A debt owed by a borrower to a lender that is not repaid within the prescribed period is called overdue debt. Return periods are established by the parties in the agreement. It is worth knowing which debt is considered overdue before signing the contract in order to control the timing of payments and fulfill your obligations.
Which receivables are considered overdue?
Accounts receivable is the amount of money that a company must receive from suppliers/customers/counterparties as payment for goods already transferred or services provided. This is a common occurrence when conducting active business activities, especially if the company has a trusting relationship with clients and is ready to provide services/sell goods, so to speak, on credit. The relationship between the parties may be as follows:
- the debtor gets the opportunity to use additional free working capital;
- the lender can expand its sales market by offering more favorable terms of cooperation.
In general, everyone benefits from cooperation, albeit in debt. But problems arise when debts become overdue. First, let's look at what an overdue debt is. debt and what its symptoms are.
What are accounts receivable?
Despite the fact that various institutions designed to simplify and make commercial activities safer are developing quite quickly, the basis of modern Russian economic reality and the world still occurs thanks to the relationships between specific people (they represent the same company).
A clear example of such a situation is the popular practice of having accounts payable and receivable between partners. It arises due to their commercial interaction.
If we talk about accounting, normal or overdue receivables are a certain amount of money that must be paid to a specific one from its own supplier, partner, client or other counterparty - as payment for goods or services already provided.
For example, a printing house is provided, which, at the request of their long-time partner (and this is advertising agency “B”), produced a print of the circulation of leaflets (in order to conduct a promotion). The volume was ten thousand copies. Advertising agency "B" has already received the entire printed edition - the courier picked it up from the printing house's office. At the same time, he has not yet carried out the financial funds (provided for as payment for the printed edition in accordance with the contractual terms between the agency and the printing house “A”).
It is worth considering that accounts receivable (as established Russian accounting practice says) have a variety of types of property rights. For example, the contractual terms concluded between printing house “A” and advertising indicate that the latter must transfer a certain number of paper packs, that is, make payment in kind.
Thus, the price of the said property to be transferred must be included in the accounts receivable. At the same time, the subjects of such debt, that is, persons with outstanding debt obligations to the specified enterprise, can be both citizens, that is, individuals, and companies, that is, legal entities.
Signs of overdue receivables
Debt is funds that were not transferred to the company for services/goods, but are listed on the balance sheet. Moreover, they can be considered a debt as a financial one. assets and property rights. But truly overdue deb. Only those debts that meet the criteria are considered debt. It is not difficult to guess what these signs are. If the debt is not repaid on time (before the date described in the agreement), it will be considered overdue. Typically, shares must be paid monthly, and if one of the shares was not paid within the designated time, such a debt may also be called overdue.
If the schedule or deadlines are violated, fines/penalties are assessed on the guilty party (fines are fixed amounts, although the delay may be a percentage). On some level, delays can bring additional income to the company. But if the statute of limitations expires, the receivable goes into the uncollectible section. To do this, it must meet the following criteria:
- the limitation period has expired;
- debt payment terms have expired;
- the debtor has been liquidated/declared bankrupt.
As a standard, enforcement proceedings are initiated regarding debt obligations. But this does not mean that it will allow you to return the money. Sometimes it happens that bailiffs stop proceedings because it is impossible to collect the debt. Thus, the debt becomes irrecoverable. Usually such a decision is made if it is not known where the debtor is or he does not have the money/property to return these funds.
Accounts receivable - classification and features
As explained earlier, overdue receivables are a debt incurred by an entrepreneur as a result of violation of the terms of contractual agreements by his counterparties. This type of debt is classified according to the following characteristics:
- type – urgent, overdue and bad debt;
- terms – short-term and long-term debt;
- form – commodity or monetary.
After how many months is the debt considered overdue?
Typically, debt is paid in monthly installments. That is why it is important to know how many months you can go without paying for the debt to be considered overdue. There are several nuances to this issue. A debt determined to be past due becomes so immediately after the payment is overdue. It is then that the statute of limitations of three years begins to count. During this time, you can file a claim for debt repayment. If the claim is not filed in court, it will become impossible to get the funds back, and the debt will be considered uncollectible.
If the debt arises during the classic operating cycle (negotiated separately or is usually a year) and is repaid no later than 12 months according to the balance sheet date, it is called current or short-term. If the period is longer, then such debt is considered long-term.
The manager or economist of the enterprise should plan the payment schedule for such debts. If the debtor violates the deadlines, the creditor uses a variety of preventive measures. They will reduce the risk of turning into a dubious debt. debt into bad debt. The accountant must include in the documents the overdue period and the balance of the debt.
About the timing of writing off overdue accounts payable
Overdue debt – how many months? This is not an idle question, since unpaid debts place a heavy burden on the shoulders of both parties to the contract. If we are talking about credit relationships, then this is the period when the first delay in payments occurred.
There is a statute of limitations for accounts payable to be written off - 3 years. The countdown begins from the moment when accounts payable are considered overdue.
The period may be interrupted if the debtor takes certain actions to acknowledge the debt:
- Acknowledges the lender's claim in writing and signs a reconciliation report confirming the absence of payments.
- Concludes a restructuring agreement.
- Partially pays debts.
- Partially admits the claims.
If one action from the list is present, then the statute of limitations is interrupted and the countdown begins anew.
Civil law provides not only for the interruption, but also for the suspension of the statute of limitations. It applies, for example, if the borrower is serving in the army, is sick, or is in prison. When the circumstances end, the countdown continues along the same trajectory.
Terms and methods of repayment of receivables
Financial stability The position of companies depends on the discipline of their clients and counterparties. If an overdue debt appears, which gradually develops into the bad debt stage, this is very bad for the company. To repay such debts, the creditor is given a period equal to the statute of limitations. If debtors have not repaid the debt within three years, they will be written off. The grounds are an inventory or an order from the manager.
But before the debt is written off, it is necessary:
- file a lawsuit to obtain a decision refusing to assign the amount of debt to the creditor;
- take all legal measures to ensure that the debtor repays the debt.
The last point is especially important since the overdue debt. debt causes quite severe damage to the creditor. Effective options for resolving the issue of writing off credit debt are:
- Debt obligations are being fulfilled. The debtor begins to fulfill his part of the obligations described in the agreement.
- Cash is paid. This is the most popular option for fulfilling obligations - the company pays the amount of money it owes in the amount that was agreed upon in the contract. True, such an outcome is possible if the company has enough money, which is not always possible.
- Innovation. This method involves changing the terms of a previously signed agreement so that debt repayment becomes more possible. If this is not done, the debtor may never be able to repay the debt. Or, instead of paying part of the debt, an alternative may be offered - performing some work, service, etc. To do this, the parties must enter into a new agreement, which stipulates the terms of the updated agreement.
- Compensation. This option is an ideal solution for companies that are going through hard times and therefore do not have free finance. Typically, compensation means the transfer of some property or real estate to the creditor. New owners can keep it all for themselves or resell it to receive financial compensation. Typically used when other debt recovery measures do not work.
- Write-off. The latest and least desirable measure, which is used when it is impossible to repay debt obligations. Then the money is simply written off as if it never existed. Debts are written off if the statute of limitations has expired, the parties cannot fulfill their obligations, or the company is liquidated.
An interesting point regarding the statute of limitations. Typically it is three years, but if the parties have contacted (in writing), the period begins to count again.
What debt is considered overdue in accounting?
What kind of debt is considered overdue? Any commercial transaction is accompanied by the conclusion of an agreement between the parties, which stipulates the terms of the transaction: deadlines for fulfilling agreements and penalties for failure to fulfill obligations. These types of transactions include:
Tax authorities agree that the debt for which the parties drew up reconciliation reports can be written off in accounting after three years from the date of the last reconciliation (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 6, 2010 N ShS-37-3/16955 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 04/17/2007 N 20-12/036354). The courts are of the same opinion (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Urals dated 02/01/2013 N F09-150/13 and dated 02/16/2010 N F09-6971/08-S2, West Siberian dated 08/11/2006 N F04-4912/2006(25117-A81 -14) districts).
Main types of overdue receivables
Accounts payable are the debts of a company. A company may owe money to suppliers, contractors, staff, tenants and others. If it is on the balance sheet, it can be used to increase working capital and avoid production downtime, for example, if at some point you do not have your own free money for a transaction. Credit and receivables are related, because if a credit debt is what you owe, then in the case of a receivable it is what is already owed to you. These are the funds that the company plans to earn from the customer.
Conventionally, this unit can be divided into normal and expired:
- a normal debtor is called a debtor whose payment period has not yet arrived, but an advance has been received (if this was provided for);
- Overdue is a receivable whose payment deadline has already arrived, but the agreed amount has not been transferred to the account.
But in the latter case, not everything is so sad, because overdue debt is conditionally divided into subtypes:
1. Doubtful. This is the name given to a debt that was not repaid on time and that is not secured by collateral, a bank guarantee or surety. It may still be returned.
2. Hopeless. Such a debt will most likely not be repaid. This debt has expired. Then any obligations between the parties cease. In addition, the debt cannot be collected if the company is liquidated.
So, the overdue debt may or may never be returned.
We identify and write off overdue debts in tax and accounting
Opinions were divided. The majority of visitors to the website www.rnk.ru (66%) believe that the debt can be written off. After all, the expiration of the limitation period is a sufficient basis for this (clause 2, clause 2, article 265 and clause 2, article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, the Tax Code does not contain a prohibition on including overdue receivables in expenses if there are other contractual relations with the counterparty. But there are also opponents to this approach. Read more about the arguments in favor of each point of view on the website e.rnk.ru in the article “Is it possible to write off the expired debt of a counterparty in tax accounting if there are other contractual relations with it?” // RNA, 2013, N 24.
Tax authorities agree that the debt for which the parties drew up reconciliation reports can be written off in accounting after three years from the date of the last reconciliation (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 6, 2010 N ShS-37-3/16955 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 04/17/2007 N 20-12/036354). The courts are of the same opinion (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Urals dated 02/01/2013 N F09-150/13 and dated 02/16/2010 N F09-6971/08-S2, West Siberian dated 08/11/2006 N F04-4912/2006(25117-A81 -14) districts).
Reflection of overdue debt in accounting
Overdue debt debt is reflected in the accounting documentation. This component is reflected in the current assets section and line with code 1230. At the same time, the accounting department carries out several operations to account for debts that were overdue:
- inventory;
- implementation of the reserve for such debts;
- write-off
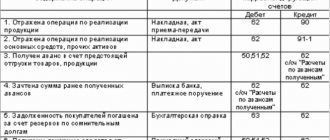
In accounting, debts are reflected as the sum of debits. balances from different accounts. For example:
- 60 – prepayment amounts for upcoming delivery;
- 62 – payment for goods/services/work that were provided but not yet paid.
Many other accounts could be included in this list (68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76).
Accounting involves the inclusion of debits. debt in working capital book. balance sheet, where, in addition to it, planned expenses for the future, inventories and many nuances should be included. For example, when a debtor must be repaid (usually this point is clearly stated in the contract).
How is an overdue but not bad debt reflected in accounting and reporting?
Overdue debt recognized as doubtful is also not reflected in the balance sheet - in accounting, outstanding and unsecured debt is subject to mandatory reservation.
The created reserve reduces the accounts receivable reflected in the accounting - in the balance sheet, the amount of accounts receivable on line 1230 should be reflected minus such reserved amounts.
To assess a debtor's debt as doubtful (for the purpose of creating a reserve), you must:
- develop and consolidate in the accounting policy criteria for classifying debts as doubtful;
- assess the probability of debt repayment on a regular basis (at each reporting date);
- when the likelihood of debt repayment increases, review doubtful debt according to the criteria and adjust the amount of the reserve.
The amount of the reserve is determined (clause 70 of the Regulations on accounting and reporting, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n):
- separately for each doubtful debt;
- taking into account the solvency of the debtor;
- based on an assessment of the likelihood of debt repayment.
Deductions to the reserve are other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n).
The article “Other expenses in accounting are…” will tell you more about other expenses.
Read on to learn about overdue accounts receivable, which need to be cleared from accounting and reporting, as well as what accounting nuances need to be taken care of.
How to count and write off debts
In accounting debit. the debt must not only be displayed, but correctly calculated, and if the need arises, written off. Write-off occurs if measures to collect them have not yielded results. Unfortunately, such cases happen much more often than we would like, so you need to study the procedure in more detail.
We have already discussed the grounds for write-off. It can be:
- inventory data;
- written evidence of the impossibility of debt collection;
- written instructions from the head of the company.
Having received one of these grounds, the procedure for generating a package of documents for write-off begins. This process is regulated by the Accounting Regulations:
- First, the amount of debt is calculated. To do this as accurately as possible, a thorough inventory is carried out.
- A document is drawn up - Inventory report (form NoINV-17).
- The existence of debts is confirmed. It describes who is owed and how much, repayment terms and overdue periods.
- A book is being compiled. a certificate indicating the details of the debtors, the amount of obligations, primary documents, grounds, date of formation of the debt and documents confirming that measures were taken against the debtor to repay the debt.
- A write-off order is issued. This must be done by the head of the enterprise. The order describes various factors - how much is written off, who is responsible for this transaction, etc.
If you need to work with doubtful debts, you need to take into account the features of this process. These debts are written off as non-operating expenses. In case of liquidation of the company, you need to take a certificate from the Unified Register about the disposal of the company. Then the tax office will not be able to challenge it.
When a debt is considered overdue in accounting
To write off a receivable in tax accounting, you must first recognize it as uncollectible. 1. You need to deal with the debt itself. If an enterprise has ceased its activities, an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities can serve as documentary evidence of the liquidation of the debtor organization. The procedure for obtaining this extract is established by Art. 6 of Law No. 129-FZ (see Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 15, 2007 No. 03-03-06/1/98). 2. It is also necessary to consider the procedure for accounting for VAT amounts on written off receivables (i.e., how to deal with the amount of VAT paid to the budget on goods (works, services) sold, in the event of recognition of receivables for these goods (works, services) ) hopeless) . The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not give an unambiguous answer to this question. In this situation, the Russian Ministry of Finance recommends that taxpayers write off the entire amount of accounts receivable as expenses, including VAT (Letter dated October 7, 2004 N 03-03-01-04/1/68). In accounting, the write-off of receivables in this case is reflected by the following entries: - Debit 91-2 Credit 62 (60, 76) - the amount of receivables is written off (including VAT); — Debit 007 — the amount of written off receivables is taken into account on the balance sheet.
Reporting: tax, accounting First of all, before drawing up the annual report, you should conduct an inventory of the company's property. As a result, a shortage or surplus of fixed assets, financial investments and other assets may be detected. The results of the inventory must be taken into account when drawing up the annual balance sheet (we wrote more about the inventory procedure in the article “How to count property”, PB No. 12, 2005, p. 29). Let us dwell on the issues of reflecting inventory results in accounting. We count property... If the inventory results in property, it must be capitalized at market value. To do this, you need to make an entry to the debit of the accounts of material assets (01 “Fixed Assets”, 04 “Intangible Assets”, 10 “Materials”, 41 “Goods”, 50 “Cash” and others) and the credit of account 91-1 “Other income” . In accounting, surpluses are classified as non-operating income (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 28 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting, paragraph 8 of PBU 9/99). The same is done in tax accounting (clause 20, article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The shortage of property is shown by an entry in the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” and the credit of accounts in which the company accounts for material assets. . and debts As a result of the inventory, overdue debts may also be identified. The Tax Code defines it as a debt for which the statute of limitations has expired (clause 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The latter, in turn, is three years (Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). After three years, the bad debt can be written off from the company's balance sheet. If they owe you, reflect this amount in other expenses in your accounting. If your organization owes - in other income. In tax accounting, written off accounts payable will be non-operating income (Clause 18, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Receivable, accordingly, non-operating expense (subclause 2, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the company did not create a reserve for doubtful debts, the overdue “receivable” must be written off as a debit to account 91-2 “Other expenses”. If it was created, debit account 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts”. Companies that used the cash method of accounting for VAT should be especially careful. Please note that any bad debts for which the statute of limitations has expired can be expensed. It does not matter whether the creditor tried to claim these amounts (resolution of the Federal Arbitration Court of the West Siberian District dated October 10, 2005 in case No. F04-7029/2005 (15574-A70-33)). Writing off a receivable at a loss does not mean that it is cancelled. It should be kept in off-balance sheet account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss” for five years. Accounts payable with an expired statute of limitations, together with VAT, are taken into account in the credit of account 91-1 “Other income” as non-operating income (clause 8 of PBU 9/99). The amount of VAT that should have been transferred to the creditor should be taken into account as a debit to account 91-2 “Other expenses”. In order to write off overdue receivables or payables, it is necessary to draw up an inventory report of settlements with counterparties and justify the need for write-off in any form. In addition, the manager must issue an appropriate order. These are the requirements of paragraphs 77 and 78 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). There is also no established form for the latter document. For example, an order may look like this: “Let’s clean up” the accounting. Of course, the shortcomings identified as a result of the inventory are only the “tip of the iceberg” of possible problems. After reviewing the accounts for the entire year, the accountant will definitely find at least one or two more blots. How to correct errors in taxes
More to read: Responsibility for Using Natsvay Drug Or Not
Effective methods of collection
Unfortunately, the relationship of trust between the parties to a transaction, where the service is provided and the money must be paid later, is not always justified. There are times when you need to return your funds almost with a fight. That is why we will consider several effective measures for debt repayment:
- Negotiable. In this case, you can communicate with the counterparty. The seriousness of intentions will be evidenced by penalties, interest, penalties and other penalties for each overdue day. As a rule, the risk of a significant increase in debt forces counterparties to rush to make payments.
- Pre-trial negotiations. The purpose of this method is to find a constructive solution to resolve the situation. For example, if the financial condition of the debtor is not in the best shape, installment/deferred payment measures or changes in the terms of their payments may be proposed. But making concessions to the debtor is usually beneficial only if he is a regular client and can be trusted.
- Trial. This is the most popular and effective method of returning money. Its disadvantage is the time that needs to be spent to achieve the desired result. In addition, paying legal fees is often not cheap. But if the decision is in favor of the plaintiff, the debt is almost guaranteed to be collected.
- Criminal procedure. A good example when you can use this method is if the supplier refuses to ship an item for which you have already paid. You can contact the criminal authorities even if bankruptcy proceedings begin. This behavior is clearly suspicious and indicates fraud.
In any case, if it is possible to collect the debt, you need to do it. It doesn't matter whether it's a large amount or not.
Share of accounts receivable: an important indicator of enterprise liquidity
This indicator, being the main one in the analysis, makes it possible to control the impact of funds diverted from turnover on the production process and the amount of liquid assets. An increase in its value is characterized by a deterioration in the financial position of the enterprise.
Before analyzing the status of accounts receivable, their share is calculated and special attention is paid to this. The indicator is calculated using the formulas:
- Share of receivables in the assets of the enterprise = (Responsible assets / assets) x 100
- in the value of current assets = (DZ / current assets) x 100
- coefficient DZ = DZ/revenue (informs how much product that has not yet been paid for per ruble of sales)
- repayment period of debt = (liability x duration of the period)/revenue from sales (using this indicator, the period during which the debt will be repaid is assessed)
When analyzing receivables, special attention should be paid to the above indicator. The trend towards an increase in the share of overdue debt indicates a decrease in the liquidity of the enterprise.
Repayment of accounts receivable: an indicator of effective customer relations
Return of receivables
Debt repayment is carried out in the manner prescribed by the terms of the contract.
When assessing the financial stability of an enterprise, they use the indicator “term of repayment of receivables”.
This is the time period during which the company hopes to receive money for its products, and at the same time it is an indicator of an effective relationship with the client.
To successfully manage debt maturities, you need an effective debt management strategy.
Its main elements are: a group of buyers and identifying among them those with whom the company is ready to work without prepayment, sanctions for late repayment of obligations, and working with debtors in the event of arrears.
The debt repayment period is determined as follows:
- Repayment time of the loan = (360*Average annual amount of the loan) / Sales proceeds
- Average annual volume of debt = Amount of debt at the end of the day / Number of working days
Repayment of accounts receivable - payments from legal entities or individuals as a result of relationships with the enterprise. The main thing to remember is that a large amount of receivables is formed at those enterprises where control over its repayment is absent or ineffective.
What is overdue debt?
Any debt not paid within the terms established by contract or law is considered overdue. At the moment of delay, the debt begins to be supplemented with penalties, accrued penalties and interest.
The causes of overdue debt can be both external and internal.
Enterprises create special reserves aimed at paying off losses from doubtful debts. The financial well-being of the company depends on the timely collection of debt.
Features of accounts payable overdue
A debt arising as a result of a company’s failure to pay for the cost of services or goods provided by a counterparty is called a debt. In other words, this is the internal debt of the organization, which it must pay to its creditors.
Loan debt restructuring. What to do if collectors threaten you - details here?
How to write a bankruptcy petition - .
The obligation has certain deadlines for its fulfillment. If this period established by the agreement between the company and the counterparty was missed, the debt will be considered overdue.
Failure to fulfill obligations in a timely manner leads to additional financial losses for the organization - the accrual of fines, interest or penalties.
The amount of overdue accounts payable must be written off or repaid. The organization's creditors have the right to first notify the debtor in writing of the need to repay the debt or go to court to force the defaulter to fulfill the obligation.
If necessary, the debtor company can agree with the lender to provide a deferment or installment plan. In this case, the parties enter into an appropriate agreement.
To write off overdue accounts payable, there must be documentary evidence that the debt is hopeless (that is, the inability to pay bills).
In accordance with accounting standards, bad debts are written off separately for each obligation. In addition, information about overdue debts is displayed in the accounting documentation.