Forms and principles of social partnership in an organization
The following forms of joint venture are distinguished:
- Collective meetings to work on drawing up various agreements.
- Consultations regarding the management of labor relations.
- Participation of workers and their representatives in the management of the company.
- Participation of company representatives and owners in pre-trial conflict resolution.
Among the legal forms of joint ventures, collective agreements are distinguished.
Basic principles of the joint venture:
- Each participant has the right to start negotiations.
- The interests of each side of the labor space must be respected.
- The law gives participants in labor relations a lot of space to resolve issues (for example, the activities of a company can be regulated by local acts).
- The agreements drawn up must not conflict with the law.
- To appoint representatives, you need to organize a meeting of workers and draw up a protocol (if it is a trade union) or an order (if it is representatives of the employer).
- Representatives are given the right to defend the interests of their group.
- The range of issues that will be on the agenda is determined by the participants.
- The basis of the joint venture is freedom of choice. All decisions of participants must be completely voluntary.
- The clauses specified in collective agreements must be fulfilled. Supervisory structures are responsible for monitoring implementation.
If the adopted provisions were not implemented, administrative liability is imposed on the guilty person.
Social partnership at school
At school, social partnership becomes important in such aspects as:
- development of communication and adaptation skills in a team;
- civic-patriotic education;
- maintaining and promoting health;
- obtaining knowledge that complements the school curriculum;
- acquaintance with the professions and places of work of parents;
- assistance in finding employment during school holidays;
- cooperation with preschool educational institutions to prepare children for entering school and with vocational educational institutions in terms of career guidance.
At this level, partnership is never limited to internal events of the educational institution and is often extended beyond the school either by holding events outside it (olympiads, competitions, trips, hikes, lectures), or by involving third parties and organizations in work on the school premises (staging performances, intensive study of a foreign language, special lecture courses).
To learn how participation in social partnerships can affect the salaries of teachers and preschool educators, read the material “Criteria for incentive payments to teachers.”
Parties of social partnership
There are two sides to the joint venture - the workers and the employer. These groups must be represented by certain people chosen by the participants. They will be considered representatives of:
- Workers . As a rule, these are trade unions. If company employees do not participate in trade unions, they can choose their representative by secret ballot.
- Employer . This is the head of the company himself or his representatives with appropriate powers. Also, the manager may be a member of a non-profit association of entrepreneurs. This is a union whose goal is to defend its interests before trade unions and government agencies.
The main rule of a joint venture is that you need to choose one person who will represent the interests of the entire group.
Organization of social partnership in the company
The basis of social partnership is an agreement between participants in labor relations. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not specify special requirements for this agreement. It is usually compiled according to the following scheme:
- Name.
- Date of creation.
- Introduction: names of participants, representatives.
- Subject of the agreement.
- Rights and obligations of the trade union.
- Rights and obligations of the employer.
- Procedure for fulfilling obligations.
- Punishment for failure to comply with contract clauses.
- Duration of the agreement.
- The procedure for considering emerging conflicts.
- Details and signatures.
The legislation does not provide for strict rules regarding the formalization of social partnerships. However, it is still worth indicating in the agreement all the details for the comfort of the participants themselves.
The JV agreement assumes a special character. In this regard, it is necessary to take some additional steps to correctly formalize the partnership:
- Developing a plan for interaction between participants.
- Coordination of the plan with stakeholders (for example, with local governments).
- Drawing up the main and additional agreements.
Each step must be agreed upon with the parties involved.
Types of social partnership in the field of education
Partnerships in education can take many different forms. Their range, obviously, will be wider than with partnership in the sphere of labor, since not only is it not limited to anything, but it also leads to the emergence of new effective forms.
The basis for the types of interaction between partners will be the exchange of information (predictive or current) that allows managing the education process. At the preschool and school level, partnership most often takes on the character of cooperation that is not formalized by contractual relations, while in social interaction with a vocational education institution, a contract (agreement) becomes the most important form of relationship. Contractual relations may take place in the following areas:
- targeted transfer of students from preschool educational institutions to certain schools, from schools to certain vocational education institutions, from a vocational training institution to a specific employer;
- training the necessary specialists with sustainable practical skills acquired during the training process through the supervision of this process by specific employers.
In partnerships in education, the role of government bodies that perform the functions of collecting, systematizing data by region, analyzing and forecasting situations regarding economic development and the demand for specialists, and adopting the necessary legislative acts to regulate the situation turns out to be quite significant.
Basic Concepts
The joint venture began to take shape in the 20th century, when it became clear that the antagonism of the working class and the employer did not lead to anything good. At the same time, trade unions began to actively develop, which are an effective tool for defending workers’ rights. SP is an entire culture, most developed in European countries. Let's look at the basic concepts of partnership.
Collective agreement
A collective agreement sets out agreements between workers and the employer. Typically this agreement covers issues such as:
- The size of salaries and various types of compensation.
- The procedure for increasing salaries depending on inflation.
- The procedure for paying compensation for overtime service, night work and weekend work.
- Employee employment.
- Duration of the working day (including for certain categories of employees).
- Duration of paid leave.
- Occupational Safety and Health.
- Obligations of the parties to the agreement to each other.
The agreement is concluded between the employer and the trade union or employee representative.
ATTENTION! A collective agreement cannot contradict the law. It should not worsen the situation of workers.
Collective bargaining
It is at collective bargaining that various agreements are adopted. They can be initiated by a representative of any of the parties. To do this, you need to send a corresponding notification. The party receiving it is obliged to enter into negotiations within a week. To conduct the event, you need to assemble a commission of representatives of the parties. The meeting agenda is also set.
IMPORTANT! Workers have the right to support their demands with rallies and pickets held in their free time.
Social partnership: concept, sides, system and forms
⇐ PreviousPage 20 of 84Next ⇒To designate the system of relationships between employees, employers, state authorities and local self-government, aimed at ensuring the coordination of their interests in the sphere of labor, the term “social partnership” is used in Russian legislation.
In the context of globalization, social partnership is becoming increasingly widespread, acting as an interaction between the state, business and society.
The specifics of the development of labor relations in modern Russia puts forward the need for more effective use of the opportunities of social partnership in the field of further improving the regulation of social and labor relations.
The concept of social partnership first appeared in ILO Convention No. 98 Concerning the Application of the Principles of the Right to Organize and to Collective Bargaining in 1949, which provided for the encouragement and promotion of the full development and application of collective bargaining on a voluntary basis between employers or employers' organizations , on the one hand, and workers' organizations, on the other hand, in order to regulate working conditions through the conclusion of collective agreements.
ILO Convention No. 154 “On the Promotion of Collective Bargaining” (1981) and its accompanying Recommendation No. 163 are also devoted to this issue.
Social partnership is considered by researchers as a method of labor law (Lushnikova M.V.) or its element (Bondarenko E.N.), a principle of labor law (Gontsov N.I.), a system of measures (Akopova E.M. and Eremina S. N.), systems of relationships between employers, government bodies and representatives of employees, based on negotiations, the search for mutually acceptable solutions in the regulation of labor and other socio-economic relations (Snigireva I.O.), forms of organizing interaction between employers, employees and the state (Chucha S.Yu., Golovina S.Yu.).
It should be noted that the given list of approaches to determining the essence of social partnership is not exhaustive.
Social partnership is a complex legal and social category. It represents, on the one hand, a system of relationships (cooperation, dialogue) between workers, employers and the state, and on the other hand, the principles of such cooperation.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 23) defines social partnership in the sphere of labor as a system of relationships between employees (representatives of employees), employers (representatives of employers), government bodies, local governments, aimed at ensuring coordination of the interests of workers and employers on issues of regulating labor relations and other directly related relations.
This concept of “social partnership” is based on the principle of tripartism (trilateralism), which corresponds to international legal regulation of labor.
In accordance with Art. 25 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the parties to the social partnership are employees and employers represented by duly authorized representatives.
State authorities and local governments act, as a rule, as intermediaries, but in some cases they can also be a party: a) when they act as employers in relations with state and municipal employees working in them, for whom they are employers and b) in other cases provided for by labor legislation in accordance with Article 34 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Social partnership can be built on the basis of the principle of bipartisanship - connections between traditional social partners (trade unions, work collectives, on the one hand, and employers, on the other) and tripartism, according to which the state or local governments join these entities. Accordingly, two types of partnership can be distinguished: bilateral and trilateral cooperation.
The social partnership system consists of the following five levels (Article 26 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The legislator encourages any expansion of social partnership, and the levels given are neither mandatory nor exhaustive. According to established tradition, levels are distinguished according to territorial and sectoral characteristics.
At the federal level, general and sectoral (intersectoral) agreements can be concluded. Currently, there is a General Agreement between all-Russian associations of trade unions, all-Russian associations of employers and the Government of the Russian Federation for 2011 - 2013 dated December 29, 2010[95].
At the interregional level (two or more constituent entities of the Russian Federation) - interregional and sectoral (intersectoral) agreements.
At the regional level (level of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation), regional and sectoral (inter-sectoral) agreements are concluded. In Moscow, the Moscow tripartite agreement is in force for 2013-2015 between the Moscow Government, Moscow trade union associations and Moscow employers' associations.
At the territorial level (at the municipal level) - a territorial agreement.
Within an organization or with an individual entrepreneur (local level), a collective agreement is concluded that provides for mutual obligations of employees and the employer.
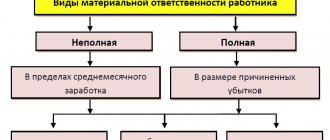
The forms of social partnership are the following (Article 27 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
— consultations with representatives of workers, employers and the state on the regulation of labor and other relations directly related to them, ensuring guarantees of the labor rights of workers, improving labor legislation (consultations on socio-economic policy) and concluding agreements on issues of social and labor relations;
— collective negotiations for the preparation and conclusion of collective agreements in the organization;
— participation of employees and their representatives in the management of the organization;
— participation of representatives of employees and employers in pre-trial and out-of-court resolution of labor disputes.
One of the forms of social partnership can be considered the decision-making by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body, the representative body of employees and the coordination of its decisions.
Ensuring the right of workers to participate in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by law is one of the basic principles of the legal regulation of labor relations and other relations directly related to them, enshrined in Art. 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the fundamental right of workers (Article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This form of social partnership is disclosed in Art. 52, 53 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Articles 2, 21, 52, 53 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Forms of social partnership also include the participation of representatives of employees and employers in the pre-trial resolution of labor disputes, when an employee applies to the labor dispute commission for resolution of an individual labor dispute. In order to form a CTC on a parity basis in accordance with Article 384 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the basic principles of social partnership are manifested (Article 384 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In the modern period of time, the role and importance of social partnership is increasing, and the legal framework is expanding.
The EurAsEC adopted the Model Draft Legislative Act “On Social Partnership” (2005), the CIS adopted the Model Law “On Social Partnership” (2006), and in Russia the main provisions on social partnership received special legal recognition in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , in the Federal Law of January 12, 1996 No. 10-FZ “On trade unions, their rights and guarantees of activity” (as amended and supplemented), including in special laws on social partnership adopted in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation: Law of Moscow dated November 11, 2009 No. 4 “On social partnership in the city of Moscow”, Law of St. Petersburg dated October 10, 2011 No. 577-114 “On social partnership in the sphere of labor in St. Petersburg”, etc.
Thus, social partnership is an independent institution of labor law .
⇐ Previous20Next ⇒
Responsibility of the parties
Violation of the terms of the joint venture implies the following administrative liability:
- A fine of 1000-3000 rubles. for avoiding negotiations regarding the conclusion or addition of a collective agreement (according to 5.28 of the Administrative Code).
- 1000-3000 rub. for the fact that the employer or his representatives hide or do not provide on time information necessary for negotiations and drawing up an agreement (according to 5.29 of the Administrative Code).
- 3000-5000 rub. for refusal without good reason to conclude a collective agreement (5.30 Code of Administrative Offenses).
- 3000-5000 rub. for failure to comply with the clauses of the agreement (5.31 Code of Administrative Offences).
- 1000-3000 rub. from evading conciliatory measures in the event of a conflict (5.32 Code of Administrative Offenses).
- 2000-4000 rub. for violation of agreements concluded during the reconciliation of the parties (5.33 Code of Administrative Offenses).
IMPORTANT! If the employer violates the provisions of the collective agreement and ignores the need for reconciliation, workers have the right to organize a strike.
Advantages
Social partnership in an organization is beneficial not only for workers, but also for those managers who are interested in the development of the company. The main benefit of partnership is the creation of an atmosphere in which the employee feels responsible for the well-being of the enterprise. The company ceases to be perceived as something alien and hostile, since the worker takes a direct part in its development. All this has a beneficial effect on employee loyalty, indicators of their ability to work, and initiative. It is beneficial for JV employees because it helps them defend their legitimate interests through legal means. Despite all the benefits, the social partnership system in Russia is poorly developed.
Social partnership in preschool educational institutions
The preschool educational institution, along with the child’s family, forms in him those basic personality characteristics that subsequently determine for him many life attitudes and, in particular, his outlook, choice of profession, the possibility of professional growth, and the comfort of existence in a team.
Social partnership in preschool educational institutions can occur:
- within the preschool educational institution with the involvement of parents, the pedagogical council of the preschool educational institution, teaching staff of schools, and specialists in any specific fields;
- at the regional level with the participation of organizations from other fields of activity (health care, culture, sports, social protection).
The forms of social partnership are:
- various joint events (concerts, holidays, performances, competitions) both at the preschool educational institution and beyond;
- lessons, meetings, educational trips;
- open days;
- general parent meetings;
- individual work with families;
- consultations with parents, conducting seminars and trainings;
- individual preparation of children for school.