Bankruptcy - what is it?
Bankruptcy (insolvency) is the inability of a debtor (individual, legal entity or state) to make payments on its debt obligations. Bankruptcy also means a judicial procedure through which the debtor goes through, during which his financial condition is determined, the circle of persons to whom it is necessary to repay the debt, the possibility of repaying the debt with available funds and the subsequent write-off of all debts.
It is customary to call a bankrupt a specific person or organization that has gone through judicial procedures and is declared insolvent by law.
The term "bankruptcy" comes from the Italian banca rotta ("broken bench"). In ancient times, on the Apennine Peninsula, moneylenders made their transactions on special benches, which were called banks. If a moneylender went bankrupt, he would break the bench, signaling the end of his activities due to his inability to pay his debts.
Approximately the same meaning is attached to the modern concept. Bankruptcy is the inability to pay debts and satisfy the financial demands of creditors, as well as make mandatory (for example, tax) payments. In this case, debts must last for at least 3 months, and for individuals, the amount of debt must exceed 500,000 rubles. Only an arbitration court can declare a person or company insolvent (bankrupt) after following a strictly defined procedure, which will be discussed below.
The bankruptcy procedure, its rules and all essential details are described in Federal Law No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” dated September 27, 2002, with subsequent numerous amendments. For example, it became possible to recognize individuals as insolvent only from the end of 2020.
Who can be declared bankrupt
Not every debtor has the right to declare himself insolvent. A person can file such an application in court if he meets certain criteria listed in Art. 213.3 Federal Law “On Insolvency”. Firstly, a citizen’s total debt must reach 500 thousand rubles, the number of creditors and the amount of debt to each of them does not matter, and secondly, loan obligations must not be fulfilled for at least three months.
Important! You can declare yourself bankrupt even if you have a debt of less than 500 thousand rubles, if a person proves his insolvency.
A citizen is presumed to be insolvent when at least one of the circumstances listed in Art. 213.6 of the above-mentioned law:
- the person stopped paying creditors;
- over 10% of credit obligations by the debtor have not been fulfilled for more than one month;
- a citizen’s debt is higher than the value of his property;
- there is a resolution to terminate enforcement proceedings due to the person’s lack of property that can be seized.
This is also important to know:
How can a manager avoid subsidiary liability in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise?
It is worth considering that a debtor is not declared insolvent if there is reason to believe that he is able to repay the debt within a short period using his income.
Purposes of bankruptcy
For a debtor, bankruptcy is a way to get rid of debts and defer the payment of fines, penalties and interest. At the end of the procedure, both an individual and a legal entity, and an individual entrepreneur are completely released from the obligation to pay debts.
For creditors, the process of declaring a debtor financially insolvent is an opportunity to receive at least something from him in payment of the debt. At the stage of competitive procedures, the debtor’s property is ensured safety, and the lessors are forcibly returned to the property transferred to the bankrupt for temporary use.
The safety of the bankrupt's property and the return of property transferred by the debtor for rent or use to other persons are ensured. If the debtor has property, at the end of the bankruptcy procedure it is sold, and the funds are used to pay off debts.
In the case of bankruptcy of legal entities, the creditor, in addition to (or instead of) cash payments on debt, may gain control over the debtor’s business, the opportunity to purchase the property of a financially insolvent person at a low price at auction, cancel the debtor’s illegal transactions and return the property.
Reasons for bankruptcy
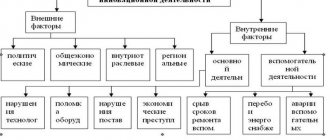
This phenomenon also has reasons, which include economic, financial, and managerial. All the reasons that lead to insolvency can be divided into two groups:
- External. This includes factors that in one way or another have an impact on the company’s activities: the size of the needs and income level of the population, the political situation and internal politics, the current state of the market. Even the level of technology and progress plays a role in this matter.
- The internal ones include the main ones: the business strategy of the enterprise, management tactics, principles of the enterprise, resources. Often, poor quality and weak marketing of a company become the reasons for insolvency.
What is bankruptcy, its types and symptoms
Let us highlight bankruptcy for those entities that the courts recognize as financially insolvent.
The following may go bankrupt:
- Individuals;
- Individual entrepreneurs;
- Legal entities;
- States.
But what bankruptcy can be like, depending on its economic essence and consequences:
1 Real bankruptcy
It occurs when a person is unable to pay off his debts and under no circumstances will be able to normalize his financial situation. Most often, this point is obvious to the debtor from the very beginning, but the law requires that all formalities be observed, and a decision on real bankruptcy is made only after going through the procedures provided for by law. As a result of such bankruptcy, the debtor’s property is sold, the legal entity ceases to exist, and the individual is released from debts with a certain loss of rights (more about this in the chapter “Consequences of Bankruptcy”).
2 Technical bankruptcy
The second type of bankruptcy is “temporary”. The debtor is unable to repay debts in a specific period due to external reasons not related to his own problems. This usually happens due to the fact that someone has not repaid the debts to the potential bankrupt himself, but the possibility of receiving them later remains. Or a large order falls through, but another one comes through. At the same time, the enterprise’s activities continue as usual, no crisis phenomena are observed.
3 Deliberate (intentional) bankruptcy
In this case, debts are built up purposefully, and the person initially does not intend to repay them. Assets are withdrawn or transferred to other persons. If we are talking about a legal entity, then a type of deliberate bankruptcy is fictitious bankruptcy, when financial statements are falsified, in which expenses are inflated and income is understated in order to create the appearance of insolvency.
This type of bankruptcy is criminally punishable under Article 196 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Let's look at each type of bankruptcy in more detail:
Bankruptcy of an individual
By bankruptcy of an individual we mean the inability of a person to pay debts totaling more than 500,000 rubles for three or more months. This amount may include loans, interest on them, mandatory payments to government agencies and other debt. The bankruptcy procedure is initiated only if it is obvious that even after selling his property, a citizen will not be able to pay off his debts.
The bankruptcy procedure of an individual can be initiated by his creditors, the Federal Tax Service, or the person himself, who feels that he is no longer able to pay the debt, and there is no hope in the future. The procedure lasts from 7 months to several years.
Step-by-step instructions for bankruptcy of an individual, a detailed description of all stages and necessary documents are described in a separate article: Bankruptcy of individuals - how to declare yourself bankrupt before the bank and write off all debts.
Please note: personal bankruptcy is not cheap. In 2018, in the capital of the Russian Federation, a full range of bankruptcy services for an individual cost the debtor 100-120 thousand rubles, but the maximum depends on the appetites of various intermediary law firms whose services you can use.
There are also unpleasant consequences of the procedure. For example, within 5 years, each application for a loan will have to indicate the fact of bankruptcy. For three years it will be impossible to manage legal entities. There are other, less tangible consequences.
Bankruptcy of a legal entity
This is a classic bankruptcy: the organization cannot pay debts to creditors, counterparties and the state. The minimum period for initiating bankruptcy proceedings is 3 months. The total debt to counterparties must exceed 300,000 rubles. There must also be a delay in payment of wages of at least 1 month.
Bankruptcy can be initiated by the management or owners of the company based on the results of an audit, creditors, the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, as well as the prosecutor's office.
The law provides for a rather lengthy bankruptcy procedure for an organization. All stages of this process, their timing, cost for the debtor, as well as the procedure for selling property are described in this article: Bankruptcy of a legal entity - main stages, signs of insolvency of a legal entity + step-by-step instructions.
At all stages of recognizing the financial insolvency of a legal entity, a specialized institute of managers is used: bankruptcy, external and administrative. Their work is paid by the debtor. Due to the fact that in Russia managers have little interest in returning legal entities to normal operations, only a small percentage of procedures result in the restoration of the organizations’ work. Most often, property goes under the hammer, creditors return a tiny part of their investments, and bankrupt founders get away with it even in situations bordering on fraudulent actions.
If an existing enterprise is declared insolvent, the main feature becomes the need to respect the rights of the workforce. We are talking about both the payment of arrears on mandatory payments (taxes and contributions to social funds) and wage arrears. Once the debt reaches 100,000 rubles within 3 or more months, bankruptcy proceedings can be initiated for the reasons mentioned (as well as for debt to counterparties).
State-owned enterprises are in a slightly different legal position than all others: their debts are paid by the state, and such a company can become bankrupt only if there is a corresponding clause in the charter.
Since an enterprise is also a legal entity, its bankruptcy procedure is the same as that of any other organization. However, we wrote a separate article on this topic, in which, in addition to the standard steps for bankruptcy of an enterprise, we also described:
- What happens to employees if the company goes bankrupt?
- What is the order of payments when dismissing employees at a bankrupt enterprise?
- What does the bankruptcy procedure look like for a company?
- How to calculate the probability of bankruptcy and how to evaluate an enterprise?
Read the article here: Enterprise bankruptcy - reasons, procedure, order of payments and procedure for dismissing employees.
The usual procedure for declaring the financial insolvency of an enterprise can last up to a year and a half or more, but there is also a simplified 6-month algorithm, when the court is initially clear that the debtor is insolvent and it is necessary to quickly begin selling his property.
Bankruptcy of individual entrepreneurs
The bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur carries signs of both recognition of the financial insolvency of an organization and a similar process for an individual. It also has its own characteristics. For example, individual entrepreneurs can go bankrupt with three months of debt only if the debt is at least 40% higher than the value of the individual entrepreneur’s property (both personal and used for business). Debts on credits and loans (taken specifically for business purposes, not personal) must be more than 10,000 for each creditor and more than 500,000 rubles in total. If the debt is in kind, the individual entrepreneur bankruptcy procedure cannot be carried out.
The same entities can initiate recognition of an individual entrepreneur as financially insolvent as in the case of organizations.
Read the procedure, necessary documents and other details of individual entrepreneur bankruptcy in this article: Bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur: procedure, consequences and nuances.
The cost of bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur turns out to be even higher than that of an organization, and on average exceeds 200,000 rubles. The minimum required to carry out all the necessary procedures using the most truncated algorithm is 45,000 rubles.
After an entrepreneur is declared financially insolvent, he is deprived of registration as an individual entrepreneur and will not be able to repeat his business activity earlier than in 5 years. There are other restrictions.
Criteria for bankruptcy of an enterprise
Official recognition as bankrupt is not possible in all cases, but only if the conditions specified by Law No. 127-FZ are met. In addition to the mandatory reasons, there are indirect signs by which an experienced manager can already understand that the organization is in crisis. This is, first of all, a lack of available funds; low level of liquid assets; refusal of credit lines by financial institutions; accumulation of debts on wages, taxes, settlements with contractors; low business profitability; tough competition in the market, etc.
But all of the listed basic criteria are still not enough - those debtors who meet the requirements of Law No. 127-FZ can be declared insolvent. These special conditions for the amount and time of debt are listed in Stat. 3, 6 and 33 of the Insolvency Law. What are they?
Grounds for declaring a debtor bankrupt:
- The minimum debt period for declaring an organization bankrupt must be 3 months. from the moment of their occurrence (stat. 3). At the same time, cases on overdue debts over 3 months are accepted for proceedings, and the total period of the procedure can stretch up to 2 years, taking into account the time for reorganization of the enterprise.
- The minimum amount of debt is set at 300,000 rubles. for legal entities (stat. 6), 500,000 rubles. – for individuals, as well as heads of peasant farms (stat. 33).
The specified grounds for declaring bankruptcy work “in pairs”, that is, the presence of only one criterion for initiating proceedings is not enough; the condition for the time of overdue debts and the amount of obligations must be met. If we talk about individual entrepreneurs, you should also remember that according to Stat. 24 of the Civil Code, citizens are liable for their obligations with all the property they own, except for their only housing, personal items, land, pets and other objects prohibited for collection by the civil procedural legislation of the Russian Federation.
Note! Full property liability does not apply to owners of legal entities - the amount is limited by the size of the authorized capital or share in it.
Consequences of bankruptcy
For legal entities
A bankrupt legal entity ceases operations and cannot reopen. Its founders are not liable, except in cases where bankruptcy is considered intentional. In such a situation, the owners of a bankrupt company bear subsidiary liability with all their property.
If the damage from deliberate bankruptcy is significant, the founder pays a fine of 500 to 800 minimum wages, and may be imprisoned for up to 6 years. For less serious guilt (concealment and withdrawal of assets, destruction of accounting documents), the punishment will be administrative, the fine will be from 40 to 50 minimum wages, and disqualification for up to 3 years is possible.
For individuals
For individuals who have undergone bankruptcy proceedings, the law introduces additional restrictions.
- For 5 years, each loan application must indicate the fact of personal bankruptcy.
- You can apply for personal bankruptcy a second time only five years after the first.
- For 3 years you cannot manage a legal entity either as a manager or as a member of the board of directors.
How long does the bankruptcy procedure take?
It’s worth saying right away that the process takes quite a lot of time. The court is given up to two months to accept the application for consideration. The proceedings themselves can last six months or more. Federal Law No. 127 establishes the following deadlines:
- debt restructuring – four months;
- sale of property – six months.
This is also important to know:
Legal support of bankruptcy procedures: description, stages, procedure
Important! At the request of persons participating in the case, these deadlines may be extended.
Where are bankrupt property sold?
Debtors' property is sold on special online trading portals - electronic trading platforms. The top five most popular sites include:
- Russian auction house;
- "Implementation Center";
- "Manufacturer";
- Interregional electronic trading system;
- Sberbank AST.
The seller is the bankruptcy trustee. To participate in the auction, you need to issue an electronic digital signature, register on the trading platform, select an object of interest, submit an application and make a deposit. The auction is carried out in three stages.
1 At the primary auction, the participant who offers the highest price compared to the initial price wins.
2 Secondary auctions are held if there are no people willing to participate in the primary ones. The initial price is reduced by 10%, from which bidding increases again.
3 If the property is not sold in the first two stages, a sale is announced through a public offer. This means that the price will decrease step by step until someone buys the property.
We have a separate large article on this topic that answers the following questions:
- What is bankruptcy bidding and how does it work?
- How to make money trading bankruptcy?
- Where to start public bidding (auctions) for bankruptcy?
- How to buy bankrupt property, equipment, cars?
Read the article here: Bankruptcy auctions – Purchase of real estate, cars and other property of bankrupts and debtors at bankruptcy auctions.
How to apply knowledge about bankruptcy in life
Let's talk about how to apply bankruptcy legislation to real everyday situations.
How to check the seller of an apartment for bankruptcy
The bankruptcy of the apartment seller (whether an individual or a legal entity) may entail the recognition of the real estate purchase and sale transaction as invalid. In addition, the buyer will have to prove that he did not know about the impending bankruptcy of the home owner. But even if the buyer is found to be in good faith, the apartment will be taken away from him, since the deal will be cancelled. And getting back the money taken from you by a bankrupt person is almost impossible.
It is impossible to completely protect against such risks: the court has the right to cancel any transaction of the debtor carried out during the last three years before bankruptcy. But you can protect yourself from transactions with a seller who is in the process of bankruptcy in several ways:
1 On the website of the Federal Bailiff Service (https://fssprus.ru/) there is a service “Find out about your debts”. You must enter the first and last name of the apartment seller in the search bar - you will receive a list of debts that bailiffs are collecting from your transaction partner. The very presence of overdue debts should cause concern, and if we are talking about large amounts, the possibility of bankruptcy is very high.
We have a separate article in which we describe in detail How to find out debt from bailiffs - TOP 5 main methods + instructions for payment and recommendations on what to do after payment.
2 All data on open and completed bankruptcy procedures is entered into the Unified Federal Register of Bankruptcy Information (bankrot.fedresurs.ru). The search is carried out in the “Debtor Search” service using full name, tax identification number and other details.
3 In the file of cases of the Arbitration Court (https://kad.arbitr.ru/) you can also find cases on the introduction of bankruptcy proceedings against the debtor.
How to check a developer for bankruptcy
Giving money to a developer who is in the process of bankruptcy means you are guaranteed to lose it. You can check a developer’s financial solvency in the following ways:
- Unified register of developers - here each market participant is assigned a rating based on the number of constructed objects. If the rating is below 0.5 points, it means that there have been delays in the delivery of houses, and with a high probability the developer is at the stage of bankruptcy or is preparing for it.
- Service of the Federal Tax Service - here you can receive an electronic extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities/Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs about a legal entity or individual entrepreneur. If these persons are in the process of bankruptcy, this fact will be reflected in the statement.
- Portals-aggregators of data on legal entities and individual entrepreneurs, for example Rusprofile.ru - information on such portals is promptly updated after changes in the relevant registers, and if a bankruptcy procedure is launched against a developer, this is immediately reflected on its page.
- Unified Federal Register of Bankruptcy Information.
- File of cases of the Arbitration Court.
What should a shareholder do in case of bankruptcy of a developer?
As soon as you become aware of the commencement of bankruptcy proceedings for the developer, you must, within 90 days, declare that your claims are included in the register of debts of the construction company. Information about how much money you have already contributed under the share participation agreement must be transferred to the Arbitration Court, where the bankruptcy process of the developer has begun, or to the bankruptcy trustee. The latter is obliged to find this data independently, but in reality this does not always happen.
Depending on the degree of readiness of the built house, you have the right to demand your money back or be given the keys to a new apartment. The second option is preferable, since the bankruptcy estate (the debtor's property) is rarely enough for all creditors. After you make a claim for an apartment, it will be excluded from the bankruptcy estate and will not be put up for auction. But you will be able to obtain ownership of housing only if the house has already been completed and put into operation. In other cases, a meeting of shareholders must be convened, who will have to decide to create a housing cooperative and independently complete the construction of the house. The meeting can also transfer the unfinished property to another developer, if one is found.
If the developer goes bankrupt in the early stages of construction, the client can be included in the register of affected participants in shared construction (valid in several regions of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Moscow region, Rostov-on-Don, Leningrad region). This list is maintained by the authorities responsible for control of the construction complex in a particular region.
Where to find out about bankruptcy of an organization
Here is a list of resources where you can find out whether a legal entity is in the process of bankruptcy (or the procedure has already been completed):
- Unified Federal Register of Bankruptcy Information.
- Service of the Federal Tax Service.
- File of cases of the Arbitration Court.
- Portals-aggregators of data about legal entities (rusprofile.ru, zachestnyibiznes.ru and others).
How to keep a mortgaged apartment during bankruptcy
According to the bankruptcy law, the bank has the right to take the mortgaged apartment to pay off the debt, even if it is the only one the debtor has. But there is one caveat. Mortgage housing does not go into bankruptcy estate if the housing loan was taken from a bank other than the one that initiated the bankruptcy procedure for the individual. But only if the mortgage is paid on time. Since the apartment is pledged to the bank that issued the housing loan, claims against it from another bank will not be accepted.
Other options to save mortgage square meters:
- buy the loaned apartment before it is included in the register of property subject to sale. The option is complicated due to the need to raise a large sum;
- restructure a problematic mortgage. This option is possible if the bank is ready to accommodate. Changing the term or size of the monthly payment will delay the bankruptcy procedure.
How to buy an apartment at a bankruptcy auction
To buy an apartment at a bankruptcy auction, you need to obtain an electronic digital signature, register on one of the electronic trading platforms and select an object. At this stage, subtleties begin: from the advertisement for sale it is not always possible to understand what the apartment for sale is. Therefore it is recommended:
1 Request from the seller (usually a bankruptcy trustee) scans of real estate documents, photographs and detailed technical specifications. Pay special attention to the location and condition of the apartment: housing located in urban slums with renovations a la the 70s will be very difficult to sell.
2 Check the apartment for the absence of arrests and encumbrances (order an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate on the Rosreestr website). If minors are registered in the living space, you will have to evict them in a long and scandalous manner. You can find out whether the lot is the subject of disputes in the file of arbitration cases.
3 If possible, inspect the property yourself or with the assistance of agents.
4 Check the sales history of the property on Fedresurs: if it was already exhibited, and then the winning bidders refused the apartment, then something is wrong with it. Sometimes it happens that the lot does not exist at all: the house has long been occupied and demolished.
How to buy a car at a bankruptcy auction
The purchase procedure is the same as in the case of real estate, but there are some nuances. Vehicles owned by organizations are very often sold in a state close to death. Therefore, a visual (not from a photo, but “live”) inspection is strongly recommended. It is imperative to check the car for arrests and liens. This can be done on the website of the Federal Notary Chamber. You can also “punch” the car using the VIN number on the website gibdd.ru, on the services of the Avto.ru or Avito.ru portals.
Bankruptcy FAQs
What is a simplified bankruptcy procedure?
Used in bankruptcy of individuals if they do not have property. At the request of the debtor, a shortened procedure is introduced to the Arbitration Court, in which an inventory and assessment of property is not carried out, and the citizen is immediately recognized as financially insolvent. There may be three conditions for introducing a simplified procedure (at least one of them must be present):
- The debtor does not have a regular source of income.
- The debtor was previously prosecuted.
- Debt restructuring had already been carried out over the previous 8 years.
What are current payments in bankruptcy?
The concept of current payments is enshrined in legislation (Article 5 of the Bankruptcy Law). These are any amounts that are paid after the introduction of bankruptcy proceedings: employee salaries, mandatory payments to the budget.
What property of a debtor can be taken away during bankruptcy?
Auctions can be held for any property, including personal property. However, there are several limitations:
- the only housing (it is possible to seize a citizen’s housing or sell it at auction only if it is mortgaged and the loan is not repaid);
- land plots for single housing;
- personal items (clothing, dishes, etc.) and household items (except jewelry);
- property necessary for professional activities (worth no more than 100 minimum wages);
- livestock not used for business purposes, premises for its maintenance;
- seeds for planting on a personal plot;
- food and money in the amount of up to the subsistence level for each family member;
- fuel for individual housing and cooking;
- personal awards;
- vehicles (for disabled people).
How many times can you file for bankruptcy?
A legal entity can go bankrupt only once, after which it ceases to exist. An individual has the right to re-file an application for personal bankruptcy no earlier than 5 years after the first one.
How much does bankruptcy proceedings cost?
For legal entities, the cost of bankruptcy is determined by the number of stages (full or shortened procedure), as well as the volume of property sold.
By law, an enterprise in the bankruptcy process is obliged to pay for the activities of arbitration managers at all stages (from 15,000 to 45,000 rubles/month + percentage of the book value of assets), postage costs, the cost of registration actions, publications in official sources, etc.
For example, for a company with a debt of 3 million rubles and balance sheet assets of 1 million rubles, with a truncated procedure, the cost of bankruptcy will be about 450,000 rubles. Read more about the costs of recognizing the financial insolvency of a legal entity here: What will the bankruptcy procedure for a legal entity cost?
For individuals, the cost of bankruptcy includes the mandatory fee of the arbitration manager (from 25,000 rubles), his percentage of the property sold and related expenses. On average, the cost of personal bankruptcy in Russia in 2020 starts from 100,000 rubles. Read more about the list of costs for bankruptcy of an individual here: How much does the bankruptcy procedure for an individual cost?
What is bankruptcy proceedings?
Bankruptcy proceedings are the last stage of bankruptcy, at which it is recognized that it is impossible to restore the normal operation of the legal entity, the company’s activities are terminated, a bankruptcy estate is formed, the debtor’s property is sold at auction, and the money is used to pay off the debt.
This stage lasts 6 months (with the possibility of extending for the same period), it is carried out by the bankruptcy trustee. From the moment bankruptcy proceedings begin, the powers of the previous managers of the company are terminated, writs of execution cease to be valid, fines and penalties are not assessed, and the sale of the legal entity’s property is almost completely prohibited.
The manager identifies all the company’s property, tries to collect receivables, announces tenders, sells the property, pays the proceeds to creditors, after which the functioning of the bankrupt company ceases, its documents are archived.
How to get into the register of creditors in bankruptcy?
Within 30 days from the date of publication of information about the beginning of the bankruptcy procedure, you must submit an application to the insolvency administrator with a request to include you in the register of creditors.
The application must be accompanied by evidence of the existence of the debt (agreements, invoices, court decisions on debt collection, if any). If the debtor objects, the issue is resolved in an arbitration court. If there are no objections, you will be included in the register and you will have the right to take part in meetings of creditors.
If for some reason you did not have time to submit your claims within a month, there will be another 30 days to do this, but then you will not be able to take part in the first, most important meeting of creditors, at which the strategy for the bankruptcy procedure is approved.
Who appoints a bankruptcy trustee in bankruptcy?
The bankruptcy trustee is appointed by the arbitration court. The bankruptcy initiator can propose a candidate, indicating this in the first application to the court. In this case, the candidate manager must be a member of a self-regulatory organization (SRO).
If desired, the plaintiff has the right to indicate only the name of the SRO, which itself will offer the court one of its participants. The meeting of creditors at its first meeting also has the right to propose a bankruptcy trustee, and then submit its decision to the arbitration court.
How to make money from bankruptcy?
There are three ways to make money selling bankruptcy.
- The first method is to purchase at the lowest possible price for subsequent resale. It is profitable, but not easy and risky. You must be able to look for liquid assets at bargain prices and then quickly sell them.
- The second method is intermediary services at auctions. Your task is to bring the seller and buyer together at bankruptcy auctions and receive a reward for this. This is a more reliable way to make money, but it is only applicable in certain types of markets (for example, in real estate) and you will not get any fantastic income here.
- The third method is agency services. You buy and sell properties on behalf and with investors' money. Your function is to look for high-quality and inexpensive lots, and then sell this property at a premium. The agent usually gets from 10 to 20% of the cost of the lot.
What should I do if the bank goes bankrupt and I have a loan there?
After the bankruptcy of a bank, all its functions are transferred to the Deposit Insurance Agency (DIA). This structure either itself handles the affairs of the bank that has ceased operations, or transfers this responsibility to another bank. Accordingly, your obligations will also transfer there.
If the loan debt was sold to a third party during bankruptcy, the DIA sends out notices of new payment details to all clients and also publishes it on its website (asv.org.ru).
Loan agreements with clients are renegotiated only if essential conditions change (loan terms, interest rate, monthly payment amount, etc.). In other cases, you simply pay using the new details.
It is impossible to avoid payment: the consequences will be the same as for late payment on a regular loan - damaged credit history, fines, collection through the court. Read more about this here: What to do if a bank goes bankrupt and you have a loan from it.
Bankruptcy of a legal entity
Concept and signs
Bankruptcy of a legal entity is the inability recognized by the court to pay debts to its creditors, wages to employees, and transfer taxes and fees to the state.
The main sign of bankruptcy is a 3-month period during which the debtor cannot pay bills. In this case, the amount of debt must be at least 300 thousand rubles. If these conditions are met, the arbitration court initiates proceedings.
The following may apply to the court to declare an enterprise bankrupt:
- the debtor himself;
- bankruptcy creditor;
- authorized bodies;
- employees, both current and former, who are owed severance pay or wages.
All costs of the bankruptcy procedure are paid by the debtor. These include postal and court costs, state fees, payment for the services of an appraiser, auditor, etc. The payment for the work of an external or bankruptcy trustee depends on the value of the debtor’s property.
Let me give you a few examples:
- if the book value of the property is up to 250 thousand rubles, then the remuneration to the manager cannot exceed 10% of this amount, i.e. 25 thousand rubles;
- from 1 to 3 million rubles – no more than 85 thousand rubles + 5% of the excess value of the property over 1 million rubles;
- from 3 to 10 million rubles – no more than 185 thousand rubles + 3% of the excess value of the property over 3 million rubles.
As you can see, the event is by no means cheap. Let's move on to the procedures.
Procedures
During the bankruptcy process, the following procedures are applied to the debtor:
- Observation. Duration – no more than 7 months under the supervision of a temporary manager. He analyzes the financial condition of the enterprise, compiles a list of creditors, and implements measures to preserve property.
- Financial recovery. Duration – up to 2 years. The administrative manager is responsible for this stage. Implementation of measures to save the enterprise. Debt restructuring and drawing up a payment schedule for its repayment.
- External control. It is introduced if the arbitration court comes to the conclusion that the company’s managers are not coping with the situation. An external manager is appointed for a period of no more than 1.5 years with the possibility of extension for another 6 months. Fines and penalties for debts are not assessed, which can lead to the financial recovery of the debtor.
- Competition proceedings. It is conducted by the bankruptcy trustee. Term – 1 year with the possibility of extension. This is essentially the liquidation of the enterprise. During this time, the debtor's property is sold to satisfy the claims of creditors.
- Settlement agreement. Although this stage comes last, it can be done at any stage of the bankruptcy process. Its essence is that the parties find ways to compromise with each other.
Bankruptcy does not necessarily mean the liquidation of a company. Financial recovery measures will help to restructure debts and introduce a moratorium on the accrual of fines and penalties. The liquidation of an unprofitable business also sometimes works to the advantage of managers, if the bankruptcy is not recognized as fictitious.