Inventory of property and financial obligations: preparation and documentation
The need to conduct inventories is provided for in Art. 11 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. The rules for conducting an inventory of property and financial obligations are established by the Methodological Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 13, 1995 No. 49.
All assets and liabilities of the company are subject to routine inspection.
The property includes:
- OS and intangible assets;
- financial investments;
- industrial reserves – materials, fuel, raw materials;
- finished products;
- goods;
- inventory;
- money and other assets.
The company's liabilities are usually represented by:
- debt to creditors - suppliers, budget, banks, personnel, funds;
- accounts receivable;
- formed reserves.
Inventory act of settlements with buyers and suppliers
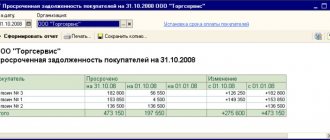
The inventory results are documented in a form that is approved for these purposes in the company’s accounting policy. An organization can develop a document independently, not forgetting to include all the required details, or use the unified form INV-17, approved. Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia No. 88 of August 18, 1998, which is called the act of inventory of settlements with buyers, suppliers and other debtors and creditors. This form can also be used as a template for developing your own form: you can add necessary or, conversely, remove unnecessary details. This act is drawn up in two copies - one each for the accounting department and the commission.
The main part of the document contains data on receivables and payables, presented in the form of tables. For each accounting account, the total amount of the balance sheet and debts are indicated: those that are confirmed and not confirmed by debtors (creditors), as well as debts for which the statute of limitations has already expired. First, data on accounts receivable is indicated, and then – on accounts payable.
It is mandatory to fill out a certificate-attachment to the act in form INV-17, which is the basis for drawing up the act. It consists of a table and contains information about creditors and debtors: location and contact information, amount of debt, date, reason for the debt, etc. After completing the certificate, you should begin filling out the act itself.
A sample act of inventory of settlements with buyers and suppliers is presented below.
Inventory of financial obligations
The need to conduct an audit of financial obligations is dictated by the norms of the Regulations on accounting (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n), which excludes the presence in the company’s accounting of inconsistencies in settlements with counterparties and discrepancies in the operating amounts. According to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 07-02-18/01 dated 01/09/2013, scheduled checks of the status of settlements are carried out on December 31, i.e. immediately after the end of the year. But the reorganization of the company will require an unscheduled inventory, the date of which is set in accordance with the plan of transformative measures.
Verification of settlements with creditors and debtors is carried out by comparing accounting data on debt balances with data from reconciliation acts with counterparties. They indicate the amount of debt, the moment of its formation, intermediate calculations, and the amount of debt as of a certain date. The act is drawn up in 2 copies (one for each party), and becomes a legal document when certified by both parties.
Similar to the reconciliation of settlements with counterparties, inventories are carried out on other obligations - reserves, settlements with employees, etc. Checks by type of obligations are carried out separately for each of them and by position.
Inventory of settlements with buyers and customers
Before drawing up annual financial statements, it is necessary to carry out an inventory of calculations. Carrying out an inventory is one of the components that guarantees the reliability of accounting and reporting. Therefore, if the untimely inventory led to distortion of reporting data, liability is provided.
It is worth understanding that violation of deadlines for conducting an inventory is not a reason why an organization can be held accountable. However, this may lead to violations of the rules for accounting for expenses and income, and reporting requirements. Thus, the tax inspectorate can fine a company up to 30 thousand rubles, or 20% of the amount of tax that was not paid, but not less than 40 thousand rubles. For violation of accounting requirements, the head of the organization (or other officials) may be fined by the court in the amount of 5 to 10 thousand rubles. If the inventory was not carried out on time due to the fault of the employee who is responsible for its implementation, disciplinary action may be applied to him.
Please note that the need to conduct an inventory does not depend on the tax system that the organization uses. Inventory must be carried out by all enterprises that maintain accounting. So, this obligation also applies to organizations that work on the simplified tax system, and to companies that apply the special UTII regime, since these companies are not exempt from accounting.
During the inventory of settlements with suppliers and contractors, the following information is checked:
- Settlements with regulatory agencies (tax office, Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund);
- Settlements with suppliers, contractors, buyers, customers;
- Claim settlements;
- Settlements with company employees regarding wages;
- Other calculations of the organization.
Before starting an inventory of payments to suppliers and contractors, it is worth preparing the following documents:
- A document on conducting an inventory - this can be an order, instruction, resolution;
- Primary accounting documents, contracts concluded with counterparties, etc.
An inventory order can be developed and approved by the company independently. As a sample for filling out an order, an organization can take the unified form No. INV-22. The main condition that must be met is the presence of all the mandatory details listed in Federal Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011. The order must be signed by the head, registered in the accounting journal (for example, according to the INV-23 form) and transferred to the chairman of the commission.
Preparation of documents based on inventory results
Information about the availability of assets and the reliability of accounted liabilities is recorded in inventory records or inventory reports. They are filled out according to certain rules: on each page the number of checked positions and their total in natural and monetary values are counted. Blank lines must be crossed out.
Established discrepancies between actual data and accounting data are recorded in matching statements. Based on the received explanations from the responsible persons, the manager makes a decision on how to write off shortages. Surplus property is accounted for.
To document the results of an inspection of different categories of property, unified forms of documentation for the inventory of assets and liabilities can be used (inventory lists for fixed assets No. INV-1, for inventory items No. INV-3, inventory reports of shipped goods and materials No. INV-4, cash No. INV-15 , settlements with counterparties No. INV-17 and others). The results of inspections by groups of assets and liabilities are summarized in Statement No. INV-26. It reflects information about discrepancies and the procedure for eliminating them in accordance with the order of the manager
Documentation of inventory debt
In order to conduct an inventory of debt liability, you must fill out 2 sample forms:
- INV 22.
- INV 17.
Carrying out an inventory is impossible without this documentation:
1. Order to conduct an inventory (Form INV-22)
The order is the basis for conducting an inventory of debt liability. Sample INV 22 is issued as a result of control and is the basis for starting the described activity.
sample order for inventory in MS Excel format.
The document contains the following components:
- Basic provisions.
- Stages of the inventory procedure.
- Inventory item size.
- Period of description of the item.
At the end of the activity, the boss certifies the documentation, and the chairman of the commission group records the completed reporting in the documentation.
Inventory report of settlements in the form of a certificate (Form INV-17)
The list is considered a mandatory condition for the settlement activities of the institution and the party supplying the product. The purpose of this form is considered to be control of residual value.
The document is certified by members of the commission group. At the same time, I make two copies: the commission group and the accounting department.
Sample of filling out the INV-17 form in MS Word format.
When completing the form, you must provide the following information:
- Personal account.
- The price range of the organization's balance sheet.
- Cash amount:
- Proof of debt.
- Unconfirmed debt.
- Debt that has expired.
Where to download INV-17
The INV-17 form is available for download on our website.
The inventory report in form INV-17 is accompanied by a certificate (appendix to form INV-17), detailing (by counterparties) the data on existing debt and reflecting information on the availability of documents confirming its amount. In the INV-17 form itself, if there is a significant number of counterparties, consolidated total data on accounting accounts can be entered without breakdown by counterparties. And if there are few counterparties, then INV-17 may also contain their names.
A sample of filling out an act in form INV-17 is available for download on our website.
Basic Rules
The general procedure for the inventory of payments is established by the Methodological Instructions of the Ministry of Finance of Russia for the inventory of property and financial obligations. They were approved by his order No. 49 dated June 13, 1995.
The inspection begins with the issuance by the head of an order for an inventory of payments, to which he also appoints members of the commission. Let us note that the legislation does not provide for a mandatory form of this document, therefore each company forms it in its own form.
An inventory of settlements with banks and other credit institutions for loans, with the budget, buyers, suppliers, accountable persons, employees, depositors, other debtors and creditors consists of checking the validity of the amounts listed in the accounting accounts.
The account “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” for goods paid for but in transit, and settlements with suppliers for uninvoiced deliveries should be checked. It is verified against documents in accordance with the corresponding accounts.
Also see “Accounting for settlements on account 60”.
In relation to debt to employees of the organization, the following is identified:
- unpaid amounts for wages to be transferred to the depositors' account;
- amounts and reasons for overpayments to employees.
When taking inventory of accountable amounts, the following is checked:
- reports of accountable persons on advances issued, taking into account their intended use;
- the amount of advances issued for each accountable entity (dates of issue, intended purpose).
Also see “Reserve Inventory Rules”.
By checking documents, the inventory commission must also establish:
- the correctness of settlements with banks, financial, tax authorities, extra-budgetary funds, other organizations, as well as with structural divisions of the organization allocated to separate balance sheets;
- the correctness and validity of the amounts of debt recorded in the accounting records for shortages and thefts;
- correctness and validity of the amounts of receivables, payables and depositors, incl. amounts of receivables and creditors with expired statutes of limitations.
Also see “Limitation period for accounts receivable.”
Write-off of bad debts
During an inventory of settlements with counterparties, business entities usually identify bad receivables and/or payables. Most often, debts for which the statute of limitations has expired become uncollectible.
For tax purposes , uncollectible
is considered debt that corresponds, in particular, to one of the following criteria (clause 14.1.11 of the Tax Code):
- debt on obligations for which the statute of limitations has expired;
- overdue debt of a deceased individual in the absence of hereditary property that can be foreclosed on;
- overdue debts of persons who were declared missing in court or declared dead;
- debt of individuals forgiven by a creditor, with the exception of debt of persons associated with such a creditor, persons who are in an employment relationship with such a creditor, and persons who were in an employment relationship with such a creditor and for whom the period between the date of termination of these relations and the date of forgiveness their debt does not exceed three years;
- debt of a person overdue for more than 180 days, the amount of the creditor’s total claims for which does not exceed the minimum amount of the creditor’s undisputed claims established by law for violating bankruptcy proceedings, and for individuals - debt that does not exceed 25% of the minimum wage (per year), established as of January 1 of the reporting tax year (in the absence of a legally approved bankruptcy procedure for individuals);
- an asset in the form of corporate rights or non-debt securities, the issuer of which is declared bankrupt or terminated as a legal entity in connection with its liquidation;
- overdue debt of an individual or legal entity that has not been repaid due to the insufficiency of the said person’s property, provided that actions to forcibly collect the debtor’s property did not lead to full repayment of the debt;
- debt, the collection of which became impossible due to force majeure circumstances, a natural disaster (force majeure), confirmed in the manner prescribed by law;
- debt of business entities declared bankrupt in accordance with the procedure established by law or terminated as a legal entity in connection with their liquidation.
For legal entities, the occurrence of bad debt is most often associated with the expiration of the statute of limitations, which is usually detected during the annual inventory.
Especially many questions arise from agricultural enterprises - VAT payers regarding the consequences of writing off bad debts in VAT accounting.
Accounts payable
Accounts 76, 60, 62. The organization's debt to suppliers (contractors) for supplies, advances from buyers (customers), and other debts to counterparties.
Accounts 68,69. Debt on taxes, payment of obligatory amounts to the Funds.
Accounts 70, 71, 73. Debt in terms of wages for personnel, compensation payments to employees, overexpenditures on advance reports of individual accountable persons.
Scores 66.67. Unpaid amounts on bank loans and interest on them.
Account 75. Dividends not paid to the founders.