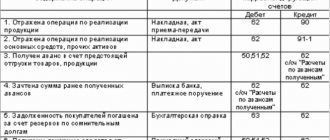
Account 82 “Reserve capital” is used by joint-stock companies and other legal entities to analyze the state and movement of funds in the company’s reserve fund.
Account 82 in accounting is used by legal entities to collect information and subsequently monitor the status of the company's reserve capital.
Account 82 is passive in accounting. Reserve capital at the enterprise is formed and replenished from the net profit of the organization that arose during the current reporting period, as well as the balances of retained earnings from previous periods. The account credit reflects the increase in the size of the organization's additional fund in correspondence with account 84. Debit – displays the expenditure of deferred funds.
Directions for spending reserve capital:
- repayment of uncovered losses of the organization incurred in the current year (correspondence from account 84);
- payment of dividends to the owners of the company if there is insufficient profit allocated for these purposes (correspondence from account 75);
- redemption of bonds in joint stock companies (account 66 or 67);
Note from the author! Bonds are understood as debt securities for which the issuer undertakes to ensure payment to the bond owner (investor) of a certain amount and additional interest in the future.
- repurchase of own shares in the absence of other funds, repurchase of shares for an LLC.
Note from the author! The repurchase of shares for the purpose of their further cancellation is permissible only in the case when the amount of the authorized capital after the procedure for cancellation of the purchased own securities remains within the legally prescribed limit - at least 100 thousand rubles.
Postings to account 82
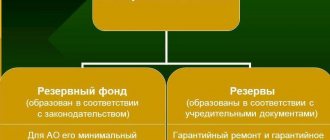
Limited liability companies decide on the formation of an additional resource fund on their own; the amount of deferred capital and the directions for using the funds are recorded in the constituent documentation.
The JSC Law establishes the minimum size of the fund: not less than 5 percent of the authorized capital. The formation of the reserve is carried out by annual transfers of funds up to the amount of the fund approved by the Charter of the company. The minimum threshold for contributions is not less than 5 percent of the organization’s net profit.
How is reserve capital formed?
After the calendar year is completed, all final entries are reflected, reporting for the year is drawn up - a meeting of the participants (founders) of the company is held, at which it is decided how the net profit will be distributed: for the payment of dividends, for the formation of a reserve, etc.
As mentioned above, for joint-stock companies the formation of reserve capital is a mandatory procedure, and it is established that the amount of reserve capital must be at least 5% of the authorized capital. The specific amount of the reserve for each individual organization is determined by its constituent documents (charter).
Therefore, contributions to the reserve each year must be at least 5% of the net profit received for the year. The specific amount of annual contributions must be such that the resulting reserve capital is not less than the amount established by the charter of the company.
Accounting entries for main business transactions with account 82
- Formation or replenishment of company reserves through contributions from company participants (organization founders).
- Formation or replenishment of company reserves by deductions of retained earnings of the current period and previous years.
- Write-off of reserve capital in order to repay issued bonds and repurchase own shares (if there are no other possibilities for performing these operations).
Dt82 Kt66 - under agreements for a period of less than 1 year.Dt82 Kt67 - under agreements for a period of more than 1 year.
- Expenditure of funds to pay off uncovered losses of the current reporting period.
- Increasing the amount of authorized capital (for LLCs, etc.).
- Directing reserve capital funds to pay dividends to the founders of the company (if there is insufficient profit).
Note from the author! The accrual of dividends from the reserve fund is unacceptable for joint stock companies.
Rubleva Elena Alekseevna, 2017-10-19
One of the cases in practice
Let's assume that a certain LLC was registered, the authorized capital of which was 130,000.0 rubles. Part of these funds, or 25%, was contributed in cash, and the remaining amount was formed by contributing a passenger car. At the same time, the accountant of the newly created LLC made the following entries:
1) Dt 75
Kt 80 – 130,000.0 rubles, debt of the founders for contributions to the management company;
2) Dt 50
Kt 75 – RUB 32,500.0, depositing cash as a contribution to the management company;
3) Dt 01
Kt 75 – 97,500.0 rubles, accounting for the cost of the car as a contribution to the management company.
Account 82 “Reserve capital”
Account 86 “Reserve Fund”
Account 86 “Reserve Fund” is intended to summarize information about the state and movement of the enterprise’s reserve fund, formed in accordance with the legislation and constituent documents.
Deductions to the reserve fund from profits are reflected in the credit of account 86 “Reserve Fund” in correspondence with account 81 “Use of profit”.
It should be borne in mind that the Instruction on the procedure for calculating and paying to the budget the income tax of enterprises and organizations stipulates that: when calculating taxable profit, gross profit is reduced by the amount of contributions to the reserve or other funds similar in purpose, created in accordance with the law by enterprises, for which the creation of such funds is provided, until the size of these funds established by the constituent documents is reached, but not more than 25% of the authorized capital. At the same time, the amount of contributions to these funds should not exceed 50% of the taxable profit of enterprises.
Enterprises created in the form of joint-stock companies also credit share premium income to the reserve fund, i.e. the amount of the difference between the sale and par value of the shares, the proceeds from their sale at a price exceeding the par value, which is recorded as a credit to account 86 “Reserve Fund” and a debit to the accounts of cash or other valuables transferred to the enterprise in payment for the shares.
If the current year’s profit is insufficient, the reserve fund may be credited with the amounts of retained earnings from previous years listed in account 87 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” from the debit of this account, as well as unused funds of special-purpose funds from the debit of account 88 “Special-purpose funds” .
If there is an appropriate decision of the founders, targeted contributions from the founders may be credited to the enterprise’s reserve fund in correspondence with account 75 “Settlements with founders.”
The use of reserve fund funds is accounted for as a debit to account 86 “Reserve Fund” in correspondence with the accounts consuming these funds. For example, with account 75 “Settlements with founders” - in terms of amounts allocated for the payment of income to participants in the absence or insufficient profit of the reporting year for these purposes; 87 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” (subaccount 1 “Retained earnings (loss of the reporting year))” - in terms of amounts allocated to cover the balance sheet loss of the enterprise for the reporting year, etc.
Analytical accounting for account 86 is carried out through the channels of receipt and use of reserve fund funds.
Account 86 “Reserve Fund” corresponds with the accounts:
┌──────────────────────────────────────── ───────── ─────┬─────────┐│ Business transaction │Corres- ││ │ponding-││ │current account │├──────── ──────── ──────────────────────────────────────┼── ───────┤│ By debit of the account │ ││ │ ││Accrual of dividends to founders (shareholders) in case of │ 75, 76,││insufficient profit │ 70 ││ │ ││Transfer of part of the reserve fund to subsidiaries │ 78 ││ │ │ │Transfer of part of the reserve fund to internal │ 79 ││divisions on an independent balance sheet │ ││ │ ││Crediting amounts to the authorized fund (in accordance with │ 85, 88 ││constituent documents) and to special │ ││purpose funds │ ││ │ ││С writing down amounts to cover losses of the reporting year │ 87 ││and previous years │ ││ │ ││Attribution of amounts to cover target expenses │ 96 ││ │ ││ To the credit of the account │ ││ │ ││Crediting amounts of share premium │ 51, 52 ││ │ │ │Crediting funds from the founders │ 75 ││ │ ││Crediting funds of internal divisions │ 79 ││on an independent balance sheet │ ││ │ ││Crediting deductions from profits │ 81 ││ │ ││Crediting funds of the authorized fund (part direction │ 85 │ │share value) │ ││ │ ││Enrollment of amounts of retained earnings in case of │ 87 ││insufficient profit of the reporting year │ ││ │ ││Enrollment of unused funds of special funds │ 88 ││appointment in case of insufficient profit │ │ └───── ───────────────────────────────────────── ────────┴ ─────────┘
Characteristics of account 75
The chart of accounts, as well as the Instructions for its use in practice, determine that the 75th accounting account is a category that summarizes all transactions between the company and its founders (shareholders).
To correctly reflect information, you need to know whether account 75 is active or passive? Legal norms establish that accounting account 75 is an active-passive account. This means that this account can simultaneously reflect not only the assets that are the property of the company, but also the sources of their formation, as a result of which the balance can be both debit and credit. For example, if a company has a debt to pay money due to the company's participants, this information should be reflected in the credit of this account, while the debt of the participants for contributions to the company's capital should be indicated in the debit of account 75.
Account 75 is used in accounting to reflect the following practical situations:
- Transactions on deposits in the management company;
- Operations for payment of dividends due to participants and other similar operations.
The following subaccounts can be opened for the “Settlements with Founders” account:
- Account 75-1 - settlements on deposits in the management company;
- Account 75-2 – calculations for payment of income;
- Account 75-3 – other settlements with debtors.
Authorized capital
Start-up capital for the subsequent activities of the company includes contributions from the founders in the form of tangible property and cash. Each shareholder has a certain share in the capital, and in the same proportion he will subsequently receive profit. The amount of capital recorded in the documents must be reflected in the organization’s balance sheet. This is the first operation with which the work of any company begins. For this purpose, the account 80 of the same name is used. This is a passive account. The first operation is to enter the cost of capital into the debit of the account. Subsequent transactions are carried out only on the loan. The account balance is adjusted only if changes are made to the statutory documents, that is, an increase or decrease in the amount of capital.
Subaccounts
The following subaccounts can be opened for account 75 “Settlements with founders”:
- 75-1 “Calculations for contributions to the authorized (share) capital”;
- 75-2 “Calculations for payment of income”, etc.
Next, we will expand each subaccount and provide typical transactions with an account of 75.
Subaccount 75-1
Here they reflect settlements with the founders (participants) of the organization for contributions to its authorized (share) capital.
When creating a joint stock company according to Dt 75, in correspondence with account 80 “Authorized capital”, the debt for payment for shares is taken into account.
When the founders’ contributions in the form of cash are actually received, entries are made according to Kt 75 in correspondence with the cash accounts. And deposits in the form of material and other assets (except money) are recorded using entries according to Kt 75 in correspondence with the accounts:
- 08 “Investments in non-current assets”;
- 10 "Materials";
- 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”, etc.
In a similar manner, they reflect settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital with the founders (participants) of organizations of other organizational and legal forms. In this case, an entry under Dt 75 Kt 80 is made for the entire amount of the authorized (share) capital declared in the constituent documents.
When an organization’s shares are sold at a price exceeding their par value, the resulting difference between the sale and par value is included in Kt 83 “Additional capital”.
Unitary enterprises use subaccount 75-1 to account for settlements with the state or local body for property transferred to the balance sheet under the right of economic management or operational management. It happens:
- when creating an enterprise;
- replenishment of its working capital;
- seizure of property.
These enterprises call this subaccount “Settlements for allocated property.” Accounting for it is made in the general manner.
Subaccount 75-2
This takes into account settlements with the founders (participants) for the payment of income to them. The accrual of income from participation in the organization is reflected in Dt 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” and Kt 75. At the same time, the accrual and payment of income to employees of the organization who are among its founders (participants) is taken into account in account 70 “Settlements with personnel for payment labor."
Payment of accrued income is reflected according to Dt 75 in correspondence with cash accounts.
When paying income from participation in an organization with its products (works, services), securities, etc., entries are made in accounting according to Dt 75 in correspondence with the accounts accounting for the sale of the relevant valuables.
Tax on income from participation in an organization, subject to withholding at the source of payment, is taken into account according to Dt 75 and Kt 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”.
Subaccount 75-2 is also used to reflect calculations for the distribution of profit, loss and other results under a simple partnership agreement. The accounting records for these transactions are similar to the general procedure.
Share price change
If capital increases due to an increase in the value of the securities, then changes are made only at the expense of the organization’s property:
- retained earnings for the previous year;
- capitalization of unpaid dividends;
- share premium;
- accumulation balances;
- funds from the revaluation of funds.
The procedure itself is more labor-intensive, since shares of a larger par value are issued. The same package of documents is being prepared as for the primary issue. Trading is conducted openly or closed, depending on the form of ownership. The primary right to purchase the company's securities belongs to its current owners.
Accounting 75: active or passive?
To correctly reflect the data, you need to know whether the account is active or passive 75 . The answer to this question depends on the type of debt that is reflected in this account. For example, the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital is displayed as a debit to account 75, and the debt of the enterprise for the payment of dividends is shown as a credit. Debt can be reflected both as a debit and as a credit, respectively, account 75 is active-passive.
Thus, in the balance sheet, the first case will be reflected as a debit balance in the asset line on line 1230 “Accounts receivable”, and the second - as a credit balance of account 75 in the liability line on line 1520 “Accounts payable” or on line 1450 “Other liabilities”, if the debt is long-term (according to the order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n).
Capital JSC
The procedure for amending the charter of joint stock companies is more complicated. The capital is divided into the number of shares of a certain value. To make changes, you need to adjust either the number of securities or their price. All these actions are registered with the FFMS before re-registration of the charter.
Changes in the number of shares are carried out by issuing a new subscription. The number of securities of all issues should not exceed those fixed in the Charter. If there is no clause about this in the constituent documents, then you first need to make changes to the Charter, and then change the number of securities.
The change in value is carried out by converting the available quantity of securities into securities with a higher/lower value. The source of cash flow can be profit, additional capital, etc. The decision to increase the company's capital must be made unanimously by the meeting of shareholders.