Each enterprise keeps records of its economic activities. According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, all transactions performed by the company are reflected using the Chart of Accounts. With its help, you can easily display every fact of the actions performed by the enterprise, grouping them by name and number. Among others, the chart of accounts contains 44 accounts.
What to consider on account 44 “Sales expenses”
44 accounting account is an active synthetic account on which, in particular, the following expenses can be reflected (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
| Kind of activity | What expenses are taken into account? |
| Industrial and other production activities | — packaging and packaging of products in finished product warehouses; — delivery of products to points of departure, loading into wagons, ships, cars and other vehicles; — maintenance of premises for storing products at points of sale; — advertising; — commission fees paid to sales and other intermediary organizations; — entertainment expenses |
| Trading activities | — transportation of goods; - salary; — rent; — maintenance of buildings, structures, premises and equipment; — storage of goods; — advertising; — entertainment expenses |
| Procurement and processing of agricultural products | — general procurement expenses; — maintenance of procurement and receiving points; — keeping livestock and poultry at bases and reception points |
The above list of expenses is not exhaustive. Depending on the specifics of the activities of a particular organization and the composition of its expenses, other expenses may be taken into account in account 44 in the manner prescribed by the Accounting Policy for accounting purposes.
Considering the variety of expenses that can be reflected in account 44, the accounting entries for the debit of this account can also be very different (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Debit of account 44 – Credit of accounts 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”, 10 “Materials”, 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”, 69 “Settlements for social insurance and security”, 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”, etc.
Analytical accounting on account 44 is organized by types and items of expenses.
Manufacturing plants
The main expenses of industrial, agricultural and other production organizations on account 44 are expenses for:
- Packaging and stocking of products in finished goods warehouses.
- Delivery of goods to the point of departure, loading into wagons, cars, water and other vehicles.
- Payment of commission fees in favor of sales and other intermediary enterprises.
- Maintenance of premises used for storing goods in places of their direct sale.
- Salespersons' salaries.
- Advertising campaigns.
- Representation and other services.
Closing account 44
The debit balance accumulated on account 44 for the month can be written off at the end of the month to the sales account, either in full or in part, depending on the choice of the organization, enshrined in the Accounting Policy for accounting purposes:
Debit account 90 “Sales” - Credit account 44
If the organization chooses to partially write off the balance of account 44, then the following expenses are subject to distribution:
| In which organizations | Allocable expenses | Distribution order |
| Industrial and other manufacturing enterprises | Packaging and transportation costs | Between individual types of products shipped monthly based on their weight, volume, production cost or other relevant indicators |
| Trade and intermediary organizations | Transportation costs | Between the goods sold and the remaining goods at the end of each month |
| Organizations procuring and processing agricultural products | Expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials, livestock and poultry | Installed by the organization itself |
Transportation costs refer to the costs of delivering goods or products to the organization's warehouse and other storage locations, and not of delivering them to customers. The undistributed amounts will form the debit balance of account 44 at the end of the month.
In organizations that procure and process agricultural products, when allocating sales expenses, account 44 is still reset to zero, since the amount not debited to account 90 is written off as follows:
- expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials: Debit of account 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” - Credit of account 44;
- expenses for the procurement of livestock and poultry: Debit account 11 “Animals for growing and fattening” - Credit account 44.
>How to work with account 44 chart of accounts
What is taken into account in account 44
Account 44 takes into account selling expenses and they depend on the type of activity of the company. For enterprises engaged in industrial activities, trade, construction or processing of agricultural products, they are different, but they will all be included in the 44th accounting account.
The main operations related to sales costs for industrial enterprises are:
- product packaging that can be used in a product warehouse;
- delivery of goods to the place of departure, loading into cars, wagons and other vehicles;
- maintenance of warehouse facilities used for storing finished products;
- commission fees paid to intermediary organizations;
- advertising;
- entertainment expenses;
- the rest, similar in purpose.
In companies engaged in trading activities, the following costs are possible:
- transportation of goods to the place of sale or delivery to the buyer;
- rental of retail premises;
- remuneration of sellers;
- storage of goods;
- maintenance of premises and equipment;
- advertising;
- entertainment expenses;
- the rest with a similar purpose.
Product storage
For enterprises engaged in the procurement and processing of agricultural products, which include milk, livestock, poultry, wool, grains, legumes, etc., account 44 may include these operations:
- procurement of products;
- rental and maintenance of premises in up-to-date condition;
- care and fattening of livestock and poultry;
- other costs.
Construction companies have the following cost items:
- maintenance of the procurement apparatus, warehouses with materials, storerooms at construction sites;
- protection of materials;
- fees for notifying the arrival of materials;
- the rest, similar in purpose.
Important! All expenses are regulated. Established and regulated by laws and regulations.
"Sale expenses"
All costs associated with the sale of goods, performance of work and provision of services are reflected in accounting through “Sale expenses” - account 44 according to the accounting plan approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n dated October 31, 2000.
Thus, accounting account 44 (for dummies) can be defined as a position in the plan, which is intended to record the enterprise’s operational data on costs arising in the process of selling goods, works, services (GWS).
In order to understand “Sales Expenses” which account is active or passive, you need to consider what is reflected in its debits and credits. Receipts of expenses are recorded as debit, and disposals are recorded as credit. This means that the count. 44 - active. It is also synthetic and analytical. Subaccounts to account 44 are opened depending on the specifics of the activity and industry of the organization, which must be fixed in the accounting policy. Analytics is carried out by types and cost items, which also depend on the type of activity of the enterprise.
What is taken into account in account 44 for institutions directly related to industry and the production process? For non-trading enterprises, the following types of costs are distinguished:
- packaging of manufactured products;
- loading, transportation and delivery costs;
- maintenance of premises intended for storing goods until sale;
- fees and commission payments;
- advertising and entertainment costs.
For organizations that engage in trade, such costs may include:
- employees' wages;
- rent;
- transportation of products;
- maintenance and storage of products;
- representation and advertising costs.
Application of count 44 in production
Account “Sales expenses” reflects information on the following types of costs at manufacturing enterprises:
- Container and packaging of products in a finished goods warehouse.
- Transport services for the delivery of goods.
- Sales intermediary fees.
- Advertising costs.
- Storage, sorting and other costs of selling goods.
It is assumed that all costs directly related to the process of selling products are accounted for on account 44. The remaining costs for the production process are reflected in the accounts of Section III of the standard chart of accounts.
Account 44 in the accounting of a manufacturing enterprise
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of a business transaction |
| 44 | 10 | The amount of materials consumed for packaging finished products is taken into account |
| 44 | 23 | The amount of expenses of auxiliary production for the manufacture of containers was written off |
| 44 | 60 | An invoice for intermediary transport services has been accepted for payment. |
| 44 | 70 | The amount of payment for labor of product packers in the warehouse has been credited |
| 44 | 69 | Mandatory payments to the budget from wages of packers are listed |
| 90 | 44 | A write-off (partial or complete) of commercial costs for the process of selling products was made. |
How to close a 44 account
Closing the account 44 is produced every month. Where account 44 is written off is illustrated by the following accounting entry:
Dt 90.7 Kt 44.
Each organization must establish in its accounting policy the methodology for accounting and writing off costs for the implementation of GWS.
Many experts have a question about why account 44 is not closed. This may be due to the fact that as of the reporting date, incomplete sales of goods were recorded, that is, the amount is partially closed due to the presence of remaining products in the warehouse.
In such situations, in order to write off, it is necessary to distribute transport costs in direct proportion to the volume of products sold. Balance - the value that is the balance of the goods will not be closed, but will be transferred to the beginning of the next reporting period (month).
For those institutions that carry out the production process, transportation and packaging costs are distributed according to the types of products shipped.
If account 44 is not closed during the balance sheet reformation (Dt 44.01 Kt 84.01), then, most likely, the methods for determining direct expenses are not filled out in the accounting system. Balances formed on the account. 44, for the most part relate to direct transport costs and are not reset to zero during the reformation.
How to close account 44
The algorithm for closing account 44 at the end of the month is quite simple. Closing is carried out manually or using routine operations. The debit reflects the amount of expenses incurred by the enterprise during the month related to the sale of products, provision of services and performance of work. At the end of the reporting period, the amounts are partially or fully, depending on the accounting policy of the enterprise, written off to the debit of account 90 “Sales”. In case of partial write-off, the following are subject to distribution:
- In trading and intermediary companies, transport costs are distributed among product and warehouse balances. Commodity items are taken based on the total sales volume for the reporting month, warehouse items at the end of the period.
- In industry and production, transport costs and packaging costs are distributed between product groups of sold products by weight, cost, volume and other factors.
- In companies engaged in agriculture, procurement costs are distributed based on the type of activity in the debit of account 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” or “Animals for growing and fattening”.
Note! All other commercial expenses related to the sale of products are written off at the close of the reporting period to the cost of goods, services or work sold.
Specifics of reflecting costs
To begin with, it should be noted that this category refers to funds allocated to establish communication between the manufacturer and the consumer. This item of costs in its content is classified as current costs. The allocation of these resources takes place annually, and their advances also occur annually.
If the head of the organization manages to increase the efficiency of these costs, then this will give him the opportunity to receive greater profits and direct it to improve the material and technical base, which will lead to an increase in the quality of goods sold and, accordingly, an increase in profits in the future.
If you try to classify the designated category of costs, you can do it as follows:
By economic content:
- material costs;
- funds allocated for remuneration of personnel;
- accrual of depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets;
- other costs.
By industry sector:
- costs of selling retail products;
- funds allocated to ensure sales of wholesale products;
- costs of selling agricultural products.
Taking into account such a criterion as the quality of trading service, it is necessary to highlight:
- related to improving the quality of trade service;
- unrelated to him.
The role of 44 accounts in accounting
Position 44 in the Chart of Accounts is active and is designed to reflect information about the costs incurred by the organization in the sale of goods or services.
Thus, existing expenses are accumulated on the debit side of the account, and their disposal is accumulated on the credit side.
In enterprises engaged in commercial activities, this account records expenses such as:
- expenses for transporting goods;
- for payment;
- rental payments;
- funds allocated for the maintenance of retail premises and equipment;
- for an advertising company;
- entertainment expenses.
This account may well be actively used by non-trading organizations. In this case, the following cost items are reflected in it:
- funds allocated for loading and delivery of products;
- resources allocated for maintaining goods in warehouses;
- costs associated with product packaging;
- for an advertising company;
- commission fees and deductions.
Analytics for this account is carried out for each type and item of expenses.
>Existing sub-accounts
In this case, organizations use such subaccounts as:
- 01 – distribution costs;
- 02 – commercial costs in production.
Account 44 in accounting
This is an active account, that is, the receipt of expenses is reflected in the Dt of the account, the disposal - in the Kt. An account can be simultaneously classified as an expense account if the expenses on the account are direct, and collective and distribution expenses if they are indirect.
What is included in selling costs?
In trade organizations, account 44 reflects the following expenses:
- for the transportation of goods;
- for payment;
- for renting premises;
- for the maintenance of retail equipment and retail premises;
- for advertising;
- for entertainment expenses, etc.
The Selling Expenses account can also be used by non-trading organizations. In this case, the following expenses are reflected on the account:
- for loading and delivery of products;
- by contents in warehouses;
- on packaging and packaging;
- for advertising;
- on commissions (fees), etc.
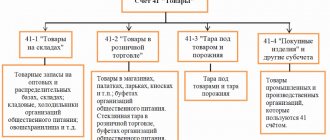
In the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance, account 44 refers to section 4 “Finished products and goods”. The synthetic account of sales expenses includes two subaccounts: 44.1 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” and 44.2 “Business expenses in organizations engaged in production and other industrial activities.”
The organization uses one of these subaccounts: 44.01 - in trading, 44.02 - in production. If it is necessary to clarify the analytics, subaccounts are created for them.
Scheme of movements on count 44:
Typical postings for account 44
As can be seen from the previous diagram, account 44 corresponds on the credit side with material, cost and settlement accounts with counterparties and “accountables”, and on the debit side - with the expense account.
The main transactions are shown in the table:
In organizations engaged exclusively in trading activities, all management costs can be classified as selling expenses. The general expenses account will be used only if another type of activity arises.
Closing 44 accounts
At the end of the period, account 44 is closed to account 90, sales expenses subaccount:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 90.7 | 44 | Closing an account |
The account is closed monthly. In conditions of incomplete sales (for trade organizations), account closure may be partial. Then transportation costs for write-off are distributed in proportion to the volume of goods sold. The amount corresponding to the balance of unsold products is not closed, but transferred to the next period.
For manufacturing enterprises, the distribution of packaging and transportation costs is made by type of product shipped.
The methodology for accounting and writing off costs is chosen by the organization independently and is prescribed in the accounting policy.
Accounting for goods and materials on account 44
The occurrence of transport and procurement costs for the buyer is due to the fact that upon delivery the counterparty allocates transport costs separately. The purchasing organization, depending on the accounting methodology used, can include the amounts of TRP in the cost of the goods, or allocate them.
Expenses for the delivery of goods by third-party organizations are allocated to account 44, if the accounting policy does not provide for their inclusion in the cost of goods, that is, capitalization to account 41 “Goods”.
General theory of accounting in Ukraine
Selling expenses are reflected in the account. 93. The debit of the article accumulates the amounts of recognized costs for the sale of services, products, and work. The write-off is carried out on credit 79 of the “Financial results” account.
Sales costs include the costs of:
- Packaging materials.
- Transportation of products based on contracts.
- Advertising and marketing.
- Salaries and commissions for sellers, sales department employees, and sales agents.
- Depreciation.
- Maintenance and repair of fixed assets and other non-current material assets intended to ensure sales.
By debit 93, the account corresponds with the following items:
- “Depreciation (wear and tear) of non-current assets.”
- "Productive reserves".
- “Wearing and low-value objects.”
- "Semi-finished products."
- "Production".
- "Agricultural products."
- "Cash".
- "Goods".
- "Bank accounts."
- "Settlements with customers and buyers."
This list is not exhaustive. In the Ukrainian accounting system there are quite a lot of accounts corresponding to the account. 93.
Example of using account 44 “Sales expenses”
Antik LLC, engaged in trading, reflected the following transactions for October 2020:
- wages - 209,000 rubles;
- insurance premiums - 62,700 rubles;
- expenses for stationery - 11,000 rubles;
- depreciation of fixed assets - 19,000 rubles;
- services of third-party organizations - 38,000 rubles;
- costs for transporting products - 42,000 rubles;
- sales revenue - RUB 849,600, incl. VAT RUB 129,600;
- cost of goods sold - 415,000 rubles;
- balance of goods in the warehouse - 113,000 rubles.
These transactions will be reflected by postings:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 44 | 70 | Reflection of labor costs | 209 000 | Accounting information |
| 44 | 69 | Insurance premiums reflected | 62 700 | Accounting information |
| 44 | 10 | Reflection of expenses for stationery | 11 000 | Accounting certificate, invoice |
| 44 | 02 | Depreciation calculation | 19 000 | Accounting information |
| 44 | 60 (76) | Cost of third party delivery services | 38 000 | Invoice, act |
| 62 | 90.1 | Reflection of revenue | 849 600 | SF, acts, invoices |
| 90.2 | 41 | Reflection of cost write-off | 415 000 | Invoices |
| 90.3 | 68 | Reflection of accrued VAT | 129 600 | Sales book |
| 44 | 60(76) | Transportation costs reflected | 42 000 | Invoice, act |
Let's do the calculations:
- The balance of goods in the warehouse amounted to 113,000 rubles.
- The total amount of goods sold and unsold was 113,000 + 415,000 = 528,000 rubles.
- Let's calculate the share of goods sold: 415,000 / 528,000 * 100 = 78%.
- Amount of expenses on invoice 44 for October: 209,000 + 62,700 + 11,000 + 19,000 + 38,000 = 339,700 rubles.
- Therefore, the amount of write-off of transportation costs to account 90 will be: 42,000 * 78% = 32,760 rubles.
The closure of account 44 will be reflected using the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 90.7 | 44 | Sales expenses written off | 339 700 | Accounting information |
| 90.7 | 44 | Transportation costs are written off in proportion to sales | 32 760 | Accounting information |
Amount 9,240 rub. (42,000 - 32,760) will remain not written off and will be transferred to the next period.
Account 44 is closed at cost:
- upon sale, written off to 90.02;
- costs during the sales process are written off on 90.07;
- trade organizations can conduct all expenses at 44;
- in 1C, closing is automated.
According to basic accounting principles, transactions should reach their logical conclusion at the end of the month. That is, the turnover on accounts necessary for the formation of cost and calculation of taxes must be minimized.
Postings to account 44
Account 44 corresponds with accounts 76, 70, 60, 10, 05 and 02. From the designated accounts, only those amounts that are related to the sale of products are collected. Operations are carried out on the debit side of account 44.
Correspondence on the loan is carried out with accounts 99 and 90. Here the accountant will be required to completely or partially close these accounts.
Account 44 “Sales Expenses” should be closed at the end of each month. If the product was fully sold in a given reporting period and all costs were included in its cost, then when closing the transaction has the following form:
Debit 90.07 - Credit 44.
But what if some of the goods remain? In this case, it becomes necessary to reflect the balance and the accountant applies the proportional write-off method. For example, if the unsold balance amounted to 30% of the total quantity of goods, then at the end of the month only 70% of the costs are written off. The remaining amount is transferred to the next period and written off according to a similar principle.
Account 44 in accounting is called “Sales expenses”. It combines the expenses incurred by the seller in the course of selling products. For a full description of accounting for operating expenses with subaccounts, postings and an example, see below.
How does expense accounting work?
Of course, this does not apply to all accounts, but only to cost ones, including 44 “Sales expenses”. This account belongs to the active ones, so its balance is exclusively debit.
The costs that accumulate on it must interact directly with sales of goods (products, work). It is customary to divide it into additional subaccounts. The use will depend on the activity in which the company is engaged:
- 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities”;
- 44.02 “Business expenses in organizations engaged in industrial and other production activities”;
- 44.3 “Expenses in organizations engaged in procurement and processing of agricultural products.”
So, from the given names it is clear which ones are suitable for trade, agriculture and all other companies.
Important point! 44 is a cost account subject to direct expenses. If costs can be classified as indirect, then they will be collectively distributed.
When a trading company, all expenses, including management, will be collected on account 44:
- Transportation and payment of goods.
- Rental and maintenance of premises and equipment.
- Advertising and entertainment expenses.
- Employee earnings and tax deductions.
- Depreciation of fixed assets.
When account 44 is used in manufacturing enterprises selling their products, or in companies providing services, the costs are reflected:
- product packaging and packaging costs;
- loading and delivery of products;
- marketing and advertising costs;
- payments to intermediaries.
Accordingly, the postings will depend on the nature of the costs:
- Dt 44 Kt 10 “Material reserves” - when purchasing containers;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - transport costs are displayed;
- Dt 44 Kt 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages.”
When to use count 44
“Sales expenses” are used when there is a need to enter into accounting data on costs that arose in connection with the sale of products. This is an active account, where these expenses are grouped by debit and written off by credit.
For companies specializing specifically in sales, the following operations are reflected in this part of accounting:
- Salaries of employees engaged in sales and contributions thereon;
- Delivery of goods, transport services;
- Rental of premises;
- Purchase of packaging containers or other materials involved in sales;
- Advertising;
- Commission to intermediaries;
- Entertainment expenses;
- Depreciation and repair.
For companies whose activities are not exclusively related to trade:
- Transportation and shipment;
- Storage of finished products;
- Advertising;
- Commission;
- Packing of goods.
Trade and non-trade enterprises keep records on different synthetic accounts: 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” and 44.02 “Business expenses in organizations engaged in production and other industrial activities”
What is account 44.01 used for in accounting? This is precisely a synthetic account created for selling companies. Accordingly, non-trading firms collect their expenses on 44.02.
By 44.01 and 44.02, you can open subaccounts, in particular: 44.01.1 - amounts not included in the income tax base and 44.01.2 - amounts included in the income tax base.
Subtleties of write-off
Account 44 is closed every month by writing off to cost. For this, 90.02 “Cost of sales”, as well as 90.07 “Sales expenses” can be used.
From the author! The organization itself must select a subaccount to close and register it in the Accounting Policy.
Balances may remain on debit, but they must be closed at the end of the year. Transport costs in trading companies are included in the cost of warehouse balances and therefore may “hang” at the end of the period. Other enterprises distribute transport costs between items by weight and volume.
For example, the trade organization Constant Plus LLC sells drinking water. Revenue for the month was 2,000,000 rubles, including VAT 18% - 305,084.75 rubles. During the period there were expenses:
- Dt 44 Kt 10 - water containers were purchased for the amount of 60,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 - monthly depreciation was accrued in the amount of 47,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 70 - wages accrued to sellers and other employees of 400,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” - insurance contributions of 120,000 rubles were calculated from earnings;
- Dt 44 Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - 18,000 rubles issued against cash reporting;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 - transport costs for delivery of 90,000 rubles are reflected;
- Dt 44 Kt 76.07 “Rent payments” - arrears for store rent 150,000 rubles.
The company's total costs amounted to 885,000 rubles. The cost of goods sold is 1,400,000 rubles. At the same time, at the end of the month there was an unsold balance of water in the warehouse amounting to 56,000 rubles. To close 44, the accountant will have to deal with the distribution of transport costs (delivery, transportation). To do this you need to make a calculation:
- 1 400 000 / (1 400 000 + 56 000)*100 = 96%.
Thus, you can find out the amount of accepted transport costs per month:
- 90,000 * 96% = 86,400 rubles.
A table is compiled for clarity.
Table 1. Calculation for closing
| Transport costs total | Share of transport costs | Acceptable shipping costs | other expenses | 44 account to be written off |
| 90 000,00 | 96% | 86 400,00 | 829 000,00 | 881 400,00 |
The remaining amount of 3,600 rubles will be transferred to another period. Therefore, the accountant will close 44 in the amount of:
- 885,000 - 3,600 = 881,400 rubles;
- Dt 90.07 Kt 44 - sales costs in the amount of 881,400 rubles were written off.
Table 2. Analysis of account 44 for August 2020 Limited Liability Company "Constant Plus"
| Cor. Check | Debit | Credit | |
| Opening balance | |||
| 47.000,00 | |||
| 60.000,00 | |||
| 90.000,00 | |||
| 120.000,00 | |||
| 400.000,00 | |||
| 18.000,00 | |||
| 150.000,00 | |||
| 881.400,00 | |||
| Turnover | 885.000,00 | 881.400,00 | |
| Closing balance | 3.600,00 | ||
Output data: BU (accounting data)
What typical wiring includes Dt 44 and Kt 44
Dt 44 Kt 44 is most often contained in the following postings:
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – debt to the supplier for services rendered;
- Dt 44 Kt 10 – the cost of materials is taken into account in expenses;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 – depreciation;
- Dt 44 Kt 70 – wage costs;
- Dt 44 Kt 69 – expenses for contributions to extra-budgetary funds;
- Dt 44 Kt 71 – expenses for accountable persons;
- Dt 44 Kt 94 – expenses for shortages.
Kt 44 is used when writing off to account 90.
Let's look at a few examples using Dt 44 Kt 44 .
Example 1
An organization engaged in trading activities recorded in March:
- salaries for consultants and sales floor cashiers in the amount of 500,000 rubles;
- expenses for renting a sales area in the amount of 150,000 rubles;
- accrued depreciation on equipment in the hall - 200,000 rubles;
- advertising expenses – 450,000 rubles. (non-standardized for the purpose of calculating income tax).
For information on advertising expenses in tax accounting, see the publication “Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2015): questions and answers.”
In the accounting for March, these transactions were reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 44 Kt 70 – salary 500,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – rental services RUB 150,000;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – advertising expenses 450,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 – depreciation 200,000 rub.
On March 31, the posting was made: Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – RUB 1,300,000. (writing off account 44).
Example 2
The trading organization reflected in its accounting for April on account 44 transportation expenses in the amount of 300,000 rubles. wiring Dt 44 Kt 60.
The balance on the account as of March 31 is 44 - 75,000 rubles.
The cost of goods sold for March is RUB 1,780,000.
The cost of the remaining goods as of March 31 is 360,000 rubles.
It is necessary to distribute transport costs.
To do this, we determine the average percentage of transport costs attributable to the balance of the goods:
(300 000 + 75 000) : (1 780 000 + 360 000) × 100% = 17,52%
The amount of transportation costs for the remaining goods is 360,000 × 17.52% = 63,072 rubles.
The amount of transportation expenses to be written off in April is 300,000 + 75,000 – 63,072 = 311,928 rubles.
On April 30, an entry will be made: Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – RUB 311,928.
For information on tax accounting registers, see the material “Maintaining analytical tax accounting registers (forms).”
Automation of write-offs
Postings to close account 44 can be manual or automated. In 1C 8.2 and 8.3, you need to go to the “Accounting, Taxes and Reporting” menu, the “Period Closing” section and select the “Month Closing” submenu. Here you can see a number of regulatory operations arranged in a strict order of execution. “Closing account 44 “Distribution costs”” takes place immediately after cost accounts 20, 23, 25, 26.
1C contains a formula for calculating transport costs by shares. For correct calculation, you need to set up the Accounting Policy. If the accounting department will cover part of the costs with manual operations, it is necessary to ensure that all analytical characteristics are correctly filled out. Otherwise, the routine operation will be rejected.
The automated operation may not work if 44 is not used by the company for its intended purpose. For example, organizations that provide services can use it to account for the purchase of materials. However, they must carry out such transactions using 20 (26) accounts. Since the accounting policy is not configured for trading, the formation of “Closing account 44 “Costs of distribution”” will not work.
For a more detailed look at the formation of a regulatory operation, watch the video:
subscribe to blog updates via e-mail
Hello, dear readers of the blog-buh blog. In the last two articles (this one and this one), I began to look at the features of setting up the closure of cost accounts (20, 23, 25, 26) in the 1C Enterprise Accounting program, edition 3.0. In today’s article I will talk about another cost account - 44.01 “Costs of distribution in organizations engaged in trading activities”, and of course not only about the account itself, but also about the routine operation of closing the month “Closing account 44 “Costs of distribution””.
As part of the article, I will touch a little on the question: in what cases should account 44 be used in accounting, and we will also talk about the accounts on which the cost is reflected: 90.02 “Cost of sales” and 90.07 “Sales expenses”. Well, as per tradition, let’s consider a clear example on this topic.
Let me remind you that the site already has a number of articles that are devoted to the issue of closing a month in the 1C BUKH 3.0 program:
- Part 2: “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26” transactions: detailed analysis of “Closing the month” in 1C ACCOUNTING 3.0
- Part 1: “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26” transactions: detailed analysis of “Closing the month” in 1C ACCOUNTING 3.0;
- “Adjustment of item cost”;
- “Revaluation of foreign currency funds”;
- “Calculation of trade margin”;
- “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of OS for the simplified tax system”;
- “Write-off of additional expenses for the simplified tax system”;
- “Calculation of shares of write-off of indirect expenses”;
- “Calculation of transport tax”;
- “Calculation of land tax”;
- “Calculation of property tax”;
- “Write-off of deferred expenses”;
- “Repayment of the cost of workwear and special equipment”;
- Accounting for depreciation of fixed assets;
- Exclusion of work in progress from the composition of material costs for the simplified tax system;
- Methods of depreciation of fixed assets in 1C Accounting.
A little theory
First, let's talk a little about account 44.01 “Distribution costs”. Sometimes difficulty arises (mainly among novice accountants) in determining in which account to reflect the organization’s expenses on 44 or 20 accounts. In principle, if you open the chart of accounts in the 1C program and look at the full name of account 44, it will become clear in what cases account 44.01 is applied - “Costs of distribution in organizations engaged in trading activities.”
There is also an official document “Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n”, which describes in some detail the purposes for which this account is intended. I will give a short excerpt:
“Account 44 “Sales Expenses” is intended to summarize information on expenses associated with the sale of products, goods, works and services. In organizations engaged in trading activities, account 44 “Sales expenses” may reflect, in particular, the following expenses (distribution costs):
- for the transportation of goods;
- for wages;
- for rent;
- for the maintenance of buildings, structures, premises and equipment;
- for storage and processing of goods;
- for advertising;
- for entertainment expenses;
- other expenses similar in purpose.”
From this we can conclude that organizations that are engaged in trading activities should reflect their expenses on account 44.01, and not on account 20. By the way, in the same order you can familiarize yourself with the purpose of the 20th accounts and many others. Let me briefly note the fact that accounts 20, 23, 25 and 26 are used to reflect costs in production organizations, i.e. where there is production.
Reflection of expenses on account 44.01
Now let's look at a small example in which a trading organization (Do It Yourself LLC) buys a large batch of goods from a supplier (Supplier LLC) and sells part of this product to its client-buyer (IP Plotnik V.M.).
So, on March 15, 300 units were purchased from the supplier. goods for a total amount of 300,000 rubles.
The supplier delivered this product and delivery costs (RUB 20,000) were reflected in a separate document “Receipt of goods and services” on account 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities.” This expenditure also took place in the month of March.
| Next, part of the goods is sold. There is a sale of goods in the amount of 50,000 rubles. also in March. This fact is reflected in the document “Sales of goods and services. Please note that the cost of goods sold is reflected in account 90.02 “Cost of sales...”. This will be reflected in the cost of sales on the income statement. But additional expenses incurred, in this example these are delivery costs, will be debited from account 44 to account 90.07 “Sales expenses...”. |
These costs will be reported as business expenses on the income statement. We will see the postings on account 90.07 a little lower when we consider the issue of closing the month.
Account 44, what corresponds with: postings
Most of the entries relate to the debit of account 44. There he collects from different places the amounts spent on selling goods. In particular, he corresponds with 02, 05, 10, 60, 70, 76, etc.
With a loan, everything is much simpler, since in this case the accountant either completely or partially closes the mentioned account. He corresponds at this time with 90 and 99.
You will have to close “Sales Expenses” every month. This is done upon completion. When closing account 44, the posting will be as follows:
Dt90.07 Kt44.
This is in the classic version, when all expenses were included in the price of the product, due to its 100% sales.
But it also happens differently. When it was not possible to implement everything completely. Then you will have a balance at the beginning of the new month. But that's not all.
If the company incurred expenses for transporting its products, then these expenses are written off in proportion to their sales. For example, if you sold 80% of all goods, then you will write off only 80% of the payment for transport into the price. The rest at the beginning of the new month will be recorded in the debit of account 44
Example of accounting for account 44 for dummies
So that even dummies do not have any questions regarding the posting of account 44, we will give examples of reflecting various types of transactions on it.
Example 1. We take into account all kinds of transactions during the reporting month.
The trading organization Limma LLC performed the following actions for June 2020 (all amounts in rubles):
- Issued salaries to employees - 400,000;
- I deducted contributions from her - 120,000;
- Purchased packaging containers - 25,000;
- Rent of premises for sale – 52,000
- Calculated depreciation charges - 27,000;
- Payment to the cargo transporter – 60,000;
- Sale of goods in the amount of 2,400,000 (VAT 400,000)
- The cost of these goods is 1,500,000;
Limma's accounting department will make entries according to the actions taken.
| Wiring | Sum | |
| Dt44 Kt70 | 400 000 | Employee earnings |
| Dt44 Kt69 | 120 000 | Showed accrued contributions |
| Dt44 Kt10 | 25 000 | We reflected the purchased packaging containers in accounting |
| Dt44 Kt60 | 52 000 | Payment of rent |
| Dt44 Kt02 | 27 000 | Shows accrued depreciation |
| Dt44 Kt60 | 60 000 | Transportation of goods |
| Dt62 Kt90.1 | 2 400 000 | Accounted for income from sales |
| Dt90.3 Kt68 | 400 000 | VAT allocated |
| Dt90.2 Kt.41 | 1 500 000 | Made a posting to the cost of production |
Example 2. Closing an account at the end of the reporting month.
We take the data from the previous example:
- Selling expenses in total are equal to: (400,000 + 120,000 + 25,000 + 52,000 + 27,000 + 60,000) = 684,000;
Closing transactions
Account 44 “Sales expenses”
Account 44 “Sales expenses” is intended to summarize information on expenses associated with the sale of products, goods, works and services.
In organizations engaged in industrial and other production activities, account 44 “Sales expenses” may reflect, in particular, the following expenses: for packaging and packaging of products in finished product warehouses; for delivery of products to the departure station (pier), loading into wagons, ships, cars and other vehicles; commission fees (deductions) paid to sales and other intermediary organizations; on the maintenance of premises for storing products at places of sale and remuneration of sellers in organizations engaged in agricultural production; for advertising; for entertainment expenses; other expenses similar in purpose.
In organizations engaged in trading activities, account 44 “Sales expenses” may reflect, in particular, the following expenses (distribution costs): for the transportation of goods; for wages; for rent; for the maintenance of buildings, structures, premises and equipment; for storage and processing of goods; for advertising; for entertainment expenses; other expenses similar in purpose.
In organizations that procure and process agricultural products (beets, milk, wool, cotton, leather raw materials, flax, livestock, poultry, etc.), account 44 “Sales expenses” can reflect, in particular, the following expenses: other expenses ; general procurement expenses; for the maintenance of procurement and receiving points; for the maintenance of livestock and poultry at bases and reception points. (paragraph as amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 18, 2006 N 115n)
The debit of account 44 “Sales expenses” accumulates the amounts of expenses incurred by the organization related to the sale of products, goods, works and services. These amounts are written off in whole or in part to the debit of account 90 “Sales”. In case of partial write-off, the following are subject to distribution:
- in organizations engaged in industrial and other production activities - packaging and transportation costs (between individual types of shipped products on a monthly basis based on their weight, volume, production cost or other relevant indicators);
- in organizations engaged in trading and other intermediary activities - transportation costs (between the goods sold and the balance of goods at the end of each month);
- in organizations that procure and process agricultural products - to the debit of accounts 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” (expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials) and (or) 11 “Animals for growing and fattening” (expenses for the procurement of livestock and poultry).
All other expenses associated with the sale of products, goods, works, services are charged monthly to the cost of products sold (goods, works, services).
Analytical accounting for account 44 “Sales expenses” is carried out by types and items of expenses.
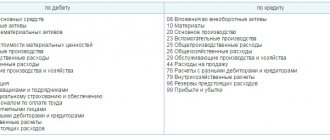
Account 44 “Sales expenses” corresponds with the accounts:
| by debit | on loan |
| 02 Depreciation of fixed assets 04 Intangible assets 05 Depreciation of intangible assets 10 Materials 16 Deviation in the cost of material assets 19 Value added tax on acquired assets 23 Ancillary production 29 Service production and facilities 41 Goods 42 Trade margin 43 Finished products 60 Settlements with suppliers and contractors 68 Calculations for taxes and fees 69 Calculations for social insurance and security 70 Settlements with personnel for wages 71 Settlements with accountable persons 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors 79 On-farm calculations 94 Shortages and losses from damage to valuables 96 Reserves for future expenses 97 Deferred expenses | 10 Materials 11 Animals for growing and fattening 15 Procurement and acquisition of material assets 45 Goods shipped 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors 79 On-farm settlements 90 Sales 94 Shortages and losses from damage to valuables 99 Profits and losses |