Types of instructions for workers on labor protection, the procedure for their conduct and registration
All types of instruction should be considered elements of learning. When instructing, special attention should be paid to workers with less than 1 year of experience, as well as experienced workers with extensive experience.
These categories of workers are most susceptible to injury. In the first case - due to inexperience, in the second - due to excessive self-confidence. Analysis of accidents and elaboration of orders is also a unique form of training.
- introductory;
- primary at the workplace;
- repeated;
- unscheduled;
- target.
Introductory briefing and initial on-the-job training are carried out according to approved programs.
Induction training
An introductory briefing on occupational safety is carried out by a labor protection engineer or a person entrusted with these duties with all newly hired workers, regardless of their education, work experience in a given profession or position, with temporary workers, business travelers, students and students who have arrived for industrial training or practice, as well as students in educational institutions.
An entry about the induction training is made in the induction training logbook with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing, as well as in the employment document or checklist. Conducting introductory briefings with students is recorded in the educational work log.
Initial briefing
Initial instruction on labor protection in the workplace before the start of production activities is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work according to labor protection instructions developed for individual professions or types of work:
- with all employees newly hired into the organization and transferred from one division to another;
- with employees performing new work for them, business travelers, temporary workers;
- with builders performing construction and installation work on the territory of an operating organization;
- with students and students who arrived for industrial training or practice before performing new types of work, as well as before studying each new topic when conducting practical classes in educational laboratories, classes, workshops, and areas.
Persons who are not involved in the maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment, the use of tools, storage and use of raw materials and supplies do not undergo initial training.
The list of professions and officials exempt from initial training at the workplace is approved by the head of the organization in agreement with the trade union committee and the labor protection service.
All employees, including graduates of vocational schools, after initial instruction at the workplace must, during the first 2 to 14 shifts (depending on the nature of the work, the qualifications of the employee), undergo an internship on safe methods and techniques of work in the workplace under the supervision of persons appointed by order (by order) for the enterprise (division, workshop, site, etc. Students and trainees are assigned to qualified specialists for the duration of their internship.
Re-briefing
All workers undergo repeated training, with the exception of persons exempt from initial training at the workplace, regardless of their qualifications, education and work experience, at least after 6 months.
It is carried out with the aim of testing knowledge of rules and instructions on labor protection, as well as with the aim of increasing knowledge individually or with a group of workers of the same profession, a team under a workplace training program. By agreement with the relevant state supervisory authorities, a longer (up to 1 year) period for undergoing repeated training may be established for some categories of employees.
Repeated training is carried out according to the initial training programs at the workplace.
Unscheduled briefing
Unscheduled briefing is carried out:
- upon the introduction of new or revised standards, rules, instructions on labor protection, as well as amendments to them;
- when changing the technological process, replacing or upgrading equipment, devices and tools, raw materials, materials and other factors affecting labor safety;
- in case of violation by workers and students of labor safety requirements, which can lead or have led to injury, accident, explosion or fire, poisoning;
- at the request of supervisory authorities;
- during breaks in work - for work that is subject to additional (increased) labor safety requirements, more than 30 calendar days, and for other work - more than two months.
Unscheduled briefing is carried out individually or with a group of workers of the same profession. The scope and content of the briefing is determined in each specific case, depending on the reasons or circumstances that necessitated its implementation. An unscheduled briefing is noted in the workplace briefing log, indicating the reasons for it.
Unscheduled briefing is carried out directly by the work manager (teacher, foreman).
Targeted briefing
Targeted briefing is carried out directly by the work supervisor and is recorded in the briefing log and, if necessary, in the work permit.
Approximate list of basic questions of induction training
- General information about the enterprise, organization, characteristic features of production.
- Basic provisions of labor protection legislation.
- Employment contract, working hours and rest periods, labor protection for women and persons under 18 years of age. Benefits and compensation.
- Internal labor regulations of the organization, responsibility for violation of the rules.
- Organization of labor protection work in the organization. Departmental, state supervision and public control over the state of labor protection.
- General rules of conduct for workers on the territory of the enterprise, in production and auxiliary premises. Location of main workshops, services, auxiliary premises.
- The main dangerous and harmful production factors characteristic of this production. Methods and means of preventing accidents and occupational diseases: collective protective equipment, posters, safety signs, alarms. Basic requirements for the prevention of electrical injuries.
- Basic requirements for industrial sanitation and personal hygiene.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE). Procedure and norms for issuing PPE, terms of wearing.
- Circumstances and causes of individual typical accidents, accidents, fires that occurred at the enterprise and other similar industries due to violations of safety requirements.
- Procedure for investigation and registration of accidents and occupational diseases.
- Fire safety. Methods and means to prevent fires, explosions, accidents. Actions of personnel when they occur.
- First aid for victims. Actions of workers in the event of an accident on the site or in the workshop.
An approximate list of the main issues of initial training in the workplace
- General information about the technological process and equipment at a given working, production site, or workshop. The main dangerous and harmful production factors arising during this technological process.
- Safe organization and maintenance of the workplace.
- Dangerous areas of a machine, mechanism, device. Equipment safety equipment: safety, braking devices and guards, locking and alarm systems, safety signs.
- The procedure for preparing for work (checking the serviceability of equipment, starting devices, tools and devices, interlocks, grounding and other protective equipment).
- Safe working practices and methods. Actions in case of a dangerous situation.
- Personal protective equipment at this workplace and means of using them.
- Scheme of safe movement of workers on the territory of the site, workshop.
- Intrashop transport and lifting equipment and mechanisms.
- Typical causes of accidents, explosions, fires, cases of industrial injuries.
Measures to prevent accidents, explosions, fires. Responsibilities and actions in case of an accident, explosion, fire. Methods of using fire extinguishing means, emergency protection and alarm systems available on the site, and their locations.
From the site: https://www.steps.ru/article/vidy_instruktazhey_rabotnikov_po_ohrane_truda_poryadok_ih_provedeniya_i_oformleniya/
Unscheduled briefing on labor protection - procedure and conditions for conducting
Any employee of a production establishment, when hired for a place of work, must undergo training, which includes the procedure, conditions, norms and standards of labor activity.
Unscheduled safety training is carried out by the employer in certain cases. According to Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the implementation of this process must be carried out without fail. If these conditions are violated, the employer does not have the legal ability to allow employees to carry out activities.
In addition to the employees of the enterprise, the manager himself must undergo safety training. Also, in production it is necessary to organize a plan for inspections in the field of work process safety. These checks are needed to identify violations, as a result of which there is a basis for unscheduled instruction on labor protection.
The procedure for conducting unscheduled briefings on labor protection
Familiarization with the basic rules for the protection of professional activities is aimed at preventing emergency situations in the organization. Unscheduled training can be carried out at any time during the work process; it is not subject to strict deadlines.
The training program is similar to primary training in that it is carried out within the organization. This obligation applies to all workers, regardless of experience, nature of work and professionalism of the person.
Familiarization with the instructions for the implementation of professional functions should be organized for new employees, seconded and temporary subordinates, as well as students and trainees, in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation. When implementing the appropriate procedure, specialists study the main changes that take place in the enterprise. This applies to both the conditions of the working environment and the rules for protecting professional activity. Each specialist, before starting to perform his work function, is required to familiarize himself with the innovations and, if necessary, pass a test on his knowledge of the basics.
Who conducts unscheduled and targeted briefings on labor protection
Unscheduled safety training can be carried out by the employer himself, who is responsible for a specific department. For example, a workshop manager, a chief storekeeper, a shift foreman, etc. The following may also act as a teacher:
- A specialist assigned to this position who is responsible for safety precautions in the organization (he monitors changes in the laws of the Russian Federation on labor protection);
- Head of the entire production.
Each training must include up-to-date information covering the essential aspects of on-site safety.
In what cases is unscheduled instruction on labor protection carried out?
Unscheduled labor safety briefings are carried out when:
- The main regulations that relate to this issue are being changed and the relevant instructions are being amended;
- Production equipment is updated, technology is changed or the enterprise’s activities are completely modernized;
- There is a systematic violation of labor regulations;
- Knowledge of the rules is checked by supervisory authorities;
- The employee is on long-term leave, for example, for maternity leave;
- The employee was absent from work for more than 30 days (under negative health and hazardous working conditions).
Instruction must be available to every subordinate, since failure to comply with safety rules leads to serious consequences.
Timing of unscheduled training on labor protection
Unplanned learning can occur at any time. This process does not involve establishing a specific time period.
Instruction is carried out during the occurrence of a special case upon request, regardless of the date of the last training. The employer can establish it for a specific subordinate, for a workshop or department, as well as for all employees of the enterprise.
Journal of unscheduled briefing on labor protection - sample
To track training periods, actions are recorded in documents such as:
- Special journal for registration;
- Certificate - admission of a subordinate;
- Worker's personal card.
There is a specific procedure for filling out the log, which includes:
- Availability of registration date;
- Signatures of training participants;
- Mandatory completion of the column - reason, briefly justifying the motive for unplanned study.
A worker who works in a particularly unfavorable area is required to provide a special certificate before starting to perform work functions. It must include an assessment of safety knowledge.
Order for unscheduled training on labor protection - sample
In the case of unplanned training, it is necessary to draw up an order, which will be the basis for starting this process. The employer's order must include the following information:
- Reasons for carrying out (links to changes in law or instructions);
- Date, place and time of the event;
- Personal data of the responsible person who will be responsible for the implementation of this procedure;
- Names of those who are trained in the basics of labor protection.
Also, a sheet of familiarization with this process is attached to the order. The order must be reviewed and signed by all parties involved.
From the site: https://russiansu.ru/oxrana-truda/vneplanovyj-instruktazh-po-oxrane-truda-poryadok-i-usloviya-provedeniya.html
Testing knowledge based on the results of targeted instruction
After targeted instruction on labor protection, a knowledge test is carried out. The legislation does not provide for a uniform procedure for carrying out this procedure that is acceptable for all categories of workers and students, therefore the instructor should be guided by the requirements of local regulations or organize it at his own discretion. The knowledge test can be carried out in the form of an oral survey, require demonstration of practical skills, or conduct a test.
People who fail the knowledge test must take the instruction again. When targeted training on labor protection is carried out before high-risk work, workers who have demonstrated unsatisfactory knowledge results should not be allowed to perform this work.
Unscheduled briefing on labor protection
Unlike the others, unscheduled briefings do not have set deadlines or frequency. The manager can assign it to individuals, departments and all personnel as a whole. Why do you need unscheduled briefing? Let's figure it out together.
Why is unscheduled training needed?
Unscheduled briefings are carried out with employees of the enterprise in order to talk about important changes that may affect their work.
According to paragraph 8.9 of GOST 12.0.004-2015, which will come into force on March 1, 2020, unscheduled training at the workplace is carried out if:
- the production process has changed at the enterprise;
- equipment, devices, tools have been replaced or modernized, which may affect the working conditions and safety of employees;
- there have been changes in legislative and other regulatory legal acts that contain labor protection requirements and the procedure for performing work;
- at the enterprise, employees created a situation that could cause an accident or an accident at work has already occurred;
- this is a requirement of officials of state supervision and control bodies, public control;
- an employee of an enterprise who works in hazardous production had a break from work for more than 30 calendar days, and for other employees - more than two months.
Who conducts unscheduled briefings?
Unscheduled briefing at the workplace is carried out by the employee’s immediate supervisor, who has completed occupational safety training and knowledge testing of occupational safety requirements. This could be a foreman, a shift or section manager, a department head, etc.
The list of employees for whom it is necessary to conduct unscheduled briefing is approved by the head of the enterprise by his order.
The order “On conducting unscheduled briefing” must indicate the following information:
- reasons for conducting unscheduled briefings with references to legislation or instructions;
- date, place and time of the briefing;
- details of the employee (name and position) who is appointed responsible for conducting unscheduled training;
- a list of employees with whom you need to conduct unscheduled training.
Unscheduled briefings can be group, for example, if an accident occurs or a group of employees needs to be notified about changes in legislation. Also, such instruction can be carried out with one employee, for example, if he periodically violates labor safety rules at his workplace.
What programs require unscheduled instruction?
Unscheduled training should be carried out using either ready-made programs that are developed and approved at the enterprise, or instructions on labor protection and safe performance of work at a specific workplace. If an unscheduled briefing concerns changes in legislation, you need to use the texts of these documents and other local regulations.
The scope and content of unscheduled briefings must be determined in each specific case separately. This will primarily depend on the reasons and circumstances that created the need for such instruction.
How to test the knowledge of employees that they received during an unscheduled briefing?
As in the case of initial, repeated or targeted briefings at the workplace, after an unscheduled briefing, the manager conducts an oral assessment of the knowledge and skills acquired by employees in safe work practices. After that, information about the unscheduled briefing must be entered into the workplace briefing log. It requires:
- set a date for an unscheduled briefing;
- sign the two parties: the person checking and the person being instructed;
- in the “Reason for the briefing” column, be sure to briefly describe the reasons for its conduct.
From the site: https://profi-cpr.ru/biblioteka/stati/oxrana-truda/vneplanovyij-instruktazh-po-oxrane-truda.html
Legislative regulation
Unscheduled training must be carried out taking into account numerous legal requirements. Therefore, the head of the enterprise should study the following regulations:
- Art. 212 of the Labor Code contains information that the responsibilities of any employer include the need to provide employees with information about the conditions under which they will cope with their main responsibilities, and the director must also conduct training and certification of hired specialists.
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor No. 1/29 includes information on the rules and procedures for training workers, as well as monitoring the knowledge they have acquired.
- GOST 12.0.004-2015 establishes special standards on the basis of which instruction is carried out.
By studying these legislative acts, you can figure out how to properly train employees.
What is the procedure for completing unscheduled training?
Unscheduled briefing is carried out when:
- changes in labor protection rules;
- changes in technological processes, replacement or modernization of equipment, devices and tools, raw materials, materials and other factors affecting labor safety;
- violation by employees of labor safety requirements, which can lead or have led to injury, accident, explosion or fire;
- breaks in work - for work associated with increased danger for more than 30 calendar days, and for others - 60 days.
Unscheduled briefing is carried out individually or with a group of workers of the same profession in the scope of initial briefing at the workplace.
A note is made in the briefing log about the conduct of an unscheduled briefing, indicating the reasons that caused it to be carried out and the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing.
From the site: https://trudova-ohrana.ru/voprosy-i-otvety/vidy-instruktazhej-i-porjadok-ih-prohozhdenija/169-vneplanovyj-instruktazh.html
Cases in which unscheduled instruction on labor protection is carried out
Unscheduled instruction on labor protection is carried out in the event of an employee being sent on a business trip, industrial emergencies, etc. It is a short-term training of workers in safety precautions (HS) in the context of the employee’s area of work.
The duration of the instruction, as well as its content, depend on the level of proficiency in the specific production task that became the prerequisite for the instruction. In particular, the level of danger of work tasks is taken into account.
The person conducting the unscheduled briefing must indicate a specific reason for conducting it. Typically, employee safety training is assigned to the person in charge of the production process.
Instruction takes place three days before the start of work. In addition, the need for re-training of personnel may arise if safety rules are ignored, and it does not matter from which branch of the organization the information about the violation came. All information is entered into a separate safety log.
Tasks
The main goal of any instruction is to teach specialists to apply knowledge in real emergency situations. The content of the briefing in most cases includes a detailed analysis of the causes of emergency situations, as well as an algorithm of actions to eliminate them.
A specific list of tasks depends on the specific type of activity. Below is a list of general tasks that are set during any emergency briefing:
- teach workers to use protective equipment (for example, when working with flammable substances, you must know the rules for using fire extinguishers);
- explain the rules for providing primary medical care before specialists appear;
- familiarize yourself with the evacuation plan, as well as evacuation rules in case of emergencies;
- teach the rules of handling production equipment.
Reasons for conducting training Below are situations when unscheduled training on labor protection is carried out:
- Receipt of new equipment into production (learning of safe working techniques is required).
- An emergency occurred at one of the structural units due to negligence or ignorance of safety regulations.
- During the inspection, the labor inspector discovered significant “gaps” in safety knowledge.
- New standards stipulated by labor legislation come into force.
- When on a business trip or a break in work that lasted more than 60 days (for work with a high level of danger the period is 30 days).
- Unscheduled briefings on labor safety for employees are carried out when required by higher management.
The list of instructed persons is not limited. This can be either individual employees of the company or an entire structural unit.
Contents of the order
The order “On conducting unscheduled briefings on labor protection” is required for extraordinary training of workers in technical safety rules. The sample order must include the following information:
- reasons for instruction (must be documented);
- duration;
- name of the inspector (head of department or safety engineer);
- list of instructed employees;
- a form where subordinates must certify with signatures that they have familiarized themselves with the contents of the decree.
Procedure for conducting the briefingOrganization of unscheduled briefing takes place according to the following algorithm:
- A document is drawn up containing information about the need for training. In addition, it is necessary to provide documentary evidence as evidence of the need for training (notice of an accident, update of legislation, order of a management person). According to the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, employees have the right to familiarize themselves with all requirements in advance.
- An order is issued for personnel training, which will indicate all organizational aspects (purpose, responsible person, place of instruction, duration, etc.).
- The plan for conducting an emergency briefing is confirmed. Its structure depends on the specific profession, therefore its universal form is not fixed at the legislative level.
- This is followed by direct instruction, which is accompanied by an explanation of all the necessary provisions of safety regulations, work on practical skills and subsequent testing of knowledge. Testing of knowledge on labor protection takes place both in written (tests, detailed answers) and orally.
- In conclusion, those conducting it must make an entry in the safety journal, which must be confirmed by the signatures of all those instructed. The journal entry must be dated. In addition, a signature may be required on personal cards in T-2 format. Mechanics, repairmen and other groups of people who are engaged in dangerous work, before performing their work duties, receive an appropriate permit, which also requires a note about the training.
Repeated or extraordinary instructions
Example: an employee of one of the structural divisions was injured at work due to a violation of safety regulations. The legislation of the Russian Federation provides that such a situation is a reason for conducting unscheduled briefings, however, according to the schedule, after a few weeks it is the turn of repeated (regular) briefings.
In this case, it is not necessary to conduct two briefings simultaneously over such a short period of time. It is enough to include a program for missed unscheduled briefings into your regular briefing. In turn, unscheduled instruction on labor protection is carried out when instruction is required urgently.
The unscheduled training program may fully comply with the content of the initial instruction. This is possible in situations where the purpose of the initial training was to familiarize the employee with the basics. Thus, the goals of these two procedures should be the same.
The same applies to initial instruction, since when applying for a job, only the arriving employee needs to provide other information. In such a situation, it is recommended that the new employee listen to both the initial and unscheduled instructions. Accordingly, the TB register must also contain two entries certified by the signatures of the person.
Distant work
The structure of the briefing for those employees who work outside the organization’s building is no different from its standard form.
The necessary information is sent via the Internet (text PDF files, images, videos). Moreover, modern technologies (in particular, Skype and other IP technology) make it possible to hold conferences with workers in real time. All details of such instruction (in what cases it is carried out and how long it lasts) are pre-registered in the local acts of the organization.
From the site: https://kadrovyhdel.ru/ohrana-truda/vneplanovyj-instruktazh-provoditsya-v-sluchae.html
When is targeted occupational safety training carried out?
Targeted briefing is one of the types of briefings conducted at workplaces by certain persons in situations regulated by law.
Organizations must clearly understand the order, forms and content in which it is carried out, as well as how documentation is carried out.
Normative base
The procedure for carrying out targeted instruction is regulated by the following legal documents:
- Labor Code;
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 1/29;
- GOST 12.0.230-2007.
general information
Let's consider what targeted training is, under what circumstances it is carried out, which categories of workers are exempt from undergoing it, and other issues.
What it is?
Targeted briefing is an event carried out with an employee/a group of employees aimed at informing about the basics of safety, labor protection and the principles of a certain activity.
Before carrying out work on cleaning the nearby area from snow accumulations, garbage and household waste, employees of the enterprise engaged in trading activities must be given targeted training, since the specifics of the main activity do not provide for the performance of this type of work.
Goals, objectives and reasons for conducting
The goals of targeted instruction are usually based on the specifics of the work for which it is carried out.
The main purpose of carrying out such training in the general case will be to inform and train employees in the techniques and methods of safe work.
The main objectives of targeted instruction are:
- informing employees about safety precautions;
- training workers in safe work practices;
- checking the knowledge acquired during the instruction and the quality of its application.
This type of instruction is carried out for the following reasons:
- if personnel are involved in performing work not related to direct job responsibilities;
- during mass events;
- when eliminating the consequences of an emergency;
- when performing work that requires a permit.
Who's passing?
All employees who in one way or another were involved in the performance of the relevant work for which targeted training is provided are required to undergo targeted training.
If the employee will continue to perform day-to-day job duties, targeted training is not required.
Who is freed?
The employee may refuse targeted instruction.
However, this possibility does not apply to situations where targeted training is carried out due to the elimination of the consequences of natural disasters and other emergency situations.
How is targeted training on labor protection carried out?
Let's consider the procedure, list of questions, documentation and frequency of execution.
Order of conduct
There is the following procedure for conducting targeted briefing:
- the manager issues an order to assign occupational safety responsibilities to a certain person;
- a person authorized to carry out targeted instruction, if circumstances arise that require it, implements a set of measures to carry it out;
- the results of the briefing are reflected in the relevant documentation;
- Persons who have shown unsatisfactory results cannot be allowed to perform work - instruction for such persons is carried out again.
The head of the organization decides to clean the surrounding areas of debris, leaves and grass in the spring.
At the same time, it issues appropriate instructions for conducting targeted training, which contain provisions on preparatory activities, the procedure for workers during cleaning, rules for working with equipment and tools, as well as safety rules when completing work.
Program and list of questions (sample 2017)
Here is an approximate list of questions for targeted instruction:
| Safety requirements before starting work | Safety requirements during work | Safety requirements after work |
| Basic requirements for uniforms (clothing, shoes) | Safe practices and methods of work | The procedure for suspending work, turning off the main components of mechanisms and assemblies |
| Equipment necessary for carrying out work, appropriate rules for handling equipment | Actions of an employee during an emergency situation | Preparing the workplace for completion of work |
| Procedure for starting work, rules for handling materials and equipment | Scheme for safe movement around the territory during unscheduled work | Removal of uniforms and final procedures |
| Operating principles of equipment, machine components and assemblies | The procedure for group work, safety measures when carrying out collective work |
Who conducts it and when?
Targeted instruction on labor protection is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work (foreman, foreman, shop manager). In other words, the person responsible for conducting it becomes the employee authorized to conduct briefings at the appropriate locations.
Briefing is required to be carried out before the directly planned work, which requires mandatory training of employees.
Specific deadlines are not regulated by law - it is assumed that briefing should be carried out in advance - in order to identify the quality of the material learned by employees and, if necessary, conduct it again.
Documenting
The conduct must be recorded in certain types of documentation. We will consider which one further.
Where is it fixed?
The general procedure for recording the briefing involves reflecting the results in the following documentation:
- magazine;
- work permit (or equivalent documentation, for example, a work permit);
- personal cards (if available in the organization).
If the enterprise uses personal employee cards, they must reflect the fact of targeted instruction indicating:
- names of instructions that were used as part of the training;
- the result of the training by the relevant employee.
Order (sample)
Before conducting the briefing, the head of the organization must issue an order assigning labor protection responsibilities to a specific person.
After the order is issued, the person to whom the responsibilities were assigned, as well as the head of the organization, sign the document.
Form and filling of the journal (sample)
After the targeted briefing, it is necessary to correctly fill out a special log.
The document is stored either in the personnel department or in the labor protection service.
Before using the journal, you must:
- stitch;
- number;
- certify the journal with the signature of the manager or other employee authorized to do this.
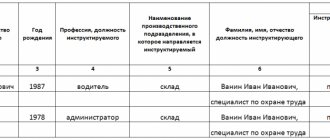
The journal form must contain empty columns, which are intended for entering data about persons who have undergone targeted training:
- Full name of the person being instructed;
- job title;
- Date of Birth;
- the name of the unit in which the instructee will work;
- date of the briefing;
- Full name and position of the instructor;
- signatures of the instructor and the instructed.
Responsibility for carrying out
The manager who sends the employee to work is responsible for targeted instruction. Responsibility can be administrative or criminal, it all depends on the severity of the incident.
For example:
- If the occupational safety inspector noticed that the employee was working at height and asked to present a work permit to perform the work. In this case, nothing happened, but the violation was noted. The inspector issues an order and brings the manager of the facility to administrative responsibility.
- The employee was carrying out instructions from management and was on a lighting support. Then he fell and fell down, after the fall he was injured: the radius bones in both arms were broken. During the investigation, it was established that the employee was not instructed and the work permit was not issued. This case is classified as a criminal offense.