At the end of the reporting period, each enterprise or organization summarizes the results of its activities. As a result, net profit or loss is determined. The second option indicates improper organization of the company’s activities, ineffective management and requires careful, in-depth, comprehensive adjustment of processes in the course of further activities. If a company receives a net profit, it can distribute it according to its needs. This affects the further development of the organization. Where can retained earnings be used, and how does this affect the company’s activities? These issues will be discussed further.
What is included in the concept
You might be interested in: Where can I get 50,000 rubles urgently? Adviсe
Where can retained earnings be used? To understand this, you need to consider the essence and features of its calculation. This income is also called accumulated profit. It remains at the enterprise after paying all taxes, fines, and other obligatory payments. Also, the concept presented closely intersects with net profit.
Profit requiring distribution is a resulting indicator that reflects the company's performance for the entire period. Net income reflects how the company performed during the reporting period.
Accounting considers profit before distribution as a final indicator, which is reflected in account 84 of the organization’s reporting. It is not distributed, but brought to a single result. How to distribute profits will be decided by shareholders at a meeting that takes place after the close of the reporting period in the spring or summer.
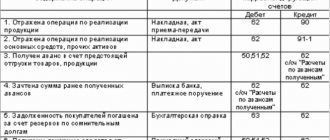
The calculation of profit before distribution is carried out according to a certain scheme. To do this, take data from account 90 “Sales”. This reflects the amount of profit from the sale of goods, provision of services or work. This information is reflected on the loan. The debit of account 90 shows the cost of production. VAT is also charged here and other costs are reflected.
In the process of generating income that requires distribution, the final balance from the specified account is transferred to account 99. It's called Profit and Loss. If a profit is made, the accountant records the funds as follows:
- Dt 90 Kt 99.
Channel PROGRAMMER'S DIARY
The life of a programmer and interesting reviews of everything. Subscribe so you don't miss new videos.
If the balance of account 90 is negative, the posting looks like this:
- Dt 99 Kt 90.
The result of operations from operating and non-operating activities is reflected in account 91. It is called “Other income and expenses.” The following transactions are reflected in this account:
- sale or lease of assets that belong to the enterprise;
- depreciation or revaluation of non-current assets;
- profit from transactions with foreign currency;
- investing in the authorized capital of other organizations;
- donation or liquidation of property;
- income (expenses) from procedures with securities.
You may be interested in: Operating hours of Sberbank in Perm. Branch addresses
The following entries can be made to this account:
- Dt 91 Kt 99 – profit for the reporting period is determined.
- Dt 99 Kt 91 – a loss was incurred.
Disposal of retained earnings from previous years
The profit received by the company can be distributed exclusively by order of the owners of the company. This norm is provided for by the laws “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ and “On Joint-Stock Companies” dated 12/26/1995 No. 208-FZ.
But there are also certain distribution frameworks that establish that when an NP is formed at the end of the year, the company is allowed to use it for the following purposes:
- issuance of dividends;
- repayment of previously incurred losses;
- to account 84 to accumulate profits for the purpose of its further use;
- formation of reserve capital;
- increase the authorized capital;
- other purposes established by laws No. 14-FZ and No. 208-FZ.
For example, the company's management has the right to reward employees from distributed profits. Find out how to correctly account for such payments in the material from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
The direction of NP for the above purposes is accompanied by the corresponding entries in accounting:
| This year's NP is aimed at: | Dt | CT |
| For accrual of dividends | 84 | 75 |
| Formation of reserve capital | 84 | 82 |
| Increase the authorized capital | 84 | 80 |
In circumstances where the company decides to use retained earnings in account 84 to compensate for losses from previous years, it is necessary to make a posting between internal subaccounts. In other words, do internal wiring.
When a company receives a loss at the end of the year, it is allowed to repay it from the following resources:
- reserve capital;
- NP of previous years;
- authorized capital (after changes in the charter);
- target funds belonging to the founders.
In this case, the following wiring is required:
| If the loss is covered by: | Dt | CT |
| Reserve capital | 82 | 84 |
| Founders' target funds | 75 | 84 |
| Authorized capital | 80 | 84 |
In addition, the company has the opportunity to significantly reduce the loss incurred in the current period due to retained earnings from previous years. In a company that decides to do this, the accountant will make an internal entry to account 84.
Formation of financial results
There are other sources of retained earnings that take into account the results of the company’s activities when forming them. Thus, writing off amounts on accounts 90, 91 in accounting practice is called balance sheet reformation. However, for some companies the procedure for generating retained earnings does not end there.
Among other things, the balance of other accounts is transferred to account 99. It can be:
- Account 76. It is called "Extraordinary Expenses and Income." This, for example, could be the loss of funds from natural disasters or compensation for losses through insurance compensation, etc.
- Count 10. It's called "Materials". This reflects the value of inventory items received on the balance sheet that cannot be used during production.
In the statement of retained earnings, the total amount is increased if errors are discovered in the financial statements. In this case, such actions lead to unreasonably inflated costs. The amount also increases if there are unclaimed dividends, if more than three years have passed since they were accrued to shareholders.
If there are errors that overstate the amount of profit, the amount of retained earnings for the year is reduced.
This result is not always generated solely by the funds in the relevant current accounts. For example, when a fixed asset is devalued, profit increases, but no additional money occurs. This must be taken into account when conducting economic analysis.
On the last day of the reporting period, the organization writes off the results of account 99 to account 84. The full amount of income before distribution is reflected here. To do this, the chief accountant must make entries when receiving profit in the reporting period:
- Dt 99 Kt 84.
If a loss was incurred, the posting would be as follows:
- Dt 84 Kt 99.
Then account 99 is reset to zero and no transactions are carried out on it until the end of the next reporting period. It is worth noting that account number 84 is active-passive. Before the amount of income is entered into it, income tax is deducted from it.
"Special Purpose Funds"
The current Chart of Accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n) does not provide for separate subaccounts for the creation of special-purpose funds (in the previous Chart of Accounts of 1992, account 88 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” provided for subaccounts “Consumption funds " and "Accumulation funds").
Sometimes the owners of an organization decide to pay bonuses to employees and financial assistance from net profits. Some even decide to create so-called consumption and accumulation funds, charitable foundations.
Important
The laws on JSC and LLC do not provide for any payments from profits to anyone other than the owners. And account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” is the account of the owners, and only they have the right to receive dividends.
And the Russian Ministry of Finance has repeatedly indicated that account 84 is not intended to reflect all kinds of social and charitable expenses, payments of material assistance and bonuses (see, for example, letters of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated June 19, 2008 No. 07-05-06/138, dated 19 December 2008 No. 07-05-06/260).
Expenses of an organization are recognized as a decrease in economic benefits as a result of the disposal of assets (cash, other property) and (or) the emergence of liabilities, leading to a decrease in the capital of this organization, with the exception of a decrease in contributions by decision of participants (owners of property) (clause 2 of PBU 10/99) .
Organizational expenses for sporting events, recreation, entertainment, cultural and educational events and other similar events, as well as transfers of funds to charity, are other expenses and should be accounted for in account 91 “Other income and expenses.”
In other words, any disposal of assets (except for dividends) is an expense of the current period (clause 2 of PBU 10/99). They have nothing to do with the organization's net profit. Such expenses cannot be debited to account 84; this is contrary to current accounting regulations.
So, if the owners want the company to buy an operating system from profits or spend money on charity, the accountant needs to record such costs in the usual way as assets or expenses. When purchasing fixed assets, organizations simply spend funds from the current account and one asset (money) is exchanged for another (fixed asset).
And the organization’s expenses for paying bonuses to employees, transferring funds to charity, and the like are always recognized as expenses of the organization and are reflected in the financial results statement. Account 84 is not used in postings.
Acquisition of fixed assets
Based on the Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, you can organize accounting for sources of capital investments, and in this case account 84 will be used. This must be provided for in the accounting policy.
The use of profit for the acquisition of fixed assets is reflected in accounting by the following entries:
DEBIT 01 “Fixed assets” CREDIT 08 “Investments in non-current assets”
- the object is included in fixed assets;
Simultaneously
DEBIT 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” CREDIT 84
“Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”, subaccount “Retained earnings aimed at purchasing fixed assets”
— net profit is used to purchase property.
EXAMPLE The accounting policy of JSC Aktiv (general taxation system) defines the source of financing for capital investments - retained earnings. The Aktiva accountant opened a subaccount for account 84, “Retained earnings aimed at acquiring fixed assets.” In April of the current year, a fixed asset worth 53,100 rubles was purchased. (including VAT - 8,100 rubles). The accountant made the following entries: DEBIT 08 CREDIT 60 - 45,000 rubles. - fixed asset purchased; DEBIT 19-1 CREDIT 60 - 8100 rub. – “input” VAT is taken into account; DEBIT 01 CREDIT 08 – 45,000 rub. - the acquired fixed asset is accepted for accounting; DEBIT 68 CREDIT 19-1 - 8100 rub. - “input” VAT is accepted for deduction; DEBIT 84-2 CREDIT 84-3 – 45,000 rubles. – the source of financing is reflected (the use of net profit for the purchase of fixed assets).
The essence of revenue before distribution and uncovered loss
Having considered to which account retained earnings should be accrued and how this process occurs, you need to pay attention to the essence of the presented category. This is an absolute indicator that reflects the efficiency of the enterprise. In accounting, there are no significant differences between profits requiring distribution and uncovered losses. The difference is in the wiring. The debit and credit of accounts when making a profit or loss are different.
You may be interested in: Operating hours of Sberbank in Perm. Branch addresses
In most cases, a company that has been operating for several years covers excess costs with the remaining revenue from previous years. Funds can also be written off from the reserve fund, additional or authorized capital.
If a profit is made, the organization has the right to independently decide for what purposes it should be directed. The decision is made at a meeting of shareholders. Depending on the current market situation, as well as within the company itself, the direction for financing is selected. There are several directions for distributing the net profit received in the reporting period.
Retained earnings are reflected in the liability form No. 1. In this case, there is an increase in capital due to retained earnings. These are the organization's own funds that can be reinvested in production. Based on the indicator of profit before distribution, one can draw a conclusion about the effectiveness of the means used in production. If you analyze in detail the information that is used to calculate the presented indicator, you can draw conclusions about what factors influenced it in the reporting period.
If the organization received a loss, its amount is reflected with a minus sign and is taken in parentheses in the balance sheet. In this case, it is extremely important to determine why the company did not make a profit in this period. There are many factors that lead to a drop in income. They must be identified, and then a technique must be developed to prevent negative effects in the future.
The procedure for recording the indicator
Retained earnings in the balance sheet is the total of account 84 of the balance sheet liability. Its value represents the accumulated amount of the company's net profit since its inception. Therefore, the amount of accumulated earnings can be a positive or negative number.
If the company did not have retained earnings or retained losses reflected in account 84, the financial result for the year will be equal to the net profit from the corresponding report.
Changes in retained earnings in the current reporting period compared to the previous reporting period are not directly reflected in the balance sheet. However, you can calculate retained earnings in the balance sheet by subtracting the value of the indicator of previous years from the corresponding value of the current year. If there is any change in the accounting policies or practices adopted by the company in the current financial year, the company may also restate opening retained earnings. The purpose of this practice is to report changes in retained earnings in the current accounting cycle due to a change in policy.
Calculation technology
Own capital and reserves can be replenished from net profit. To calculate it correctly, simple technology is used. To do this, you will need to determine the amount of net profit, income before distribution at the beginning of the year, as well as the amount of dividends. If the company is a joint-stock company, payments are made to the owners of the relevant securities. For an LLC, dividends are paid to the founders.
The corresponding data is presented in the balance sheet in line 1370 and in the income statement in line 2400. If the company received net profit, the calculation looks like this: NP = NPn.g. + PE – D. Where:
- NPN.g. – profit before distribution at the beginning of the year.
- PE – net profit.
- D – dividends paid to owners.
If no income was received in the current period, it will not be able to replenish capital and reserves. In this case, the calculation is made using the following formula: NP = NPn.g. – U – D. Where:
- Y – the amount of the company’s net loss.
The loss may be greater than the amount of accumulated net profit at the beginning of the year. In this case, a negative value is indicated in the balance sheet. It is placed in parentheses. This is already an uncovered loss that reduces the balance sheet currency.
Retained earnings. Check
All NP for the past years is summarized in accounting account 84, the balance credit balance is placed in line 1370 of the balance sheet. The same line contains the amount of uncovered loss (if any), which is indicated in parentheses. Uncovered loss means the difference between the company's expenses and income during the year, according to which the first point exceeds the second.
The account contains information about the denomination and changes in the amount for the reporting year. At the end of the year, the amount is credited to account 84, while the loss is written off as a debit. The main task of this account is to store information about the purposes for which the funds were used.
An uncovered loss is sometimes called a deficit profit. The loss can be fully or partially compensated using reserve capital funds. In the case of compensation, data on the initial loss is not filled in (in case of partial compensation, only the remaining amount of the loss is indicated in parentheses).
IMPORTANT! At the request of the accounting department, additional lines – 1371 and 1372 – can be entered in the balance sheet to differentiate the figures for the reporting and previous years.
Types of accounting
The amount of retained earnings can be accounted for in different ways. There are two options:
- Cumulative.
- Yearly.
With a cumulative accounting system, separate sub-accounts are not opened for profits from previous periods and the current year. The entire amount is reflected in account number 84. It accumulates starting from the first year of operation of the organization. If a loss occurs, it is covered by previously created savings.
The cumulative accounting system is most often found in small enterprises. The weather approach is more detailed. In this case, there are separate sub-accounts for accumulating amounts for previous reporting periods. Second order accounts can come in different formats. For example, there are accounts 84.1 and 84.3. The first of them is used to account for profit before distribution for the reporting year, and the second - for previous periods.
To obtain detailed information, data is taken from the explanatory note of the annual report (attached to the balance sheet by large and medium-sized organizations) or from accounting entry account 84. Reporting from previous periods is also used for analysis. If errors are identified from previous years, they will be taken into account in the current year's results.
Introduction
Retained earnings are earnings that have not been distributed to shareholders. This is why these funds are called “retained” rather than distributed. Retained earnings are a cumulative figure. This means that the amount of retained earnings shows the sum of all the profits that a company has retained up to a certain date. Therefore, it does not apply to just one financial year but applies to all financial years up to the above date.
Reflection of retained earnings in the balance sheet of the enterprise is carried out in the 3rd section of liabilities. Its value decreases when losses occur, and increases as a result of profit. This indicator is also called “accumulated profit”, “accumulated income” or “indivisible profit”.
The amount of the balance of retained earnings for previous years can be calculated as the amount of the credit turnover of account 84. As a result of the factors that determined the receipt of a retained loss by a company in the current year, this company can compensate for it at the expense of the residual value of retained earnings accumulated over previous years.
Information in the current period
The company's retained earnings are reflected for the current period in various subaccounts. For example, accounting can be kept like this:
If the company receives net income this year, the accounting department reflects it using the following entries:
- Dt 84.1 Kt 84.2.
If a transaction was carried out with an account of 84.3, this means that the profit was used for various needs of the company.
When using different accounting methods, using the last entry in the reporting period, the accounting department will write off funds from account 99 and transfer them to account 84. Tax must first be deducted from this amount, and only then it is applied to the result. The following wiring is done:
- Dt 99 Kt 68 – tax calculation is carried out.
- Dt 84 Kt 75 – calculation of dividends (account 70 – bonuses to employees can be used).
Use of profits
The decision on the distribution of net profit is made by the owners (founders) of the organization (general meeting of shareholders or meeting of participants in an LLC). Such a decision is usually made at the beginning of the year following the reporting year.
Important
The distribution of net profit is within the exclusive competence of the general meeting of participants (shareholders) and cannot be carried out by the sole direction (order) of the head of the organization.
Net profit can be used for:
- payment of dividends to shareholders (participants) of the organization;
- creation and replenishment of reserve capital;
- repayment of losses from previous years.
In the first two cases, reflect the use of net profit in the debit of account 84:
DEBIT 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” CREDIT 75 (70)
– dividends accrued to shareholders (participants) of the organization;
DEBIT 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” CREDIT 82
– net profit was directed to the creation and replenishment of the organization’s reserve capital.
If the owners of the organization decided to use the net profit to pay off losses of previous years, make an entry in the accounting to the subaccounts of account 84:
DEBIT 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” CREDIT 84 subaccount “Uncovered loss”
- net profit is aimed at paying off losses of previous years.
Important
The meeting of shareholders (participants) of the organization may decide not to distribute the profit received at all (or leave some part of it undistributed).
After you have recorded the use of profits (repayment of losses), the balance in the “Profit to be distributed” subaccount of account 84 shows the amount of retained earnings. This amount can be transferred to the appropriate subaccount:
DEBIT 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” CREDIT 84 subaccount “Retained earnings”
- reflects the amount of retained earnings of the organization.
EXAMPLE 1 Based on the results of the past year, the net profit of JSC Aktiv amounted to 70,000 rubles. In the analytical accounting for account 84, the accountant of Aktiv JSC provided the following subaccounts: - 84-1 “Profit to be distributed”; — 84-2 “Retained earnings.” On December 31 of last year, when reforming the balance sheet, the Aktiva accountant made the following entry: DEBIT 99 CREDIT 84-1 – 70,000 rubles. – net profit is reflected. In February of this year, at the general meeting of shareholders, it was decided to use net profit as follows: - allocate 5% to replenish reserve capital; - 50% should be used to pay dividends to shareholders. Based on this decision, the Aktiva accountant reflected the use of profits with the following entries: DEBIT 84-1 CREDIT 82 - 3500 rubles. (RUB 70,000 × 5%) – funds were allocated to replenish reserve capital; DEBIT 84-1 CREDIT 75 – 35,000 rub. (RUB 70,000 × 50%) – funds were allocated to pay dividends to shareholders; DEBIT 84-1 CREDIT 84-2 – RUB 31,500. (70,000 – 3500 – 35,000) – reflects the amount of retained earnings.
Who has the right to use?
You may be interested in:Drafting 3-NDFL declarations for individuals
Before considering where retained earnings can be used before distribution, you need to pay attention to who can use it for certain needs. Only the owners of the company have the right to decide what expenses to cover at its expense. These may be shareholders or members. Therefore, the accountant’s account 84 is often called the owner’s account.
According to current legislation, the decision on the distribution of profits is made at a general meeting of participants or shareholders. Accounting for the distribution of revenue will depend on what decisions the owners make through open voting. Next, the accounting department receives the appropriate instructions recorded in the minutes of the meeting.
But owners sometimes make serious mistakes in the process of distributing profits. But the future fate of the company depends on the correctness of this decision. It is the accountant and analyst who can tell shareholders what is the right thing to do in this case.
There are several options for using retained earnings. The procedure for carrying out this process is regulated by legislation in the field of regulation of LLCs and JSCs. There are several options for how to distribute the organization's net profit.
The essence of the agreement
If you invest all the profit received in the reporting year in additional capital, this will be a decision in favor of those who want to refinance. If all profits are given out as dividends, then there will be no profit, and the enterprise will not be able to increase its economic power. Therefore, collective owners assume: part of the profit of the reporting year, which remains from the distribution of shares, can be claimed by the owners not based on the results of this year, but based on the results of economic activity in future reporting periods.
From a legal point of view, this is normal, but from a moral point of view it’s even good: I lend funds to an enterprise, but I can take them back later. However, there is a difficult point here. These funds are invested in the operating capital of the company, they work as part of it, sometimes for several years, become part of the enterprise, without which it is difficult to imagine its life and, suddenly, I or someone else demands huge dividends. If these whims are shared by other shareholders, the consequence may be a limitation of the company's future activities or even its economic collapse.
Reserve Fund
When considering options where you can use such income, you first need to pay attention to it. The law stipulates that joint stock companies are required to form a reserve fund from net profits. Moreover, its size must be at least 5% of the amount of the authorized capital.
In the event of losses, the accumulated reserve funds will be able to cover it. This fund is also used to repurchase its own shares and repay bonds. If the organization is a limited liability company, they can create a reserve fund at will, on a voluntary basis. The charter of such a company must specify the size of such a fund, the purposes for which these funds can be spent, as well as the amount of annual contributions.
To create a reserve fund, the accountant records the following entry:
- Dt 84 Kt 82.
In the balance sheet, this amount is reflected in line 1360 of the third section. This allows us to improve the capital structure. Owners are prohibited from withdrawing funds from the organization to the amount of the reserve fund. This increases the safety of the company, increases its stability and, as a result, investment attractiveness.
What to do with retained earnings
There are several main ways to refer an NP. Among them:
- payment of dividends to owners/shareholders;
- compensation for earlier losses;
- accumulation of reserve fund funds;
- other goals agreed upon by managers.
IMPORTANT! Regarding the last point, it is worth making a small clarification. In this case, managers do not mean nominal officials, but business owners. As a rule, they resolve such issues during the final annual meeting, at which the corresponding minutes are drawn up.
Dividends
Dividends are paid from retained earnings. This leads to a decrease in the organization's assets. This is the amount of compensation that owners receive for providing their capital to the company. This procedure is reflected in accounting by posting:
- Dt 84 Kt 75.
When the money is paid to the owners, the following entry will be reflected:
- Dt 75 Kt 51.
Money can be withdrawn from the account in advance. In this case, they are issued in cash from the cash register. And the wiring will be as follows:
- Dt 75 Kt 50.
Dividends can be paid not only in money, but also in property. But this practice may be declared unlawful in court. Therefore, the company must first sell the property, deduct VAT from the resulting amount, and then pay the owners. If goods or fixed assets are issued as dividends, the sale of which does not require payment of this tax, VAT is not charged. This, for example, could be land plots.
Payment of dividends from retained earnings of previous years
Joint-stock companies can initiate the payment of dividends after mandatory contributions to the reserve fund have been made. The remaining amounts are allowed to be used entirely for dividend payments. There is no requirement for preliminary replenishment of the reserve base for LLCs.
At the time of accrual of dividends, the amount of retained earnings decreases. When reflecting a transaction to transfer dividend amounts, the decrease affects the assets of the enterprise (cash resources or property). Dividends can be paid in cash or in kind. Postings:
- When dividends are accrued, retained earnings from previous years (account 84) are debited while account 75 is credited.
- When funds are actually sent to the recipients' bank accounts, an entry is made between D75 and K51.
- For cash payments, correspondence will include D75 and K50.
In order to make settlements with the participants of the organization for dividends by transferring property to them, it is necessary to charge VAT on these assets. The norm is explained in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 15, 2014 No. GD-4-3 / [email protected] Payment of dividends in kind is equivalent to sales transactions. In this situation, accounting entries are made:
- D76 – K90.1 when reflecting revenue from goods transferred to shareholders or members of the company;
- D90.2 – K41 after writing off the cost of the transferred assets;
- D75 – K76 – the accumulated debt on dividend payments was offset.
Loss Coverage
If a company has received an uncovered loss, it must write it off in different ways. There are several possible ways:
- At the expense of the reserve fund.
- From the accumulated profit fund for previous years.
- Due to additional capital.
- Reduction of authorized capital.
- At the expense of the owners' own funds.
The reasons why the company suffered a loss must be established. Measures are being taken to prevent this from happening in the future.
Source
Typical entries for account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”
The correspondence of accounts and the main entries for account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” are presented in the table:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description |
| 99 | 84.01 | Reflection of the amount of net profit based on the final turnover for the reporting year (December) |
| 84.01 | 75.02/70 | Reflection of dividend payments (as of the date of decision making) |
| 84.01 | 82/80 | Net profit attributed to reserve capital/authorized capital |
| 80 | 84 | Reflection of the reduction of the authorized capital to the amount of net assets (as of the date of state registration) |
| 84.02 | 99 | Reflection of the amount of loss based on the final turnover for the reporting year (December) |
| 99 | 84.03 | Reflection of the total amount of retained earnings between shareholders |
| 82/75/80 | 84.02 | Reflection of covering the loss at the expense of reserve capital (as of the date of the decision)/own funds of the founders/authorized capital (after state registration of these changes) |
| 84.03 | 84.02 | Covering the loss with the accumulated amount of retained earnings |
| 84.03 | 84.04 | Reflection of the fact of use of retained earnings when creating property |