Hello, Vasily Zhdanov, in this article we will consider a basic concept in financial analysis: net working capital. The value of the index can be used to determine how much a company can independently cope with its obligations. The indicator determines the enterprise's independence from short-term external sources of financing.
Net working capital (NWC) is used to determine solvency in the short term, lasting up to a year. The calculated NOL index indicates the amount of the balance of current assets cleared of short-term liabilities. The amount of PSC is formed from the enterprise’s own funds and long-term liabilities. The NWO indicator is also called working capital - the amount in circulation.
The optimal amount of net working capital
Calculation of the value of NER is necessary for an enterprise to determine the amount of resources consumed in the course of current activities, free from current obligations. Based on information about the value of the indicator, a scheme for rationing and financing working capital is built. When using PSC data, internal working capital management policies are taken into account.
Enterprises use several methods of using working capital:
- Conservative, assuming a full supply of working capital and the presence of excess reserves in case of uncontrollable force majeure circumstances.
- Moderate, providing a sufficient amount of current assets to support normal non-stop business.
- Aggressive, the essence of which is to ensure the normal functioning of the enterprise in the absence of reserves and reserves.
There is a dependence of the NER value on the selected method.
An example of the characteristics of an indicator in the case of using a conservative method. To ensure a conservative method, external sources of financing are increased by attracting short-term liabilities.
The NER indicator shows a level above the optimal value. An enterprise should strive to increase NER, taking into account the fact that a significant increase in the index due to excess reserves is not a positive indicator. An unreasonably high NER indicates low business activity and capital turnover.
The purpose and objectives of working capital management
The purpose of working capital management is to ensure continuous operations while reducing the operating cycle. This allows you to achieve an increase in free cash flow ( Free Cash Flow, FCF)
) and, therefore, increase economic value added (
EVA
).
To achieve the main goal, the following tasks must be solved.
- Cash management. The key point is to determine a cash balance that would allow not only to uninterruptedly finance operating activities, but also to reduce the cost of maintaining the cash balance.
- Accounts receivable management. It is necessary to develop a credit policy that would be attractive to buyers and allow reducing the collection period.
- Inventory Management. The focus is on determining the order size, reorder point and safety stock that will ensure uninterrupted operations while minimizing inventory investment, storage and ordering costs.
- Management of short-term financing. The challenge for managers is to identify suitable sources to finance seasonal or unexpected working capital needs.
Formula for calculating the NER indicator
The NER indicator is a calculated value. When calculating the amount of net working capital, data from Form 1 of the balance sheet (BB) is used.
NOC = OA - KP, where OA are current assets, KO are short-term liabilities. Taking into account the encoding applied to BB lines, the formula is used:
An example of calculating the NEC of an enterprise. According to the balance sheet, the company has, as of the reporting date: current assets in the amount of 120,000 rubles, debt on short-term loans in the amount of 35,000 rubles, accounts payable to suppliers in the amount of 23,000 rubles. The value of the NER indicator was: NER = 120,000 – 35,000 – 23,000 = 62,000 rubles. The indicator was obtained with a “plus” sign. After calculation, it is necessary to compare the value with a sufficient minimum standard.
Second calculation method
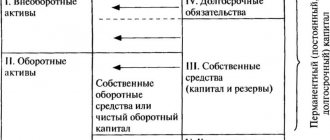
The second method of calculating a company's own working capital is also based on using balance sheet data, but using a completely different algorithm. In this case, data from sections I, III and IV are used.
In this case, the calculation of RNS is carried out using the following formula:
JUICE = SC + DO - VNA,
Where:
SK – equity capital (section III of the balance sheet);
DO – long-term liabilities (section IV);
VNA - non-current assets of the company (section I)
That is, the amount of equity capital (authorized, reserve, additional, retained earnings) and long-term liabilities (repayment for a period of 1 year or more) of the company is reduced by the amount of non-current assets.
Return on net working capital ratio
Important! Along with the indicator of net working capital, the profitability ratio of the NSC is used for financial analysis - the profitability received from investing a ruble.
Rchok = Pch / NOS x 100%, where Rchok is the return on net working capital, Pch is net profit. For the calculation, the average value of the NER indicator calculated for the period is used. The coefficient is calculated based on the results of the annual period. When using a quarterly or other period, the data is multiplied by the number of reporting periods of the year.
Changes in the index determine the growth or decline of economic indicators and the ability to use assets to make a profit.
| Condition | Increase in the coefficient value | Reducing the index size |
| Net profit | Increase in indicator | Decrease in value |
| Asset turnover | Increase value | Downsizing |
| Product price changes | Growth subject to decreasing or equal costs | Reduction in product prices subject to increased or equal costs |
Where is it used?
Knowing the SOC indicator, we can calculate the share of the SK in the formation of the company’s OA:
DSC = SOK / OA
A value of this coefficient of at least 0.1 is considered acceptable. Comparison of this indicator over several periods (over time) will show an increase or decrease in the company’s dependence on external borrowings.
The capital agility ratio illustrates how much the firm's capital is involved in turnover and is calculated as follows:
KMK = SOK / SK
Another important indicator is the availability of inventory sources of financing. If the amount of inventories at the reporting date is less than the value of the SOC, the enterprise is characterized by absolute short-term financial stability. When calculating the supply ratio, the SOC value is divided by the amount of reserves. The normal value of this coefficient is 0.5.
Comparison of the obtained indicator with its optimal value
Analysts compare the actual size of net current assets with the standard value of NWO. The standard level is understood as a sufficient amount of OA required for a particular company. A sufficient NER value is determined by conducting an analysis for each specific enterprise. The information obtained as a result of comparison reveals the level of solvency of the company.
| Correlation with sufficient NER | Characteristic | Peculiarities |
| The value of the indicator exceeds the size of the optimal NER standard | The obtained value indicates wasteful use of resources, overstocking, a significant amount of receivables and excess inventories. As a result of inefficient management of farms, the enterprise will experience a shortage of current funds | A significant excess of the optimal requirement is considered a negative indicator. Unreasonable growth in some cases is associated with additional issue of shares, attraction of irrational loans |
| The indicator size is below the optimal NER value | When the ratio is above zero (the excess of assets over liabilities), the company retains the ability to be liable for current obligations, short-term loans and credits | At the same time, a lack of resources is identified, indicating the possibility of insolvency. Indicates the likelihood of low profitability and wasteful use of resources |
| NER value equal to zero | Indicates the formation of working capital at the expense of own and short-term borrowed capital, indicating that all available funds are aimed at use in circulation | The situation mainly arises at the stage of starting to conduct activities after the registration of the company. For a long-term enterprise, the indicator requires monitoring |
| NER value below zero mark | Indicates a lack of funds to maintain current assets and financial stability. Covering the need for OA is covered exclusively by earthly capital | A negative value of the indicator (excess of liabilities over current assets) indicates losses that, in the worst case scenario, lead to bankruptcy |
An NER indicator below zero is considered risky for investors and company owners. If a negative NER is identified, it is necessary to review the structure of borrowed funds with an increase in the share of long-term lending in the total.
Normal coefficient value
First of all, it is worth noting that the previously mentioned ratio has not been used by foreign companies in financial analysis for quite a long time. For Russian enterprises, the working capital ratio was introduced at the legislative level in order to determine which companies are on the verge of bankruptcy and are undesirable for receiving credit sponsorship. To date, one of these orders has been canceled and has completely lost its force. However, despite this, companies still use it to this day.
According to the documents that prescribed the calculation procedure, the normal value of the coefficient should not be lower than 0.1. According to the experts who drew up this order, this value indicates that the company is not bankrupt and is solvent at the time of reporting. If the company's SOC ratio is below the established standard, then the company's balance sheet is considered unsatisfactory.
It is also worth mentioning that this criterion is quite strict for Russian companies, since almost no one manages to achieve the standard value. In this situation, it would be much more reasonable, as in foreign countries, to cancel the calculation of this coefficient.
Standard value of the NER indicator
The sufficient size of the NSC of an enterprise, recognized as a standard value, differs depending on the industry of activity and the individual characteristics of the enterprise. General unified standards for PSCs have not been developed. Even within the same enterprise, the indicator varies from period to period. Rationing working capital is a prerequisite for running a business.
The minimum (sufficient) value of NSC is defined as the amount of funds required to finance low-liquidity inventories. Objects with low liquidity include mainly inventories stored in raw materials and supplies, as well as work in progress. When identifying criteria for grouping by degree of liquidity, additional economic indicators are used, for example, turnover.
When calculating the standard value of NER, the formula changes:
NOW min = Inventories of materials and raw materials + Work in progress
Features of determining the value of PSC standards:
- When calculating the standard value, the basis is the rule: equity capital should finance the least liquid reserves from among the working capital. When using borrowed funds, investment is aimed at securing reserves with the greatest liquidity.
- As a company develops, the constituent elements of inventories change from a liquidity point of view. Current assets often move from one level of liquidity to another due to the passage of stages of the technological process.
- The data obtained when calculating the indicator is used only in the current calculation period. When business conditions change, the size of the indicator changes and shows an irrelevant size.
To obtain standard indicators, it is necessary to group current assets by degree of liquidity. Each enterprise is based on individual conditions. The grouping is based on the turnover period. Several liquidity groups are used - high, medium, low. For example, for an asset with high liquidity, a company may set a conversion period of a month, for medium liquidity - a quarter, and so on.
Based on the analysis of the structure, a sufficient NER value is determined for each element and working capital as a whole. In order to obtain up-to-date information, the standard and categories of inventory liquidity must be regularly reviewed. Calculation of the indicator is also required when changing the structure of assets, introducing a new nomenclature, or additional types of activities.
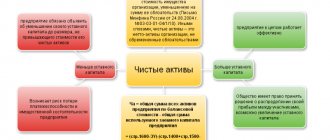
How are net assets calculated in practice?
The formula for calculating net assets, in principle, has a very simple structure. The main thing is to have access to the numbers that are used in it. The main source of these, as we noted above, is the organization’s balance sheet. If we take the corresponding accounting document in the format in which it is approved in Russia, then information about the company’s assets is contained mainly in line 1600, about liabilities - in lines 1400 and 1500.
Moreover, if we follow the recommendations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and subtract from the first the debts of the founders for payments to the authorized capital, from the second - the income of future periods, then we will also need accounting data reflecting the value of the first indicator (as a rule, this is the debit of account 75), as well as numbers on line 1530 (for the second parameter).
Thus, the net asset formula will be applied according to a certain algorithm. Let's study it in detail.
The value of the NSC is higher or lower than the optimal size
Significant deviations of the NER indicator from the optimal value have positive or negative characteristics. The properties that arise when the indicator fluctuates in one direction or the other are taken into account when conducting activities. In practice, the most common occurrence is low compared to sufficient levels of NER. Exceeding the indicator rarely occurs during the operation of the enterprise.
| Conditions | High NER value | Low NER value |
| Positive characteristic | Indicates that the enterprise has high levels of liquidity and solvency, free from current obligations | Shows rational consumption of current assets, optimal capital turnover, low debt load under long-term contracts |
| Negative characteristic | Indicates that the company is irrationally using current assets intended for investment in the production process. There is a high probability of using long-term liabilities | The value indicates an insufficient amount of working capital and the need to attract borrowed capital. Capital in circulation is formed mainly through short-term loans |
What are net current assets?
This indicator is calculated using the following formulas:
CHOA = SK + DZK - VA CHOA = OA - KZK
where NOA is the amount of net current assets (net working capital) of the enterprise; SK - the amount of the enterprise's own capital; DZK - the amount of long-term borrowed capital used by the enterprise (the amount of its long-term financial liabilities); VA is the total value of the enterprise’s non-current assets; OA is the total amount of current assets of the enterprise (its working capital); KZK - the amount of short-term borrowed capital used by the enterprise (the amount of its short-term financial liabilities).
The dynamics of the amount and level of net current assets serves as one of the most important indicators of changes in the financial condition of the enterprise as a whole, as it characterizes the dynamics of sources of financing assets, financial stability and efficiency of use of equity capital.
Net current assets are necessary to maintain the financial stability of an enterprise, since their presence means that it is not only able to pay off its short-term obligations in the current year, but also has the financial resources to expand its activities in the future.
The presence of net current assets and their amount is an indicator of the feasibility of investing in the relevant company for investors and creditors. The presence of net working capital ensures greater financial stability of the company and independence in the face of slower turnover of working capital, depreciation or loss of current assets.
If, with a constant volume of short-term financial liabilities and non-current assets, the volume of equity and long-term borrowed capital increases, then the size and level of net current assets will increase. In this case, the financial stability of the enterprise will increase, but the effect of financial leverage will decrease and the weighted average cost of capital as a whole will increase (since the interest rate on long-term financial loans, due to their greater risk, is higher than on short-term loans).
Accordingly, if, with the constant participation of equity capital and long-term borrowed capital in the financing of assets (with a stable value of the enterprise’s non-current assets), the amount of short-term financial liabilities increases, then the level of net current assets (their share in the total amount of current assets) will decrease. In this case, the weighted average cost of capital can be reduced, a more efficient use of equity capital can be achieved (due to an increase in the effect of financial leverage), but at the same time the financial stability and solvency of the enterprise will decrease (the decrease in the level of solvency will occur due to an increase in the amount of current financial liabilities and an increase in frequency of payments for their repayment).
Thus, the level of net current assets (their share in the total amount of working capital) ultimately determines the relationship between the level of efficiency in the use of equity capital and the level of risk of reducing the financial stability and solvency of the enterprise, and, accordingly, the type of asset financing policy chosen by it (aggressive, moderate, conservative).
Optimization of net working capital
Based on the data obtained on the acceptable minimum rate of NFC and the identification of deviations, measures are taken to optimize working capital. The measures include:
- Reduction of inventories to the optimal value in accordance with the established method of using working capital.
- Revision of management, logistics, warehouse schemes with subsequent optimization of operating costs.
- Inventory of inventories with identification of low-liquid assets subject to write-off or sale.
- Revision of the terms of obligations on borrowed funds with a view to converting them into long-term lending.
- Inventory of receivables and payables with subsequent write-off of uncollectible amounts.
- Monitoring the terms of contracts, reviewing the duration of periods of commercial loans (deferred payment).
In order to prevent disruptions in the provision of current assets, companies are developing a system of risk prevention measures.
Net asset structure
As we noted above, the indicator under consideration is calculated as the difference between the actual sum of all assets and liabilities. In accordance with the point of view widespread among Russian economists, the first should include:
- non-current assets represented by fixed assets, intangible resources, construction in progress, long-term investments;
- current assets represented by various inventories, accounts receivable, short-term investments, VAT on purchased inventories.
At the same time, experts recommend excluding from the composition of current assets the costs of the enterprise for the repurchase of shares for the purpose of their sale or withdrawal from the market, as well as the debts of the founders for payments to the authorized capital. In turn, the structure of liabilities should contain:
- long-term and short-term obligations on corporate loans;
- accounts payable;
- reserves related to future expenses;
- debts to the founders for the transfer of income.
Also, the formula for net assets, based on the structure of such assets under consideration, involves the inclusion in the first and second indicators of any other information that can be classified in one way or another as the company’s resources or its liabilities. We noted above that various legal acts can be used as sources of methodology that can be applied to calculate the financial indicator in question. Thus, one of the main current legal regulations governing the calculation of net assets is Order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n. Let's consider how to calculate net assets (the formula for determining them, in fact, is also presented in the specified legal acts) is proposed by the Ministry of Finance.
Net assets formula: structure and diagram
- First of all, we subtract from the figure on line 1600 the indicator reflecting the debts of the founders to the company for contributions to the authorized capital.
- Then we summarize the indicators on lines 1400 and 1500 of the balance sheet.
- Next, subtract the number on line 1530 from the resulting result.
- The final action will be to subtract from the figure obtained by subtracting the amount of debts from 1600 the indicator obtained after the last calculation.
How might the net worth formula look schematically? Let us agree to abbreviately call the indicator under consideration as NA, the balance sheet lines - STR, and the accounting accounts - SCH.
As a result, the formula for calculating net assets on the balance sheet will look like this:
- NA = (STR 1600 - SCH 75) - (STR 1400 + STR 1500 - STR 1530).
Having studied how the corresponding financial indicator is calculated, let's consider how it can be used in practice.
How to correctly interpret the value of net assets?
Much in the interpretation of the indicator under consideration depends on the specific stage of business development. For young companies, startups, negative values are not as critical as for businesses that have been on the market for a long time. For firms that are present in highly profitable segments, a negative net asset ratio is also acceptable, but again, it is advisable that it does not last long.
It is useful to observe an indicator such as net assets in dynamics over several years. Or, using data from current accounting, track it monthly or quarterly.