The activities of any company are based on the use of material assets and production resources. And all these objects often await a period of their operation in warehouses. A special person in charge (most often a storekeeper) is responsible for their safety on site. But what happens after the designated goods are sent directly to their intended destination - they deteriorate, triple, or lose value for some objective reasons. And sometimes they are completely absent, although they are listed according to documents. To find out, just read our current review. We will analyze the methods, methods, and basis for writing off materials and inventories in accounting, why this procedure needs to be performed, and to which account everything should be written off. We will also look at the process itself in step-by-step instructions.
Techniques
The regulations for accounting of inventories approved by the Ministry of Finance introduce strict procedures that are generally followed. More precisely, these are three options, respectively, the same number of ways to get rid of the entries made in the documentation.
Values can be calculated based on:
- The cost of an individual unit of inventory. And it doesn’t matter in what specific form it is contained. The unit can be chosen arbitrarily, but for convenience it is usually divided into equal parts. By box, by weight (ton, kilogram), by piece products (one set). Thus, the company has the opportunity to eliminate the inventory at the purchase price, the cost of the actual purchase.
- Average cost. Perhaps the most popular method. After all, several groups of different valuables often go into a warehouse at once. And how to write off materials, the regulations for such a procedure with the calculation of each unit is a dubious idea. In fact, one cycle of the production process can require hundreds of different related products: coatings, catalysts, packaging, all kinds of lubricants, while at the same time disposable personal protective equipment, gloves, protective suits, and various equipment used during the procedure are consumed. Calculating the purchase price of each object and, based on this, calculating consumption is like scooping up the sea with a ladle. It is much easier to look at the total price for all lost resources and, based on this, form some kind of average cost.
- FIFO method. Recently it has become increasingly popular. And it should be noted that it is also effective. Although its use remains situational. In fact, the technique allows you to include all costs in the cost calculation. For resources that were purchased at the initial stages of the cycle, processed long ago, removed from the list, as well as for the services provided by third-party companies that were necessary in the production cycle. And the work expended by employees of their own company, based on their wages, which they will receive during the period of participation in the cycle or in a practical way. Many experts are confident that this method is the standard for how to correctly write off materials in accounting and consumables in production. But it cannot be denied that this is a resource-intensive method that wastes a lot of time on the part of those responsible for preparing the documentation.
As a result, we see that each approach has a number of positive and negative aspects. And the organization, guided by its own needs, the number of positions of various resources spent during work, as well as the desired type of reporting, must decide which methodology will be more profitable in the current conditions. But at the same time, no one bothers you to combine several options at different stages. The main thing is to clearly understand when exactly to use this or that technique.
Do you want to implement Warehouse 15? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted!
Related documents
- Act on liquidation of fixed assets (in relation to standard form No. os-4)
- Certificate of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets. Form No. os-1
- Cash audit report (instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated 10/04/93 No. 18 (as amended on 02/26/96)
- Act of markdown of goods
- Act-receipt for the performance of warranty and paid work on the repair of telephone sets. Form No. tf-2-22 (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 22, 1994 No. 16-36)
- Act-request for replacement (additional supply) of materials. Form No. m-10
- Analytical data on accounting for the costs of procuring and purchasing materials for journal order No. 6
- Analytical data on accounting for deviations in the cost of materials for journal order No. 6
- Certificate of assessment of the value of buildings and structures approved. Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation on January 22, 1992 (appendix to the regulations on the commission for the privatization of land and reorganization of the collective farm (state farm)
- Certificate of assessment of the cost of machinery, equipment and transport (appendix to the regulations on the commission for the privatization of land and reorganization of the collective farm (state farm), approved by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation on January 22, 1992)
- Certificate of assessment of the cost of unfinished capital construction (appendix to the regulations on the commission for the privatization of land and reorganization of the collective farm (state farm), approved by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation on January 22, 1992)
- Act on the assessment of the value of working capital (appendix to the regulations on the commission for the privatization of land and reorganization of a collective farm (state farm), approved by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation on January 22, 1992)
- Act of transfer (sale) of collective farm (state farm) property to the rural (settlement) council of people's deputies (appendix to the regulations on the commission for land privatization and reorganization of the collective farm (state farm), approved by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation on January 22, 1992)
- An acceptance certificate
- Balance sheet of an insurance organization (quarterly). Form No. 1-insurer (Order of Rosstrakhnadzor dated April 16, 1996 No. 02-02/12)
- Balance sheet of the enterprise (Form No. 1 for capital) (approved by Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 1993 No. 114 for annual reporting for 1993)
- Balance sheet of an insurance organization - form No. 1 - insurer. (approved by the Russian Federal Service for Supervision of Insurance Activities in agreement with the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation for quarterly reporting in 1993)
- Balance sheet of economic and financial activities of the enterprise
- Balance sheet of economic and financial activities of the enterprise form 1.
- Statement of uncollected overdue receivables and violations of settlement discipline on synthetic accounts
Rules for writing off materials in accounting with industry nuances
The Russian Federation has a huge number of enterprises from small businesses to large holdings. And a significant number of production and non-production areas. It is noteworthy that virtually every industry has its own small nuances that slightly change the general procedure. This means that the exclusion of objects from the list will be stored on the basis of different principles. Now we will focus on this aspect. But it is worth understanding that there are thousands of spheres in the country. Therefore, in our review we clearly do not need to divide them into the narrowest parts and go into deep specialization. We will go through the most broad and in-demand areas. Let's figure out how to properly write off materials in various industries.
Construction
The main nuance is considered to be the fact that a significant number of different resources are involved in the processes. Such as sand, cement, gravel, brick, cinder block, aerated concrete, crushed stone. The list goes on for a long time. As a result, accurate accounting must be maintained at all times. After all, calculations are not carried out on a monthly cycle. This means that you will have to take inventory. And based on the identified expenses, exclude resources from the general list in connection with the number of units spent (cubic meters, kilograms, tons, pieces).
There is one more aspect that distinguishes this type of write-off of materials in accounting and tax accounting, paperwork. You will need an unexpectedly large package of papers. More specifically:
- Comparison of the specified standard resource consumption and the actual one. And in the vast majority of cases there will be a difference.
- Estimates. There are two types of techniques used. The first is by event or its duration. And the second - specifically for the object, after its delivery to the customer or contractor.
- Reports from local responsible persons. Often this means documents submitted by foremen or a single package that is compiled by the head of the entire site, based on cumulative reports.
- Standards set by management at the facility. That is, a certain resource consumption that is regulated on the site.
- Object logs.
The list, as you can see, is quite massive. And this is perhaps the central feature of the entire sphere. Indeed, during construction, when consumable resources are often simply piled up on the site (sand, crushed stone), it is very important to conduct a complete analysis of product care. Otherwise, uncontrollable shortages will constantly appear.
Agriculture
There are also plenty of documentary reports in this area. Among them:
- Act of consumption of planting seeds.
- Feed list.
- Livestock disposal act.
And what’s noteworthy is that in the industry, for every unaccounted item, an exact justification is required. If an animal died, then it is necessary to understand the reasons, and if it was a disease, then an accurate diagnosis should be made, a veterinarian should be involved, and the threat of an epidemic should be analyzed. If this is some kind of injury, it is required to give a clear definition under what circumstances it was received. Determining the presence of the culprit. When this is an oversight of an employee, or his negligent attitude, then the expense is indicated in the form of debt of a particular employee or deduction of his bonuses and wages. That is, how materials are written off in accounting in the agricultural sector is a complex issue. And it is entirely based on rational spending.
If the furniture is damaged
Furniture purchased by an organization for use in public premises (offices, hotels, cafes, shops, doctors' offices, concert halls, etc.) falls into disrepair much more often than its domestic counterparts. As a result of intensive use, individual items may be broken, dirty, the upholstery may be torn, etc.
Information that the organization’s property has fallen into disrepair is recorded in the process of drawing up annual inventory documents or at the time such facts are discovered. The documents drawn up indicate the types of damage to furniture for further write-off, for example:
- damage to the furniture frame (legs, seats, backs of chairs and armchairs, walls, shelves and doors of cabinets and cabinets, legs and table tops, etc.);
- breakdown of mechanisms that ensure the operation of furniture (door hinges, drawer mechanisms, chair casters, etc.);
- deformation of individual parts of furniture due to wetness, excessive heat, etc.;
- wear and tear of the upholstery (fading, thinning, tearing, etc.);
- defects in furniture surface cladding (cuts, cracks, chips, etc.);
- irremovable stains on furniture surfaces, etc.
All of the listed damages can become a reason for writing off the furniture in the write-off act if an essential condition is met: the costs of eliminating these defects are equal to or exceed the cost of purchasing a similar new piece of furniture.
Information on the cost of repairs can be provided by organizations specializing in this type of service.
Valuation of unusable resources
Of course, such a situation is not at all uncommon. In no production facility is there a 100% guarantee that human errors or machine malfunctions will not lead to waste. And here two factors become important. The first is whether a particular employee or group of employees was to blame for such a result. And also whether the indicated loss falls within the normal limit or is already beyond it.
If all losses are within acceptable limits, then even if someone is at fault, the account will be production. But it will become personal if the guilt of the employees is obvious, and the expense has gone beyond the regulated norm.
Shock absorption group for furniture
Currently, there is no depreciation group in the Classification for office furniture (chairs, tables, etc.). Previously (before its adjustment) furniture was classified in the fourth depreciation group.
The useful life for this group is 5-7 years. Currently, the service life of furniture for write-off by group can also be set within these limits. Or take into account the manufacturer’s recommendations and technical data sheet data.
How materials are written off in accounting, drawing up an order and a sample
The first stage of the procedure is the order. It is authorized to be issued by the director, manager, or the person replacing him and acting. The first point of the order is the creation of a commission. In principle, we understand that the main task will be to identify shortcomings. This means that an inventory will be needed. It is clear that even for a routine inspection it is always necessary to appoint a full commission. Where there will be both representatives of the accounting department and responsible persons, for example, a storekeeper or someone who receives products and is personally responsible for its safety.
The question often arises of how to write off consumables in production that are not available, and whether it is possible to immediately proceed to document processing. That’s the simple answer; in fact, this procedure should always be preceded by an inventory. And the initiative that appears in the form of an order has a standard or atypical version. The first option is when the work regulations are already assigned in advance in the form of a separate document. And the second - in cases where the order itself contains the entire regulation. This is an inconvenient form, so often everyone uses the first one.
To make the process of inventory, checks, and exclusion of a resource from the list of available ones easier, you will need software of the appropriate level. And the Cleverence software can help with this issue. This:
- Simplifying the inventory procedure, you only need one smartphone.
- Combining reporting, write-offs and inventory itself into a single system, which is again controlled from one device. Significant savings of time and effort.
- The ability to install both packaged software and individual software developed specifically for the needs and specifics of a particular company.
- Mobile applications that integrate into the general reporting system, for example, Bitrix.
- Solutions in accordance with all the latest amendments to Russian legislation.
- Current support. If the law changes, applications immediately adapt to it through updates.
Now let's figure out what should always be in a standard order. Without which points it simply will not be such:
- Full name of the enterprise.
- Date and serial number of a specific order.
- The purpose of the enterprise.
- Composition of the commission.
- Manager's signature.
How and when is upholstered furniture written off?
In addition to typical office furniture, upholstered furniture can also be written off. Boarding houses, sanatoriums, hotels of state or private subordination are familiar with this procedure.
As a result of careless or intensive use, negligence in relation to furniture, chairs and sofas that are placed in the halls, guest areas and other common areas of such institutions become unusable. The reasons for the write-off of upholstered furniture manifest themselves in the form of wear and tear of the upholstery, sagging springs, cracks and chips on wooden elements.
It is clear that an unaesthetic interior can easily spoil the reputation of an establishment, as a result of which the influx of customers may decrease. Therefore, it is advisable to promptly engage in inventory and write-off of damaged items, and systematically update inventory.
The procedure for decommissioning materials, postings and documents
This procedure is a rigorous process. Order, inspection, reporting. And the last point often raises a lot of questions. And in vain, because this is a common operation with its own nuances.
The first of them is that the set of inventories is credited, that is, 10. In all cases, no matter what part of the operation is involved. But expense accounts are debited by their number.
We get this form:
| Debit part | Credit part (always identical number) | Explanations |
| 20 | 10 | Cost write-off in favor of main production |
| 23 | 10 | Analysis and assessment of resource for auxiliary production processes |
| 94 | 10 | Write-off in case of loss. This includes damage, theft, exceeding the service life, initial defects, breakdown during the production process and similar |
| 99 | 10 | This category includes resources damaged by natural disasters. |
| 91.2 | 10 | All products that were sold under a gratuitous contract. That is, often gifts are for marketing purposes or as a result of charity events |
Common criteria for furniture write-off
Basically, when people talk about recycling items, they mean office furniture items. Although this category also includes the furnishings of public catering establishments, industrial premises, trading floors, etc.
The main reasons for writing off furniture:
1. One hundred percent or partial loss of basic performance characteristics:
- breakdown of structural parts of furniture (legs, back, armrests);
- deformation of the seat (for armchairs and chairs) or work surface;
- breakdown of mechanical parts (accessories);
- weakening or complete unsticking of tenon joints, resulting in the appearance of gaps;
- cracking, warping of parts or functional units of furniture.
2. Unsatisfactory indicators of the appearance of an interior item, affecting the reasons for writing off furniture:
- persistent pollution (indelible);
- darkening or destruction of the structure of varnished parts, aging of the film, the appearance of white spots on the varnish coating after contact with hot objects, chemicals, alcohol, acetone or cologne;
- fading, change in the strength level of the upholstery, deformation of the veneer;
- damage to wooden furniture associated with high indoor humidity: swelling of facades, drawers and other parts;
- active occurrence of corrosion processes;
- damage to the upholstery or facing material of upholstered furniture by mold;
- change in the appearance of the upholstery due to the influence of direct sunlight.
All the factors considered contribute to the process of writing off furniture. The reasons (examples) given above arise due to active use, and it is not always possible to prevent wear of parts or objects in general.
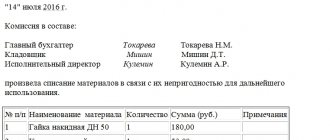
Act of write-off of inventories
This is the only way to exclude inventories from the list of active ones when stored in warehouses. It is noteworthy that since 2020, this, in principle, allows the use of any calculation and analysis option: by piece cost or by total cost. In this case, a document is always drawn up in form 0504230.
It consists of two parts. The header contains basic information, order number, date, composition of the commission, full name. leader. The main part, in the form of a table, provides information on the actual loss of inventories. Contains graphs of expenses expected according to the norm, the reasons for such an outcome. In fact, this act is the only legal way to properly write off materials from the warehouse.
Do you want to implement “Store 15”? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted.
Sample defect report
There is no established template according to which the write-off procedure is carried out, so the enterprise has the opportunity to independently develop and approve it. The completed act must contain the following information:
- the name of the furniture structures that are being written off;
- total quantity (in units);
- identification codes and signs;
- the results of the inspection by a commission including senior employees of the organization;
- causative factors (breakage, deformation, defects);
- general conclusion;
- signatures belonging to responsible parties.
Documents for download (free)
- Form No. OS-4b
If we look at a specific example of a document, we can note that it includes several points:
- “Hat”, which indicates the word “I approve”, the name of the general director, and the date of compilation. Then it is signed with the word “Act” in the center, and the title of the document from a new line in the middle is “write-off of furniture, inventory, equipment.” All members of the commission are listed below, it is indicated that they examined certain pieces of furniture and found them to be written off on certain grounds.
- The basic part, represented by a table. The first column displays the name of the structures to be decommissioned. The second indicates the inventory number, then the unit of measurement, quantity. The last column is the general technical condition and causal factors.
- The final part begins below the table and includes the immediate conclusion, information about the group members, and results.
The document must be drawn up in a special form and include the necessary signatures and seals.
What to do if there is a balance
In principle, it is permissible to create a separate sub-account where all excesses are indicated. But this is an optional procedure. Just a way to make your work easier and make your accounting more transparent. But the aspect has nothing to do with the issue under discussion. Since it is strictly prohibited to enter this information into act 0504230, even with reverse values.
Disposal procedure
When writing off furniture, a budgetary institution can be guided by a document such as the Rules for the Management of Municipal Solid Waste, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 12, 2016 No. 1156.
According to this document, furniture must be removed by a regional operator, or the organization itself delivers it to the place of storage and disposal. The institution may also dispose of the objects itself. The procedure must be described in the local regulations of the institution. Typically it is as follows:
- By order of the manager, a commission is appointed to identify non-functional furniture. Such a commission can be formed once or it can be assembled for each case.
- The commission prepares a list of objects for write-off and disposal.
- The manager issues an order for the write-off and disposal of furniture. It indicates the deadlines, a list of objects, and the method of disposal: independently or with the help of a special organization.
- A write-off occurs. A corresponding act is drawn up.
- Recycling takes place. They draw up a disposal act or an act of transferring OS objects for disposal to a specific company.
Let's sum it up
In fact, the write-off of inventory and materials in tax accounting and accounting has no differences. If we are talking about white accounting, which does not try to mislead the competent authorities. And it is worth remembering that although the law does not put forward actual rules on the procedure, and a lot remains at the discretion of the manager, the final reporting will be significant documents for the Federal Tax Service. Which they can check at any time. Therefore, it is worth approaching the procedure with all responsibility. At the same time, it is also undesirable to refuse such events or minimize them. Otherwise, accounting will turn into a tangled mess, and expenses will “mysteriously” increase.
Number of impressions: 267
Memo for writing off inventory items
If the financially responsible person discovers damaged property, it is necessary to conduct an inventory. You can initiate it by submitting a written request to the manager. For this purpose, a memo is drawn up for the write-off of inventory items.
It is impossible to use them for their intended purpose in the future, because the set of consumer properties has been partially or completely lost. Write-off also occurs due to moral and physical wear and tear.
However, you must remember that this is just a sample document “Act on the write-off of materials for current repairs” and requires a legally competent adaptation of the form to the needs of an individual or legal entity. And remember: Any business relationship must be secured by contract - no verbal agreements. Paper and signature are the best proof of your intentions.
In essence, the act is a statement indicating the material assets that were written off, the reasons and the date.
Product quality acceptance certificate
—————————————————————————————————————— ¦ Act ¦ ¦ consumption of materials N ______ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ Date of compilation¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ Organization _____________________________________¦ ¦ Department (shop) _________________________________¦ ¦ Responsible person ______________________________¦ ¦ ¦ ¦—————————————————————————— ———————————-¦ ¦¦Name¦ Unit ¦Name¦Consumption rate¦ Actually consumed ¦ Consumption ¦ Accounting¦¦ ¦¦ material, ¦measurement¦ products ¦ (quantity +—————— —————-+above norms¦ entry ¦¦ ¦¦ raw materials ¦ ¦ ¦ for volume ¦Quantity¦ Price ¦Amount, rub.¦ (column 5 -+—————+¦ ¦¦ ¦ ¦ ¦produced) ¦per unit,¦ (column 5 x¦ column 4) ¦ Debit ¦Credit¦¦ ¦¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ products) ¦ ¦ rubles ¦ column 6) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦¦ ¦+————+———+ ————+————-+———-+————+————+———-+——-+——+¦ ¦¦ 1 ¦ 2 ¦ 3 ¦ 4 ¦ 5 ¦ 6 ¦ 7 ¦ 8 ¦ 9 ¦ 10 ¦¦ ¦+————+———+————+————-+———-+————+————+— ——-+——-+——+¦ ¦¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦¦ ¦+————+———+————+————-+——— -+————+————+———-+——-+——+¦ ¦¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦¦ ¦+————+———+— ———+————-+———-+————+————+———-+——-+——+¦ ¦¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦+————+———+————+————-+———-+————+————+———-+——-+——- ¦ ¦¦Total ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦————-+————————————————————+———— ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦Responsible person ¦ ¦ ___________ ________________________ ¦ ¦ (signature) (signature decoding) ¦ ¦Accountant ¦ ¦ ___________ ________________________ ¦ ¦ (signature) (signature decoding) ¦ ———————————————————————— ——————————————
Source - “Accounting Bulletin”, 2009, No. 11-12