Start of accounting. Who should do the accounting?
Keep records and submit all reports to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat through Kontur.Accounting.
Get free access for 14 days
The obligation to maintain accounting records is dictated by Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”. It states that accounting must be maintained by all legal entities, commercial and non-profit organizations, and neither the form of ownership nor the taxation system removes this obligation.
Until 2013, companies using the simplified tax system could not keep accounting records, but in 2013 this right was taken away from them. However, there are concessions especially for small organizations. For example, Federal Law No. 209-FZ allows small businesses to keep accounting records in a simplified form.
The only exception is individual entrepreneurs: they are not yet required to maintain accounting. Lack of accounting records or gross violations of accounting rules are punishable by fines.
What documents regulate accounting in an organization?
As already mentioned, the main document regulating accounting nationwide is Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”. Other basic documents are accounting regulations (APS), which describe how to conduct accounting in practice. Among the options offered in the PBU, you need to choose those that will be most beneficial for the business financially and will eliminate unnecessary questions from representatives of regulatory authorities and investors.
And, finally, another fundamental document - the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (the latest edition was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 8, 2010 No. 142n). The organization's chart of accounts is drawn up and approved on the basis of this chart of accounts.
Where to start accounting in an organization?
Keep records and submit all reports to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat through Kontur.Accounting. Get free access for 14 days
Accounting statements are submitted once a year, but accounting must be kept regularly and systematically, so that after the end of the reporting period you do not have to search for primary documents among counterparties and hastily post accounting entries to accounts. Moreover, accounting in an organization begins before the first transaction occurs. As soon as the title documents for the company are received, local regulations can be drawn up that regulate accounting in the organization.
First of all, the accountant must:
- Develop accounting policies
- Prepare forms of primary documents
- Approve the chart of accounts
Accounting rules and key concepts
The basis of accounting is the processing of primary documents that correspond to specific business transactions. These are expense reports, invoices, invoices, etc. You can use unified forms of primary documents or those developed independently - the main thing is that they contain all the details specified in paragraph 2 of Art. 9 of Law 402-FZ. For some types of “primary” the use of standard forms is mandatory.
Information from primary documents is recorded in accounting registers - paper or electronic documents in the form of statements, journals, tables, etc. Each enterprise independently chooses which registers to use, using standard ones or ones developed “for itself.”
Information from the “primary” is entered into registers using the double entry , which reflects the receipt and expenditure of material goods. For example, the purchase of raw materials means the receipt of materials for production and at the same time the expenditure of funds. the receipt (debit) is recorded in one column , and the expense (credit) in monetary equivalent is recorded in the second.
The same fact of economic life is “passed” through both columns and marked with two different numerical codes. These numeric codes are called accounting accounts and correspond to specific groups of related business transactions. Each company independently decides which accounts to use, selecting the ones they need from the general plan. Recording debits and credits with accounts is called an accounting entry .
Based on the transactions for each account, a balance - the difference between its debit and credit turnover for a certain period, which can be zero. Accounts are divided into active - reflecting the assets of the enterprise, passive - reflecting the sources and expenditure of funds - and active-passive. If the debit of the account is greater than the credit, the balance is called a debit; if less, it is called a credit; if the debit and credit are equal, then the balance will be zero. The balance of an active account can be debit or zero, the balance of a passive account can be credit or zero, and the balance of an active-passive account can be both debit and credit, and possibly simultaneously.
Data for each account helps to compile a balance sheet , which groups all the assets and liabilities of the company for the reporting period, and a statement of financial results (also known as profit and loss statement). These two documents, as well as the appendices to them, are the financial statements that each enterprise submits to the Tax Service once a year. The list of appendices includes: a statement of changes in capital, a statement of cash flows, a report on the intended use of funds and explanations to the statements.
In a properly prepared balance sheet, assets always equal liabilities.
How to write an organization's accounting policy?
An accounting policy is an internal document of a company that defines the principles and options for accounting. The accounting policy must be drawn up and approved within 90 days from the date of state registration of the legal entity.
In small companies where accounting is not rich in features, accounting policies are often adopted once for the entire life of the enterprise. However, if necessary, changes are made to the academic policy, for example: due to the emergence of a new area of activity of the organization or changes in legislation.
If an audit comes to you, be prepared to present your accounting policy: this will be the first thing they ask for. To ensure that inspectors do not have the opportunity to interpret the ambiguities of the law not in your favor, describe in your accounting policy the features of accounting in your business.
What to write in the accounting policy?
Keep records and submit all reports to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat through Kontur.Accounting. Get free access for 14 days
The accounting policy regulates the maintenance of both accounting and tax accounting, so it is convenient to divide it into two parts.
In terms of accounting, the accounting policy must contain:
- Working chart of accounts of the organization
- Form of explanations for the balance sheet and profit and loss statement
- Classification of the organization’s income and expenses into income and expenses from ordinary activities and other income and expenses (taking into account the specifics of the organization’s activities)
- Level of materiality of error for financial statements items
- The procedure for revaluing fixed assets or information that fixed assets are not revalued, methods for determining the useful life and calculating depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets
- The procedure for assessing inventories (at the cost of each unit, at the average cost, or using the FIFO method - at the cost of the first acquisition of inventories)
- Information about who will do the accounting: manager, accountant or accounting service.
In addition, small businesses indicate whether they will apply PBU 18/02 “Accounting for corporate income tax calculations” and PBU 8/2010 “Estimated liabilities, contingent liabilities and contingent assets.”
Tax accounting rules must contain
- Tax accounting registers developed by the company in accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code
- The principle of distinguishing between direct and indirect expenses for the purpose of calculating income tax
- Method for estimating work in progress
- The procedure for assessing inventories during release into production and other disposals, during the sale of purchased goods (at the cost of a unit of inventory, at the average cost, at the cost of the first in time of acquisition - FIFO)
The LIFO valuation method (based on the cost of the most recently acquired inventory) cannot be used from 01/01/2015. Taxpayers who have used this method to value inventory must make changes to their accounting policies.
- The procedure for forming the cost of products and purchased goods for tax purposes
- The procedure for assigning the value of property to material expenses: one-time upon commissioning or (from 01/01/2015) over several reporting periods
- Methods for calculating depreciation of property (linear or non-linear)
- Rules for creating and using reserves
- Norms for recognizing standardized expenses as income tax expenses: entertainment expenses, expenses for voluntary medical insurance, etc.
Organizations working in the field of information technology indicate whether they classify computer equipment as depreciable property or consider the costs of its acquisition as material expenses.
The list of items is open; each organization compiles it independently, taking into account its specifics.
Accounting
The organization of accounting in an organization begins with the formation and approval of accounting policies. The objects are the company's property, its obligations and business transactions carried out in the course of its activities. In addition to preventing negative business results and obtaining a complete picture of the state of affairs of the company for every day of work, the accountant receives data for calculating taxes and paying them to the budget.
To ensure the tasks assigned to the accountant, he must adhere to certain principles that are common to all:
- ensure data autonomy, i.e., take them into account only in relation to one organization;
- apply the double entry method (use a chart of accounts and postings);
- ensure objectivity and impartiality of data;
- exercise caution and caution, avoid dubious transactions;
- ensure regular recording of data on all operations and summing up;
- maintain confidentiality;
- depending on the accounting policy, use the accrual method (accounting for transactions as they occur) or the cash method (accounting for transactions as they are paid for);
- use the national currency of the Russian Federation (ruble) for calculations.
Accounting features may differ depending on the status of the company, its legal form and the chosen tax regime. For example, a small business has the opportunity to take into account data and submit reports in a simplified manner.
Primary documents and chart of accounts
Keep records and submit all reports to the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat through Kontur.Accounting. Get free access for 14 days
Facts of economic life are reflected in accounting on the basis of primary accounting documents. Since 2013, organizations can develop forms of primary documents independently. The main thing is to enter all the required details into the forms and approve them in the accounting policy.
However, if there are no non-standard operations in the economic life of the organization, it is better not to create individual forms of documents. In order not to complicate the document flow, it is better to use the forms recommended by the State Statistics Committee.
If necessary, the list of documents can be supplemented.
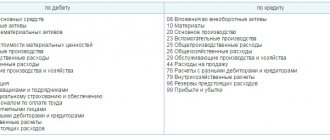
In addition to the forms of primary documents, the accounting policy requires approval of the organization's chart of accounts and accounting registers. From the chart of accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance, select those that you will use. And for a more accurate classification, you can enter subaccounts.
If the company is small and its economic life does not involve non-standard operations, the manager does not need to dive into all these subtleties. The online service Kontur.Accounting already has an accounting policy that is suitable for most companies, all that remains is to read it and print the order prepared in the service.
And then the actual accounting begins, but that’s another topic.
What are the types of accounting - 3 main types
There are three types of accounting.
Let us describe them briefly.
Type 1. Financial accounting
Financial is accounting information about the costs and income of the company, about accounts receivable and payable, about the composition of property and funds, etc.
Type 2. Management accounting
Management is a type of accounting necessary for collecting, processing and providing information for the management needs of the company.
Type 3. Tax accounting
Tax - processing of information to determine the tax base based on primary documents grouped according to the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.