Account 05 Amortization of intangible assets is used in an organization if it has intangible assets (intangible assets). Amortization of an intangible asset is a gradual transfer of its value to the cost of products (works, services) over the established period of its useful use.
According to the Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, the amounts of accumulated depreciation can be reflected not only on account 05 “Depreciation of intangible assets”, but also on the credit of account 04 “Intangible assets”. The most popular and convenient way to reflect depreciation is using 05 accounts.
Account 05 Amortization of intangible assets
Depreciation for each intangible asset must be accrued monthly, starting from the month following the month when the intangible asset was accepted for accounting and its value was reflected in account 04 “Intangible assets”.
Depreciation of intangible assets is accrued over their specified useful life. Not accrued for intangible assets with an indefinite useful life.
The amortization period for the acquired business reputation of an organization is always set equal to 20 years, but not more than the life of the organization.
Depreciation can be carried out in three ways: linear, reducing balance method, and write-off method in proportion to the volume of production (work).
Depreciation on positive goodwill is calculated using the straight-line method. Negative business reputation in full is attributed to the financial results of the organization in the form of other income.
The depreciation of intangible assets is reflected by posting:
Debit 20,23,25,26,…. Credit 05 - amortization has been accrued on an intangible asset.
Debit 08 Credit 05 - depreciation has been accrued on intangible assets used in the process of creating non-current assets: other intangible assets or fixed assets.
Debit 97 Credit 05 - depreciation has been accrued on intangible assets used in the performance of work, the costs of which are taken into account as deferred expenses.
When selling intangible assets, writing off, gratuitously transferring or transferring as a contribution to the authorized capital, the following entry is made:
Debit 05 Credit 04 - depreciation of intangible assets is written off to reduce its residual value.
How is SPI determined?
The useful life of intangible assets is determined taking into account the following recommendations:
- For intellectual property, the IPR is determined by the validity period of the patent, certificate or other limitation on the period of use, in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
- For other intangible assets of property, SPI is determined in accordance with the agreement on the basis of which the use of this intangible asset is carried out.
- If it is impossible to determine SPI on the property, then set the period of use equal to 10 years.
- For certain categories of intangible assets, the owner has the right to establish personal identification information independently, but for at least 2 years (24 months). Such categories of property are named in paragraph 2 of Art. 258 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note that the SPI established during commissioning can be increased. For example, if, as a result of reconstruction, technical re-equipment or modernization, the characteristics of the object make it possible to increase its service life.
Instructions for account 05 Amortization of intangible assets
According to the instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations in accordance with Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000:
Account 05 “Amortization of intangible assets” is intended to summarize information on depreciation accumulated during the use of the organization’s intangible assets (with the exception of objects for which depreciation charges are written off directly to the credit of account 04 “Intangible assets”).
The accrued amount of depreciation of intangible assets is reflected in accounting under the credit of account 05 “Amortization of intangible assets” in correspondence with the accounts of production costs (selling expenses).
Upon disposal (sale, write-off, transfer free of charge, etc.) of intangible assets, the amount of depreciation accrued on them is written off from account 05 “Amortization of intangible assets” to the credit of account 04 “Intangible assets”.
Analytical accounting for account 05 “Amortization of intangible assets” is carried out for individual objects of intangible assets. At the same time, the construction of analytical accounting should provide the ability to obtain data on the depreciation of intangible assets necessary for managing the organization and drawing up financial statements.
Calculation example
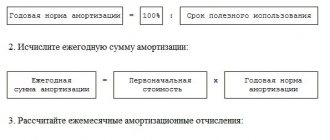
VESNA LLC acquired ownership of an intangible asset worth 5,000,000 rubles. SPI of property - 5 years. The company chose the straight-line method of accrual AM. AM calculation:
- We determine the rate of depreciation per year: 100% / number of years = 100% / 5 = 20%.
- We calculate the amount of depreciation for the year: cost × AM rate = 5,000,000 × 20% = 1,000,000 rubles.
- We determine the size of the monthly payment: annual amount AM / 12 months = 1,000,000 / 12 months = 83,333.33 rubles.
Consequently, VESNA LLC can monthly recognize AM as expenses for the purpose of calculating income tax in the amount of RUB 83,333.33.
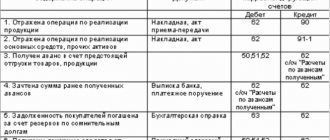
Typical postings for account 05
By debit of the account
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| Depreciation on intangible assets disposed of as a result of sale, gratuitous transfer or liquidation is written off to reduce its original cost | 05 | 04 |
| Depreciation on intangible assets transferred to a branch allocated to a separate balance sheet was written off (posting in the accounting of the head office of the organization) | 05 | 79-1 |
| Depreciation on intangible assets transferred to the head office of the organization was written off (in the accounting of the branch) | 05 | 79-1 |
| Depreciation on intangible assets transferred to trust management was written off (posting in the accounting of the management founder) | 05 | 79-3 |
| Depreciation on intangible assets previously received for trust management and returned to the management founder was written off (on a separate balance sheet of trust management) | 05 | 79-3 |
By account credit
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| Depreciation has been accrued for intangible assets used in the reconstruction or modernization of fixed assets | 08 | 05 |
| Depreciation is accrued on intangible assets used to create other intangible assets | 08 | 05 |
| Depreciation was accrued for intangible assets used during the construction of the facility for the organization’s own needs | 08-3 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets used in the main production | 20 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets used in auxiliary production | 23 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets for general production purposes | 25 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets for general business purposes | 26 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets used in service production | 29 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets intended to support the sales process (by trademark) | 44 | 05 |
| Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets of a trading organization | 44 | 05 |
| Depreciation on intangible assets received from the head office of the organization is taken into account (posting in the branch accounting) | 79-1 | 05 |
| Depreciation on intangible assets received from the branch is taken into account (posting in the accounting of the head office of the organization) | 79-1 | 05 |
| Depreciation has been accrued for intangible assets used in the performance of work, the costs of which are taken into account as deferred expenses. | 97 | 05 |
Non-depreciable fixed assets: used and NU
The differences in the procedure for calculating depreciation of non-current assets represented by fixed assets are broader, starting with the listing of fixed assets that are not subject to depreciation:
- BU - objects of natural resources (land, water, subsoil); museum values; OS NPOs and OS that make up defense reserves;
- NU - objects of natural resources (land, water, subsoil); works of art; OS NPO; ships registered in the international registry; OS resulting from budget or targeted financing; received free of charge; under conservation for more than 3 months or under reconstruction (modernization) for more than 1 year. It is possible that depreciation on electronic computer equipment for organizations working with information technologies (clause 6 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and movable property arising from cultural and educational budgetary institutions (clause 7 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) is not calculated.
What is not considered as intangible assets
Intellectual achievements or abilities of its employees, expenses for creating a business entity, scientific research or development that cannot bring future economic benefits cannot be included in the composition of non-materialized objects.
Important! The results of intellectual work (programs, developments, films, other works) on electronic media that are not confirmed by the exclusive right of ownership to them also do not apply to intangible materials.
Coefficients applied for OS
To calculate depreciation for accounting purposes, it is possible to use only one coefficient: not higher than 3 when calculating deductions from the reducing balance. The range of operating systems to which it is applicable is unlimited.
For options for calculating accounting depreciation with examples, see the article “Formula and example of the reducing balance method for calculating depreciation .
The set of coefficients used to calculate the depreciation rate in NU is much wider, but they can only be applied under certain conditions:
- in an aggressive environment or with an increased shift (no more than 2) - applies to operating systems put into operation before 2014, and does not apply to operating systems of groups 1–3 using the non-linear method;
- from agricultural producers or residents (participants) of special economic zones (no more than 2);
- for energy-efficient facilities included in the list developed by the Government of the Russian Federation (no more than 2);
- for fixed assets serving as the subject of leasing (no more than 3) - not applicable to fixed assets of groups 1–3;
- on OS involved in scientific and technical activities (no more than 3);
- for fixed assets used in oil and gas production at new fields (no more than 3) - the application of the coefficient is canceled (depreciation is recalculated and surpluses are included in income) if at the time of the start of use for other activities the cost of fixed assets is written off by less than 80%.
The taxpayer has the right to independently establish reduction coefficients for tax purposes, but cannot simultaneously apply several different coefficients.
Account card
Inventory accounting of individual units of intellectual property is maintained in a standard NMA-1 card. The document provides basic information about the object:
- how acquired, created
- location
- direction of use
- value determined upon registration
- period of use in economic activity, depreciation procedure
A brief description of the accounting object is also provided.
How to record intangible assets, watch the video:
Examples of accounting for intangible assets
The private enterprise "Molot" acquired the right to a new industrial design for 50,000 rubles (excluding VAT) (1). Additional costs (consultations, fees) amounted to 4,000 rubles. (2)
The sample is planned to be used for 5 calendar years or 60 months.
The initial cost of the intangible asset is 54,000 (50,000 + 4,000). (3)
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method. Monthly amount 54,000: 60 months = 900 rubles (4).
Table 1. Accounting entries.
| Dt | CT | Sum | |
| 1 | 08 | 60 | 50 000 |
| 2 | 08 | 60 | 4 000 |
| 3 | 04 | 08 | 54 000 |
| 4 | 25 | 05 | 900 |
Reflection in the accounting department of intangible assets:
Reflection of investments in intangible assets in the balance sheet
Investments in intangible assets are recorded by enterprise accountants on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, subaccount 08-5 “Acquisition of intangible assets”. Today, there are 2 opinions on how to reflect such investments in the balance sheet (when deciding on the choice of method for reflecting investments in intangible assets, it is advisable to apply a unified approach to reflecting all types of investments in non-current assets):
| Options for reflecting a company’s investments in intangible assets in the balance sheet | Justifications |
| Include “intangible assets” in the indicator of line 1110 and reflect one of the lines deciphering the value of line 1110 separately. | An example of the design of Explanations to the balance sheet and OFR (see Appendix No. 3 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 66n, section 1) contains table 1.5 “Unfinished and unregistered R&D and unfinished transactions for the acquisition of intangible assets,” and section I of the balance sheet does not have a special line for reflecting in it the company’s unfinished capital investments. |
| If the indicator takes on significant values, reflect in section I of the Balance Sheet form “Non-current assets” on a separate and independently entered line. If the indicator takes on insignificant values, reflect on page 1190 “Other non-current assets”. | Investments in intangible assets do not comply with the requirements of paragraph 3 of PBU 14/2007, which means they cannot participate in the formation of the indicator line 1110 “Intangible assets”. |
Intangible assets that are not recognized as intangible
Some IP do not have the expressed properties of intangible assets and cannot be recognized as such.
For example, to confirm know-how, documents are needed that allow it to be identified as individual, belonging to a given business entity and capable of bringing economic benefits in its activities. The presence of copyright in industrial designs, drawings, and formulas also requires documentary evidence. Expenses (sometimes significant) for the creation of new scientific and technical research that do not lead to a positive result cannot also be included in intangible assets.
Internally-created intangible assets
Business entities can create new intellectual property objects on their own:
promising scientific research, as a result of which it is possible to obtain- economic benefits
- new computer programs or useful samples, models, databases
If they are not created for sale to other business entities and will be used for a long time at the enterprise, they are finally assessed taking into account all expenses incurred and registered as intangible assets.
Intangible assets purchased separately
To produce and promote new products in the markets, business entities acquire exclusive rights to:
new patents, inventions, know-how- scientific, technical developments
- brands, trademarks, franchises
- electronic programs and databases
Another type of intangible assets are licenses that provide an exclusive right to operate, use natural resources, and generate income.
OS cost: accounting and tax
Differences in cost between BU and NU are determined by the following:
| Index | BOO | WELL |
| Establishment costs | All costs | All costs other than interest on special purpose borrowings, exchange rate differences, insurance costs, excess costs, non-refundable taxes and registration fees. |
| The amount of cost to be attributed to depreciable fixed assets | Not limited. At the discretion of the taxpayer, OS with a cost of no more than 40,000 rubles. can be accounted for as inventories | More than 40,000 rub. (from 01.01.2016 - more than 100,000 rub.) |
| Cost change | Possible during completion (retrofitting), reconstruction (modernization), partial liquidation and revaluation | Possible during completion (retrofitting), reconstruction (modernization), technical re-equipment, partial liquidation |
Since 2020, the limit on the value of property classified as fixed assets and intangible assets in NU has been increased. See about this in the article “From January 1, 2016, the cost of depreciable property is 100,000 rubles.” .
Intangible assets acquired in a business combination
One type of intangible asset is goodwill - the estimated value of the business reputation of an enterprise resulting from the merger of business structures. Typically, a merger involves leveraging the company's brand awareness in international and domestic markets and can bring a significant increase in revenue.
In addition to business reputation, when merging business structures, other new separate intangible assets may arise:
- research and development
- quotas, licenses with an unexpired period of use, transferred to
- merged business by inheritance
- customer base and regular order packages
Accounting and amortization of goodwill is carried out similarly to other types of intangible assets.