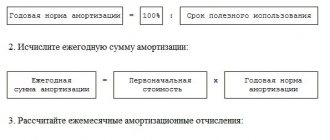
Business processes and business operations
In the activities of a manufacturing enterprise or organization that performs work or provides services, three processes are distinguished:
- supply,
- production,
- implementation.
Processes consist of a set of business operations.
A business transaction in accounting is an action (fact), the result of which is changes in the composition, distribution of property and the sources of its formation. For example, the movement of cash, material assets, liabilities.
Business processes in accounting are reflected as business transactions are carried out - in this case, the subject of accounting becomes the fact of the transaction and the result.
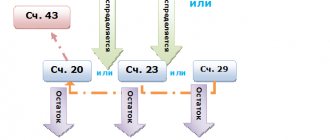
Business operations and processes of the enterprise - diagram
Features of reflecting accounting entries
Each production action must be documented. Changes arising from the operation are of a dual nature and occur in two interrelated accounting objects. A characteristic feature of the operation is that it is shown on the accounts twice: in debit and credit. This relationship represents the correspondence of accounts.
Transactions are reflected on accounts at the time of their occurrence, i.e., as they are completed. Double entry reveals the opposite nature of the asset and liability accounts, linking them to the form of the balance sheet. On the left they reflect the balances of the property (debit), on the right - the sources of its appearance (credit).
Correspondent accounts and balance form a single system, connected by double entry, which is based on three principles: (click to expand)
- Duality of reflection;
- Fixation of amounts for Dt and Ct accounts;
- In both accounts, changes are shown in the same amount.
For control, the registration of the action in accounting is repeated twice. First of all, it is reflected as a fait accompli confirmed by documents, then - by the distribution of amounts among correspondent accounts.
Example 2. Posting
Contents of the operation: materials worth 85 thousand rubles were received from the supplier.
Reasoning:
The changes affected two accounts: account. 10 — balances of inventory items and invoices increased. 60 - the debt to the supplier has increased.
Account 10 - active, takes into account assets, growth is put in Dt;
Account 60 - passive, height - according to Kt.
The increase in assets and liabilities corresponds to operations of the third type. The posting is written as follows: Dt 10 Kt 60.
Types of business transactions
Accounting in the business accounting system distinguishes 4 types of transactions depending on their impact on the balance sheet.
Business transactions in accounting: classification table
| Impact on balance | Correspondence account sign | |
| by debit | on loan | |
| active | active |
| passive | passive |
| active | passive |
| passive | active |
Type I are transactions that reduce one asset item “at the expense” of another. Examples: arrival of finished products at the warehouse, receipt of funds from the current account to the cash register. There is a change in the composition of the organization’s property, but not its total amount:
Types of business transactions in accounting - examples
Business operations are divided into 4 types. All of them influence the balance, but the equality of the balance is not violated.
Example 1
Funds in the amount of 5,000 rubles were transferred to the bank account of Zvezda LLC as payment for the goods received.
Wiring: Dt 51 Kt 62 - 5,000.
As a result of such an operation, the balance sheet currency remained unchanged; changes occurred only in the balance sheet asset items. The item “Current account” increased by 5,000 rubles, and the item “Settlements with buyers and customers” decreased by the same amount.
Example 2
Zvezda LLC made a profit at the end of the reporting period. The company's participants decided to calculate and accrue dividends in the amount of 10,000 rubles.
Wiring: Dt 84 Kt 75 - 10,000.
As a result, the balance sheet currency again remains unchanged, but the liability items on the balance sheet have changed. The item “Settlements with founders” increased, the item “Retained earnings” decreased by 10,000 rubles.
Example 3
The warehouse of Zvezda LLC received goods from the supplier Rozmarin LLC in the amount of 3,000 rubles.
Wiring: Dt 41 Kt 60 - 3,000.
The result will be an increase in the balance sheet currency, since in this case changes occurred in both parts of the balance sheet (asset and liability). The liability item “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” and the asset item “Goods” were increased by 3,000 rubles.
Example 4
After the goods were delivered to the warehouse, Zvezda LLC transferred funds to the bank account of Rozmarin LLC in the amount of 3,000 rubles.
Wiring: Dt 60 Kt 51 - 3,000.
As a result, the balance sheet currency changed again, only downward. Changes occurred in both the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet. The liability item “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” and the asset item “Current account” decreased by 3,000 rubles.
Business transactions in accounting: examples
Let us consider, as an example, the list of business operations of an enterprise engaged in the assembly and sale of wristwatches. In April, a batch of goods was assembled: the cost of components was 284,000 rubles, wages for assemblers were 110,000 rubles. The product was sold for RUB 655,018. (including VAT RUB 99,918).
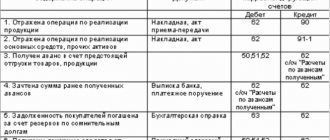
Correspondence of accounts and content of business transactions: table
| № | Contents of a business transaction | Sum | D-t | Kit |
| 1. | Components are written off for production | 284 000 | 20 | 10 |
| 2. | Payments to production employees were accrued | 110 000 | 20 | 70 |
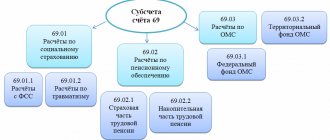
| 3. | Insurance premiums accrued | 33 220 | 20 | 69 (according to subaccounts) |
| 4. | The cost of a batch of watches has been formed | 427 220 | 43 | 20 |
| 5. | Personal income tax withheld from salary | 14 300 | 70 | 68-1 “NDFL” |
| 6. | Transferred to the personal income tax budget | 14 300 | 68-1 “NDFL” | 51 |
| 7. | Insurance premiums transferred to the budget | 33 220 | 69 (according to subaccounts) | 51 |
| 8. | Salaries issued from the cash register | 95 700 | 70 | 50 |
| 9. | A batch of goods has been sold | 655 018 | 62 | 90-1 “Revenue” |
| 10. | The cost of the sold batch was written off | 427 220 | 90-2 “Cost” | 43 |
| 11. | VAT charged | 99 918 | 90-3 "VAT" | 68-2 "VAT" |
What are they, their types
A business transaction is a fact that reflects information about calculations made, changes in the composition of property, its own and borrowed sources of education .
It should be considered as an event that serves as the basis for drawing up accounting entries. A prerequisite for recognition of the fact of the commission of an action is the presence of all necessary supporting documents.
Any operation performed by an enterprise changes one or both indicators simultaneously:
- size of property;
- composition and volume of sources of its formation.
Values can either decrease or increase. These movements directly affect the balance sheet currency, that is, the total identical amount of assets and liabilities.
Depending on how exactly property and sources interact with each other, there are 4 types of operations:
- permutation active;
- permutation is passive;
- increasing modification;
- reduction modification.
Classification into one of these types depends on how this action affects the composition of the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet.
Instructions for generating these operations are presented in the following video:
Registration of a business transaction
To record chemical weapons at enterprises of all forms of ownership and with any production volumes, special journals are used. They record every transaction carried out by the company. The following data must be recorded in the log:
- XO number
- the moment of its implementation
- information from primary documentation about chemical equipment
- operation description
- posting in accounting
- its monetary value
Some aspects of registration in different organizations may differ, but the basic principle remains the same:
- Each subsequent registration of a chemical enterprise is carried out from a new line
- the transaction number in order, the date of its completion and description are indicated
- the numbers of the corresponding accounts and the transaction amount are displayed
- the number of the identification document is indicated
Accounting for Dummies: Lesson No. 3 “Types of Business Operations”
All business transactions affect the balance sheet, and although they do not violate the equality of the balance sheet, changes may occur in the items and currency of the balance sheet.
There are 4 types of business transactions.
Let's consider their influence using the example of a balance sheet.
You can read more about the balance sheet in the second lesson.
1. Operations of the first type make changes to the composition of property; such operations affect only the balance sheet asset. The balance currency does not change. Both accounts involved in the operation are active. Formula A + X - X = P.
Example: funds in the amount of 2,000 rubles were received from the current account.
As a result of this operation, the balance sheet currency did not change, changes occurred in the items - the item “current account” decreased by 2,000 rubles, “cash”, in turn, increased by this amount.
The balance took the following form.
2. Transactions of the second type cause changes in liability items, while the balance sheet currency does not change. Both accounts are passive. Formula A = P + X - X.
Example: at the expense of own profits, the Authorized capital was increased by 5,000 rubles.
As a result of this operation, changes occur in the Liability side of the balance sheet, an increase in the item “Authorized Capital”, and a decrease in the item “Retained Earnings”.
The balance took the following form.
3. Transactions of the third type make changes to both the Asset and Liability of the balance sheet. The balance currency increases. Formula A + X = P + X.
Example: materials received from a supplier in the amount of 1,000 rubles
As a result of this operation, the Asset item “Materials” and the Liability item “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” increase. The balance currency increases by 1,000 rubles.
The balance took the following form.
4. Operations of the fourth type also cause a change in balance sheet items in both assets and liabilities, but at the same time the balance sheet currency decreases. Formula A - X = P - X.
Example: an enterprise paid a debt to a supplier in the amount of 2,000 rubles.
As a result of this operation, the item “Current account” in the Assets of the balance sheet will decrease, and the item “settlements with suppliers and contractors” will also decrease, and the balance sheet currency will decrease accordingly.
The balance took the following form.
Do not forget that any business transaction does not violate the equality of the balance sheet.
Homework.
Determine the impact of business transactions on the balance sheet.
- The short-term loan was repaid in cash.
- The company purchased equipment.
- The shareholders decided to increase the authorized capital by contributing cash.
Type of business transaction: examples and postings
In order to better understand how this classification is applied in practice, let's look at some examples of each type, as well as the entries that an accountant must make in each specific case.
The first example will characterize a business transaction classified as +A -A, that is, creating an influx of property within the company itself, or rather its movement from one active account to another. The simplest and most typical business transaction that can be characterized in this way is the withdrawal of money from the company's current account, for example, to issue their accounts. Before the money is issued to the final addressee-accountable person, it should be credited to the cash register. In this case, the organization has an increase in cash and a decrease in non-cash funds, but the balance sheet currency does not change. The wiring will look like this: