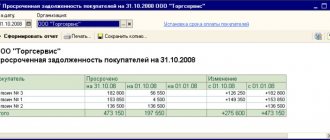
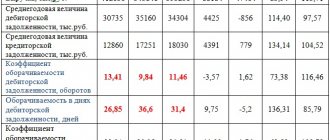
What is tax arrears?
If a legal entity or individual entrepreneur misses the deadline for paying taxes or insurance premiums, thereby violating tax legislation (paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), then he will develop a debt to the budget.
This is arrears in taxes (insurance contributions), that is, in this case, debt (clause 2 of article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To learn about what violations there is liability for and what its extent is, read the article “Liability for tax violations: grounds and amount of sanctions .
In addition, there are situations when, while checking a taxpayer, inspectors discover an excessive amount of taxes reimbursed to him from the budget, for example, for VAT. And this is a tax arrears too.
The following taxes can be reimbursed from the budget:
- VAT, when the amount of deductions exceeds the amount of calculated tax, including taking into account the amounts of tax subject to restoration (clause 2 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- excise taxes, when the amount of tax deductions is greater than the amount of excise tax calculated on transactions with excisable goods - objects of taxation under Art. 182 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 203 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
About illegal VAT refunds and subsequent liability for this, read the material “What is an illegal VAT refund and what is the responsibility for it?” .
Arrears on insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund, Pension Fund and Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund
Arrears under the Social Insurance Fund is the debt of the policyholder to the Social Insurance Fund. It is calculated as the difference between the contributions already paid and the total amount. The work of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation is aimed at collecting social contributions and paying various types of benefits to citizens of the Russian Federation at their expense.
The Pension Fund recognizes arrears as debt on mandatory pension contributions.
The FFOMS recognizes arrears as debt for mandatory payments for compulsory medical care.
As with tax arrears, liability arises for non-payment of insurance premiums; as a rule, it is expressed in the accrual of penalties. If a debt arises, the regulatory authorities draw up a demand for forced repayment of the debt that has arisen.
Such arrears will arise if the payer does not transfer contributions by the 15th day of the month following the reporting month. These contributions are required to be paid by persons who employ employees. For example, an individual entrepreneur hired a salesperson to work in his store, from that moment he is obliged to pay all mandatory contributions.
For those persons who do not have employees, contributions are paid once at the end of the year. Mandatory and basic payments include medical and pension payments. Social payments are paid voluntarily.
When does a tax arrear arise?
Tax arrears arise the very next day after the violation of the deadline established by law for paying taxes to the budget.
If an excessively refunded amount of tax is recognized as arrears, then the day of its formation will be (paragraph 4, paragraph 8, article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the day on which the taxpayer actually received the refunded amount of tax from the budget, in the case of transferring funds from the budget to the current account;
- the day on which the decision was made to offset the tax amount, in the event of a tax offset.
Read about the refund procedure in the article “How is VAT refunded: return (refund) scheme?”
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail what to do if you independently discover tax arrears:
Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
What are the consequences of arrears?
You must always remit taxes on time, otherwise there may be consequences - tax arrears, as well as the accrual of penalties.
The arrears can be repaid by the taxpayer voluntarily. However, in addition to the tax itself, you will also need to transfer penalties to the budget, calculated taking into account the number of days of late payment.
Our calculator will help you calculate penalties.
If the taxpayer does not independently pay off his debt in the form of tax arrears and penalties to the budget, then the tax authorities will collect these amounts by force.
If it is impossible to collect arrears of taxes and penalties from the taxpayer, the tax authorities may write off this debt as bad.
Summarize
If a company has arrears in taxes, this can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences. Firstly, there will be extra expenses in the form of penalties, and in some cases, fines, which can be quite significant in the case of a large amount of debt. Secondly, officials may be brought to administrative and, under certain circumstances, criminal liability.
Thirdly, blocking accounts and seizing property can paralyze the entire business and threaten the very existence of the enterprise.
The paradox of this situation lies in the fact that the director and/or owner of the company find themselves in a dependent position. Because they may suffer due to low qualifications, inattention or irresponsibility of the accountant.
In this case, you can be sure that taxes will be calculated correctly and transferred on time using the correct details. We also regularly conduct reconciliations with the tax authorities to ensure that the company does not have tax debts.
What is the procedure for collecting arrears by tax authorities?
Let's consider the procedure for collecting debt to the budget from a taxpayer step by step.
Step 1. If a tax arrears are detected, the tax authority must issue a demand to the debtor to pay taxes, penalties, fines, and interest within the following terms:
- If a tax arrears are identified during a tax audit, then no later than 20 working days from the moment when the decision made based on the results of the audit came into force (clause 6 of article 6.1, clauses 2, 3 of article 70, clause 1 Article 87, paragraphs 7, 9 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- If the arrears are identified outside the scope of the taxpayer’s audits, then the deadline for sending the demand will depend on the amount of the debt (clauses 1, 3, article 70, clause 10, article 101.4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). So, with a debt of 500 rubles. or more, the demand must be sent within 3 months from the date of discovery of the arrears, and if the debt is less than 500 rubles. - within 1 year from the date of discovery of the arrears.
Step 2. The taxpayer must fulfill the requirement within the period specified therein (clause 6 of article 6.1, paragraph 4 of clause 4 of article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The minimum period within which he must meet the repayment of arrears on taxes, penalties, etc. is 8 working days from the date of receipt. If the debtor does not fulfill the demand, then:
- According to paragraph 3 of Art. 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, no later than 2 months after the deadline for fulfilling the requirement, the tax authority makes a decision to collect the debt from the debtor’s accounts opened with banking and credit institutions. Let us note that if we are talking about a consolidated group of taxpayers, then the period for making this decision by the tax authority is extended to 6 months from the moment when the deadline for fulfilling the requirement sent to the responsible member of the group has expired (subclause 5, clause 11, article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The procedure for collecting debt from taxpayer accounts is regulated by Art. 46 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If there are no funds in bank accounts or there are not enough funds to pay off the debt, the debt is placed in a card index and will be written off as funds become available.
To learn about from which taxpayer accounts debts on taxes and fees can be collected, read the material “From which accounts can tax authorities collect?” .
Step 3. If it is not possible to collect the debt at the expense of the debtor’s funds, then:
The inspectorate, no later than 1 year after the end of the deadline for fulfilling the requirement to pay the debt, makes a decision on its collection at the expense of the taxpayer’s property (clause 7 of article 46, clause 1 of article 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, foreclosure can be applied to both movable and immovable property. After making such a decision, the Federal Tax Service has the right to seize him (Article 77 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Collection of arrears, penalties, etc. at the expense of property is carried out in the manner prescribed by Art. 47 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This decision is carried out by bailiffs. To do this, the Federal Tax Service sends them a resolution on the collection of property. Bailiffs have the right to seize the debtor's assets, evaluate them, seize and/or transfer them for storage and other measures provided for by the Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ. If the debt cannot be repaid within 2 months, the bailiffs transfer the seized property of the debtor to a special organization for sale.
Step 4. If the above measures do not lead to full repayment of the debt, the bailiffs issue a resolution on the return of the writ of execution, and the Federal Tax Service, on the basis of this document, makes a decision on the bankruptcy of the company or individual entrepreneur (clause 4.1, clause 1, article 59 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read more about the collection procedure here.
If the amount of arrears exceeds 5 million rubles. or the debt is collected from a consolidated group of taxpayers, then the Federal Tax Service has the right to go to court:
- After 2, but no later than 6 months after the expiration of the deadline for fulfilling the demand for payment of arrears, penalties, fines, etc., the tax authority has the right to submit an application to the arbitration court in order to recover the required amount of debt from the taxpayer. The deadline for filing an application regarding the collection of debt from members of a consolidated group of taxpayers is extended to 6 months after the expiration of the 6-month period for indisputable collection of debt from the bank accounts of these persons (subclause 5, clause 11, article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Please note that if the inspectorate, for good reason, missed the deadline for filing this application, the court can reinstate it (paragraph 1, paragraph 3, subparagraph 5, paragraph 11, article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, article 117 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
- No later than 6 months after the end of the deadline for fulfilling the requirement, the tax authority submits an application to the arbitration court in order to recover from the taxpayer the necessary amount of debt in those cases that are provided for in subsection. 1–4 p. 2 tbsp. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with the provisions of sub-clause. 2 p. 2 art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in this case, tax authorities have the right to go to court only if the arrears are identified during a tax audit and are registered with the debtor for more than 3 months. Indisputable collection of arrears in such situations is impossible.
How to get rid of arrears for which the tax authorities missed the collection deadlines
The inspectorate made a mistake when reflecting tax accruals on the entrepreneur’s personal account card. Having corrected it after 2 years, she made a demand for additional tax payment within 3 months from the moment she discovered her error and made corrections to the card. But the court refused to collect this arrears, arguing it as follows.
Please copy the link below into your RSS feed reader. Thank you.
During a tax audit, when tax arrears are identified, the taxpayer must be sent a request to pay the identified arrears within twenty business days from the date of entry into force of the tax authority’s decision based on the results of the tax audit.
Which, in fact, at the moment, according to the above algorithm, the tax inspectorate is sending out to “willful” non-payers of insurance premiums. Everything would be fine if it weren't so sad. Fiscal authorities are endowed with some kind of privileged position to identify arrears whenever I want.
When is it possible to write off tax arrears?
If the statute of limitations for debt to the budget has expired, then the tax authorities will not be able to oblige the debtor to pay the arrears, despite the fact that the debt will still be registered with him. However, if such a debt is deemed uncollectible, it may be excluded from the card for settlements with the budget.
According to sub. 1–4.1 clause 1 art. 59 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a debt is recognized as uncollectible in the following cases:
- upon liquidation of the company;
- when an individual entrepreneur is declared bankrupt;
- in the event of the death of an individual, if he was a debtor for taxes and fees;
- if there is a court decision, according to which the tax authorities do not have the right to demand payment of arrears of taxes, penalties, etc. from the debtor;
- when a bailiff makes a decision to complete proceedings on an executive document with the return of such a document to the claimant (clauses 3, 4, part 1, article 46 of the federal law of October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ “On Enforcement Proceedings”), provided that a this debt is more than 5 years ago, in the following cases:
- the amount of debt is equal to or lower than the amount of claims against the debtor established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on insolvency (bankruptcy) for initiating bankruptcy proceedings;
- the court returns the application for declaring the debtor bankrupt or terminates the bankruptcy proceedings due to the lack of funds necessary to compensate for legal costs for the procedures applied in the bankruptcy case.
For information on liquidating an LLC with tax debts, read the article “Liquidation of an LLC with tax debts.”
How to find out if there is debt and calculate penalties for land tax?
To find out the debt, an application can be submitted during a personal visit to the local tax office at the location of the tax office; information can be easily obtained online. To do this, you need to register on the official website of the Federal Tax Service. Then create a request about the existence of a debt indicating the personal data of the taxpayer.
find out the land tax debt using your TIN on the website of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
If information about arrears is provided, interested parties will be able to independently calculate the amount of the penalty and pay what is due before penalties are imposed.
To do this, one should proceed from the reasons for the underpayment, since the amount of the penalty is established based on the motivations:
- For persons who made mistakes in calculations and other bona fide taxpayers, 20% of the amount of arrears is charged.
- For unscrupulous debtors, a fine of 40% of the amount of arrears is provided.
Based on these points, we can draw conclusions about how land tax penalties are calculated . Below are a couple of examples for clarity.
For example, a citizen did not pay 1 thousand rubles in tax. He was given a fine of 200 rubles for the year. If he comes to his senses after six months, he pays half the amount, that is, 100 rubles. after three months he should pay 50 rubles, and after 9 months - 150.
And if an individual entrepreneur received a notice of arrears of 10 thousand rubles, but ignored the demand and did not pay the amount collected, in a year he will owe 4 thousand rubles, in six months - 2 thousand. His debt will be 1 thousand rubles for every 3 months.
Results
Arrears on tax payments arise if the deadlines for payment are missed. It is recognized from the first day following the date determined as the deadline for payment. The consequence is penalties accrued for each day of delay.
If the taxpayer does not pay off the arrears and penalties voluntarily, the Federal Tax Service will resort to a forced collection procedure.
In certain situations, debt is considered uncollectible. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.