What debt can be written off?
Not all of a company’s debts can be written off, but only those that meet the criteria for a debt that is unrealistic to collect. The concept of bad debt is given in paragraph 2 of Art. 266 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is a debt with an expired statute of limitations, as well as a debt of a liquidated company or a company that is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities as inactive. In addition, the bailiff can establish the impossibility of receiving money and issue a ruling to end enforcement proceedings.
| Note! “Closing” an individual entrepreneur does not make his debt hopeless. |
If an individual entrepreneur owes you money, you cannot carry out the procedure of writing off receivables only because of his exclusion from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs, since the individual entrepreneur is liable for debts with all his property (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 16, 2015 No. 03-03-06/53157). Write-off of a businessman's bad receivables is possible only after the completion of the bankruptcy procedure, in the event of the death of the individual entrepreneur or a judicial authority makes a decision on the impossibility of collecting money due to the fact that it was not possible to establish the whereabouts of the businessman. That is, before writing off receivables, you should make sure that the above conditions have been met.
If two companies owe each other, first of all, it is necessary to offset the debts, reducing the amount of receivables by the amount of debt to the counterparty. If the partner company still owes you, this money is considered uncollectible, and you can write off the overdue receivables.
So, you found out that the debtor company went bankrupt (or it was excluded from the register of legal entities later than September 1, 2014). In this case, you understand that you will not be able to repay the debt. How to write off receivables that are past the statute of limitations?
As a general rule, it is 3 years, but it can be interrupted or suspended.
The limitation period is interrupted if (clause 20 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2015 No. 43):
- the debtor accepted and signed the reconciliation report;
- sent a letter - an acknowledgment of the debt or a request for a deferment;
- paid interest or penalty;
- The firms drew up an additional agreement to the contract, under which the debtor acknowledged its obligation.
The company must begin counting the interrupted statute of limitations anew. However, it cannot exceed 10 years from the date of formation of the debt (clause 1 of Article 181 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The limitation period is suspended on the grounds provided for in Art. 202 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in particular, for the period when the parties carry out the procedure for resolving a dispute out of court provided for by law (mediation procedure, mediation, administrative procedure, etc.). Also, the statute of limitations does not run while judicial protection of the violated right is carried out (Article 204 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). When the relevant circumstances end, the statute of limitations continues to run (and is not counted again).
| For more information on how to write off receivables with an expired statute of limitations, read the article “How to write off bad receivables with an expired statute of limitations . |
Why is it necessary to write off accounts receivable?
Accounts receivable are included in the list of assets that will soon become a source of cash for the enterprise.
But if there are delays in transfers from debtors, the debt may become uncollectible, that is, impossible to collect. The existing accounting procedure establishes that the reflection on the balance sheet of an enterprise of overdue debts with an expired statute of limitations distorts reporting data.
After all, in fact, this asset will no longer bring any benefits for the enterprise. This means that in order to comply with the principle of reliability, the organization must monitor the timing of existing debts of debtors and promptly identify those that are overdue or impossible to collect.
Attention! The deregistration of accounts receivable is specified in the Accounting Regulations. In this case, special procedures are used that must be followed, since the inspectors of the Federal Tax Service very carefully check these points.
Not all debts of debtors can be removed from the company’s assets. The legislation establishes certain criteria for such situations. First of all, the statute of limitations on the debt must expire. You can withdraw a receivable if it receives the status of impossible to collect. For example, the debtor was liquidated and deregistered as a legal entity.
How to document the write-off of bad receivables
So, you have determined that there is money that is unrealistic to receive for the reasons listed above. To write off receivables and payables, you need to draw up an order for debt inventory, and its results are entered into the INV-17 form. Then the manager issues an order to liquidate the company’s debt on the basis of an inventory report and an accounting certificate, in which the amount of the debt should be given, a description of the situation, why the debt became uncollectible, and a reference to the number and date of the inventory report.
IMPORTANT! Tax authorities check written-off debts especially carefully, so it is necessary to attach to the debt inventory report the history of its occurrence and documents confirming the reality of the transaction: contracts, invoices, invoices, certificates of services rendered, reconciliation reports, as well as the basis for recognizing the debt as bad (for example, an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or a bailiff's order).
Statute of limitations
The general limitation period is three years. It will be easier to correctly count these three years using the table.
| Situation | From what date does the statute of limitations begin? |
| The deadline for fulfilling the obligation is determined | Upon expiration of the obligation |
| The deadline for fulfilling the obligation is not determined | From the day the creditor made a demand to fulfill obligations (for example, sent a letter) |
| The execution period is determined by the moment of demand | |
| The creditor gave the debtor some time to fulfill the obligation | At the end of the last day of the obligation fulfillment period |
This follows from the provisions of Article 196 and paragraph 2 of Article 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of determining the limitation period. The limitation period was not interrupted
Trading LLC shipped goods to Alpha LLC on January 13, 2020. According to the contract, payment must be made no later than 10 calendar days after shipment, that is, no later than January 23, 2016. However, payment was not received from Alpha on time.
The limitation period must be calculated from January 24, 2020 to January 24, 2020 inclusive (provided that the limitation period was not interrupted).
The limitation period may be interrupted when the debtor commits actions that indicate recognition of the debt.
After the break, the limitation period begins again. At the same time, do not count the time that elapsed before the break into the new limitation period. However, there is a limitation: the limitation period cannot exceed 10 years from the date of violation of the right, even if the period was interrupted. The exception is the cases established by the Law of March 6, 2006 No. 35-FZ on countering terrorism.
This is stated in paragraph 2 of Article 196, Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The debtor can recognize his debt even after the statute of limitations has expired. In this case, from the moment the debt is recognized, the limitation period begins anew. Such rules are established in paragraph 2 of Article 206 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of determining the limitation period. The limitation period was interrupted
On January 13, Trading LLC shipped goods to Alpha LLC. According to the contract, payment must be made no later than 10 calendar days after shipment, that is, no later than January 23. However, payment was not received from Alpha on time.
The limitation period begins to count from January 24.
On January 25, Hermes sent a letter of claim to Alpha. On February 1, the parties drew up a reconciliation report. This means that Alpha has admitted its debt. In this case, the limitation period begins to count again - from February 2.
Situation: what actions of the debtor indicate recognition of the debt and are grounds for considering the statute of limitations interrupted?
The legislation does not establish a list of actions by the debtor that indicate that he has acknowledged the debt. And which may serve as a basis for interrupting the limitation period (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
However, an approximate list of such actions is named in paragraph 20 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2020 No. 43. In particular, it includes:
- recognition of the claim. However, the response to the claim does not in itself indicate recognition of the debt. It must indicate that the debtor has acknowledged the debt;
- a change in the contract, from which it follows that the debtor acknowledged the existence of a debt. Or the debtor’s request to change such an agreement (for example, on a deferment or installment plan);
- signing the debt reconciliation act.
For example, three years have passed since the date when the obligations were due. But during this period, the parties signed a debt reconciliation act. This act is the basis for interrupting the statute of limitations (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 19, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/426). Therefore, the three-year period must be counted from the day on which the last reconciliation act dates. There are exceptions to this rule - these are events due to which the receivables have become unrealistic for collection. A similar position is set out in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 6, 2010 No. ШС-37-3/16955.
The contract may provide that the obligation can be fulfilled in parts (in the form of periodic payments). In this case, if the debtor has performed actions indicating recognition of only some part of the obligation, they do not constitute grounds for interrupting the limitation period for other parts of the obligation. This is stated in paragraph 20 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2020 No. 43.
Write-off of overdue receivables in accounting
In accounting, creating a provision for doubtful debts is the responsibility of the company. She does not have the right to choose whether to create a reserve or not. It is possible not to form it only if there is strong confidence that the debt will be repaid (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 27, 2012 No. 07-02-18/01).
| For more information on creating a reserve for doubtful debts, read the article “Provision for doubtful debts: the procedure for creating and calculating deductions . |
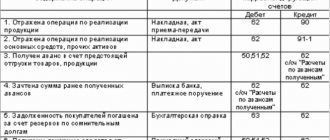
The formation of the reserve in accounting is reflected in the credit of account 63 in correspondence with account 91.
When writing off debt from the reserve, an entry is made: Dt 63 Kt 62 (76 or other accounts for accounting for debt to your organization) - writing off accounts receivable from the reserve for doubtful debts.
If the debt is greater than the reserve, then the difference is charged to the account of other expenses: Dt 91.2 Kt 62 (or another accounts receivable account).
A similar entry (Dt 91.2 Kt 62) is used to write off debt that suddenly became hopeless and was not reserved (for example, the counterparty was liquidated, and the company learned about this after the fact of liquidation).
The debt written off within 5 years should be recorded as the debit of account 007 in the full amount. And only after this period is it written off completely.
For accounting purposes, you need to store documents confirming the fact of writing off receivables for at least 5 years from the date of writing off the overdue debt to your company. On account 007, analytical accounting should be maintained for each counterparty.
The nuances of writing off accounts receivable in various situations are described in detail in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Write-off sources
- Due to the reserve for doubtful debts. One of the sources through which accounts receivable can be written off is the creation of a reserve for doubtful debts. However, only companies that determine shipment revenue can create it. The general reservation procedure is determined by Art. 266-4 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The reserve includes the full amount of the debt, the term of which exceeded 3 months, half the amount - if the period is from 45-90 days. Receivable amounts with a shorter term are not taken into account. At the same time, the amount of VAT expected to be transferred from the debtor is also reserved. The amount of reserved funds is limited, above 10% of revenue for the tax and settlement period.
- If there is no reserve in the organization. The receivables must be written off at the expense of other expenses, i.e. it will affect the value of the final indicators in one way or another.
- Source: net profit. The decision to write off receivables is made exclusively by the general meeting of founders, since such actions directly affect the financial result.
Write-off of accounts receivable in tax accounting
Only organizations that consider income tax on an accrual basis can write off unreceivable receivables as expenses. Accordingly, simplifiers and UTII payers cannot take bad debt into account in expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13, 2007 No. 03-11-04/2/274). Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO also do not have the right to carry out the procedure for writing off receivables.
Unlike tax accounting, the formation of a reserve for doubtful debts is a right, not an obligation of the organization. That is, for tax purposes, the algorithm for liquidating receivables depends on whether a reserve for doubtful debts has been created. If there is one, then the enterprise writes off accounts receivable from the reserve, and assigns the part of the debt not covered by the reserve to non-operating expenses.
All details on writing off bad receivables using the reserve for doubtful debts are set out in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
If the reserve is not formed, then the receivables are written off for non-operating expenses. An expense is recognized on the date of the earliest event:
- the statute of limitations has expired;
- an entry about the termination of the debtor’s work appeared in the register of legal entities;
- documents were received from bailiffs.
Supporting documents for tax accounting purposes should be kept for at least 4 years.
If you paid an advance to a supplier and then recognized this debt as bad, then the VAT accepted for deduction must be restored.
| However, there are certain nuances in this issue, which can be studied in our article “How to take into account VAT amounts when writing off accounts receivable . |
IMPORTANT! If the company decides to recognize an individual’s debt as bad and, after writing off the receivables, to charge it as expenses, it is necessary to transfer personal income tax from the amount of the debt. From the point of view of officials, in this case the individual benefits from cost savings, and the company must act as an agent for personal income tax. In particular, the Ministry of Finance of Russia writes about this in letter dated March 19, 2018 No. 03-04-06/16933 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia in clarification dated December 31, 2014 No. PA-4-11-27362.
In what time frame can this be written off?
In order to recognize a receivable as overdue with the end of the claim period, according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, three years must pass. It is this period of time that is allotted to the creditor in order for him to take all available measures to collect the debt.
You definitely need to decide at what point you should start calculating the three-year period. It is stipulated that if the contract specifies the period for repayment of the obligation, then the limitation period must be calculated from the next day after it.
When the exact dates for making payments are not provided for in the executed agreement, the limitation period begins to be determined from the moment the creditor announces his claims to the debtor.
You also need to remember about such a point as interrupting the limitation period. If the debtor partially transfers the amount of the debt, or interest on it, or draws up and signs a reconciliation act with the organization, then the calculation of the limitation period is postponed to the next day after one of the listed events.
Thus, interruption of a given period can occur many times. However, at the level of laws, the limitation period is fixed, which is 10 years.
According to it, interruption of a claimable debt is possible until 10 years have passed from the moment the obligation arose; after that, the receivable in any case will be recognized as expired and will need to be removed from the organization’s balance sheet.
Attention! In addition, do not forget that the collection of receivables must be carried out in the reporting period when the statute of limitations expired. Excluding it from the composition of the property at the time of carrying out or issuing an order for write-off will be considered incorrect. It is desirable that all these dates coincide, so you need to constantly monitor this information.
Results
The process of writing off accounts receivable is simple, but strictly regulated. Violation of it is fraught with claims from tax inspectors and additional assessment of income tax or fines for accounting errors. Therefore, before writing off receivables, make sure that an inventory has been taken and the appropriate order has been issued.
However, we still advise you not to increase the company’s expenses by writing off receivables and to make every effort to liquidate the counterparty’s receivables, offering him, for example, an installment plan or debt restructuring.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
On what basis is it legal to write off receivables?
When can accounts receivable be written off? It is legitimate to talk about three main scenarios for its write-off:
- Write-off upon repayment of debt by the debtor. Such a write-off does not imply that the creditor has any additional rights or obligations in terms of taxation - if we are talking about the principal amount of the debt. Exceptions will be observed:
- when receiving income from interest - in this case, tax on it will have to be calculated and paid;
- when the debtor is an individual not registered as an individual entrepreneur, and the interest rate on the loan is less than the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation: in this case, the creditor as a tax agent will need to calculate and pay tax on the debtor’s material output.
- Write-off upon forgiveness of the debt to the debtor. Similarly, the creditor does not have any tax rights or obligations here, with the exception of the need to calculate and pay tax on material benefits on a forgiven debt to an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur. Debt forgiveness is regarded as a gratuitous transfer of property and therefore cannot be included in expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 4, 2012 No. 03-03-06/2/34, clause 4 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated July 15, 2010 No. 2833/10 provides for the possibility of writing off a debt as an expense if the creditor company has a commercial interest in forgiving the debt. But in legal disputes with the Federal Tax Service, it is not always possible to defend such an expense (resolution of the Fifteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated November 14, 2013 No. 15AP-13132/13).
- Write-off upon recognition of a debt as bad. Here the situation from the point of view of tax consequences is more interesting: the written-off bad debt can be taken into account in non-operating expenses when forming the tax base for the special income tax (subclause 2, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Under the simplified tax system, such a preference is not provided (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13, 2007 No. 03-11-04/2/274).
A debt can be recognized as bad if (clause 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the statute of limitations for judicial debt collection has expired;
- the debt is canceled due to the impossibility of repaying it;
- the debt is canceled by a decision of the authority;
- the debtor organization was liquidated;
- bailiffs were unable to collect the debt from the debtor’s property.
Let's consider the grounds for writing off accounts receivable in accounting due to the recognition of the debt as bad - with the prospect of including it in expenses, in more detail.