Account 62 in accounting
Settlements are reflected in correspondence with the account. 90 “Sales” and 91 “Other income and expenses”, for which settlement documents were provided:
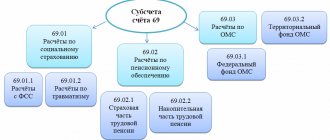
Account 62 has two sub-accounts - account 62.01 and 62.02:
- account 62.01 shows the amount of income. Debit turnover reflects the amount of shipped products, goods, and services. Loan turnover is the amount received from customers.
- account 62.02 shows information about advances received from customers. Debit turnover reflects the shipment made against advances. Loan turnover is the amount of advances received from customers.
Non-monetary payment of obligations
The contract may stipulate that the buyer will repay his debt with non-monetary means.
When repaying a debt with a bill of exchange, you need to open a separate sub-account for it in account 62. And when repaying the debt, the following entries are made:
- Debit 62 Credit 62 – a bill of exchange was received to repay the debt
The organization shipped goods worth RUB 223,742 to the buyer. (VAT 34130) their cost is 112,120 rubles. The buyer issued a promissory note to repay the debt. He paid it off after 2 months.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 62 | 90.1 | Revenue from the sale of goods is reflected | 223 742 | Packing list |
| 90.3 | 68 | VAT on sales reflected | 34 130 | Invoice ref. |
| 90.2 | 41 | Products written off | 112 120 | Packing list |
| 62.3 | 62.1 | Bill received | 223 742 | Accounting information |
| 62.3 | The bill has been repaid | 223 742 | Bank statement |
Postings to account 62 Settlements with buyers and customers using an example
Let's study an example when a product is sold remotely through an online store. Payment for goods purchased through the online store can be made in one of the following ways:
- Bank card (transfer of funds is regulated by law dated June 27, 2011 No. 161-FZ);
- Cash to the courier upon delivery of goods (when selling goods through an online store, OKVED code 52.61.2);
- Through electronic payment systems (regulated by law dated June 27, 2011 No. 161-FZ).
Example
The VESNA organization sells goods through an online store. The organization entered into an Internet acquiring agreement with the bank, on the basis of which the remuneration is 1.5% of the receipt amount. Consequently, the amount of revenue minus remuneration is transferred to the current account.
Buyer Ivanov I.I. in January 2020, I paid for the goods with a bank card in the amount of RUB 50,000.00, incl. VAT 18% - RUB 7,627.12. After receiving the bank statement, the organization ships the paid goods to the buyer.
To carry out the operation, the accountant creates the following entries:
| Debit Account | Credit Account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 57.03 | 62.02 | 50 000,00 | The buyer made an advance payment by bank card | Payment register |
| 76.AB | 68.02 | 7 627,12 | We charge VAT on the advance received | Invoice issued |
| 51 | 57.03 | 49 250,00 | Receipt of proceeds to the current account | Bank statement |
| 91.02 | 57.03 | 750,00 | Bank remuneration under the agreement | Bank statement |
| 62.R | 90.01.1 | 50 000,00 | Accounting for sales revenue | Sale of goods and services (act, invoice), Invoice issued |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 7 627,12 | VAT accrual on shipment | |
| 90.02.1 | 41.11 | 50 000,00 | Write-off of shipped goods | |
| 62.02 | 62.R | 50 000,00 | Settlement of advance received | |
| 68.02 | 76.AB | 7 627,12 | VAT deduction on advance received | Book of purchases |
Buyer Petrov P.P. I ordered goods worth RUB 12,000.00 through an online store, incl. VAT 18% - RUB 1,830.51. The buyer paid the goods in cash to the courier upon delivery of the goods. The delivery cost is 20% of the cost of the goods and is included in the price of the goods. According to the accounting policy, goods are accounted for at sales prices using 42 accounts, the trade margin in the organization is 15%.
To reflect the operation, the following transactions are generated:
| Debit Account | Credit Account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 50.01 | 90.01.1 | 12 000,00 | We take into account retail revenue | Help - report of the cashier-operator (KM-6) |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 1 830,51 | We charge VAT on retail sales | |
| 90.02.1 | 41.11 | 12 000,00 | We write off sold goods at sales prices | |
| 50.01 | 90.01.1 | 12 000,00 | Delivery of proceeds to the cashier by courier | Receipt cash order (KO-1) |
| 90.02.1 | 42.01 | — 1 105,38 | Calculation of trade margins on goods sold | Help for calculating the write-off of trade margins on goods sold |
Buyer Sidorov A.P. through electronic payment systems paid for goods in the amount of 95,000.00 rubles, incl. VAT 18% - RUB 14,491.53. The money was first credited to the seller’s “electronic wallet” and then transferred to a bank account minus a commission. The commission is 3.5% of the transfer amount – RUB 3,325.00. The next day the goods were shipped to the buyer.
Postings for the operation:
| Debit Account | Credit Account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 55.04 | 62.02 | 95 000,00 | Advance received from buyer using electronic money | Register of payments. |
| 76.AB | 68.02 | 14 491,53 | We charge VAT on the advance payment | Invoice issued |
| 51 | 55.04 | 91 675,00 | Funds were transferred to the current account | Bank statement. |
| 76.09 | 55.04 | 3 325,00 | Bank commission withheld | Bank statement. |
| 44.01 | 76.09 | 2 817,80 | The commission amount is included in expenses | Packing list |
| 19.04 | 76.09 | 507,20 | Input VAT included | |
| 76.09 | 76.09 | 3 325,00 | Advance credited | |
| 68.02 | 19.04 | 507,20 | VAT is accepted for deduction | Invoice received |
| 62.R | 90.01.1 | 95 000,00 | Accounting for sales revenue | Sale of goods and services (act, invoice), Invoice issued |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 14 491,53 | VAT accrual on shipment | |
| 90.02.1 | 41.11 | 95 000,00 | Write-off of shipped goods | |
| 62.02 | 62.R | 95 000,00 | Settlement of advance received | |
| 68.02 | 76.AB | 14 491,53 | VAT deduction on advance received | Book of purchases |
Receivables from buyers for goods, works or services
Both individuals and legal entities can act as buyers. For each of them it is necessary to maintain analytical records.
The buyer's debt arises after the posting is made Debit 62 Credit 90.1 (91.1, ).
Recognition of debt depends on the recognition of the moment of sale established in the accounting policies of the company, as well as in the terms of the supply agreement. In accounting, the buyer's obligations are always reflected at the time they arise. There are two possible options for debt to arise:
- At the moment of transfer of ownership upon shipment of goods to the buyer. The organization reflects sales (Debit 62 Credit 90.1 (91.1))
- Ownership of goods passes only after payment. In this case, the organization does not reflect the fact of debt in any way
Repayment of debt is reflected by posting Debit (50) Credit 62
The company sold goods in the amount of 124,500 rubles. (VAT RUB 18,992). Their cost amounted to 75,250 rubles. Under the terms of the contract, the buyer became the owner of the goods at the time of shipment.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 62 | 90.1 | Sales of goods | 124 500 | Packing list |
| 90.3 | 68 | VAT on sales reflected | 18 992 | Invoice ref. |
| 90.2 | 41 | Products written off | 75 250 | Packing list |
| 62 | Money transferred for goods | 124 500 | Bank statement |
Account 62 which is reflected in debit and credit
Account 62 in question is active-passive in accounting. Therefore, it can reflect both the organization’s debt to customers (credit balance) and the buyer’s debt to the organization (debit balance). Thus, the debit balance on account 62 indicates that products, goods, services have been shipped and there is a debt from buyers for goods shipped or services provided.
The credit of accounting account 62 displays funds from the sale of products (goods) and for services rendered, as well as prepayments and advances received. But payments and advances are accounted for in different subaccounts:
- Subaccount 62.01 – takes into account payments received in the general manner;
- Subaccount 62.02 – takes into account advances received from customers.
Thus, the credit balance on account 62 means that the enterprise has a debt to customers for advances received.
How is account 62 used in accounting?
Since the account is active-passive, the balance on it can be either positive or negative. A debit balance indicates that companies or private clients have debts to the organization, and a credit balance indicates that the company has not made payments to third-party companies.
The remaining amount of the account is determined taking into account the initial balance. The debit turnover is added to the positive balance, and then the credit turnover is subtracted. If a negative balance is obtained, then it is transferred to the account credit, but without the minus sign. The situation is similar with the credit balance.
Balance sheet for account 62
It is important before closing the month and drawing up a report on the financial condition of the enterprise to check that the accounting registers are filled out correctly. One of the verification options is the formation of a balance sheet (hereinafter referred to as TSA) for the period under audit:
What the balance sheet shows for account 62 and how to read SALT is shown in the following table:
| Accounting section name | Initial balance | Turnover for the period | Final balance | |||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | |
| Score 62 | Buyer's debt balance | Remaining debt to the buyer | Amount of shipped products (goods, services) | Payment from buyers for the period | Buyer's debt balance | Remaining debt to the buyer |
- Account 10 Materials in accounting: postings, examples, subaccounts
- Accounting 26 for dummies: examples and postings
- Account 41 in accounting: typical entries, subaccounts and examples
- Accounting 20 in accounting: examples and postings for dummies
Characteristics of account 62
Accounting account 62 is an analytical account that summarizes information on all customers of an organization, including legal entities and individuals. Using the account 62 the accountant of an enterprise at any time and on the required reporting date can, on the one hand, formulate the amount of debt for sold products and services, and on the other hand, determine the amount of planned shipments.
Thus, we can say that account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is a mirror copy of the account. 60. And the turnover and balance generated by the seller duplicate the buyer’s data. The information obtained is clearly used by the parties to the transaction when conducting reconciliations by drawing up reports. For the convenience of direct users (executives, managers, accountants), account 62 in the accounting department has analytics on counterparties, documents (invoices, acts), contracts. Additionally, if necessary, you can classify mutual settlements:
- By payment method - upon shipment, prepayment, mutual settlement, etc.
- According to the timing of settlements - whether the debt is overdue or not.
- According to the presence of the bill - discounted (discounted) at the bank, overdue or the maturity date has not yet arrived.
The accounting service of the organization has the right to decide independently how to use account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, taking into account the legislative norms of Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000. The main thing is to provide external and internal users with reliable and timely information. If the activity is carried out by a group of interconnected enterprises account 62, the postings are given below and are carried out separately in relation to such operations.
Typical accounting entries for account 60
There are several standard entries for account 60 that allow you to record transactions in the company’s accounting. The most common ones include:
| Debit accounts | Credit accounts | the name of the operation |
| , , | 60 | Receipt of valuables |
| 60 | 50.01, 51, 52 | Payment of debt for previous deliveries |
| 94, 76 | 60 | Write-off of shortage |
| 19 | 60 | VAT on purchased goods |
| 50, 51, 52 | 60 | Payment by supplier invoice |
| 10, 15, 41 | 60 Non-faculty supplies | Receipt of materials without documents |
| 60 Non-faculty supplies | 60 | Payment for uninvoiced goods |
| 60, 91.02 | 91.01, 60 | Write off exchange rate differences |
| 91.02, 63 | 60 Advances issued | Write-off of previously paid advance |
When drawing up a balance sheet, account balances 60 are indicated in different sections. Accounts receivable are recorded as assets, and credit balances are recorded as liabilities.
Transfer
Loan turnover from the second section at the end of the period is transferred to the first section of the new journal, and then to the general ledger. Account balances 60 are displayed in the Analytical Data table. Turnover according to KT60 (first section) is recorded in the column of the same name in the general ledger. DT turnover is displayed in the “From credit account” section. 60". Entries are created on the last page of the journal.
Let's look at how auditing (accounting) is carried out at enterprises in different industries.
Count 60:
- Catering: DT07, 10 - with data 46-APK.
- Manufacturing enterprises: account. 20-1 - with data from report No. 18A, account. 20-2 - with data from report No. 18B.
Score 11 of enterprises from all industries is compared with:
- 73-APK;
- DT60, KT51 revolutions and 2-APK data; KT55 and 3-APK data; KT66 and 4-APK data, etc.
The results of form No. 6-APK must correspond to the synthetic accounting data:
payment amount + write-offs for the month + outstanding debts + unwritten amounts = total of column 14 + debt at the beginning of the month.