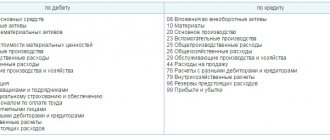
Active passive accounts examples
Account 71 is used primarily for settlements with persons to whom funds are issued on account. This category includes enterprise employees purchasing goods or services for business needs, as well as business travelers. As a rule, we are talking about relatively small amounts.
After a company employee spends the money received, he is obliged to report to the accounting department. For this purpose, receipts for hotel accommodation, air, railway and other tickets, as well as receipts for the purchase of goods are submitted to the financial department. All documents are submitted in the form of an advance report.
Using account 76
Accounting on account 76 is carried out in the event of situations not described in the explanation to accounts 60-76. Such operations usually include settlements of issued and received claims and insurance amounts. This account is also used to record deductions in accordance with judicial, executive and other administrative documents.
Let's look at typical wiring:
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 76.01 | 44 | Selling expenses incurred in connection with the insured event are written off | Insurance contract |
| 76.02 | 60 | The amount of the claim due to the fault of the supplier is taken into account | Claim |
| 76 | The amount of funds due to the employee from other organizations is taken into account | Performance list | |
| 58 | 73.03 | Securities were capitalized as dividends | Minutes of the board's decision |
| 66 | 76 | The loan was repaid by offsetting similar claims | Loan agreement |
Active and passive accounts
In general, active-passive accounts reflect accounting transactions not only with individuals, but also with organizations for which accounts payable and receivable are kept.
An enterprise that uses borrowed or borrowed funds in its activities forms its accounts payable to individuals and organizations at their expense. In this situation, the mentioned counterparties act as creditors.
When individuals or organizations owe a certain amount back to a company after a predetermined period, it is called a receivable.
Types of actively passive accounts
The most common among active-passive accounts:
- 99 – Profits and losses
- 91 — Other income and expenses
- 90 - Sales
- 76 — Settlements with various debtors and creditors
- 62 – Settlements with customers
- 60 — Settlements with suppliers.
But how to determine what function the account currently performs - passive or active?
Imagine that, based on documents, the fact of sale of goods in favor of buyers is recorded. Based on this event, accounts receivable appear, which are included in the group of enterprise assets. The occurrence of such debt is recorded in the debit of 62 accounts, and after its repayment the amount will be transferred to credit. If the addition of an asset is shown as a debit and its decrease is shown as a credit, 62 shows signs of an active account.
- Active;
- Passive;
- Active-Passive.
Active accounts are accounts in which the assets of the enterprise are recorded.
Their opening and closing balances are always debit, the debit reflects an increase in the asset of the enterprise, and the credit a decrease. The main active accounts include:
- 01 Fixed assets;
- 04 Intangible assets;
- 10 Materials;
- 20 Main production;
- 43 Finished products;
- 50 Cashier;
- 51 Current accounts;
- 52 Currency accounts;
- 58 Financial investments;
Passive - accounts that take into account the liabilities of the enterprise, that is, the sources of formation of assets. The opening and closing balances of passive accounts are always in credit. Their distinctive feature is that an increase in liabilities is reflected as a credit, and a decrease as a debit.
The main passive accounts include:
- 60 Settlements with suppliers and contractors;
- 66 Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings;
- 67 Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings;
- 68 Calculations for taxes and fees;
- 69 Calculations for social insurance and security;
- 70 Settlements with personnel for wages;
- 80 Authorized capital;
- 82 Reserve capital;
- 83 Additional capital;
- 99 Profits and losses.
Active-passive - accounts that take into account both the assets of the enterprise and liabilities. They usually have both a debit balance and a credit balance.
The main active-passive accounts include:
- 71 Settlements with accountable persons;
- 75 Settlements with founders;
- 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors;
- 99 Profits and losses.
HOW TO DISTINGUISH ACTIVE OR PASSIVE ACCOUNT IN ACCOUNTING?
Let’s carry out an analysis and find out how you can determine whether an account is active or passive.
Is count 62 active or passive?
This account reflects relationships with customers. When a product is sold to a buyer, the latter incurs a debt to the organization, which we will reflect in debit 62. Accounts receivable is an asset of the enterprise, that is, an increase in the asset is reflected in the debit.
When paying for goods, the debt decreases; we will reflect the decrease in the asset on credit 62. At first glance, 62 is an active account, since it is characterized by the characteristics of active accounts.
However, a situation is possible when the buyer transfers an advance payment (prepayment), in this case the organization accounts payable to the buyer (liability), it will be reflected on loan 62. After the goods are shipped to the buyer to offset this advance, the accounts payable decreases, we will reflect the decrease in liabilities as debit 62. We see that in this case the account. 62 fits the definition of passive accounts.
From all of the above, we can draw the following conclusion: count. 62 corresponds to the characteristics of both active and passive accounts, that is, it is active-passive.
You can also take 60 “Settlements with suppliers”. Is 60 account active or passive? Having analyzed it similarly, we conclude that the count. 60 is also active-passive. Accounts can also be divided into synthetic and analytical.
Accounting also uses synthetic and analytical accounting
Synthetic accounting is the recording of generalized accounting data on types of property, liabilities and business transactions according to certain economic characteristics, which is maintained on synthetic accounting accounts.
Analytical accounting is accounting that is maintained in personal and other analytical accounting accounts, grouping detailed information about property, liabilities and business transactions within each synthetic account.
Relationship between synthetic and analytical accounts
- The opening balance for all analytical accounts opened according to the synthetic account data is equal to the opening balance of the synthetic account to which they are opened;
- The turnover of all analytical accounts opened using the synthetic account data must be equal to the turnover of the synthetic account;
- The final balance for all analytical accounts opened for this synthetic account is equal to the final balance of the synthetic account.
Groups of analytical accounting accounts are called subaccounts. A subaccount is an intermediate accounting link between synthetic and analytical accounting accounts.
For example, our company purchases materials in the form of products: flour and sugar, and we want to keep separate records for each type of material.
In accounting, we open a synthetic account. 10 “Materials” and to it two analytical ones “Flour” and “Sugar”. Moreover, on a synthetic account. 10 flour and sugar will be accounted for in rubles, and in analytical ones they can also be calculated in other quantities (pieces, kilograms, tons), as will be convenient for the accountant.
Which accounts are passive and which are active?
When working with active accounts, transactions to increase the asset are recorded in the debit part. In the same part, the final balance of the selected account at the end of the reporting period is recorded, if there is such a balance. If the transaction caused a decrease in the asset, it is recorded in the credit column. In general, active accounts are used to record the organization’s property, which includes goods, materials, equipment and cash.
Passive accounts display the change, movement and status of the company’s sources of funds, i.e. accounting of all events occurring on them.
Definition and structure of the concept of “account” in accounting
Definition 1
An account is a form of economic grouping of business transactions that allows for ongoing monitoring of the movement and condition of the enterprise’s economic assets, as well as the sources of their formation.
In accounting accounts, business transactions are grouped according to accounting objects. The purpose of this grouping is to obtain information about the movement and actual presence of these objects.
It is convenient to represent the account in a T-shape, the left side of the ledger is called a debit, and its right side is called a credit.
The state of the business entity being accounted for at the beginning of the study period is called the opening balance in accounting terminology. The state of the object at the end of the period under study is the final balance.
The total value of entries in the debit of an account or in its credit is called debit or credit turnover, respectively.
Each account in the accounting system is designed to reflect a specific object or sources of its formation.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Passive accounts 490 rub.
- Abstract Passive accounting accounts 230 rub.
- Test work Passive accounting accounts 210 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
The difference between an active account and a passive one
The main difference is the nature of the balance. In addition to the company’s property, active accounts reflect its rights to claim receivables, which are registered with certain individuals or legal entities. The balance of active accounts falls into the “Asset” balance column.
Passive accounts serve to record the organization’s obligations and record all events related to the movement through sources of increase or decrease in the enterprise’s property. The balance on such accounts falls into the “Liability” balance sheet column.
The balance on active-passive accounts has an expanded form in the balance sheet - an asset is recorded as a debit, and a liability as a credit.
Advice from Sravni.ru: Let's summarize. Active-passive accounts record the settlements of our enterprise with legal entities and individuals. If they owe us, this is an asset, the transaction is recorded as a debit. If we owe is a liability, the result is recorded in the credit column.
Postings to account 68
Analytical accounting is carried out for all types of taxes. The correspondence of account 68 depends on the nature of the operation, as in some cases account 68 is characterized - active or passive. So, debit account. 68 is formed in the following cases:
- When paying to the budget - Dt 68 - Kt 51.
- If there is “input” VAT - Dt 68 - Kt 19 - deduct VAT for goods and services received.
For a loan, account 68 in accounting entries can generate the following:
- Dt 99 - Kt 68 - calculation of income tax;
- Dt 91 - Kt 68 - reflected VAT on sales for other (non-core) activities;
- Dt 90 - Kt 68 - VAT is included in the cost of the goods;
- Dt 70 - Kt 68 - personal income tax is charged when calculating wages, account 68 is used. 1.
When offsetting tax liabilities, the posting will look like this:
- Dt 68 ― Kt 68, according to count. 68 subaccounts will correspond to the types of taxes that are involved in the transaction. Tax crediting is carried out if there is confirmation from the tax inspectorate within the budgets of one type (federal, regional, local).
Example 1
Salary accrued in the amount of 45,000 rubles. Withheld and transferred to the personal income tax budget in the amount of 5850 rubles. To reflect personal income tax in transactions, account 68 1 is used:
- Dt 26 - Kt 70 - 45,000 rubles - wages accrued;
- Dt 70 - Kt 68 1 - 5850 rubles - personal income tax withheld;
- Dt 68 1 - Kt 51 - 5850 rubles - personal income tax is transferred to the budget.
Example 2
Goods were purchased for the amount of 47,200 rubles, including VAT 18% 7,200 rubles. Products worth 88,500 rubles were manufactured for sale, including 18% VAT of 13,500 rubles. It is necessary to transfer tax in the amount of 6,300 rubles to the budget. VAT is reflected as 68 subaccounts 2.
- Dt 26 - Kt 60 - 40,000 rubles - goods from the supplier have been received;
- Dt 19 - Kt 60 - 7200 rubles - “input” VAT is reflected;
- Dt 62 - Kt 90 - 88,500 rubles - sales of products to the buyer;
- Dt 90 - Kt 26 - 75,000 rubles - reflects the cost of goods sold excluding VAT;
- Dt 90 - Kt 68 2 - 13,500 rubles - VAT is charged when selling goods to customers;
- Kt 68 2 - Dt 19 - 6300 rubles - the amount of VAT payable.