Most cargo delivery operations are carried out using transport. A correctly selected route is one of the key points during transportation. It will allow you to minimize time and financial costs, reduce fuel consumption and set the timing as accurately as possible from the moment of dispatch to the point of shipment of the goods. Transport logistics solves the identified problems. It is responsible for the systematic movement of goods along the most suitable route.
Transport logistics is
People come across the concept of transport logistics when they begin to engage in cargo transportation. The term means transporting cargo in a certain time along the optimal route to a destination with minimal costs. In her sphere of influence:
- control at every stage of the cargo along the route;
- measures to organize the delivery of goods to a given point;
- providing the cargo owner with up-to-date information about the passage of cargo along the route.
Vehicles serve as the basis of transport logistics. They must meet the stated requirements in order to transport the required consignments of goods over the required distance with short time intervals.
Selecting a means of transportation
Transportation management and logistics are impossible without freight transport. The most accessible and versatile type comes to the rescue - automobile. Next, rail, water, and air are used. Each has its own approach, where logistics takes into account the advantages and disadvantages.
- Transport logistics. The main advantage is its low cost compared to other types of cargo vehicles. The car is able to get to any point if there are roads. Door-to-door delivery is possible, the product does not need to be overloaded. The routes are flexible; along the way, it is almost always possible to find a detour if an unforeseen situation arises. Small quantities can be delivered. Competition forces carriers to offer favorable conditions to customers. Road transport is prone to accidents on the road, depends on the weather, and movement within the city is difficult.
- Railway logistics. Rail tracks in Russia are significantly inferior in length to highways - 85 thousand kilometers versus 1.5 million road surfaces. However, the railway reaches key points in the country, tariffs are relatively low, trains are regular, and delivery is carried out over long distances regardless of the weather. The disadvantages are the attachment to a specific route, restrictions on cargo transportation (without additional approval, cargo will not be allowed for transportation with dimensions exceeding 2.2 * 2.5 * 5 m, weight - 2500 kg). The price of services is higher; the actual monopoly of the railway carrier sometimes sets inflated tariffs.
- Water logistics. Transporting goods by water is a method of delivering goods that has come down to us since ancient times and has not lost its relevance. The low cost is due to lower energy consumption for the movement of ships. The container system speeds up the work process in ports. Vessels are capable of delivering most cargo: liquid, solid, bulk, metals, cars. Spacious cargo space allows you to ship oversized cargo. For example, for oil platforms this is the only available method of transportation. Significant disadvantages accompany water transport along with the advantages. In many regions delivery in winter is not possible. Perishable products require refrigeration facilities and fast delivery. The journey may take days and weeks. You can forget about door-to-door delivery: the goods must be reloaded onto another transport.
- Air logistics. Least used. The obvious reason is the high cost of flying. It is advisable to use transport aviation in two cases:
- Time plays a significant role;
- Delivery is not possible in any other way due to lack of infrastructure.
Aircraft are limited by weather conditions and airports. The undeniable advantage of such cargo transportation is speed, which plays into the hands of cargo safety.
Types of transport logistics
There are two types of transport logistics:
- Internal . Transportation of goods between branches of one organization.
- External . Delivery of cargo from manufacturer to consumer.
Transport cargo transportation is divided into:
- Unimodal. The only mode of transport used.
- Multimodal. Several types of vehicles are involved.
- Intermodal. The cargo is transported by one operator and several carriers.
- Mixed. Transportation from one vehicle to another.
- Combined. They differ from mixed ones by using more than two modes of transport.
Basic goals and objectives
The purpose of the created mechanism for managing the movement of goods is to use the full potential of the available carrying capacity and organize continuous deliveries without the use of warehouses.
As for the main task, it should be noted the formation of a transport chain along which goods will subsequently be transported. As part of the implementation of this final task, a number of intermediate ones must be completed, including:
- research of final destinations. In this case, a preliminary route for the cargo is laid out, taking into account the characteristics of the route. And taking this factor into account, the most optimal vehicle is selected. In some cases, different types of transport may be required for certain sections of the route;
- studying the properties of the cargo, which will also determine the choice of mode of transport and the most suitable route. If the task is to transport hazardous substances, for example, then the road should pass away from densely populated areas;
- choosing an acceptable type of vehicle, without which it is impossible to ensure timely delivery;
- development of an acceptable transportation plan, which will allow the order to be completed in the shortest possible time; And
- ensuring cargo control during transportation.
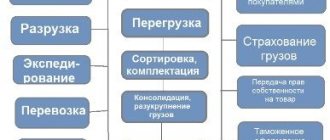
Functions of transport logistics
The implementation of transport logistics is designed to ensure the successful storage and movement of cargo from point “A” to point “B”. The process must be profitable both in terms of execution time and price. Key logistics functions:
- comprehensive forecast and organization of goods delivery;
- legal support and support for cargo transportation;
- making payments for services provided;
- loading and unloading of products;
- distribution in warehouses, packaging and packing of goods;
- optimization of the transportation process;
- preparation of the required documentation;
- information support for transportation;
- insurance and customs support services.
Career opportunities
There are many professions involved in organizing transport and passenger flows. To deliver cargo, we need couriers, truck and loading equipment drivers, pilots, order pickers, forwarders, machinists, service engineers, auditors, freighters, customs brokers and, of course, logisticians.
If you are educated as a logistician, then you can build your career ladder as a dispatcher or a logistics assistant. After 1-3 years of work experience, you will be willingly hired as a logistician. You can become a specialist in foreign trade activities, night logistics, operational logistics specialist, transport logistics quality manager, or transportation manager. Over time, you have the opportunity to grow to management positions - logistics manager, head of a department of a freight forwarding company, head of the supply and logistics department of an enterprise. Highest positions in the industry
is a logistics manager for international transportation, director of the international logistics department in large corporations. They are responsible for analyzing the actions and controlling several departments, interacting with brokers and the customs service, and searching for new transport partners.
Tasks of transport logistics
Main tasks of transport logistics:
- coordination of the transport and warehouse process;
- selection of carrier and other logistics partners;
- creation of working systems for transporting goods;
- choosing a suitable type of transport (air, railway, car) and method of transportation;
- determining the optimal delivery route;
- optimization of transportation parameters (increasing delivery speed, reducing fuel consumption).
The goal of transport logistics is to transport cargo to its destination with minimal costs. Neither the volume nor the quality of the cargo should be affected.
Basic concept
The definition of “transport logistics” was announced for the first time in history in 1974 at the European Congress in the capital of Germany. The key tasks and spheres of influence of the designated market sector were also identified there.
In general, this term can be understood as organizing the process of cargo transportation to a specified destination along an optimized route in an N amount of time and at the lowest cost.
If we talk about the Western market for logistics services, it was formed back in the 90s. According to experts, the average annual growth of this market is 20%. As for Russia, transport logistics appeared here after the country’s transition to market relations.
Currently, of all types of logistics, transport is extremely popular. All basic operations within this type of activity are carried out through land, water or air transport.
It is better to consider this concept from several angles, including:
- organization of the cargo transportation process;
- efficiency of the means of transportation used;
- service consumers.
Cargo transportation consists of 6 key stages:
- choosing the most suitable type of transport;
- drawing up cost estimates for cargo transportation;
- preparation of the required package of documents;
- loading of goods;
- its transportation;
- unloading at the delivery point.
Today, the market for goods transportation services is ready to offer its consumers a variety of types of services. And the existing huge competition, dictating its principles, contributes to the creation of more acceptable terms of relationship for clients from a price point of view.
How to choose a transport company
When choosing a transport company you need to consider:
- Experience. The longer a carrier operates in the cargo transportation market, the more connections it has. And many processes are automated.
- Car park. The variety of your own vehicles, the availability of employees, standard containers and packaging for different goods directly affects the efficiency and speed of delivery of goods.
- Specialization. Firms offering a narrow range of services can be chosen for transporting goods over short distances. The offer of large companies is distinguished by a variety of services. They are more suitable for long-distance transport. And thanks to the organization of groupage cargo, the delivery price will be lower.
- Features of the cargo. The presence of special packaging and shipping requirements affects the choice of a company that has experience in transporting such goods.
- Customer reviews. If it is possible to contact a real client of the company, you can trust his recommendations. Fake reviews may be published on the company's website.
One of the proven companies is transport and logistics. The Internet address is elk-ural.ru. When contacting the center, it is enough to state the main provisions:
- type and volume of cargo;
- dispatch and delivery points;
- requirements for support and documentation.
The center staff will provide you with the following information:
- approximate route,
- delivery time of goods;
- service cost;
- suitable mode of transport;
- availability of groupage cargo.
Logistician - who is this?
To contents
If you are interested in who logisticians are and what they do, then first of all it is important to understand that there are three main basic processes in the work of these specialists: optimization, planning, control.
Who is a logistician? This is a specialist whose tasks include: analysis and optimization of transportation, procurement, supply, warehousing, delivery, distribution of goods and finished products to potential consumers or sellers.
Having your own specialized department within a company is relevant if the organization has many branches in other cities or countries, when constant control of supplies and purchases is required. In the operating conditions of a large enterprise, it will be enough to have at least several employees of this qualification on staff.
As we have already found out, logisticians are specialists involved in supplies, organizing transportation, and optimizing purchasing operations. Their activities are aimed at rationalization, modeling, and control of services, processes, and information flows. The logistician is entrusted with the task of developing the most successful route for transporting goods and services to the customer/consumer from the supplier.
It is important to know! An employee in this field plans processes and reduces costs, helps the company quickly and profitably transport products (goods or services). The point comes down to the rational use of all available resources. Competent promotion of a product towards the final goal is carried out thanks to the professionalism of a specialist, his ability to control flows, organize marketing, receive and fulfill orders, plan, see the future, calculate strategy and tactical moves.
You can demonstrate the task of a logistician using a specific example.
There is a customer A: he wants to receive a product in a certain quantity, quality, at a low price, on an agreed day. The customer naturally wants to receive the best service. Supplier B: aims to build a trusting relationship with the Customer for a long period, to establish the process of production, sales, delivery in an optimal way, to obtain maximum profit from the transaction at minimal costs. What do logisticians do? They, being at the intersection of interests A and B, provide the best ways to realize the desires of the parties.
An important task of a specialist is to carry out logistics control.
This is a multi-directional process, including aspects such as:
- Analysis of demand in the product market.
- Concluding contracts and maintaining special documentation.
- Work in cooperation with customs authorities.
- Inventory Management.
- Development of a scheme for order delivery to the consumer.
- Minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Based on the analysis of the characteristics of the profession, the main goals can be identified:
- Management of product and service flows.
- Optimization of enterprise operation.
- Increasing the efficiency of the economic system.
To achieve goals, setting tasks is required:
- Competent development of commodity flows.
- Product transportation management.
- Control over all processes of transfer of goods or services from the enterprise to the customer.
- Monitoring the market of goods and services.
- Minimizing the cost of transporting products.
- Search for the best options and transportation routes.
So, let’s summarize a preliminary result: a logistician is a specialist who can skillfully manage financial, information, and commodity flows. The prosperity of a company in its chosen field of activity depends on the professionalism of a logistics specialist.
Transport tariffs in logistics
Freight tariffs are part of the pricing system for logistics services. Tariffs include:
- freight transportation fees;
- fees for additional actions during transportation;
- rules by which fees and charges are calculated.
Features of tariffs for different types of transport:
Tariffs should be clarified at the time of upcoming cargo transportation. The final cost is determined based on the following factors:
- transportation range;
- technical equipment;
- traffic congestion;
- required load capacity;
- degree of automation when working with cargo.
Comparative characteristics of various types of transport
| Types of transport | Advantages | Flaws |
| Railway | Reliability and relatively high speed of delivery of goods and passengers, independence from weather conditions, regularity, mass distribution, versatility | Reliability and relatively high speed of delivery of goods and passengers, independence from weather conditions, regularity, mass distribution, versatility |
| River | High carrying capacity, low costs for organizing transportation | Transportation range due to the tortuosity of the rivers, relatively low speed of movement, seasonality of work, low vessel load due to uneven depths |
| Automotive | High cross-country ability and great maneuverability, high speed of delivery of goods and passengers, rationality of transportation over any distance, ensuring the required frequency of traffic and placement of roads in all zones of the country | Relatively expensive type of land transport, lower labor productivity compared to other types of transport |
| Nautical | Use of long-distance natural communication routes, unlimited capacity of sea routes | Requirement for expensive port facilities, high share of costs for initial and final operations, dependence on weather conditions |
| Air | Shorter air routes, longer non-stop flight range, high speed delivery of cargo and passengers | Dependence of flights on weather conditions, high cost of transportation |
Cargo control during transportation
Without high-quality cellular communications and the Internet today it is difficult to imagine modern transport logistics. With their help, satellite monitoring of transport becomes possible. The navigation system allows you to:
- establish the geographic coordinates of the cargo at any time;
- inform the customer about the location of the goods and the stage of delivery;
- avoid force majeure situations and adjust the route in a timely manner;
- ensure the safety and conditions of cargo transportation.
The following equipment helps control the movement and safety of cargo:
- car trackers;
- autonomous GPS beacons;
- sensors for temperature and humidity, tilt angle, shock, door opening, axle load;
- PS fillings;
- video cameras.
Automation of transport logistics
Managing the transport logistics of an enterprise is impossible without the introduction of new technologies. Software has been specially developed for this purpose:
1C TMS Logistics . Transportation management to help a modern transport company. The program allows you to optimize work in any area of the operation:
- drawing up a chain of multimodal transport;
- assembling flights, creating routes, distributing resources;
- generation of accompanying documentation;
- control over the movement of cargo using GLONASS/GPS;
- management of fleet assets, tracking orders, pricing;
- collection and analysis of the information received.
1C: GLONASS/GPS Satellite Monitoring Center . Allows you to ensure the efficiency and safety of cargo transportation. Software package capabilities:
- tracking the location and route of cargo movement on an electronic map;
- timely notification of unauthorized entry, deviation from the route, violation of delivery deadlines, damage to packaging;
- control over compliance with transportation conditions;
- generation of analytical reports, waybills;
- control of cargo transportation costs.
Documentation in transport logistics
No transport company can do without accompanying documents. The discipline and control of the process depends on the documentary evidence of each business transaction at each stage of the supply chain. The shipper himself is responsible for the papers transferred to the carrier. It is stipulated in the concluded contracts. Main accompanying documents:
- Waybill (from the carrier).
- Agreement between the customer and the carrier.
- Consignment note (from the shipper/customer).
- Consignment note (if the CTN does not contain a complete list of goods).
- Certificate of conformity and quality, passport (depending on the nature of the cargo).
- Invoices and agreement between the supplier and the buyer (optional).
For international delivery of cargo, the package of documents is somewhat wider.
Questions and answers on transport logistics
No. 1. Features of international cargo transportation?
The order of traffic flows when the borders of different states are crossed are regulated by Incoterms rules. It is not enough to go through customs control. It is also necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the legislation of the country through which the route is laid.
If a company is engaged in international transport logistics, its functions are much broader than those of a regular cargo carrier. It is responsible for labor-intensive customs procedures, resolving issues of intermediate storage, etc.
No. 2. The main problems of transport logistics in Russia?
First of all, this is the lack of professional personnel. Not very competent business projects often lead to an inaccurate distribution of responsibilities between the company's structural divisions. It is not uncommon for one employee to be forced to perform different types of work in which he lacks qualifications. This approach affects the efficiency of transport logistics. Enterprises are suffering losses.
The transport infrastructure leaves much to be desired. Poor quality roads and a lack of cargo terminals and warehouse space create additional problems.
Russian logistics requires a clear legislative framework. Technologies are significantly ahead of it and should be “legalized” as soon as possible. For example, the law does not yet contain the concept of “electronic waybill”.
No. 3. What goods are prohibited from being transported?
No transport company will engage in the transportation of prohibited goods. This includes weapons, alcohol, poison, drugs, explosives, combustible and flammable substances, radioactive compounds.