Hello! In this article we will talk about marketing in simple words - what it is, why and how to apply it in an enterprise.
Today you will learn:
- What relates to marketing, functions and types of marketing;
- What are the marketing strategies for an enterprise, and what does a marketing plan consist of?
- What is marketing in business, and how to distinguish it from business for the consumer;
- What is network marketing and how not to confuse it with a financial pyramid;
- What is Internet marketing and its advantages.
What is marketing
It so happened that the majority of people, by the word “marketing” mean the creation of advertising offers.
This is due to the fact that many foreign marketers are involved in organizing advertising campaigns. However, this is only the outer shell that is visible to the average person. In fact, the internal scheme involves multi-stage strategic planning of meticulous work.
The marketing system includes three tools, which in practice are used in stages:
- advertising;
- RY-activity;
- sale.
Initially, the work includes advertising communications, the purpose of which is mass awareness and interest of potential buyers in the advertised product or service. This can be done by establishing cold contact with the consumer, through advertising in the media and other methods of attracting customer attention.
As a result of an effective advertising campaign, the consumer should learn about the product, and ideally want to find out more about it when contacting an online store in person or directly to the seller. At this stage, the art of selling comes into play, when the “prepared client” has a strong belief that he should make a purchase from you.
At first glance, the marketing cycle seems complete, but in fact, the main work is just beginning. The task of a successful marketer is not a one-time purchase, but the formation of a “return anchor” in the client. So that he becomes a regular customer and returns for your products again and again, while the company receives a stable income.
This result can only be achieved by selling a quality product against the backdrop of a positive reputation of the company under whose brand it is released to the consumer market.
Marketing areas
Marketing areas (areas of application):
- consumer goods - all those products that we purchase in stores (food, clothing, equipment, etc.);
- consumer services - the market for services provided to ordinary people (education, law, air travel, hairdressers, etc.);
- means of production - products related to the production of other products (equipment, raw materials, production services, etc.);
- property – real estate and securities market;
- experience – employment market;
- ideas and information – the area of activity for offering new ideas and information;
- events – events of various types, from exhibitions to sports competitions;
- personalities – the celebrity market;
- geographical territories – market struggle for territories (tourist points of attention, location of offices, production facilities).
At its core, marketing is a universal tool that can be applied almost anywhere. Anything that requires promotion or competition falls under the scope of marketing.
Objectives and principles
To achieve the desired result, the marketing department solves the following tasks:
- analysis of the market and consumer psychology;
- monitoring the activities of competitors;
- anticipating the needs of potential clients within the company's activities;
- expansion of the range;
- formation of a commodity matrix;
- participation in pricing;
- sales of products;
- development of loyalty programs for the company’s clients;
- after-sales service;
- representing the company in the market and in sales – advertising, public relations and others.
The efforts of the company’s specialists should be aimed at increasing the competitiveness and attractiveness of its products, which can be achieved by observing the following marketing principles:
- The production and sale of goods should not exceed consumer demand and the company's capabilities.
- By regularly updating the product in accordance with the technical level of our time, we must achieve complete customer satisfaction.
- Respond in a timely manner to changes in demand and ensure the company’s presence in the consumer market at the right time.
- Innovate to keep customers engaged.
- Instant response to changing demand and building a new strategy.
Marketing goals and objectives
From the definition, the main task of marketing is clear - increasing the market position of the enterprise and making a profit. In addition, the tasks that marketing activities can solve include the following.
- Market analysis - current situation, supply and demand, trends, etc.
- Analysis of the target audience - its needs, pain points, signs, features.
- Analysis of competitors - prices, assortment, identification of strengths and weaknesses, development of strategies to “overtake” market leaders.
- Competent development of the company's pricing policy, study of the pricing system.
- Creation and improvement of assortment.
- Improving the quality of service and services provided.
- Establishing relationships with the client, increasing consumer trust and loyalty.
- Promote your products and services in offline and online spaces.
- Increasing brand awareness, business reputation and image.
- Increasing the company's conversion rates.
- Increasing production and sales volumes.
As you understand, this list can be continued for a very long time, since there are so many problems that marketing can solve. All of them are in one way or another related to increasing the company’s competitiveness and its profits. Each organization determines its goals and objectives individually. They must correspond to the financial and production capabilities of the enterprise. Otherwise they will simply be unattainable. These can be either single-level or multi-level tasks.
- For example, the company noticed that in the previous quarter there was a drawdown in the percentage of completed transactions. Out of 1000 received requests, 690 (69%) were converted into a real deal; in normal times, this figure does not fall below 90%. The company sets itself a one-level task - to improve the quality of service (qualifications of managers, terms of the transaction, etc.).
- An example of a multi-level task: conduct a competitive analysis - develop individual strategies that will allow you to beat competitors - implement them - increase the market share occupied by the company.
The task of a marketer is not only to correctly set goals, but also to correctly implement them.
Marketing functions
To ensure the successful and coordinated work of the organization, marketing performs the following sets of functions:
- analytical;
- production;
- sales;
- management and control.
The analytical function of marketing involves researching the consumer market and the internal environment of the company, which includes:
- analysis of fluctuations in consumer demand;
- studying the preferences of potential clients;
- assessment of the manufactured product;
- compilation of databases of suppliers and regular customers.
The production function of marketing exists to maintain product quality and high competitiveness, which can be achieved through:
- introduction of new technologies into the production process;
- procurement organization;
- quality monitoring in production;
- reducing costs to minimum values.
The sales function of marketing is the organization of the stages that a product goes through from the moment of its manufacture to use by the consumer:
- distribution of products depending on demand;
- creation of advertising offers;
- using tools to stimulate sales;
- delivery of goods in the required quantity;
- monitoring product delivery times;
- pricing.
The management and control function provides for rational planning of the work of all links of the production chain, which is achieved by:
- developing a strategic plan with clearly defined deadlines;
- control over compliance with marketing tactics;
- ensuring timely receipt of information;
- rational conduct of economic activities;
- communication component.
In practice, marketing functions are applied in a cyclical sequence, due to which a stage-by-stage study of the market, production and promotion of goods is carried out with the formation of a permanent client environment.
Practical examples and cases of using marketing techniques in business
Below is an interesting video with the famous intellectual Anatoly Wasserman, which will surely bring a smile to your face. This is the so-called viral marketing.
Viral marketing is an effective way to promote goods and services; its essence is to advertise a company, product or service through word of mouth. That is, people themselves will recommend this offer to each other by sending a link to the content.
Types of Marketing
Depending on the stage of development, scope of application, demand, various types of marketing mechanisms are distinguished.
Undifferentiated Marketing
This type of marketing is used by large companies to promote generic products to large masses. At the same time, the consumer market is not divided into separate segments, but is perceived as one whole. Most often, such goods are drinks, toothbrushes, furniture, and cars. This is the production of large quantities of products for the mass consumer with the dissemination of information through media advertising.
Differentiated Marketing
The company aims to promote and produce goods to satisfy a specific target audience, which is limited by age or gender. The main direction of this marketing strategy is to stand out from competitors and gain a strong foothold in the chosen niche.
Concentrated Marketing
Concentrated marketing is based on the focus strategy developed by renowned scientist Mark Portal. The company selects one product and begins producing it for a certain circle of people. When using this tactic, there are great risks that the product may lose its attractiveness to the consumer.
Integrated (marketing mix)
The essence of the integrated direction comes down to the simultaneous use of the four main principles of marketing to achieve the desired result in the shortest possible time. It is believed that if the proposed plan is accurately implemented, no difficulties should arise during work.
Connected Marketing
The second name is communication marketing. It is characterized by a spread beyond the usual marketing tasks and distribution to all personnel involved in the process of creating and selling a product.
Conversion Marketing
Used when there is no demand for the product being produced. The objectives of conversion marketing are to change the consumer’s attitude towards the product, which is achieved by improving quality characteristics, using new advertising techniques and reducing the cost of the product.
Incentive Marketing
This marketing tactic is used when consumers are indifferent to the product and there is no demand in this market segment. In this case, the main goal is to promote the product through advertising, attracting customers with promotions and discounts.
Developmental marketing
The key task of developmental marketing is to transform potential demand into real demand. To do this, research is carried out to identify areas that do not satisfy potential customers, correct them and generate interest in a fundamentally new product.
Remarketing
This marketing model is effective when sales decrease due to falling demand, which may be the result of a deteriorating economic situation, or due to the transition of a product from one technological stage to another.
To restore balance, measures are taken to improve the quality of the product or enter new markets.
Synchromarketing
This type of marketing is necessary to regulate demand for products when an increase or decrease in sales is associated with external factors: time of year or day. Stability is achieved through a flexible pricing policy or the introduction of loyalty programs for consumers.
Supportive Marketing
The marketing concept is carried out to maintain the popularity of the product and its implementation at the highest level. To maintain customer interest, packaging upgrades and other measures may be carried out.
Demarketing
Measures that prevent excessive sales growth by increasing costs, stopping advertising, franchising (transferring products for sale to another person).
Adversarial Marketing
The program is aimed at suppressing demand if it threatens the health or well-being of society or individuals (alcohol products, tobacco products, etc.). The goal of this method is to reduce sales as much as possible, which is achieved by raising prices, anti-advertising, and the formation of negative public opinion.
Considering the scope of application of the marketing strategy, the following are distinguished:
- Consumer (b2c) – to obtain maximum benefits from the interaction between producer and consumer.
- Industrial (b2b) – in cooperation between an industrial enterprise and an organization that subsequently uses the products or acts as an intermediary.
- Partnership marketing is needed to control sales markets.
- Marketing of services is carried out simultaneously with the promotion of goods.
- Network marketing - for the sale of products, a multi-level chain is created, the links of which are individuals who act as distributors.
Among the new types of marketing that have emerged in the context of the continuous evolution of the sales system are:
- Guerrilla - the use of non-standard techniques, individual development of a creative marketer.
- Viral is an action plan aimed at a person’s subconscious with the goal of “infecting” an idea, then the consumer himself begins to advertise the product (rebroadcasting photos, videos on social networks).
- Buzz marketing works like word of mouth by transmitting information through rumors.
- Lateral marketing is an unconventional method of combating competition by operating outside the consumer market for a specific product.
- Expomarketing is strengthening demand and strong positions through holding fairs and major presentations.
All forms of marketing change regularly, acquiring new features in an evolving economy.
Types of Marketing
The division into types occurs depending on the tasks being solved and the tools that are used for this.
Conversion Marketing
It is used in conditions of negative demand, when services and products sell poorly or are completely rejected by the audience or a large part of it. For example, certain dietary supplements, expensive brands of everyday goods, etc.
Poor performance is the result of an incorrect assessment of the needs and capabilities of customers, forecasting, and errors in market research. The reason may be even simpler - the consumer does not know enough about the product, its benefits, features and advantages.
Therefore, the main marketing tool is PR campaigns and advertising.
The goal is to create a long-term need for the product and match it with supply. How it's done?
- Products are re-released;
- Pricing policy changes;
- The promotion strategy is changing.
Incentive Marketing
The goal is to stimulate audience interest in certain product categories. This problem is not related to the denial of the product, but to its lack of demand.
This may occur due to the loss of value of the product, its irrelevance in some conditions (for example, the offer of skis in the southern regions), or the unpreparedness of people to perceive something new.
In the latter case, the buyer has not formed an attitude towards the company; this problem can be solved with the help of competent promotion.
Stimulating promotion draws attention to the right products, shapes consumer attitudes towards them, or directs sales through other, more relevant channels with an interested audience.
Developmental marketing
Specialists in this field work with potential, or emerging, demand. In simple words, they study the needs of the population for those goods that have not yet been developed and offered for sale. For example, everyone wants modern smartphones that can hold a charge for several days.
Identifying such desires and looking for ways to satisfy them first is the main task of specialists in this field. Potential interest must be converted into real interest.
Demarketing
It is a process of permanent or temporary reduction in demand . In some cases, such actions are necessary to maintain the image and stable operation of the enterprise.
For example , at the dawn of the Internet “to every home,” the number of applications from the population significantly exceeded the technical capabilities of many providers. To maintain the quality of services and avoid operational errors, many were forced to increase the cost of Internet connection and limit the number of daily requests.
Also among the examples of restrictions on the quantity of purchased goods is purchasing with cards, since it is impossible to fully satisfy the needs of the population.
Remarketing
Combating declining sales levels and declining profits. It is logical that over time, certain products lose relevance and risk completing their “life journey”.
If sales levels drop significantly compared to the previous period, it is time to take measures to stabilize demand. If this is not done, income risks falling to zero.
Remarketing is the “revitalization” of sales, the return of market positions to certain products. This is done by improving products, creating new values associated with them, and finding other ways to harmonize the supply with modern market conditions.
Synchromarketing
Activities related to this type of promotion are necessary when the company is not satisfied with the demand in a certain time period. Needs for some things are seasonal.
Therefore, in certain periods, an enterprise may not cope with the volume of requests (not enough resources, production capacity) or, conversely, feel a lack of clients.
Selling seasonal products carries the risk of going bankrupt during a period of low customer interest.
How to sell ice cream in winter and fur coats at the end of the winter season? A number of advertising, psychological and production techniques are used:
- Discounts during “unclaimed times” (promotions and gifts when ordering food at home in the morning, sales of warm clothes at the end of winter, etc.);
- Motivation of the buyer to purchase the service in advance (for example, “book hotels for a summer vacation without rush and queues in November”);
- Change of sales channels (at different times of the year, wholesale suppliers of vegetables and fruits trade in different regions);
- Offer of additional services and related products;
- In conditions of shortage of production capacity and labor resources at “peak” moments, a restructuring of the production process is necessary (automation, additional hiring of workers, the use of computer technology to simplify work, etc.).
Supportive Marketing
The ideal state of affairs for a company is the matching of supply and demand . But even in this case, you should maintain a favorable situation, monitor market conditions and factors affecting consumer demand.
Within this variety, specialists control sales volumes and costs, pricing, and conduct advertising campaigns to maintain audience interest.
Any modern successful corporation constantly releases new commercials, holds promotions and sweepstakes, not allowing customers to forget about themselves.
Adversarial Marketing
Targeted anti-advertising. The clearest example is social advertising about the dangers of smoking and alcoholic beverages. There is a constant irrational demand for them, so public organizations and the state are trying to reduce it.
Such methods are also used in competition. The tools include discrediting competitors, counter-advertising directed against a specific item), dumping. Resistance can manifest itself at the level of interpersonal relationships.
For example , face control in an establishment is designed to limit the access of non-target audiences to the establishment; customs and the Federal Migration Service also, in their own way, limit the flow of unwanted visitors into the country.
Mass Marketing
It is used to bring to market products from the category of “universal goods”, necessary for any segment of consumers.
Studying customer categories and segmentation are not required, the task of specialists is to offer the product to the masses at a favorable (minimum) price, the role of quality here is minimal, differentiation is not required.
Availability is what matters, not product variety. Therefore, the product is unified as much as possible. This applies to consumer goods (hygiene products, basic food products, etc.).
The company's offer in this case is universal and focused on the general needs of consumers. In this case, channels of mass communication and widespread distribution are used.
Concentrated (targeted) marketing
Unlike mass, targeted is designed to promote the manufacturer among a certain group of the population to achieve maximum effect at minimal cost.
For example , it makes sense to promote jewelry among wealthy people, since mass advertising events will not pay off. It is necessary to clearly define your audience and work “for them”.
Differentiated Marketing
Promotion strategy targeting several market segments. The market offer, promotion strategy and product characteristics for each differ depending on the desires and needs of the population.
An example is the release by one company of both expensive smartphones and inexpensive affordable phones. This tactic allows you to study and select the most promising niche or continue to work in several to ensure the stability of the company.
Opportunities for strategic moves also arise, and the favor of buyers towards the company is ensured.
Strategic Marketing
A full range of activities related to planning the provision of services and positioning the company in the market.
This type is characterized by systematic data collection, analysis of the audience and its preferences, and conditions for selling products.
Specialists are engaged in solving the following problems:
- Pricing and assortment development;
- Development of optimal conditions for transportation and storage of a product group (it is necessary to find the most cost-effective ways to increase the competitiveness of the enterprise);
- Planning wholesale and retail sales (how, where, ways to increase the attractiveness of products in the eyes of the buyer);
- Monitoring customer service (quality of service, providing assistance in choosing, consulting customers, providing credit);
- Conducting advertising campaigns, conveying the information the company needs to the audience (advertising on TV, on the Internet, outdoor structures, promotions, etc.)
Internet Marketing
The newest and most profitable way to promote a company. In part, this means transferring traditional methods of promotion to the Internet environment; unique methods of promotion on the Internet are also being formed.
Advantages of this type
- The ability to accurately target (“hit” the target group);
- Reaching a wide audience;
- Dynamic market development;
- Low costs for promotions and quick payback;
- Ease of analysis and control (the response to advertising on the Internet is easy to evaluate and draw conclusions about its feasibility).
The key point of promotion on the Internet is to involve users in dialogue.
An example is working on the quality of the content of an online store website, the functionality of the portal, so that the buyer can easily navigate the assortment and stay on the site for as long as possible. In this case, the specialist’s task is to turn users into buyers.
Sales tools and channels
- SEO optimization of the company's web resource;
- Contextual and banner advertising;
- Promotion on social networks (the ability to build a dialogue with the audience, effective direct sales);
- E-mail newsletter – information and direct appeal to potential clients.
Marketing Strategies
To achieve a high result, a scheme for planning and implementing the work of an enterprise is important, taking into account all possible aspects.
Marketing strategy can also be considered as the art of reducing costs and losses in the process of active enterprise activities. For every strategic development, an executive plan is important, which allows you to implement marketing development in the company's work.
Strategy for entering the consumer market
The tactic is used if a company successfully sells its products, but the enterprise needs to expand the consumer market to increase the profitability of the production process. The methods will be effective with growing demand and little competition. The main methods that stimulate sales growth include strengthening marketing, holding promotions and other tools to improve consumer activity.
Innovation strategy
The creation and introduction of a new product to the market involves the use of traditional sales methods. A product that has no analogues is in a winning position, but it takes time to build interest and trust among potential buyers.
Market expansion strategy
This method of business development is acceptable if there is dissatisfaction with the buyer’s needs for the manufactured product of new market areas.
In this case, the success and speed of implementation of the marketing plan depends on the capabilities of the company and its willingness to take a certain risk.
Offensive
Tactics of active actions aimed at promoting a product, conquering the consumer market and obtaining maximum profits, which is determined by the market share occupied. If the share decreases, performance decreases significantly. To retain market space, offensive marketing strategy methods are used in the following cases:
- if the market share is below the expected level;
- the company was forced out by competitors;
- when introducing new products;
- an offensive position will help expand due to the losses of competitors.
Retaining
When a company is in a leadership position, it is important to conduct activities that support sales and brand image. Most often it is used:
- for thriving companies;
- when using all methods of offensive strategy;
- for insurance before new actions.
Retention tactics require careful study of the company's competitors.
Retreat
The strategy is aimed at reducing the company's market share. In most cases, such tactics are used after a decision is made to terminate the company’s activities: product production ceases, advertising activity decreases.
Community Marketing Strategy
One of the most profitable areas, which is aimed at mass interest in consuming a universal product.
The main goal of a marketing strategy is to influence a large audience to tap into a huge consumer market. The main condition for success is the production of an interesting and useful product for the masses.
Differentiated
It is used when deciding to introduce an innovative product to the market that has no analogues or has advantageous differences from the products of competing companies. In this case, the company determines the target audience, a kind of consumer differentiation.
Focused Marketing Strategy
Used for companies that focus their activities on developing a specific market segment. In this case, the company promotes the product with marketing that is interesting to the selected category of customers.
Despite significant differences, all strategies are united by a focus on the target market and maintaining a leading position due to advantageous differentiation from competitors' products.
Network marketing
Network marketing (MLM - multi level marketing) is a technology for selling products from manufacturer to consumer, which is advisory in nature and transferred from person to person. At the same time, the so-called distributor can not only sell the product, but also attract new sales agents to the company.
The business plan of an MLM company assumes that distributors:
- Have you used this product yourself?
- Sold the product to customers;
- They attracted other sales agents to create a network of business entrepreneurs.
The manufacturer himself is responsible for organizing delivery. He ensures that the goods are delivered to the distributor's home. For effective work of sales agents, master classes and seminars are provided to develop sales skills and achieve success in their business.
For an entrepreneur, network marketing is an attractive business because it does not require experience and a large initial investment in capital.
For the buyer, network marketing also looks beneficial, since truly responsible MLM companies provide high-quality products and a guarantee for them. In addition, before purchasing a product, the consumer receives all the necessary information about it and receives the product at home.
Network marketing provides for active and passive income. The agent receives active income based on sales volume. And passive income is created through the creation and active development of a subnetwork of distributors.
However, although at first glance, network marketing seems to be an attractive business, in addition to its advantages, it also has a number of disadvantages.
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of network marketing
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low barrier to entry into an MLM company | Reputation |
| The product meets high quality workmanship | Business is growing at a slow pace |
| Underemployment | Only a few achieve great success |
| You can do business online | Deterioration of relationships with friends and family |
| Training programs available |
To attract a potential distributor to an MLM business, you can use the following methods:
- Look for partners among your surroundings;
- Look for partners among your friends and acquaintances;
- Create your own website to promote products;
- Look for partners through social networks;
- Meet new people and attract them to this type of business.
When it comes to network marketing, there is an immediate association with such a definition as a financial pyramid, the activities of which are prohibited in the Russian Federation.
The main difference between network marketing and financial pyramids is that the profit received by MLM companies is divided between distributors, taking into account the contribution of each. And the financial pyramid receives income due to the number of people attracted and their contribution to a non-existent product.
In addition, network marketing can be distinguished from a financial pyramid by the presence of:
- Marketing plan;
- Company guidelines and articles of association;
- The products themselves;
- Training systems.
The financial pyramid does not have a specific marketing plan; it is very confusing and incomprehensible. The company's management is anonymous and, moreover, there is no charter of the enterprise. There is no assortment of goods, there are only a couple of units of questionable products. There is also no training system provided or it costs a certain amount of money, for which they issue cheap advertising brochures.
Network marketing provides training for sales agents on a free basis, or training CDs, books or videos on the Internet are issued for a symbolic amount.
Vivid examples of the successful development of network marketing are the companies Amway, Avon, Oriflame, Faberlic and Mary Kay.
To summarize, we can conclude that network marketing is aimed at promoting a product and rewarding the distributor for the work done, and the main goal of a financial pyramid is to attract people and their financial investments.
Strategy Development
The correct choice of tactics determines the efficiency of the enterprise in the future.
Therefore, the marketing strategy includes:
- planning the company’s activities in the consumer market taking into account long-term goals;
- conducting structural market analysis;
- forecasts for the development of consumer demand;
- pricing conditions;
- highlighting the product's advantages among competitors.
The company makes organization of new production, methods of introducing new products, determining partnerships with other companies and other decisions taking into account the developed strategy. Choosing business tactics includes the following steps:
- assessment of the company's profitable and losing sides;
- market activity research;
- industry direction analysis;
- identification of market opportunities for the enterprise;
- study of competitive firms;
- research of interaction with clients and partners;
- assessment of the possible influence of the external environment on the activities of the enterprise;
- marketing effectiveness assessment;
- control over product quality;
- studying the possibilities of product improvement;
- marketing planning;
- monitoring the execution of the chosen tactics.
Detailed development of a marketing strategy helps to take sales to a new level, expand the customer base, allow you to take top positions among competitors, and improve the quality of customer service.
Goals of modern marketing
The goals of marketing today are a little different from those that marketers set for themselves in the past. If previously the main task was to sell a product to a client, regardless of his needs, modern marketing is focused on the consumer and offers him, first of all, to satisfy his personal needs and desires.
Nowadays, companies can no longer afford to concentrate solely on maximizing profits: due to high competition in the market, such tactics are doomed to complete failure. Thus, marketing activity should be aimed at satisfying customer needs, because this is the only way to encourage the target audience to buy a certain product.
This is why niche markets or meeting specific consumer needs and requests are especially popular. Moreover, some companies successfully create the problem themselves by providing the solution to those who are willing to pay for it.
Goals related to marketing activities:
- creating new needs for customers. If a new product is launched on the market, the marketing department must ensure that demand for the product is maintained;
- market analysis to determine the client’s needs for which he is willing to pay;
- building long-term relationships between the company and the client, with an emphasis on loyalty from the latter.
This point is especially important in niches where it is easy to lose or gain a client by promising to provide high quality goods or services: it is very important that such promises coincide with reality! Otherwise, the company will face a damaged reputation and financial losses.
Marketing plan
Without careful planning, the company's development will follow a spontaneous scenario from success to failure. The company begins to randomly purchase raw materials and produce an unreasonable amount of products.
All this leads to waste and loss of time. To synchronize and coordinate the work of all departments, you will need to draw up a plan for a marketing strategy that has been determined in advance.
The plan is drawn up taking into account the following criteria:
- Primary research of the situation around the company. An assessment of the company's position from the economic, legal, technological side is carried out, as well as an analysis of competitors, interaction with suppliers and consumers.
- After the initial analysis, when an objective picture of the company’s condition emerges, short-term and long-term goals are set for the main indications.
- Based on the goals set, a marketing strategy is developed to achieve the desired result with minimal losses for the enterprise.
- To successfully develop a strategy, choose the appropriate tactics. At this stage, numerous marketing tools are used. For the successful implementation of a strategic idea, those responsible for execution are appointed at each stage.
- Everything planned is associated with financial costs, so a budget is planned in advance, within the framework of which the company’s goals are achieved.
- The work of strategic development does not end with drawing up a plan. The marketing department monitors the effectiveness of the actions taken. If the performance is unsatisfactory, the company's strategy is reviewed and adjusted.
A well-written marketing plan will not only guide you in choosing the right path for your company to thrive, but will also help you determine whether you are moving in the right direction.
Who is a marketer and what does he do?
So, who is a marketer and what does he do? If a person has received a marketing education, this does not mean that he is a good marketer, just as a philosopher does not need an education in philosophy and a musician does not need a musical education. Five, ten or twenty years of experience does not guarantee that a marketer will be successful, although a person becomes wiser as he gains experience.
And yet, what qualities should a marketer have to be successful? What separates non-professionals from marketing gurus who actually have deep knowledge of the field and are excellent at it? To answer this question, it is necessary to analyze what makes marketing truly successful?
What makes marketing successful? In simple terms, marketing is any action through which a client is voluntarily willing to give his money to a company (business). Marketing is considered most successful if customers are willing to give their money to the company for the rest of their lives. Such buyers have qualities that indicate even before purchasing a product that buyers will be loyal to this company for the rest of their lives.
While many people may feel that manipulation and persuasion are necessary to get clients to part with their money, marketing and sales are two different things.
A good marketer does not need to manipulate the client into buying the product; the product sells itself, and the marketer effectively advertises it, reaching an interested and action-ready audience.
Therefore, the quality of a truly good marketer is a clear understanding of the target market. A marketer who can read other people, put himself in their shoes, and minimize perceptual bias is a truly good marketer.
Perceptual bias occurs when a person sees in a group of people something that they actually do not have. A person who has no connection with the target group is likely to have a perceptual bias. People with the least bias have knowledge about different cultures, personalities, and are able to distinguish between the emotions of people in the target group, their desires and needs.
What would make you successful if you, a fresh college graduate, were hired by Proctor and Gamble and asked to sell Tide laundry pods to other students? It is likely that you are a recent college graduate and are the target audience for the product yourself.
Your understanding of the target audience of Tide capsules will be so good that you will have minimal bias, because you know what emotions other students are experiencing, their thoughts, desires and needs.
Now imagine that Proctor and Gamble asks you to sell diapers to African-American women living in rural areas. It will be very difficult for you to understand this group of people; your understanding will be greatly limited.
Proctor and Gamble is better off finding a marketer who fits the target group themselves, except you are an excellent marketer and have not made mistakes in the past. This situation clearly demonstrates the second quality of a good marketer - continuous learning and the ability to adapt.
The history of marketing is a long and gradual transition from traditional to digital marketing. Modern marketing has changed significantly from its origins. There was a transition from print advertising to broadcast advertising, then came the Internet era with digital advertising, and now the transition to mobile advertising.
All this indicates that modern Internet marketing has changed a lot compared to the marketing of the time when it first began to develop. Exactly because of this reason; Adaptability is a quality that marketers must have.
In order for a marketer to adapt to the environment using the latest technologies, he must always be ready to learn from old knowledge. For the same reason, many experienced marketers can negatively influence the marketing team, the company, and clients, which is the result of the marketer's reluctance to learn from others, constantly learn new things, and trust their own intuition.
Summary of qualities of a marketer
- Real understanding of different target markets . How to achieve this?
- Openness, ability to study and understand different cultures, groups, ability to establish contacts with people from different social strata
- Travel, gain experience, constantly try new things, acquire new knowledge, expand your horizons
- Adaptability . How to achieve this?
- Continue learning, for example here.
- Try to predict what will be important for marketing in the future and develop knowledge related to marketing
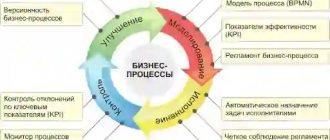
Marketing mix
In a professional environment, a marketing mix is the simultaneous use of several marketing tools.
Back in 1960, the 4P complex was proposed:
- Product – this term refers to material objects, services, ideas that can satisfy consumer demand.
- Price – the amount of finance or benefits that the client is willing to give for the product offered.
- Place – organization of delivery and after-sales service.
- Advertising offer (promotion) is the process of familiarizing potential buyers with a product and developing interest in purchasing the product.
The marketing mix can be called a set of tactical decisions to define specific objectives. With proper implementation of the complex, there should be no questions about who should do what in the team to implement the marketing campaign.
Main types of modern marketing
Nowadays, marketing is developing so dynamically that new concepts and theories are constantly appearing. Let's try to understand the already established definitions:
- permission marketing. This explanation was proposed in 1999 by Seth Godin, a real marketing guru. He argued that communication with the client should be personalized, unobtrusive and interesting;
- inbound marketing. The term was first used in 2005 by Brian Halligan, co-founder of Hubspot. It involves building a marketing strategy based on the voluntary consent and interest of customers (as opposed to intrusive and aggressive methods). The essence of such marketing is to attract the attention of the consumer by differentiating the product on the market;
- outbound marketing. The complete opposite of the previous concept. In short, this is “classic” marketing in all its manifestations: one-way communication, a typical propaganda offer, its repeated repetition;
- real-time marketing (RTM). Involves conveying a very specific message to a target audience in a specific place at a specific time (taking into account the characteristics of the place or event). Today, a large number of brands use current events that attract the attention of the whole world to communicate using RTM: an eclipse of the sun, the birth of a royal heir, major sporting events;
- multi-channel marketing. It involves the construction of a number of possible channels that directly reach customers and provide them with an advantageous shopping opportunity on any medium (for example, on a smartphone, tablet or computer). Multichannel marketing allows the consumer to decide on the device themselves, while ensuring, on the other hand, the convenience of any choice.
Digital marketing
The use of digital technologies to attract and retain consumer attention is called information marketing. The main task is to promote the brand and create a positive image through television, radio, mobile technologies and the Internet.
As part of digital marketing, the following is carried out:
- optimization for search engines;
- activities to increase website traffic;
- posting useful content;
- direct mailings to potential clients;
- placing advertising offers on social networks;
- influencer marketing;
- advertising on thematic websites and others.
Currently, there are more than 100 marketing tools, and each of them has its own purpose. The most popular include:
- Contextual advertising – advertising in search engines, thanks to the settings, is shown to the target audience.
- Web analytics – to track the behavior of visitors on the site.
- Advertising on social networks - placed in the form of posts, banners in popular groups, in news feeds.
- Banner, teaser advertising - blocks are placed on thematic websites.
- CRM systems are programs for planning and conducting negotiations with clients in accordance with certain regulations or instructions.
- Business analysis programs are designed to process a large number of numbers.
- Media viruses are unique content that is promoted due to its quality and benefit to the visitor.
- Blogging – creation and support of corporate or personal channels, groups or accounts.
- Network branding – brand promotion on social networks.
- Posting is the dissemination of information on open network platforms.
- Network event marketing – creation of a network platform for announcing an event.
- Network guerrilla marketing is the dissemination of information in an unusual form in public pages with the maximum number of users.
Digital marketing has an undeniable advantage over analogue marketing. With its help, marketing tasks can be solved in a few hours, which significantly reduces the cost of conveying information to the target consumer.
Internet marketing as an innovative type of promotion of goods and services
Internet marketing is the most relevant type of product promotion today. This activity can be defined as the practice of applying all aspects and components of traditional marketing in the Internet space.
The main goal of online marketing activities is still the same: to obtain maximum income. In this case, this is done by increasing website visitors and turning them into consumers of goods and services.
Comparison of conventional (offline marketing) and online marketing:
| № | Comparison criterion | Classic marketing | Internet Marketing |
| 1 | Hitting the target client | Not always accurate (±) | Almost always accurate (+) |
| 2 | Market growth dynamics | Average (up to 10% per year) (±) | High (more than 40% per year) (+) |
| 3 | Payback period | Average (±) | Fast (+) |
| 4 | Convenience of analytics and control | Inconvenient (-) | Convenient (+) |
| 5 | Transparency of advertising budget spending | Opaque (-) | 100% transparent (+) |
| 6 | Degree of trust | High (+) | Average (±) |
Based on these criteria, you can see that online marketing is gaining momentum and has a number of undeniable advantages.
Online marketing services use all available channels for promoting and advertising products on the Internet. To increase website traffic and sales growth, the following tools are used:
- SEO optimization;
- Contextual advertising (we have already written about it in detail here);
- Advertising on social networks;
- Banner advertising;
- Traffic arbitrage.
The basics of online marketing are the same as traditional marketing. Web promotion strategies are handled by professionals - agencies and studios specializing in this type of activity.
Effective Internet marketing involves stage-by-stage work on the site: determining the needs of the audience, creating content for successful promotion, involving site visitors in active sales processes.
Involvement is the key criterion for marketing effectiveness. This component helps increase user interest in your site and determines the profitability of a commercial endeavor. The tasks of Internet marketers are not only direct sales, but also the creation of interesting content that will attract users to the resource and turn them into active participants.
One of the reliable marketing tools on the Internet is e-mail newsletter, since personalized contact with a potential client by e-mail brings solid profits to marketers.
Benefits of Internet Marketing:
- The consumer has the maximum necessary information about the product without leaving his seat.
- Relatively inexpensive costs for advertising campaigns.
- Wide audience coverage.
The number of consumers of products on the Internet is not limited: in theory, these are all network users, since placing an order for the purchase of goods is possible from anywhere in the world.
More specific goals of electronic marketing: increasing traffic, developing, promoting and introducing new services, increasing awareness of specific brands and products, improving the company’s image, monetizing a web resource.
A mandatory stage of an online marketing campaign is SEO optimization*.
SEO optimization is a set of measures aimed at increasing the position of a particular site in the search engine results list.
This is the main tool for promoting and promoting a commercial project. SEO optimization attracts customers to the website pages, and also allows you to highlight the target audience that comes to the resource with the specific purpose of purchasing certain goods.
Today, hundreds of companies and Internet studios of various levels and directions are engaged in optimization. High-quality promotion of a web resource is a long and gradual process. This is discussed in more detail in other articles in our business magazine.
B2B marketing
A strategic direction that includes a set of activities aimed at promoting a product and generating profit between companies through direct contact or through intermediary services. The target audience of the enterprise is legal entities (other firms) who purchase goods or services.
Interaction with corporate clients differs from the consumer market:
- selling a product in the B2B segment is a long process that can last several months;
- products for companies have a complex structure;
- small customer base;
- when working with companies, unequal sales volumes prevail;
- in the B2B segment there are no thoughtless purchases, unlike B2C, where emotions predominate;
- For companies, the corporate brand is of great importance, not individual products;
- pricing also makes a significant difference; for B2B, purchase volumes, client status, payment method, and service play a role;
- methods of advertising products have significant differences;
- Market research focuses on product features, competitive advantage, and other factors.
Tools
Let's look at the most effective marketing tools that can be used in any organization.
Product policy
This tool is based on the following principle: you need to produce what is in demand on the market, and not try to sell what is already perceived by the consumer as “ordinary”. The category of product policy includes such levers as:
- products;
- package;
- trademark;
- customer service.
Using these levers, you can create the perfect tool that applies exclusively to your company.
Price policy
The pricing policy includes such levers as pricing, the formation of a customer loyalty system, and a product/service cost strategy. The pricing process depends on many factors, including costs, expenses and risks. Properly placed levers help optimize the cost and make it comfortable for both the seller and the buyer.
Sales policy
Includes activities carried out to support sales and guarantee high quality service. Sales policy, most often, is considered in a very broad sense, however, in simple words, it is simply the process of delivering a product/service from the seller to the buyer.
Communication
Communication policy solves problems related to the promotion and promotion of a product/service. Promotion is the cumulative actions taken by a company to inform customers to further their purchases.
The role of marketing in a company's work
The activities of the manufacturing marketing team are aimed at researching the market to determine the type and quantity of the product that will be in demand among consumers, further developing a plan and choosing a strategy to achieve large sales volumes in order to provide the company with a given profit.
Essentially, the marketing department is the nerve center of the enterprise. And it is on him that the coherence and productivity of the production, research, marketing, legal, and financial departments of the enterprise depend.
Thus, identifying the magnitude of predicted demand is the basis for sales planning, which determines the amount of work for the production department. Consequently, based on these data, the enterprise’s need for the purchase of raw materials is determined, which affects the interaction with suppliers.
Regular analysis of the work of the marketing team allows you to timely find weaknesses and change the strategy, which will lead to a more advantageous position. If you imagine that there is no marketing at the enterprise, it is not difficult to predict what problems the company would have to face - from financial to organizational difficulties.
General concept of marketing
Of course, marketing is a market, but some are still blindly convinced that all success lies in distributing leaflets, advertising on television and holding promotions in supermarkets. At the same time, marketing represents a powerful theoretical and practical basis, where advertising is only part of the whole mechanism. Among its other important elements, it is necessary to mention knowledge in the field of economics, sociology, psychology, mathematics, and the media.
The marketing activities of every small or medium-sized business begin not with flyers, but with group discussions over ordinary sheets of paper, that is, with strategic marketing. It involves the exchange of ideas, heated discussion, testing the market, visualizing intentions, defining goals, choosing a strategy and concept.
Conclusion
For an entrepreneur, marketing is a way of planning the success and prosperity of your own company. In this area of business there are no universal “recipes for everyone”; there is no point in following the prescribed rules. In each case, you need to show imagination and creativity to win the trust of customers. Remember, there are no bad products, there are sellers who don’t know how to sell. By developing an optimal marketing strategy, you can remain competitive for a long time and receive a stable income.
Does the product need marketing? How do you think? Write your opinion in the comments and don’t forget to rate the article!
Rate this article:
[Total: 7 Average: 4.7/5] (Article Rating: 4.7 out of 5)
Author of the article Victoria Pchelinova Freelancer, creative and business
Marketer in simple words
Marketer - what kind of profession is this? Every marketer has habits. It's not easy work, but by following a few habits you can become an instant rock star. Start your marketing with a buyer persona.
Who is a marketer and what does he do? What should a marketer do?
Like copywriting, marketing can seem confusing from the outside. Those who have not been in the marketing industry may not see the full picture. For this reason, marketers are often confused with crazy advertisers, or considered the arts and crafts division of the sales department.
But don't worry. This article is to enlighten and prove once and for all to everyone that marketing serves a purpose.
Let's take a look at what a marketer does and doesn't do.
Top 8 books about the marketing profession
- Hacking Marketing. The science of why we buy. Author: Phil Barden. I put this book first because it changed me forever. This book will take you beyond the client into the mind. A must read! Liters rating 4.53.
- 100+ Hacks for Internet Marketers: How to Get Traffic and Convert It into Sales. Authors: Evgenia Kryukova, Denis Savelyev. Rating 4.13.
- Marketing from A to Z: 80 concepts every manager should know. Author: Philip Kotler. This is the book you need to start immersing yourself in the world of marketing. By the way, I didn't read it :). Rating 4.30
- Marketing 100%: remix: How to become a good marketing manager. Author: Igor Mann. Rating 4.13
- Marketing without a budget. 50 working tools. Author: Igor Mann. Rating 4.18
- The whole truth about marketers, or Marketing as it is. Author: Lyudmila Afanasyeva. Rating 3.80
- How brands grow. What marketers don't know. Author: Byron Sharp. Rating 4.04
- Ideal Marketing: What 98% of Marketers Forgot. Author: Neeraj Dawar. Rating 4.13
If I missed any book, please write in the comments. In general, it is better to study at specialized courses, but be careful, in most places they stupidly pour water and give you outdated and primitive information for a lot of money, various info-businessmen, trainers and other “trainers”.
Modern marketer – who is this in the simplest words?
If you think that a marketer is a person who gathers focus groups, conducts various marketing studies on real people, shows them product samples and asks them what color product they would be more willing to buy, then you are... partially right.
This is how marketers most often worked in the past. But modern realities dictate new requirements. And today marketing is a completely different area of activity.
Relatively speaking, marketing is one of the most important parts of sales in a company. The entire sales process is divided into 2 stages:
- Attracting potential buyers (this is actually called marketing);
- Sales (this is when we take a potential buyer and turn him into an actual buyer).
A marketer today is a person who attracts the target audience. Compared to hunting, marketers are beaters. And the sellers are the ones who pull the trigger.
An example of how a marketer works today
Let's say a company sells snow to Eskimos. Kidding. Let our company sell cellular services and mobile Internet.
As a marketer, you will need to make sure that as many people as possible know about your offers. Roughly speaking, you will work with advertising.
Your director tells you that the company's brand is aimed primarily at a youth audience. Because your services are “cheap and cheerful”, and your target audience is young people and girls aged 18 to 25 years.
Great. Now you figure out where the best place to advertise your offer is, and how best to phrase that offer:
- At the entrances
- In the elevators
- On billboards
- In VKontakte groups X, Y and Z
- On leaflets in student canteens;
- In entertainment centers and cinemas;
- And so on and so forth...
There the guys will see your offers and call your good sales colleagues. Their task will be to properly process the incoming call so that the potential client you attract becomes a real client.
In other words, a marketer is not formally involved in sales. But in essence, what he does greatly influences the final result in the form of fulfilling the sales plan. Therefore, at sales planning meetings you will be asked no less than sellers (and maybe even more).
By the way, what will they even ask you to do, and what kind of salary will they pay for it?
What is the salary of a marketer and requirements for the candidate?
If you open the Yandex.Work service right now and find marketing vacancies in your city, you will see that the requirements for candidates are very different.
Here, for example, is a vacancy from one mobile operator that targets a youth audience (what a coincidence).
Here we see a lot of scary and incomprehensible words:
- “Distribution of quotas by segment programs...”
- “Escalation in case of channel failure...”
- “Initiating download plan optimization...”
To be honest, I would personally tear off the hands of anyone who writes such advertisements. But the fact is a fact - there are many requirements and they are not always clear.
Some require the ability to master Excel and special analytical programs. Some people need SEO and contextual advertising specialists.
The salary is most often not indicated or is indicated very modestly - slightly above the regional average. You may be asked to have one or five years of work experience. Somewhere you need a higher education (specifically marketing or economics). And somewhere the good old “desire to actively work and earn money” and “desire to develop” is enough.
In short, the picture turns out to be very motley.
Of course, the work of a marketer greatly depends on the specifics of the company. But there is one general requirement that is repeated in all advertisements. This is something you definitely need to have and be able to do if you want to work as a marketer.
The main requirement for a marketer
If we discard all the tinsel with which they like to fill job advertisements, then the bottom line is that we get the ability and love to work with numbers.
A marketer is 90% an analyst. By the way, this is exactly what this position is called in many companies. You need to be able to work with a large amount of digital data, analyze indicators, compare results, and draw logical conclusions.
In other words, if you are a humanitarian to the core, then it will be difficult for you to be a marketer.
Below we will talk about where to start if you have seriously decided to become a professional marketer. For now, let's look at another important issue.
What is the salary of a marketer and what do they pay for?
As I said above, a marketer is a person who is very closely associated with sales. Your work will determine how many applications sales managers receive per day, what the quality of these applications is, and, as a result, how much money your company will earn per day/month/quarter.
Accordingly, there is good and bad news here. Bad - they will put a lot of pressure on you and demand specific results. Being a marketer is not just about “let’s repaint our banners green because it sells more, according to the latest research.”
You will have a strict budget for various experiments, and you will have to report on where everything was spent, and what result it gave.
Good news about salary
The good news is that, like all sales people, a marketer has virtually no limits to growth. If you produce real results, they will be willing to pay you more and more. Just to avoid losing such a valuable employee. You yourself know that very often there is a situation when a good sales manager earns more than the general director. It's the same here.
Another thing is that for this you really have to work first. So don’t be afraid that you won’t be offered a huge salary right away. Let this be the average level for your city. But when you learn to attract a truly powerful flow of clients to your company, your premiums and rates will increase.
One of my friends, who worked as an Internet marketer, earned 200-300 thousand a month. And he did not work in Lukoil or Gazprom. True, it was in Moscow. But even for Moscow this is a very high salary. He reached this level after about 5 years of hard work. Agree, not so long.
So that you can better understand what awaits you if you get a job as a marketer, here is a short sketch on this topic.
Secrets of a successful content strategy
One of the important conditions for successful marketing activities is building an effective content strategy. Bill Gates also said that “content is king.” According to modern research, it was found that 82% of top marketers consider quality content to be the main factor in effective product promotion. Indeed, it is difficult to overestimate the importance of quality content when building relationships with your audience. In this case, the statement of the Strugatsky brothers is true that: “You should write either about what you know very well, or about what no one knows.”
What is content and how to build a strategy for its creation? By content, we mean any text, graphic, audio and video materials about the company, its products and proposed solutions. The fundamental principles when creating content should remain the reliability and usefulness of information for the audience. And when developing a content strategy, we must consider:
- Interests of our audience;
- Communication channels used;
- Material format;
- Stylistics of presenting information;
- Structure and ease of perception;
- Sequence of publications;
- Relevance.
Internet marketer - who is he?
Who is an Internet marketer?
In short, then: An Internet marketer is a specialist who attracts customers from the Internet. Sounds confusing, right? Ok, let's look at an example:
Imagine that there is some kind of online clothing store. Initially, no one knows about this store and, accordingly, will not find out until the store starts advertising and actively publishing on the Internet, communicating with users.
The owner of the online store himself physically cannot manage 100,500 things to do, so he hires an Internet marketer who will develop his business on the Internet.
The Internet marketer, in turn, comes up with a strategy for promoting an online store, works out a sales funnel and begins to connect various advertising tools to generate traffic.
It is clear that this specialist also cannot break into all directions at once, so usually other specialists are hired to help him (copywriters, targetologists, SMM specialists, directologists, etc.), who deal with one separate channel for attracting traffic.
To summarize: An Internet marketer is a specialist who helps promote a customer’s business on the Internet using various advertising channels, tools and methods. In most cases, a marketer comes up with a business promotion plan, receives a budget and other specialists (copywriters, targetologists, SMM specialists, etc.) for this plan and makes sure that these specialists fulfill the plan.
Marketing Models
Let's start with the most common one, which everyone is talking about, on the coordinates of which much is built, and this is the 4P model.
Four P model
It was founded by Theodore Levitt, an American economist and professor at Harvard Business School. Why is it called that? It is logical that all words begin with the letter P and let’s decipher them:
| Product | Place | Price | Promotion |
| Product | Place | Price | Promotion |
We’ve sorted out the definitions, but why is such a system of four Ps needed?
The model will help to analyze the four parameters of the company's work and helps to identify strengths and weaknesses and direct the company's marketing policy in the right direction.
Product – the product range must be balanced. Ask yourself the question: are all the products of your enterprise really needed, which ones and how many. What functionality, warranty, design, brand, reliability, quality, size are the indicators that need to be analyzed. The Product sector answers all these questions.
Place – well-calculated sales of products is the basis for the success of product distribution. The consumer must receive the goods in a comfortable place, in a place that is comfortable for him, quickly and efficiently. The more optimal the sales channels, the more the costs of organizing sales are reduced. By the way, it is at the Place stage that many organizations sag or at least have problems with it. The question immediately arises: will there be product distribution through intermediaries or an independent call, how many channels need to be used and we must not forget about merchandising, that is, the proper display of goods on the shelf, because this moment has a strong influence on whether the consumer will buy the product or not even pay attention.
A few words about the price. Let's look at what the price tag consists of. From the costs of the manufactured product, the volume of planned profit, the psychological factor. You can stop at the average price in the market, or you can stop at the segment of noble quality and service, or sell cheaper. To understand whether it is worth reducing the price of a product, it is necessary to conduct a survey among buyers about how many goods they are willing to buy at different cost levels.
Promotion - this part of the coordinates will tell you about the product, show you, depending on the product, let you taste it, try it through different information channels. As for the methods, marketers are running wild: sales, promotions, etc.
Model 3M
It consists of three words according to the same logic as the four letters P. The model is divided into three components: market, message and channel. If you look at the original, it’s market message media.
Model 3M
The market is all the company’s clients and potential ones too.
The message is the information that the organization intends to convey to the target audience.
A channel is the medium through which an organization will send a message to the market.
And thus we can build a logical chain: A competent message - in a competent way - to competent people.
PEST analysis
This is a marketing tool designed to identify political, economic, social and technological aspects of the external environment that affect the company's business. It is used to analyze the external and macro environment of the organization. Such analysis is a long-term planning tool. They are always drawn up for 3-5 years, but no more, then they are updated. The point is to identify how resources are distributed at the state level according to the factor-enterprise scheme.
SWOT analysis
This is a method of strategic planning, it identifies factors of the external and internal environment, here SWOT is divided into four components, yes, again an abbreviation, again decoding.
SWOT analysis
S – strengths, W – weakness. Here, strengths are identified, factors in the internal environment of the object being studied are identified, which the object itself is likely to influence.
O – opportunities, T – threats. Abilities and threats - here, on the contrary, environmental factors come into play, what influences the object from the outside, this also applies to threats.
Porter's 5 forces
Let's move on to the five great powers of Porter, not Potter!
Unlike SWOT analysis, which is not able to see special cases, this analysis can identify them. To be honest, in a matter of hours the analysis helps to understand the level of economic competition and tells you how to avoid it.
Porter's 5 forces
The model is based on the theory of Michael Porter, who says that there are 5 forces that determine market potential. Porter called the forces under pressure and if these criteria are not taken into account, the risk of falling down in a competitive environment looms. Let's take a look at the filling itself:
1. Buying pressure;
2.Supplier pressure;
3. Pressure from existing competitors;
4. Pressure from new competitors;
5. Pressure of new substitute products.
Porter seems to be hinting with his model: the less pressure from the outside, the more we earn. That's all the magic.
The final model is the BCG matrix
A tool for strategic analysis and planning in marketing. And here it’s even more interesting: the model contains a quartet of non-standard names for product classification.
The final model is the BCG matrix
1. "Stars"
Companies shine, the bourgeoisie flourishes when a product has a high growth in sales volume and market share. It is important to preserve and increase part of the market. Stars bring a very high income, but even if the product is attractive, its net cash flow is quite low because it requires significant investments to ensure a high growth rate.
2. "Cash cows"
In this case, the products also have a huge market share, but there is a low sales growth rate. Such friends need to be protected and taken under maximum control. Their charm is that they do not require additional investments and at the same time provide a good cash income.
3. "Dogs" or "lame ducks"
I would like to say stooped dogs, but we can do without it, they already have a bad life. There is nothing to boast about here, the growth rate is low, the market share is also low, and the product has a low level of profitability. Such a product requires a lot of attention and needs to be gotten rid of.
4. "Wild Cats"
These guys have low market share but high growth rates. These guys need to be studied. Their prospects are ambiguous and it is unknown how the card will fall; they can become both stars and dogs. If there is a possibility of transferring to the stars, then you need to invest, and if not, get rid of it.