Share capital is a type of capital of an enterprise that is formed through the issue of shares by this enterprise.
There are two types of share capital, debt and equity.
- Own is a type of share capital in which more securities are issued and sold from existing own funds, reminiscent of a kind of whirlpool. From such profits, shareholders receive annual dividends, but only after paying taxes and salaries.
- Borrowed capital is a type of capital that is formed mainly by borrowing money. They can be bank loans and loans.
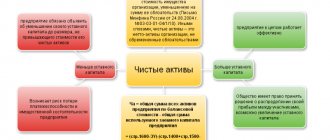
Using the concept of share capital, we can define the equity capital of a joint stock company. The main thing is not to confuse net assets and equity. Since net assets are assets, they represent the difference between the company’s assets on the balance sheet and all debt obligations they have.
What is an organization's equity
This is a financial indicator that characterizes the amount of funds belonging to the participants of the organization.
The definition of equity capital (SC) is given in paragraph 66 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). It says that the IC includes:
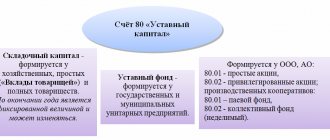
- capitals: authorized (share), additional, reserve;
- retained earnings;
- other reserves.
REFERENCE
Essentially, equity capital (also called equity) is the company's assets minus its liabilities. Another indicator is determined in a similar way - the value of the organization’s net assets (clause 4 of the Procedure for determining the value of net assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n). Therefore, the concepts of “equity” and “net assets” are often equated.
Assess your organization's financial condition and get tips on how to improve it
What is equity?
Own capital can be determined in two ways:
- The net assets of the company are determined. In particular, you need to take into account only assets without taking into account liabilities (debts, etc.).
- A set of values that form equity capital.
Let's consider the features of these methods.
First method
Under the first method, equity is the combination of net assets and retained earnings. The admissibility of using this method is confirmed by the presence of a number of relevant regulations. For example, paragraph 3 of Article 35 of Federal Law No. 208 “On JSC” dated December 26, 1995 states that instead of determining net assets, one’s capital is calculated. Paragraph 29 of Order No. 208 of the Ministry of Agriculture dated January 20, 2005 states that the concept of net assets corresponds to the concept of equity capital.
Second method (as directed by the Ministry of Finance)
The second method assumes that equity includes these values:
- Authorized capital. Formed upon registration of a company. It is formed from the contributions of the founders.
- Extra capital. Appears when the founders of the entity invest funds in the company in excess of their share in the management company. It can also be formed through income from the issue, revaluation of non-current assets, and retained earnings.
- Reserve fund. It represents funds set aside by the company intended to cover losses in the event of an emergency.
- Retained earnings. Represents the balance of funds formed after paying all tax payments and covering other obligations. This also includes the balances of special funds, if the company has them.
Own capital also includes shares of the company purchased from the auctioneer. The parameters necessary for calculations are contained in lines 1310-1370 of the balance sheet.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Which method is better to use? It all depends on the specific circumstances, business practices in a particular environment. For example, the desired method may be recommended by investors, banks and other interested parties.
Methods for calculating equity capital
In practice, two methods are usually used.
The first one is very simple. Its essence is to take the figure indicated in a certain line of the balance sheet as the value of the capital account.
The second method is a little more complicated. It is based on the equality of the concepts of “equity” and “net assets”. For calculations, you must use the procedure for calculating net assets approved by the Ministry of Finance. Take the resulting value as the SC. Note that for the second method (as for the first), the data sources are balance sheet indicators.
Return on Equity
Profitability is an indicator of the efficiency of using a particular resource of an enterprise, which is calculated as the ratio of profit to the balance sheet line. The higher this indicator, the more efficiently the resource is used. Read a separate article about profitability here.
Return on Equity
One of the most important performance indicators for business owners and potential investors is return on equity. It is calculated by the formula:
✅ Cancer=Chp/((K1+K2)/2) , where
- Cancer - Return on Equity
- PE – net profit
- (K1+K2)/2 – average annual cost of capital of the company
Share capital is the money of the company's owners, and the profitability indicator in this case shows the return on every ruble invested in the business.
Net income is taken from the statement of profit or loss, and the average annual cost of capital is taken from the statement of financial position. In the screenshot above, the latter is indicated (K). For 2020, PJSC Rosseti's net profit amounted to 105,292 million rubles, and for 2018 – 124,678 million rubles.
Cancer=105,292/((1,584,105+1,494,962)/2)=0.07
At Rosseti PJSC, the return on equity for 2020 was 0.07. This means that for every ruble invested by shareholders in the enterprise, they receive 7 kopecks of net profit. In fact, this is comparable to a bank deposit, where the current rate is even less than 7% per year.
This indicator needs to be considered in dynamics. For 2020, Cancer was 0.09. This means that, despite the increase in equity capital, its use has become less efficient compared to the previous period. The owners began to receive 2 kopecks (2%) less profit than in the previous period.
Based on the return on equity ratio, we can draw a conclusion about the investment attractiveness. For example, if an investor hesitates between several companies with approximately the same parameters, then he needs to calculate Rak and compare the resulting coefficients. The higher the indicator, the higher the company's profitability.
Return on debt capital
The return on borrowed capital (Rzk) characterizes the efficiency of using borrowed funds. It is calculated by the formula:
✅ Rzk=Chp/Io , where Io is the total obligation.
Rzk 2020 = 105,292/1,065,474 = 0.09
Rzk 2020 = 124,678/1,023,670 = 0.12
For each ruble of borrowed capital in 2020, Rosseti PJSC received 0.12 kopecks of net profit, and in 2020 this figure decreased to 9 kopecks. This indicates less efficiency and possibly a deterioration in the quality of management decisions made.
Overall return on equity
The return on capital indicator (Rk) reflects the efficiency of using own and borrowed resources. It is calculated as the ratio of net profit to the total amount of capital and liabilities (TCL).
✅ Rk=Chp/IKO
RK 2020 = 105,292/2,649,579 = 0.04
RK 2020 = 124,678/2,518,632 = 0.05
The overall return on equity for 2020 decreased by 1 kopeck/ruble compared to the previous period. A bank deposit would generate approximately the same amount, but the capital is usually lent at a higher interest rate. Those. from this point of view, the efficiency of the Rosseti company is also low.
Which line of the balance sheet contains the equity indicator
To apply the first method, you need to know where the company's own funds are reflected on the balance sheet. In the liability, in line 1300 “TOTAL capital”. The number in this line is the sum of the indicators of six lines.
- 1310 “Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners).”
- 1320 “Own shares purchased from shareholders.”
- 1340 “Revaluation of non-current assets”.
- 1350 “Additional capital (without revaluation).”
- 1360 “Reserve capital”.
- 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).”
Fill out and print the balance sheet using the current form in the web service Fill out for free
Structure
Share capital, as an indicator of financial statements, includes the following capital:
- Authorized (paid up share capital).
- Additional (formed during the revaluation of assets, receipt of share premiums, as well as gratuitously received values).
- Reserve (reserve fund created from net profit, consumption fund, etc.).
- Retained earnings (formed due to the effective operation of the company, remains at its disposal).
Net Worth Formula
To apply the second method, you need to use a formula that determines the value of net assets. This formula is enshrined in Order No. 84n of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014.
SC = ASSETS (minus receivables of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital) - LIABILITIES (minus deferred income associated with receiving government assistance)
Table
Decoding the indicators involved in the formula
| Index | Decoding |
| ASSETS | Numbers from balance line 1600 “BALANCE (asset)” |
| Accounts receivable from founders for contributions to the authorized capital | Debit balance on account 75 “Settlements with founders” subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the management company” |
| OBLIGATIONS | The sum of the indicators in two lines of the balance sheet: 1400 “TOTAL long-term liabilities” and 1500 “TOTAL short-term liabilities” |
| Deferred income related to receiving government assistance | Credit balance of account 98 “Deferred income” sub-account “Gratuitary receipts from the budget” |
Reduction of accumulated capital
A decrease in the absolute values of accumulated capital may be caused by unprofitable activities of the company, or withdrawal of funds from funds to finance activities. If the accumulated capital is negative, this means that losses in the current reporting period and for previous years are higher than the funds in the company's funds and accumulated profits.
For financial analysis, absolute and relative indicators of accumulated capital are of decisive importance, since this is a key source of increase in equity capital. Also, accumulated capital plays the role of an indicator of the organization's performance, reflecting its profitability. With the growth of accumulated capital, the financial condition of the company is at an acceptable level in the current period and is likely to maintain a positive trend in the near future.
If accumulated capital shows a downward trend, it means that the company begins to waste the results of its own activities at an accelerated pace. If the fall is long enough, the absolute value of losses can exceed the amount of equity capital, which in turn reduces the level of financial stability.
A sign of serious problems in the financial well-being of an enterprise caused by a negative value of equity capital is an excessive level of accounts payable. There are delays in staff salaries, growing debt to the budget, and late payments for used loan funds. Since the company is unable to attract internal financial sources to finance current activities, it has to reduce the turnover of current liabilities and increase debt. New loans, as a possible option to correct the situation, are becoming increasingly difficult to attract, since current financial indicators are alarming to lenders. Exceeding the accumulated debt to critical standards inevitably leads to penalties, which further increase the company's unprofitability.
Optimal average equity capital
This indicator must be equal to or exceed the amount of the authorized capital (AC) of the company. If this condition is met, the business can be called successful.
IMPORTANT
By law, it is prohibited to allow the equity capital of an LLC to be less than the authorized capital. When faced with such a situation, society must take one of two paths. Either increase net assets to the level of the authorized capital, or reduce the authorized capital to the amount of net assets. If, as a result, the capital company turns out to be less than the minimum established by law (10,000 rubles), the LLC will have to be liquidated (clause 4 of article 4 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Get a sample accounting policy and do accounting in a web service for small LLCs and individual entrepreneurs Get it for free
Sometimes financiers use the following approach to determine the optimal average amount of equity capital. Add up the value of assets with minimal liquidity (these usually include inventories, non-current assets and work in progress). Own capital must be equal to or greater than the value found.
Capital turnover
Capital turnover is understood as the process by which an enterprise's capital passes through all stages of the production process. It is characterized by the turnover ratio (Ko), which reflects how many turnovers the company’s capital makes during the year.
It is calculated by dividing revenue by the total for the line capital and liabilities of the enterprise (Revenue/ICO). There is no standard value for this indicator, but the higher it is, the faster the money invested in the production cycle is returned to business owners.
The revenue of PJSC Rosseti for 2020 amounted to 1,029,654 million rubles, and for 2020 – 1,021,602 million.
By 2020 = 1,029,654/2,649,579 = 0.38
By 2020 = 1,021,602/2,518,632 = 0.4
The turnover ratio decreased slightly in 2020, indicating an insignificant decrease in the company's activity.
Optimal amount of equity capital
Simply calculating your net worth is not enough. It is also necessary to correctly decipher the calculation results. What should you pay attention to? First, you need to make sure that the net asset value is positive. If the indicator is negative, this indicates a high credit load. That is, the company has few assets and many liabilities that are not covered by these assets.
During the analysis process, it is recommended to determine the average annual amount of equity capital. The following formula is used for this:
Average equity capital = (SC at the beginning of the year + SC at the end of the year) / 2.
All the necessary information can be taken from the balance sheet.
A good sign is that the amount of equity capital exceeds the size of the authorized capital. It indicates the investment attractiveness of the company. It is equity capital in sufficient size that is evidence of the success of the business model. If the size of net assets is less than the size of the authorized capital, then the LLC will be liquidated on the basis of paragraph 4 of Article 90 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
WACC calculation
Let's consider the formula for calculating WACC for an enterprise: WACC = (US*TS)+(UZ*TsZ), where:
- ES - equity capital, share;
- CV – cost of equity capital;
- УЗ – borrowed capital share;
- CP – price of borrowed capital.
In this case, the value of the CS can be assessed as follows: CS = PE/SC, where:
- PE – the company’s net profit, thousand rubles;
- SK – company’s equity capital, thousand rubles.
The value of the central lock can be estimated as follows: central lock = Perc/K*(1-Kn), where:
- Percent - the amount of accrued interest, thousand rubles;
- K – amount of loans, thousand rubles;
- Кн — taxation level.
The level of taxation is calculated using the formula: Kn=NP/BP, where:
- NP - income tax, thousand rubles;
- BP – profit before tax, thousand rubles.
Examples of WACC calculations
Let's consider an example of the WACC formula based on the following initial data:
| Income tax | 25431 thousand rubles. |
| Balance sheet profit | 41048 thousand rubles. |
| Interest | 13450 thousand rubles. |
| Loans | 17900 thousand rubles. |
| Net profit | 15617 thousand rubles. |
| Equity | 103990 thousand rubles. |
| Own capital, share | 0.4 |
| Borrowed capital, share | 0,6 |
- Calculation of the tax level: Kn=25431/41048=0.62.
- Calculation of the price of borrowed capital: CC=13450/17900*(1-0.62)=0.29.
- Calculation of the price of equity capital: CA=15617/103990=0.15.
- Calculation of the WACC value: WACC=0.4*0.15+0.6*0.29=0.2317, or 23.17%. This indicator means that the company is allowed to make investment decisions with a profitability level above 23.17%, since this fact will bring positive results.
Let's look at calculating the cost of WACC using another example based on the data in the table below.
| Financial sources | Accounting estimate, thousand rubles | Share, % | Price, % |
| Shares (ordinary) | 25000 | 41,7 | 30,2 |
| Shares (preferred) | 2500 | 4,2 | 28,7 |
| Profit | 7500 | 12,5 | 35 |
| Long-term loan | 10000 | 16,6 | 27,7 |
| Short term loan | 15000 | 25 | 16,5 |
| Total | 60000 | 100 | — |
Below is an example of the formula for calculating WACC: WACC=30.2%*0.417+28.7%*0.042+35%*0.125+27.7%*0.17+16.5%*0.25=26.9% .
The calculation showed that the level of costs for maintaining the economic potential of the company with the existing structure of the enterprise’s sources of funds is, according to calculations, 26.9%. That is, an organization can make certain investment decisions in which the level of profitability is not lower than 26.9%.
Therefore, in analysis, the WACC indicator is often associated with the internal rate of return IRR. This relationship is expressed as follows: if the IRR value is greater than the WACC value, then it makes sense to invest. If the IRR is less than the WACC, then investing is not advisable. In the case where the IRR is equal to the WACC, the investment breaks even.
Therefore, the WACC indicator is decisive when studying the rationality of the structure of financing sources in a company.
Brief description and composition of the enterprise’s capital
The capital of an organization can be monetary (i.e., in monetary terms, in money) or real, implying its expression in the means of production. This approach is considered the most optimal in terms of capital.
As is customary, money capital (MC), in other words, money is used by an organization for the purpose of purchasing means of production. At the same time, the funds that go to support households. activities can be either own or borrowed. Characterizing equity capital from this side, it should be noted that:
- it means the monetary value of property owned by the enterprise;
- it is taken into account as the difference between the book value of this property and the liabilities that the enterprise has at that moment;
Important! The value of the property includes, among other things, amounts unclaimed from debtors.
- its composition takes into account different sources, such as: profits from the results of its activities, authorized capital, share capital, as well as contributions and donations.
Thus, the composition of its capital includes the amounts of: authorized, reserve, additional capital (MC, RK and, accordingly, DC), as well as retained earnings (RE) and targeted financing.
Own capital (hereinafter also abbreviated as SK) gives the right to participate in the management of the organization. The sources of its formation can be external and internal, and the key area of its financing is long-term assets. Meanwhile, specific terms with terms of payment and return have not been determined.
Generalized calculation formula
The process of assessing the cost of capital takes place in several stages:
- identification of the main components - sources of capital formation;
- calculation of the price of each source;
- calculation of the weighted average price using the specific weight of each element;
- measures to optimize the structure.
In this process, you should pay attention to the tax factor, since the calculations take into account the income tax rate.
In a generalized version, the formula looks like this: WACC = Ʃ (Be*Ce)+(1-T)* Ʃ(Vd*Sd), where:
- Be — equity capital, share;
- Вд – borrowed capital, share;
- Ce is the cost of equity capital;
- Сд – cost of borrowed capital;
- T is the tax rate of profit.
A line in the balance sheet reflecting the amount of equity capital
Having chosen the standard method as the preferred approach to solving the issue of calculating the volume of equity capital, it is enough to use the data from page 1300. That is, just take the result of the 3rd section:
SK = line 1300 f. No. 1.
If the company is interested in using the calculation of net assets, then equity capital in the balance sheet is not just a single value from page 1300, but a full-fledged calculation with several variables in its composition. Let's look at how this calculation is done in the next section.
The essence of the term “equity capital”
When characterizing equity capital as an object of economic analysis, two options for its definition are most often given:
- the value of the enterprise's assets unencumbered by the presence of external liabilities;
- a list of sources of financing the organization’s activities that make up the amount of its capital.
The first interpretation is often given in legal acts issued by government agencies:
- in Art. 35 Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ for institutions of the credit and financial sector it is proposed to calculate the value of equity capital, and not net assets;
- in paragraph 29 of the order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated January 20, 2005 No. 6, attention is drawn to the fact that the amount of equity capital is the difference between the assessment of all assets and liabilities of the company, or, in other words, is identical to the term net asset value.
It can be seen that the recognition of the equivalence of the terms equity and net assets is justified, and both of these categories are defined as the difference between the assets and liabilities of a business entity.
The following version of the description of equity in the balance sheet is a combination of elements:
- authorized, additional, reserve fund;
- volume of shares purchased from shareholders;
- retained earnings of the company;
- amounts of revaluation of fixed assets and intangible assets.
All elements are reflected on pages 1310–1370 of the balance sheet. This idea fits well into the global theory of determining the size of equity capital.
The choice of method for calculating equity capital depends on the tasks facing the specialist performing the calculation. In this case, quite often it is necessary to take into account the wishes of investors, credit institutions or company owners. Management’s own views have a significant influence on the choice of algorithm.
Balance calculation
Let's look at an example of the formula for calculating WACC by balance. For this purpose, the following steps must be completed:
- find the company’s financial sources and costs for them;
- multiply the cost of long-term capital by factor 1 - tax rate;
- determine the share of equity and borrowed capital in the total capital;
- calculate WACC.
A sample of the steps for calculating WACC (balance formula) is presented below in accordance with the table.
| Total capital | Balance line | Amount, thousand rubles | Share, % | Price before taxes, % | Price after taxes, % | Expenses, % |
| Equity | Page 1300 | 4206 | 62 | 13,2 | 13,2 | 8,2 |
| Long-term loans | Page 1400 | 1000 | 15 | 22 | 15,4 | 2,3 |
| Short-term loans | Page 1500 | 1544 | 23 | 26 | 18,2 | 4,2 |
| Total | — | 6750 | 100 | — | — | 14,7 |