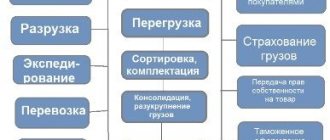
In the article we will analyze what it is - warehouse logistics, and give a clear definition of the concept. This is the basis for the correct and successful operation of any large production or trading enterprise. Without safe storage, distribution and timely delivery of products, their normal functioning is impossible. At the same time, it is extremely important to adhere to a certain order and fulfill specific conditions. We’ll talk further about how to organize the most efficient process, successfully automate and optimize it, as well as what principles to adhere to when conducting business.
Basics of warehouse logistics
Compliance with the terms of the concept means that a trading or manufacturing enterprise has a separate premises in which storage and distribution of goods are carried out with their subsequent transportation to the place of sale. This means that the main task of warehouse workers is to constantly accumulate stocks and supply them to consumers when they receive a request.
Naturally, at least 3 rules should be followed:
- Ensure that requested products are always available in sufficient quantity.
- Ensure their normal storage to ensure high quality products.
- Timely transfer to the place of subsequent sale.
Only in this case can you set up efficient work, avoid delays in deliveries, and save money at the same time.
Business Solutions
- shops clothing, shoes, groceries, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
Warehousing logistics functions
The functionality of the warehouse premises is very high. Its main tasks include:
- Formation of the assortment in such a way that there is no shortage or excess of any items.
- Creation of not only small, but also large quantities of goods, allowing simultaneous servicing of several companies and stores.
- Proper placement and storage of all incoming cargo.
- Unpacking, packaging, product assembly and other services that allow you to organize fast and efficient work.
In this case, all of the above actions are carried out simultaneously with several flows of cargo; as an additional function, one can highlight the distribution of time and labor.
Warehouse management information systems
In order for the warehouse to operate quickly and efficiently, various information systems can be introduced into its operation.
WMS (Warehouse Management System) is a warehouse management system that involves the use of automatic identification technology for targeted storage and remote management of employees. With its help, the influence of the human factor on warehouse processes is significantly reduced, and the speed of order fulfillment and the accuracy of data on stored products also increases. The operator receives a task from the system where the cargo needs to be moved or where it needs to be picked up. Using barcoding, information is entered into a database, where it then becomes clear where the pallet has been moved, what is on it and in what quantity. The most frequently turned or used items are placed on the closest shelves for quick removal from storage areas at the required time. Heavy and infrequently used materials are distributed to the high and low areas of the warehouse storage area.
There are 3 main types of WMS systems:
- Systems with a set of standard options, without additional services. They are usually used by small companies.
- Systems created to order in accordance with client requirements. Such systems are aimed at large warehouses with complex technology for performing operations.
- Adaptable systems aimed at large and medium-sized companies that own warehouse complexes with complex technological processes.
Automating a warehouse using a WMS system is a serious issue that requires a very responsible approach. Only adaptable systems are able to adapt to new user requirements. If there is a need to use additional functions of the WMS system (for example, the spy function allows you to see from the office at any time what a warehouse employee is doing using CCTV cameras), companies that purchased the basic version are forced to buy a new one, because This version cannot be updated or expanded. As a result, a huge amount of money is lost, which the resulting savings cannot cover. The occurrence of such situations implies that warehouse logistics is not working efficiently enough.
What kind of logistics warehouses exist?
All premises used for storing products can be divided according to their main purpose:
- Transit and transportation points where cargo is stored for a limited time between delivery to a seaport, railway station or airport and its final destination.
- Customs, where the goods are stored until they are inspected by customs.
- Seasonal storage.
- Reserve – used if delivery to the main warehouse is impossible for some reason.
- Wholesale and distribution rooms are the most popular premises used by large suppliers of products to stores.
- Retail – the last storage facility located directly at the point of sale.
It is possible to divide logistics premises according to storage conditions, type of construction and some other features, but one way or another, they will all be part of the general classification.
Warehouse classification
The classification of warehouses depends on:
- Type of product (warehouse of waste, tools, materials, components, raw materials, finished products, containers);
- The relationship of the warehouse to the links of the logistics chain (warehouse of intermediary, forwarding, transport, trade organizations, manufacturers, intermediaries);
- Forms of ownership (production supply warehouse, distribution, seasonal storage);
- Functional area of logistics (warehouse production, sales, supply);
- Type of warehouse buildings and structures (open area, area under a canopy, closed structure, multi-story, high-rise);
- Degrees of technical equipment (partially mechanized warehouse, mechanized, automatic, automated).
Work carried out in the warehouse:
- Division of the warehouse into zones (storage of products, equipment, acceptance, preparation, temporary storage) for the most efficient use of the available limited warehouse area, eliminating the confusion of main and auxiliary processes;
- Acceptance, shipment, repackaging, labeling, additional assembly, preparing cargo for shipment, storage, creating an assortment for shipment, ensuring uninterrupted production.
Principles of organization
As stated earlier, the main task of warehouse logistics is solved in compliance with certain norms and rules. They allow us to build not only an effective, but also a cost-effective process.
How many warehouses are needed?
The first step is to determine how many rooms will be needed to build an efficient operation. Here you should find a middle ground: their lack will require constant transportation of goods, which means transportation costs will increase, excess means money for maintenance, but does not increase income. A final decision can only be made after analyzing all aspects of the process.
Buy or rent storage
The next stage in the management and organization of warehouse logistics at an enterprise should be the acquisition or removal of storage facilities suitable for operation. In some cases, you have to resort to the help of outsourcing companies.
The first two options will most likely cost less, but business development will definitely go faster, because the entire process will be implemented in a way that is more convenient for the operation of a particular enterprise.
Outsourcing is more expensive, but at the same time it will improve the quality of logistics services. Most likely, this method will be profitable only when transportation costs are too high to be recouped in profit.
How to choose a warehouse services company
If the choice nevertheless fell on a specialized logistics service, it is necessary to choose the most suitable one from a huge number. It is important to pay attention to the following factors:
- Warehousing and logistics of the company must be united by a single information flow.
- Work must be carried out at high speed, and orders must be completed accurately and on time.
- It is better if the company has been providing services on the market for several years, which means it has extensive experience.
It would be useful if, in addition to the main service - warehousing, the organization provides additional opportunities to its clients: transporting cargo, dealing with customs issues, etc.
Warehouse location
Transportation costs depend on the location where the logistics center will be based. Accordingly, you will have to calculate from which part of the city you can quickly deliver goods to the place of sale without increasing the company’s expenses too much. It is better to consider suitable options from several companies, because in the end problems with rent may arise, for example, the most convenient premises will already be occupied or their cost will become too high.
Warehousing systems, cargo management methods
A warehouse in logistics is a place where a huge number of clearly defined actions are performed. It all starts with choosing a specific cargo unit in which the goods will be stored (pallets, box or tank, depending on the type of product).
Then, in accordance with it, the storage method is selected. Pallets and boxes can be stacked on top of each other, boxes can be placed on shelves. It is important to make the most of available space while ensuring staff access.
All cargo can be stored in accordance with its grade, batches, names and other methods. This sorting is designed to provide easy orientation in the warehouse.
Rational planning
Schemes for placing cargo in storage should be developed at the preparatory stage. At the same time, it is important not only to place the largest possible number of goods, but also to ensure easy access for people and special equipment. Otherwise, it will be impossible to care for the products, control their quality and free movement from the loading site and back.
It is important to place all products in a certain order. Those that are updated most often are in the part of the room closest to unloading. Rarely moved - deeper into the warehouse. The same principle should be followed in relation to perishable and durable goods.
Storage equipment
To increase functionality, it is necessary to purchase special equipment and technology. Mandatory items include racks and means that allow you to move cargo around the premises (forklifts). It is also necessary to take care of a normal ventilation system, fire safety, and alarm systems. All this will allow you to maintain the goods in proper quality.
Organization of information flow system
Here we are talking about maintaining documentation, including in electronic form. The appropriate software allows you to track the time of receipt of a specific batch of goods at the warehouse, its current location, and promptly dispose of cargo whose shelf life is coming to an end. Cleverence is developing mobile accounting systems. The company will help you choose the appropriate option, taking into account the needs of your company.
Recruitment
The number of employees is determined by the size of the storage facility, but usually among them there are: premises manager, accountant, storekeeper, loaders and forklift operators, packers or sorters, labelers, security service.
Activity control and inventory management
It is necessary to monitor the work of the logistics department according to several indicators:
- How often applications are submitted, how long it takes for them to be processed and executed.
- What volume of cargo is regularly received at the warehouse and whether all of it reaches the place of final sale.
- At what level is the stock of goods kept?
If all operations are carried out quickly enough, and the cargo does not stay in the premises and reaches the customer and consumer in a timely manner and in proper quality, then management efficiency can be considered high.
WMS storage management systems
As mentioned earlier, the influence of the human factor on the operation of a storage room is enormous. To minimize it, you can use the Warehouse Management System. This system allows for remote control through automatic identification. At the same time, the speed of processing and fulfilling applications is significantly reduced, and the efficiency of operations increases.
What is warehouse logistics and how to manage a warehouse
A warehouse is an indispensable thing for storing products from both large manufacturing companies and small organizations whose activities are aimed at selling goods. It is the basis of the entire trading process. Every company needs inventory as demand fluctuates and delivery takes anywhere from hours to months. That is why a company needs inventories that need to be kept somewhere. The organization and management of a warehouse must be approached consciously and thoughtfully in order to further ensure the efficient operation of the enterprise and the sale of goods.
However, the presence of a warehouse raises many questions for many. It is believed that a warehouse is an expensive pleasure. This is either payment for rent, or maintenance and repair of your own. It is necessary to assemble equipment: racks, shelves, lifting mechanisms. And also take into account the fire safety system. On top of everything else, the payment of service personnel - warehouse workers - is added. These are mandatory expenses, and the warehouse operation is almost the majority of the activity.
Despite all this, a warehouse is an irreplaceable and necessary thing. It is necessary so that the necessary product can be provided to the consumer at any time. It is effective if there is a turnover of goods, and balances are strictly controlled and recalculated. This is a place for receiving, unloading and loading goods, inventory, and placement.
It is needed for storing dry substances, fruits or vegetables, fish products, canned food, semi-finished products or frozen products. And each type and type of product requires its own warehouse, which takes into account the specifics of the business. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully select the premises, because rebuilding it or completely changing the scope of business is quite expensive and labor-intensive.
Maximum profits and minimum losses are possible only if the warehouse is equipped, its transport system, personnel qualifications and, of course, the turnover of goods. And warehouse logistics is responsible for managing the enterprise’s inventories and their distribution, which closely interacts with transport logistics.
Warehouse functions
The warehouse performs many functions, but the main ones are the following:
- creating an assortment in accordance with consumer needs - purchasing and production logistics are responsible for this. They provide the enterprise with resources at all phases of production. Distribution logistics studies customer requests and forms a production range on this basis. This contributes to the efficient fulfillment of orders and regular deliveries in the required volume
- storage - reduces the difference between production, release and consumption. This allows you to create a continuous production process and work with consumers. Particularly useful if the consumption of certain goods is related to the season of the year
- unitization and transportation of goods - allows you to combine small deliveries of goods for several clients until the vehicle is fully loaded in order to reduce transport costs
- provision of services - to ensure a high level of service, it is possible to provide customers with additional services, such as preparing goods for sale, checking functionality, installing or dismantling equipment, making it look marketable, etc.
Logistics in general is responsible for managing food and material and technical bases. Logistics flows are responsible for the directed movement of any product in space in a specific period of time.
Consider the following categories of flows in logistics:
- material - it includes material resources, work in progress, finished products at the movement stage. This is the process of transition from producer to consumer, movement in space and time. In this case, material flows are considered from the point of view of belonging to the enterprise, assortment, type of transportation, specific gravity of the cargo, its consistency and compatibility with other supplies.
- financial - responsible for the functioning of the logistics system. Responsible for moving a certain amount of material and intangible resources. This also applies to the movement of fixed and working capital. They determine the purchase of goods, the reproduction of labor, the movement of financial resources
- informational - inseparable from financial and material flows. And they are necessary to manage the latter.
There is also an activity approach, according to which flows are characterized by services provided over a certain time. Flows represent the scope of activity to meet needs: transport, consulting, information and others. Such flows are responsible for the arrival of goods, the length and trajectory of movement, speed, time and intensity.
Logistics flows are also divided into:
- incoming - these include cargo arriving at the warehouse and subsequent work with it
- internal - movement of goods in the warehouse
- outgoing - comprehensive preparation of products for shipment
What types of warehouses are there?
Warehouses, as an important element of the logistics system, are responsible for maintaining inventories. For each type of product there is its own type of warehouse that fully meets storage conditions.
Warehouses vary in size. There are both small rooms and special places with an area of several tens or hundreds of thousands of square meters.
Depending on the area of logistics, warehouses are distinguished:
- supplies
- production
- distribution
In relation to participants in the logistics system:
- manufacturers' warehouses
- warehouses of trading companies
- warehouses of transport companies
- warehouses of forwarding companies
- warehouses of logistics operators, etc.
Warehouses are classified according to their form of ownership:
- personal
- commercial
- rented
- state, municipal
By functional purpose:
- long-term storage - seasonal, reserve
- transit and transhipment - platform warehouses, cargo terminals
- distribution - distribution centers
- customs
Depending on the assortment:
- specialized
- universal
- mixed
According to the type of product, warehouses are divided into:
- raw materials
- materials
- components
- work in progress
- finished products
- containers
- residues and waste
- tools
According to storage mode, warehouses are divided into:
- heated
- unheated
- refrigerators
- with fixed temperature and humidity conditions
According to equipment technology:
- mechanized
- non-mechanized
- automatic
- automated
Depending on the type of warehouse buildings and structures, warehouses are divided into:
- open areas
- covered areas
- closed structures
- multi-storey
- one-story
- up to 6 m high
- high-rise under one roof
- high-rise
Depending on the material flow, warehouses are distinguished:
- open - for collective use
- closed - for one enterprise
Based on the availability of external transport links:
- with berths
- with railway tracks
- with road access
- complex
Logistics organization
Now it’s worth considering the organization of warehouse logistics, which takes place in several stages.
Stage 1 - choosing a room. First you need to find a place where the warehouse will be located. These can be rented warehouses or personal ones. Warehouses for rent are often equipped with everything necessary, when personal use requires repairs and equipment. It is also necessary to pay attention to the location of the warehouse and its volume. It shouldn't be too big or small. Let’s assume an option with several storage rooms.
Stage 2 - choosing a storage system. It is based on a group of goods that will be stored in the warehouse. The choice should be based on the storage location of the goods (boxes or boxes), equipment for lifting and transportation, storage method (blocks, racks, etc.).
Stage 3 - equipment of the warehouse. It is necessary to equip the warehouse in accordance with the following systems: communications arrangement, storage systems, ventilation or air conditioning, fire safety system, security alarm and video surveillance system.
Stage 4 - personnel selection and training (if necessary). The functioning of a warehouse requires highly qualified and trained workers. Their number depends on the type of warehouse and products and its volume.
Step 5 - launching the warehouse. The finished warehouse can be put into operation. However, it requires constant monitoring, analysis and adjustments.
Warehouse selection
Choosing a warehouse space is a big responsibility. The further activities of the organization depend on this step. When choosing, you should pay attention to the following parameters:
- building type
- flooring material, type of coating, thickness, etc.
- wall decoration, material
- ceiling height
- presence of heating or ventilation
- loading and unloading gates and related equipment
Please pay attention to the storage and loading conditions of the goods. Are the racks, pallets built-in or are they provided with fastenings?
Be sure to check the size of your entry gate. Are they suitable for loading operations, are access roads provided?
Assess the lighting. Some products do not allow natural light. Pay attention to the heating, cooling and ventilation system. Is there a fire protection system?
Is there a bathroom for workers, is there a utility room?
Evaluate the general appearance of the warehouse and repair work. Check the dimensions. A big advantage would be the availability of warehouse equipment.
Warehousing systems
The warehousing system refers to the placement of goods in a warehouse and its management. It is worth paying attention to the connection between incoming flows and internal ones.
To organize it you need to choose:
- folding unit - boxes, racks, nets, pallets or cassettes
- type of storage - selection of equipment on which the cargo will be stored, placement in space. For example, blocks or racks
- maintenance equipment - hoisting and transport machines and mechanisms
- picking system - cargo movement control - cargo technological equipment
- information processing - managing the receipt and dispatch of cargo, maintaining product databases, preparing documents, etc.
Warehouse equipment
To store goods in a warehouse, several types of equipment are used: technological, handling, weighing, and packaging.
Technological equipment includes:
- racks - there are shelf, box, frame, cage, rack, mechanical hanging racks. Serve for storing several or single items
- pallets - designed for forming cargo packages and transportation. There are flat, rack or box types.
- bunker devices - designed for storing bulk or bulk cargo. At the bottom there is a discharge hatch with a shutter
- bins - places for bulk cargo with a partition
- tanks - places for liquid cargo
Lifting and transport equipment is designed to facilitate loading and unloading operations. Divided according to the following criteria:
- functional purpose - lifting (cranes, elevators, winches), loading, unloading machines (electric or forklifts, stackers), transporting machines (trolleys, tractors)
- according to frequency of action
- type and physical properties of the cargo
Weighing equipment includes weight scales, scale-weight scales, automatic or semi-automatic, stationary or mobile scales.
Packaging equipment - automatic dispensers, ceiling lines, automatic stackers of goods in containers, nets.
Recruitment
The operation of even an ideally equipped warehouse is impossible without qualified and trained personnel. His choice should be approached responsibly and thoroughly.
The main employees of a warehouse are the warehouse manager, storekeeper and loader.
The warehouse manager is responsible for what is happening in the warehouse: documentation, receipt of goods, storage conditions, release to the consumer. It is considered a leadership position, for which a person with a higher or secondary specialized specialized education and work experience is suitable.
The warehouseman is responsible for the receipt and release of goods in the warehouse. Depending on the volume of the warehouse, there may be several of them. He must know the purpose, properties, features of storage, loading and unloading of goods. Suitable for people with specialized secondary or general secondary education.
A loader is needed in large warehouses where large quantities of goods are in motion. This is a performer subordinate to the storekeeper and warehouse manager. He is involved in loading, moving and unloading goods.
Also, accountants, drivers, labelers, and guards most often work in the warehouse.
When selecting employees, you need to pay attention to work experience in this field, reasons for applying for this vacancy, as well as level of education. A new employee must be registered in accordance with the Labor Code.
Using a WMS system
WMS systems can increase warehouse productivity by automating goods accounting, storage, inventory and other processes.
WMS is a warehouse management system that ensures automatic operation of warehouse facilities. It allows you to reduce the costs of managing warehouse operations.
Often WMS can solve the following problems:
- management of the process of receiving, packaging, loading goods
- calculation of options for shipping units and packaging of goods taking into account its size
- automatic document management
- personnel Management
The main advantage of this system is that it adapts to the characteristics of each business.
It can also increase the efficiency of warehouse operations:
- control over the quantity of goods and their placement
- increasing warehouse productivity, increasing turnover
- reduction of time for warehouse operations
- reduction in equipment operation: the system calculates more rational routes and paths for loading and other operations
- possibility of remote warehouse management
- automation of warehouses and food equipment
WMS systems are necessary in all areas where goods are accounted for and moved, since many management systems are carried out automatically: storage, reception and processing. It can also be used for accounting and document management. The choice of program depends only on functionality: for small companies a minimum set of functions is sufficient.
Monitoring warehouse operations and inventory management
Logistics warehouse optimization allows for proper management of goods in the warehouse.
The optimal inventory level is the average value between insufficient quantities of goods and excess quantities. In this case, each category of goods is considered separately.
Inventory management is carried out depending on:
- deadlines for applications and their execution
- economic volume of the batch
- inventory levels
Each warehouse determines its own type of system for promoting goods through distribution channels. It can be:
- pulling systems - shipment of goods depends on received orders
- push systems - goods are provided according to a predetermined schedule
- combined - there is a computer connection between the manufacturer and intermediaries, orders are received electronically
Innovative computer systems have greatly facilitated warehouse management, allowing remote monitoring of all ongoing processes.
Packaging orders
And the last thing I would like to discuss is cargo packaging. Without it, neither storage, nor transportation, nor subsequent operation is possible.
Packaging in logistics has important functions:
- protective - protection from the external environment during transportation and storage
- manipulation - universal shape and design for ease of transportation and loading
- informational - contains the name of the product, manufacturer, labeling, barcode, production date and expiration date
- recycling - is it possible to reuse the packaging, what are the conditions for its disposal?
Containers are also considered a type of packaging that prevents damage during operation, transportation, loading and storage. These can be barrels, containers, bottles, cans, etc.
They are divided according to the following characteristics:
- material: metal, glass, wood or combination
- Dimensions: small or large
- service life: disposable, returnable or returnable
- strength: hard, soft, semi-hard
- properties: sealed, non-sealed, temperature retaining
- access options: open, closed
- purpose: storage, transportation, for consumer use
Let's sum it up
The warehouse is intended for storing goods of an enterprise of any business sector that requires supplies. The organization and management of a warehouse must be approached consciously and thoughtfully in order to further ensure the efficient operation of the enterprise and the sale of goods.
Warehouses are needed for storing dry substances, fruits or vegetables, fish products, canned goods, semi-finished products or frozen products. And each type and type of product requires its own warehouse.
It allows you to create an assortment, store goods, unitize and transport cargo, and provide additional warehouse services.
Logistics organization takes place in 5 steps:
- room selection
- selection of storage system
- warehouse equipment
- personnel selection and training
- warehouse launch
When choosing a warehouse, you should pay attention to the building, floors and ceilings, walls, heating and ventilation, loading location and related equipment, storage conditions for goods, lighting. Don't forget about fire safety and security systems.
The warehousing system is the connection between internal and external flows. Involves product placement and management.
Warehouse equipment includes devices for storing goods, lifting and transport mechanisms, weighing and packaging devices.
Take a responsible approach to personnel selection: the quality of folding processes will depend on their work. For a small business, a warehouse manager, a storekeeper and a loader are enough. For large enterprises, accountants, drivers, markers, and watchmen are also needed.
Using a WMS system increases warehouse productivity by automating goods accounting, storage, inventory and other processes. They allow you to manage the process of receiving, picking, and loading goods, calculate options for shipping units and packaging of goods taking into account its size, automate document management, and manage personnel.
For storage, transportation and subsequent operation of cargo, packaging is required that performs protective, informational, and recycling functions.
What is packaging in warehousing logistics?
It would be impossible to move and store any cargo without proper packaging. Therefore, choosing the right container is also important for quality work. It must perform several basic functions:
- Protect the product from the influence of external factors and unfavorable environment.
- Withstand all transport manipulations, do not tear during loading and unloading.
- Contain information about the product.
- Be easily recyclable.
At the same time, its price should not significantly increase the company’s overall costs.
Services of a logistics warehouse for responsible storage of goods
The company provides custody services in Moscow and the Moscow region in the following areas.
Loading and unloading:
- Mechanical – for standard loads;
- Manual – for small and light loads;
- Unloading using special equipment or technologies for heavy and oversized cargo.
Storage in a warehouse complex:
- pallets - in standard cells on racks;
- small boxes and piece goods – storage in specially organized cells;
- oversized cargo – floor storage.
Standard Operations:
- acceptance of cargo, its recalculation, acceptance (processing) of goods, placement in the storage area;
- formation of orders for shipment, preparation of goods and relevant transport and shipping documents.
Accompanying services:
- weighing, measuring;
- piece count;
- sticker or other marking of cargo compliance;
- pre-sale preparation;
- rejection;
- packaging, container strengthening: palletizing, use of stretch film, lathing.
Cross-docking (for non-perishable goods):
- unloading goods, receiving cargo;
- placement in a dedicated express storage area;
- shipment, generation of accompanying documents
Modern logistics in Russia
The level of logistics services in our country is not yet high. There are too many obstacles preventing an efficient process. The main ones include:
- Lack of professional staff.
- Poorly developed infrastructure.
- Use of outdated technologies in work.
- Lack of proper knowledge and experience in the field of logistics warehousing.
But at the same time, the prospects for the development of the industry are high, since the demand for services is constantly increasing.
Functions
The main functions of a properly organized warehouse:
- acceptance and shipment of goods,
- processing, checking and sorting,
- optimal placement,
- secure storage,
- inventory control,
- proper execution of accompanying documents,
- disposal of scrap, etc.
One of the main tasks is to create optimal conditions for minimizing time and material costs for processing and processing cargo. Prices depend on the level of organization of the work process and the capabilities of the premises.
LIST Logistic warehouse logistics services have the following advantages:
- high quality of work performed;
- guarantee of product safety in secure storage warehouses;
- the opportunity to significantly expand the geography of activity;
- there is no need to look for qualified personnel or buy specialized equipment.
The disadvantages of cooperation include high cost and lack of prospects for the development of the enterprise.
Examples of warehouse logistics problems in the domestic market
In addition to the obstacles listed above, larger shortcomings also hinder the effective activities of logisticians. We'll talk about them further.
Lack of markings
Enterprises have not yet learned to assign a unique code to each unit of their goods, which means that later in the warehouse, it is much more difficult for specialists to identify them. This takes a lot of time and the work is done more slowly. But in recent years, the government has been actively developing legislation requiring labeling on all types of products. Some of them are already included in the group of mandatory markings, while others will be marked in the near future. This means that the problem will be solved by itself at the production stage.
Dilution of job responsibilities
In an effort to save money, managers of logistics companies shift too much responsibility onto one employee, while highly specialized personnel could work more efficiently without being distracted by additional tasks. This would increase overall productivity, and therefore increase the profitability of the enterprise.
Organization of work process in a warehouse
After preparing the premises, purchasing equipment, machinery and obtaining permission to put the warehouse into operation, it is time to recruit personnel, organize the operating mode, and develop appropriate management mechanisms and documentation.
Organization of the warehouse and its elements includes:
- determining the number of staff;
- development of job descriptions;
- hiring employees and management;
- choice of management strategy, including labor incentives and employee control;
- office work and document flow;
- development and fixation of internal regulations.
The personnel composition and its competence are of decisive importance in organizing the work of a warehouse in production. The job description must take into account the specifics of the warehouse's activities and contain requirements for skills and abilities, and the responsibilities of the relevant employees.
Note! Selection and training of employees is a mandatory component of organizing warehouse operations, which requires considerable material and time costs.
Warehouse logistics management: 5 steps for optimization
High results can be achieved by solving just a few tasks, completed step by step. They have already been discussed earlier:
- Determining the number of required warehouses.
- Choosing a company to rent premises and organizing your own storage.
- Selection of the optimal location.
- Organization of an effective warehouse system.
- Activity analysis.
By solving these problems, you can organize proper logistics work with minimal costs.
Functions and tasks of warehouse logistics
Warehouse logistics allows you to reduce (or eliminate) excess inventory, unnecessary transportation, sending defective products to customers, and overproduction. It significantly improves the efficiency of business processes, but only when it is considered inextricably with the business processes of the entire company.
Warehouse management functions at the micro level are performed by the logistics department, which is responsible for the management, placement, storage and distribution of material resources to consumers.
The main objectives of warehouse logistics are:
- Choosing a storage method.
- Selecting a warehouse location.
- Organization of labor in a warehouse.
- Optimization and standardization of warehouse technological processes.
- Determination of the number of warehouses.
- Selecting the technical equipment of the warehouse system (mechanized, automated, automatic).
- Development of a logistics process in a warehouse.
- Analysis of the efficiency of using existing warehouses.
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more