- KtoNaNovenkogo
- FAQ
- Are you here
September 24, 2019
- Accounts receivable is...
- Types of receivables
- Why is turnover so important?
- An example of calculating the receivables turnover period
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. Accounts receivable is one of the key concepts in accounting.
Today we will look in detail at what accounts receivable is (it is also called “receivable”), how it is classified and what parameters it is characterized by.
What are accounts receivable?
Accounts receivable are the financial and commodity assets of a company working for the counterparty as a result of a transaction, agreement, etc.
The role of the counterparty can be buyers, contractors and other accountable persons. Accounts receivable relate to the company's property (its assets) and are subject to inventory, regardless of the maturity date. In simple words, the concept of a company's receivables is the amount of debt that has not yet been returned to the borrower for certain services or goods.
Here is an example of accounts receivable:
The MAX company specializes in the production of building mixtures. He has several debtors (debtors), these are companies that do not have the financial ability to pay for the goods immediately. The two parties enter into an agreement indicating the repayment period of the debt and all the nuances in case of non-fulfillment. Thus, without refusing a loan, he will receive economic profit in the future.
Back to contents
What is included in accounts receivable on the balance sheet?
Accounts receivable includes the following components:
| Name of business transaction | On what debit of the account is it reflected? |
| Settlement transactions with suppliers and contractors (if the company issues an advance for the supply of goods) | 60 |
| Settlement transactions with buyers and customers of services (the organization supplies goods or provides services first, payment from the counterparty is received later) | 62 |
| Settlement transactions for taxes (if overpayment of taxes and fees to the treasury is identified) | 68 |
| Payment transactions via social networks insurance and security (if, as a result of the inventory, the accounting department revealed the fact of overpayment to social, pension and health insurance funds) | 69 |
| Settlement transactions with employees for remuneration of labor activities (if funds are withheld from the employee in favor of the company) | 70 |
| Settlement transactions with accountable employees (in the event that a company employee has not returned the money given to him on account) | 71 |
| Settlement transactions with personnel for other transactions (unrepaid loans issued to employees, material damage, etc.) | 73 |
| Settlement transactions with founders | 75 |
| Settlements with various counterparties (if there are arrears in compensation due to insured events, settlements on claims in favor of the company, settlements on due dividends, etc.) | 76 |
In accounting, uncollectible debt is recognized as other expenses. To record these amounts, account 91, subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses” is intended.
The main accounting entry, if the debtor nevertheless repays the obligation:
- debit 51;
- credit 62.
Accounts receivable are classified into various types. This is necessary primarily for accounting purposes.
After all, reporting will depend on how correctly the relevant transactions are reflected. Properly executed documents are the key to the success of any company.
How to collect receivables through the court is described in the article: collection of receivables. You can find out the tax debt of an individual entrepreneur using the TIN in this article.
Receivables settlement is discussed on this page.
What is the difference between accounts receivable and accounts payable?
With accounts receivable, your company has debtors, and with accounts payable, you are the debtor. On the one hand, the absence of receivables indicates the company’s caution, since not all debtors ultimately have the opportunity to repay the debt. But even in this case, the company deprives itself of potential income from bona fide counterparties.
Regarding accounts payable, the same story, its high level indicates the company’s problems, and its absence demonstrates the success and payback of the business on its own. But since KZ is third-party capital, it would be foolish not to take advantage of the opportunity to develop at the expense of other people’s investments. It follows from this that it is not the presence itself that matters, but the volume and ratio of receivables and payables.
Back to contents
How do accounts receivable arise?
It is a rare company that can boast of having no accounts receivable. This is due to production needs and the characteristics of the competitive environment. It is beneficial for the buyer to purchase goods or services in installments, and the seller is interested in expanding his customer base by offering better conditions. As a result, a situation arises when the goods have already been shipped, but payment for them has not yet been received.
Also, accounts receivable are increased by the amount of advance payments transferred to suppliers as prepayments. This also includes overpaid amounts to tax authorities and insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds. In simple terms, any prepayment or release of goods on credit forms a receivable.
Settlements with the organization's personnel are reflected in a separate line. This could be either an overpayment of wages or amounts issued on account. The latter will be reflected as a debt until the employee provides an advance report indicating the purchased goods and documents confirming the fact of expenses.
List of options and conditions for the occurrence of receivables:
- Goods or services were purchased from the company in installments.
- Erroneously paid excess amounts to tax authorities and insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds.
- Erroneous overpayments of wages.
- Amounts issued to employees for reporting purposes and more.
Types of accounts receivable
There are many criteria by which types of receivables can be classified, but we will turn to the main ones.
Depending on the repayment period:
Depending on receipt of payment:
To avoid serious consequences of non-payment of debt, firms create reserves for doubtful debts. The volume of reserves is approved individually, it all depends on the financial situation of the debtor and the likelihood of repayment of obligations. A provision for doubtful debts is established after an inventory has been taken.
Back to contents
Debtor and creditor for the year in f. 1 balance sheet and in other forms of annual reporting
Depending on the repayment period, the creditor is divided into long-term (more than a year) and short-term (less than a year) and, in accordance with this classification, is shown in the balance sheet. Accounts payable on the balance sheet are either a long-term liability, which is reflected in Section IV, or a short-term liability, which is reflected in line 1520 of Section V.
For more information on the procedure for filling out a balance sheet, read the article “Filling out Form 1 of the balance sheet (sample).”
Accounts receivable are reflected on line 1230 in section II of the balance sheet.
For more information about how receivables are reflected in the balance sheet and the procedure for deciphering article 1230, read the article “Deciphering the lines of the balance sheet (1230, etc.).”
Accounts receivable and payable are important indicators of an enterprise’s financial statements, which must be explained in the explanations to the statements (clause 27 of PBU 4/99 “Accounting statements of an organization,” approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 1999 No. 43n). The decoding of accounts receivable and accountable is of primary interest to reporting users, since these assets and liabilities can be sources of risks.
Enterprise accounts receivable management
There are often situations when an enterprise, in an effort to increase profits, begins to overload itself with debtors, which can ultimately lead to a large amount of unpaid debt and even bankruptcy of the enterprise. Smart managers pay great attention to the volume of debts and maintain strict accounts receivable records using various tools, such as Excel.
Accounts receivable management methods:
- Strengthening work with accounts receivable - collecting debts without resorting to the help of judicial authorities.
- Balance control and analysis of accounts payable and receivable.
- Motivation of sales department employees (regarding taking measures to ensure the fastest possible return of funds from debtors).
- Calculation of the real value of the property, taking into account the possibility of its sale.
- Creation of a sales system in which payments will be made regularly and guaranteed, for example, a system of discounts for punctual customers.
- Calculation of the maximum level of accounts receivable.
- Audit of losses from remote work (what profit the company could have received in case of instant payment and use of this money).
With proper control and management of receivables, an enterprise can protect itself as much as possible from the risks associated with non-payment of debts, decreased solvency and lack of working capital.
Back to contents
Accounts receivable inventory
An inventory of accounts receivable is a reconciliation of documents with counterparties, confirmation of the existence of debt and its size. They carry out an inventory before an annual report, a change of chief accountant, during the liquidation or reorganization of an enterprise and in case of emergency situations, such as a fire.
The inventory is carried out on a certain date, the company sends data on the debt to its borrowers, and they must confirm or deny in writing the existence and amount of the debt. This is ideal, but in reality not everything is so smooth, firstly, inventory can take a lot of time, in some companies the indicators reach up to a month. Secondly, not all debtors respond to requests, especially those whose debt has been waiting for a long time to be repaid.
The next problem is resolving data inconsistencies; in this case, you have to reconcile all transactions performed with a given enterprise; this creates particular difficulty if the enterprise is located in another city or, even better, in another country. When sending a certificate of receivables, you need to take into account the fact that an enterprise can be both a debtor and a creditor at the same time. Even if, according to calculations, you turn out to be a debtor, you need to send a statement, indicating the amount of both receivables and payables.
After reconciliations, the company must draw up an inventory report; some set their own form template, or use a standard one, for example: .
Back to contents
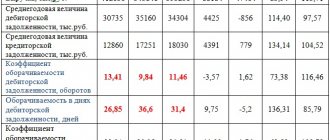
Accounts receivable turnover
Accounts receivable turnover shows how quickly a company receives payment for goods and services sold.
The accounts receivable turnover ratio shows how effective measures the organization is taking to minimize debt. This metric quantifies how many times a firm has received payment during a period equal to the average outstanding balance from its customers.
*The average balance of accounts receivable is calculated as the amount of accounts receivable from customers according to the balance sheet at the beginning and end of the analyzed period, divided by 2.
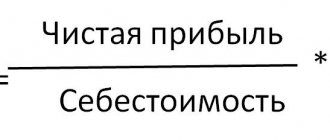
Receivables turnover formula
Accounts receivable turnover period in days formula:
* DZ in days shows the number of days during which the debt remains unpaid.
As such, there is no norm for the turnover ratio; it will be different for each industry. But in any case, the higher the OPL, the better for the organization, this means that buyers quickly repay the debt.
Back to contents
Decoding
Until recently, line 1230 was displayed as code 240, which contains a decoding regarding accounts receivable.
The line displays the amount of debt obligations that the organization has to its direct partners, counterparties and other persons for a certain time period.
It is worth noting that until recently line 230, which reflected debt subject to repayment no earlier than in a year, also belonged to this category.
Code displays of balance sheet lines include certain information:
- the first number indicates that it belongs to the balance sheet and not to another type of documentation;
- the second number indicates that the asset belongs to a certain category;
- third number – displays the location of the asset in the liquid ranking (the greater the liquidity, the greater the code value);
- the fourth number is used to directly detail the rows.
Thanks to this, you can easily find out all the necessary information that is encrypted in the code.
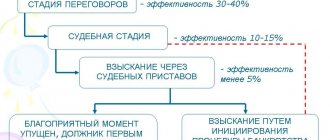
Collection of accounts receivable
Any enterprise faces the problem of non-payment of accounts receivable. Of course, the buyer may have various valid reasons, but who cares? The company wants to recover its money for the goods provided.
Repayment of receivables can be carried out using different methods, for example, hiring the mafia, but if it is legal, then it is better to file a claim or contact the judicial authorities. If you decide to resolve the conflict amicably, you should send a complaint to the debtor to clearly explain your position and find out whether he has any reasonable objections.
When applying for collection of receivables, you must indicate the following points:
- Call
- Detailed calculation of the amount of debt incurred
- Interest calculation
- Debt repayment deadline
- Warning about going to court
In addition, the claim must be signed by an authorized person, and copies of all documents related to the debt must be attached. If the debtor received your letter (there must be evidence) and did not respond within the established time frame, then with a clear conscience you can go to court demanding the return of receivables.
Back to contents
Write-off of accounts receivable
By law, a debt is considered overdue if the statute of limitations on the debt has expired (3 years) and bad debt if the company is unable to pay the debt. On these grounds, the company has the right to write off the debt. The write-off of hopeless overdue receivables is permitted on the final day of the period in which the statute of limitations has passed.
There are two methods for writing off expired accounts receivable. The first is to use the reserve for doubtful debts for this purpose; if a reserve was not provided for this debt, then write it off as financial results. Postings for writing off accounts receivable must be carried out exclusively for each obligation separately. The reason for this may be the results of the inventory, written confirmation or an order from the head of the enterprise.
Sample order to write off accounts receivable: .
Writing off a bad debt is not an actual cancellation of the debt, therefore, for five years after the write-off, receivables are reflected in the balance sheet. And throughout the entire period, you need to monitor the financial condition of the debtor to see if he has the opportunity to repay the debt.
Back to contents
Long-term and short-term accounts receivable
The division of receivables into long-term and short-term is determined by the timing of debt repayment by accountable persons, borrowers, customers, and buyers.
Long-term accounts receivable are those in which debts are repaid after a period of 12 months after the conclusion of the contract. This is a non-current asset of the enterprise. This debt is assessed and displayed on the balance sheet at its current value, taking into account accrued interest.
There are several types of long-term receivables:
- for property transferred under financial lease, for example, equipment, buildings, housing;
- received long-term bills, which are a tool for long-term attraction of financial resources to finance the acquisition of specific assets, the implementation of long-term projects related to the implementation of real investments, etc.
That is, this is a large loan of funds from an organization that is subject to long-term repayment.
Short-term receivables are debts that are characterized by a short time to repay the debt - up to a year after the reporting date. It includes the debt of buyers and customers for goods and services - it is possible to secure them with bills of exchange.
This type includes settlements with the budget, repayment of debts on advances paid, accrual of income for the provision of funds for use, internal settlements, etc.
Short-term receivables are treated as payment subject to adjustment of the allowance for doubtful debts or overdue and bad debts. It dominates the total amount of debt because deferment of payment on debt for a period of more than a year is very rare.
Sale and purchase of receivables
If you do not have the slightest desire to deal with debtors, but want to return the funds, you can sell the receivables, if there are persons who would be interested in this. Often these are people who themselves have a debt to the debtor. The company has the opportunity to buy receivables at a lower price, at a discount, so to speak, and then present documents to the debtor and demand repayment of the debt at full cost. To sell a debt, the debtor’s consent is not required; it will be enough to notify him of the sale of the debt.
Optimization of the enterprise sales system and minimizing risks in working with receivables and payables
Long-term accounts receivable: line in the balance sheet
In the second section of the balance sheet “Working capital”, line No. 1230 is provided to reflect the amounts of short-term receivables. Previously, the balance sheet provided for the division of receivables by maturity (up to a year and more), in the form used today there is no such division, but long-term debt has not gone away.
Often, accountants record the entire amount of debt in line 1230, but this is legal only if the company does not have long-term debtor obligations. The fact is that all accounts receivable according to PBU 4/99 are considered a highly liquid asset, therefore they are given a place in the 2nd section of the balance sheet, however, supply arrears are significantly less liquid than payment arrears, and advances issued for construction are generally less liquid. And since it would be incorrect to combine assets of different liquidity in one line, we note that the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation recommended that debt on advances for construction be included in line 1190 “Other non-current assets”.
Having dealt with the issue of reflecting debt in financial statements, we will consider the classification of an asset according to the time of formation and the probability of repayment. Based on these conditions, it happens:
- Normal;
- Doubtful;
- Hopeless.
Debt is considered normal if the repayment date for which, in accordance with the terms of the agreement, has not yet arrived. It’s another matter if counterparties delay payments under concluded agreements or do not deliver paid goods/services.