they can withstand long-term transportation.
When growing roses for sale, you will have to take care of preserving the flowers until they are shipped to customers. The fact is that the metabolism in cut buds does not stop, and it can only be slowed down by cooling. In practice, dry and wet cold storage are used. For dry storage:
- Barely colored buds are placed in sealed bags to isolate them from the external environment and placed in a refrigerator with a temperature of 0–1°C;
- Slightly blossomed flowers are wrapped in packaging with holes for gas exchange and kept at a temperature of 3–8°C;
- Roses are stored horizontally or hung vertically on special lattice shelves for 10–15 days.
The wet method allows you to slightly extend the life of flowers by feeding the buds with useful substances from the solution:
- To store flowers, prepare an aqueous solution from sugar and special preparations such as Vitant, Nora, Bud;
- One-third of the plants are placed in vessels with bars and placed in refrigeration chambers at a temperature of 1–2°C;
- With constant control of temperature and humidity, plants are stored in a wet way for at least 15–20 days.
Growing technology
To improve the quality of greenhouse roses and increase the flower yield, carbon dioxide can be used. In this case, you will need to lay pipes under the seedlings and provide a place to drain the resulting condensate. You should also monitor the level of carbon dioxide (no more than 0.07%), exceeding it will make it impossible for plants to carry out photosynthesis. In the winter and cold autumn seasons, you can increase the yield by using sodium lamps with a power of up to 600 W. To prevent powdery mildew, sulfur sprayers are used - sulforators. It is better to plant seedlings at a temperature of +1 degree, followed by a gradual increase by 2-3 degrees to 19-20 degrees.
How to sell roses?
Cut flowers look fresh and attractive for only a few days, and therefore, as a business, growing roses in a greenhouse for sale requires prompt sale of products. If the entrepreneur does not agree with buyers in advance, he will most likely have to simply throw away the wilted plants. In what ways and where can you sell roses:
- To flower shops. A farmer can build his own distribution network when he comes to an agreement with the owners of city pavilions. If the product is fresh and of high quality, it is more profitable for the latter to work with local suppliers;
- Wholesale resellers. Entrepreneurs involved in growing and caring for blackberries may know that such intermediaries buy any goods in large quantities at a wholesale price for resale to stores;
- Florists and designers. Such specialists carry out orders independently, work in symbiosis with construction teams and collaborate with organizers of special events. A large wedding sometimes takes up to a thousand flowers;
- Through social networks. You can create your own group, hire a florist and start selling and delivering ready-made bouquets ordered via the Internet. In the composition, the cost of the flower increases by at least 30–50%;
- Through your website. The resource can be intended both for retail buyers of bouquets and for clients purchasing large quantities. With some investment in advertising and promotion, it will turn into an online store;
- Through trading platforms. An entrepreneur can register on the Internet on special exchanges and portals designed to publish offers and search for wholesale clients from among other businessmen;
- In our own pavilion. If you have the opportunity to set up your stall somewhere in a walk-through area or at a wholesale center, you should take advantage of it. Prices in this case will be retail, but the farmer will have to grow several varieties;
- In the store at the greenhouse. If the enterprise is located next to a busy road, you can put signs on the side of the road and organize the sale of cut flowers or seedlings directly from the garden.
Rates
Standard
- Greenhouse business plan for growing flowers: roses and growing indoor flowers - for sale
Volume: 55 pages
MS Word
Buy
Brief business plan without financial model
VIP
- Detailed business plan for a greenhouse for growing flowers: roses and growing indoor flowers - for sale
- Detailed financial calculations of a greenhouse for growing flowers: roses and growing indoor flowers - for sale
Volume: 75 pages
MS WordMS ExcelPDF
Buy
Complete business plan with financial model
Premium
- Detailed business plan for a greenhouse for growing flowers: roses and growing indoor flowers - for sale
- Detailed financial calculations of a greenhouse for growing flowers: roses and growing indoor flowers - for sale
- Optimizing the project to suit your conditions
Volume: 75 pages
MS WordMS ExcelPDF
Buy
VIP tariff Turnkey work
We invite you to read: Secrets of growing watermelons in a greenhouse from experienced agronomists
How to register a business?
Many farmers grow chrysanthemums, gladioli or roses in a greenhouse without registration, in the format of a personal subsidiary plot. In this case, the products can be given to resellers who are not particularly interested in their origin. But in order to work with other enterprises, you will have to create an individual entrepreneur or peasant farm on the unified agricultural tax with the following OKVED codes:
OKVED for growing roses
| 01.19 | Growing other annual crops |
| 01.19.2 | Floriculture |
| 01.19.21 | Growing flowers in open and protected ground |
Activities such as growing lavender from seeds at home, growing roses or other flowers do not require mandatory product certification, although, if desired, a farmer can obtain a declaration of quality from some testing laboratory. But when selling the harvest you will need:
- Phytosanitary inspection report from Rosselkhoznadzor;
- Quarantine certificate for selling flowers to other regions.
Legal side of the issue
To carry out business activities, all documents must be completed. To do this, register as an individual entrepreneur (individual entrepreneur) or LLC. Although, if the volumes of flowers grown do not exceed certain standards for sale, then the private subsidiary plot (personal subsidiary plot) form of doing business will be more profitable.
Since this activity relates to the agricultural sector, it is worth taking advantage of government programs that provide assistance to aspiring entrepreneurs in this area. Having completed everything properly, you can count on benefits when paying taxes, and there is also a chance to receive a grant or other form of material compensation for development.
Equipment for growing roses
Just as when growing strawberries at home, for roses they collect a homemade one or buy a factory greenhouse made of a polycarbonate-coated metal profile. The structure is mounted on a shallow strip foundation to prevent soil freezing, after which it is equipped with microclimate control systems. Such equipment performs the following functions:
- Ventilation. For the summer, the greenhouse is equipped with windows up to 50 x 100 cm in size, controlled automatically or manually. In winter, air is supplied using wall fans equipped with filters and heating heat exchangers;
- Hydration. To mix the air volume and increase its humidity, fans with water fog generators - hydrohair dryers - are attached to the upper beams. In summer, they also help reduce the temperature inside;
- Lighting. The main light sources are sodium lamps or LED panels with a flux of 48–60 thousand lumens, fixed in rows above the beds at a height of 2.5–3 m with an interval of 1.5–2 m;
- Watering. The system includes two large-volume tanks - for heating water and for dissolving fertilizers. Through the pipes, the moisture from them enters capillary ribbons laid in the beds along the rows of bushes;
- Shading. To protect from hot sun rays, electrically controlled curtains made of a special material are installed under the ceiling of the greenhouse; they transmit up to 50% of light and reflect 30% of thermal energy;
- Carbon dioxide saturation. The carbon monoxide concentration of 0.05–0.07% required for plant development is achieved by burning fuel in generators. Gas analyzers are used to monitor air composition;
- Disinfection. To prevent the spread of fungal diseases, in particular powdery mildew, evaporators are installed between the beds, heating sulfur to the melting point - sulfators;
- Heating. The air is heated using registers with a diameter of 60–80 mm, which are connected to a solid fuel or gas hot water boiler. Pipes are laid along the walls of the greenhouse and in the passages between the beds.
Taking into account the climatic and technical requirements for equipping a greenhouse, you can try to draw up an equipment specification for a factory-produced arched complex with dimensions of 8 x 24 m. It will become the basis for further drawing up a business plan for growing roses:
Video on the topic
Equipment for growing roses
| Name | price, rub. | Quantity, pcs. | Amount, rub. |
| Structural elements | |||
| Greenhouse 8 x 24 m | 233000 | 1 | 233000 |
| Strip foundation | 128000 | 1 | 128000 |
| Window for ventilation | 3000 | 10 | 30000 |
| Heating system | |||
| Gas boiler 100 kW | 189000 | 1 | 189000 |
| Circulation pump | 6500 | 2 | 13000 |
| Heating pipe | 70 | 100 m | 7000 |
| Shut-off valves | 8000 | – | 8000 |
| Heating register | 5300 | 20 | 106000 |
| Ventilation system | |||
| Fan 5000 m³/h | 8700 | 4 | 34800 |
| Circulation pump | 4600 | 2 | 9200 |
| Air intake | 2500 | 4 | 10000 |
| Heat exchanger 20 kW | 9200 | 4 | 36800 |
| Hydrofen | 12600 | 4 | 50400 |
| Air filter | 3200 | 4 | 12800 |
| Lighting system | |||
| Cables and machines | 15000 | – | 15000 |
| Lamp DNat400 48000 lm | 340 | 50 | 17000 |
| Curtain system | 22500 | 1 | 22500 |
| Drip irrigation | |||
| Irrigation tank 2 m³ | 27500 | 1 | 27500 |
| Fertilizer tank 1 m³ | 12500 | 1 | 12500 |
| Water well | 45000 | 1 | 45000 |
| Pump and compressor | 75000 | 1 | 75000 |
| Irrigation pipe | 70 | 25 m | 1750 |
| Drainage pipe | 100 | 210 m | 21000 |
| Drip tape | 2 | 350 m | 700 |
| Other equipment | |||
| Refrigerator for flowers | 96000 | 1 | 96000 |
| garden tools | 10000 | – | 10000 |
| Thermohygrometer | 1600 | 2 | 3200 |
| Luxmeter | 2400 | 1 | 2400 |
| Carbon dioxide generator | 6500 | 4 | 26000 |
| Sulfator | 2500 | 2 | 5000 |
| Gas analyzer | 24700 | 1 | 24700 |
| Flower picking trolley | 5400 | 2 | 10800 |
| Van with isothermal booth | 380000 | 1 | 380000 |
| Total: | 1664050 | ||
Industrial greenhouse complexes
If we are talking about the construction of not just one greenhouse, but an entire greenhouse complex, then its dimensions will differ. The height of the columns can be 4.5-5 meters, the span width can be 8-9.6 meters. The columns are installed at a distance of 4-6 meters from each other. A large volume of air allows for slower cooling or heating of the air (which is especially important in the summer months) and maintains the optimal air temperature with lower heat consumption. Often, such enterprises purchase farms where greenhouses have already been built with a spacing of up to 6.5 meters and a stand height of up to 3 meters. In this case, the air volume is increased by lengthening the support posts to 4 meters. The cost of such reconstruction is estimated at about $500 thousand/ha.
“Industrial” greenhouses are equipped with a heat distribution system with the ability to adjust it automatically (using a computer). For heating, it is optimal to use built-in boiler rooms within the greenhouse complex. In addition, you will need a drip irrigation system, which includes a system of main pipelines with filtering equipment, storage tanks for irrigation water, drip lines of various types with compensated drippers, equipment for preparing fertilizer solutions, mixers for solutions, and aeration systems for irrigation water.
To reduce overheating of the greenhouse in the summer and to reduce heat loss in the winter, curtain systems with a capacity of 50% are used. Such curtains can save up to 30% of heat. And when using backlighting, they help increase the level of illumination for plants.
To establish the same temperature throughout the greenhouse, circular hydrofen fans are used, to which water is supplied for fine spraying. In summer, they help reduce air temperature and increase humidity. In addition, the supply of fresh air increases the rate of photosynthesis of flowers.
To sublimate sulfur used to combat powdery mildew, so-called sulfurators are used, which are evenly hung over the entire area of the greenhouse and connected to the power supply through a timer or an automation system for the entire greenhouse. A special computer is used as a climate control system, which controls heating, ventilation, plant power and watering systems, CO2 feeding, and evaporative cooling.
The construction of 4 hectares of such greenhouses costs about 4.5 million euros. This amount includes materials and equipment, customs duties on equipment, work, transportation costs for the delivery of equipment and materials, refrigeration equipment, sorting line, design and survey work.
Business plan for growing roses
Entrepreneurial activity differs significantly in capital intensity from growing roses at home: as you can see, only the necessary equipment will cost the farmer 1.6 million rubles. In addition, you will have to assemble the greenhouse and fill it with soil, connect it to the water supply and gas supply network, and also buy planting material.
In nurseries, varietal seedlings are sold for an average of 250–320 rubles. The usable area of the beds minus the space for paths and climate control devices in a greenhouse with dimensions of 8 x 24 m will be 105 m². Thus, with a planting density of 10 seedlings per square meter, the farmer will need 1050 bushes:
Investment in growing roses
| Article | Amount, rub. |
| Registration of individual entrepreneur or peasant farm | 800 |
| Opening a current account | 2500 |
| Greenhouse soil | 56700 |
| Planting material | 262500 |
| Equipment | 1664050 |
| Installation of equipment | 120000 |
| Connecting utility networks | 50000 |
| Household expenses | 12000 |
| Total: | 2168550 |
The costs of maintaining a greenhouse are determined largely by heating and lighting. In addition, growing roses as a business is difficult to imagine without assistants - hired workers caring for the bushes:
Annual cost of growing roses
| Article | Winter, rub. | Summer, rub. | Amount, rub. |
| IP contributions | 18120 | 18180 | 36240 |
| Banking services | 3600 | 3600 | 7200 |
| Payroll of two workers | 180000 | 180000 | 360000 |
| Electricity | 86400 | 0 | 86400 |
| Gas for heating | 82000 | 0 | 82000 |
| Fertilizers | 1200 | 1200 | 2400 |
| Insecticides | 2500 | 2500 | 5000 |
| Acaricides | 4500 | 4500 | 9000 |
| Fungicides | 2800 | 2800 | 5600 |
| Household expenses | 9000 | 9000 | 18000 |
| Packaging for flowers | 4000 | 6000 | 10000 |
| Documents for flowers | 8500 | 8500 | 17000 |
| fuels and lubricants | 36000 | 36000 | 72000 |
| Total: | 710840 | ||
Financial part
To understand how profitable it is to grow roses, you should first draw up a business plan with calculations. To do this, all expenses and future income are taken into account. And although it is quite difficult to predict individual indicators, it is nevertheless possible to derive average figures based on the experience of existing companies.
| Start-up investment (for the first year) | Amount, in rubles | |
| 1 | Installation and arrangement of the greenhouse | 400 000 |
| 2 | Planting material | 120 000 |
| 3 | Fertilizers and insecticides | 36 000 |
| 4 | Hand tools | 10 000 |
| 5 | Public utilities | 30 000 |
| 6 | Business registration | 10 000 |
| Total: | 606 000 |
From 100 sq. m of sown area you can get about 20,000-25,000 roses per year, but a lot depends on the chosen variety and maintenance conditions. When selling plants for 40-50 rubles per unit, you can count on an annual income of 1 million rubles.
Even with the costs of maintaining a greenhouse and forcing bushes, there remains a good profit in its pure form for the entrepreneur. Payback occurs after the first season and makes it possible to develop and expand the business.
Video: rose growing technology.
Is it profitable to grow roses?
According to reviews from experienced farmers, when growing garden roses, you can collect 200–300 flowers per square meter of bed per year. Minus two months of winter dormancy, the harvest on an area of 105 m² in the cold season will reach 10,500 pieces, and in the summer - 15,750 pieces. If you sell flowers wholesale and retail, your revenue will exceed 2.2 million rubles:
Revenue from growing roses
| Income item | Winter | Summer | Amount, rub. | ||
| Qty | price, rub. | Qty | price, rub. | ||
| Selling roses wholesale | 8000 | 100 | 12000 | 60 | 1520000 |
| Retail sale of roses | 2500 | 160 | 3750 | 90 | 737500 |
| Total: | 10500 | – | 15750 | – | 2257500 |
Further calculations show that growing flowers in a greenhouse as a business, with proper care of the plants and timely protection of them from diseases or pests, will recoup the initial investment in just a year and a half:
Profitability of growing roses
| Index | Meaning |
| Revenue for the year, rub. | 2257500 |
| Expenses for the year, rub. | 710840 |
| Profit, rub. | 1546660 |
| Unified agricultural tax 6%, rub. | 92800 |
| Net profit, rub. | 1453860 |
| Profitability, % | 204,5 |
| Capital investments, rub. | 2168550 |
| Payback period, years | 1,5 |
Step-by-step plan for starting a business growing roses in a greenhouse
Roses are quite capricious flowers. It is not possible to grow them outdoors all year round, given the climatic conditions of our country.
That is why the entrepreneur will need to build a heated greenhouse with an area of about 100 square meters.
There is an option to purchase a finished structure, which will only need to be delivered to the land plot.
If a novice businessman has chosen the option of building a greenhouse on his own, then it makes sense to build it using a material such as polycarbonate.
This will create the required microclimate, which will have a beneficial effect on flower growth.
The average cost of building a heated greenhouse with an automatic watering system will be about 4 thousand rubles.
Thus, the total investment in the construction of such a structure will be equal to 400 thousand rubles.
The entrepreneur will also need to include the cost of planting material in the budget of his business project. About 400 rose bushes can be planted on an area of 100 square meters.
However, some of the flowers will not take root, so the businessman will need to purchase an additional 100 bushes. The cost of planting material will be about 115 thousand rubles.
A small part of the investment capital (about 3 thousand rubles per month) will have to be spent on purchasing fertilizers to stimulate the growth of roses and chemicals for pest control.
To care for flowers, a businessman will need to hire several assistants. At the initial stage, they may become members of his family.
How to properly organize a greenhouse
The rose is a rather capricious flower that is susceptible to external influences. In order to organize the cultivation of roses in the best possible way, it will be necessary to maintain the proper temperature and optimal humidity, as well as protect the flowers from external weather conditions. An excellent solution for growing roses would be a permanent greenhouse made of polycarbonate. Artificial lighting, heating and the possibility of regular irrigation must be organized inside the premises. The greenhouse must be ventilated.
Equipped greenhouse for growing roses
Important! To grow roses, the height of the foundation must be at least 30 cm, since freezing is possible at a lower height.