Briefly about the regulatory framework
The financial liability of the employee and the employer is established in three chapters of Section XI of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, namely:
- general provisions are established in Chapter. 37, which contains two articles that establish the obligation of a party to an employment contract to compensate for damage caused by it to the other party to this contract (Article 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), defines the conditions for the onset of material liability of a party to an employment contract;
- The employer's responsibility to the employee is discussed in Chapter. 38;
- The financial liability of the employee is regulated by Ch. 39.
Please note that:
- under the terms of contracts (labor or financial liability), the employer’s liability to the employee cannot be lower, and the employee’s liability cannot be higher, than it is established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal laws;
- in the event of termination of an employment contract, the party to this contract is not released from financial liability;
- financial liability can be applied exclusively to persons with whom employment agreements have been concluded, including part-time workers, temporary and seasonal workers. Individuals with whom civil contracts have been concluded are liable to the other party only within the framework of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
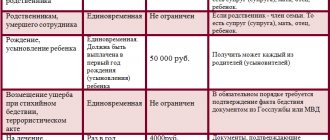
All types of financial responsibility of the employee and employer to each other are shown in the diagram.
Financial liability - what is it?
Liability is one of the basic legal terms that denotes the legal obligation of the person responsible for causing property damage to compensate the injured person. The amount and procedure for compensation for damage is regulated by labor legislation. This type of obligation is a response from one party to a business relationship to violations by the other.
The financial liability of the parties to the labor relationship has its own distinctive features.
- Firstly, it is always personal. This means that the employee must independently compensate for the damage caused by him. This also applies to minor employees with whom an employment contract was concluded.
- Secondly, the obligation to compensate for harm arises only after the guilt of the person himself has been established directly. The owner of the entrusted property must prove the existence of an offense.
- Thirdly, when establishing an employee’s guilt, the limit of liability is correlated with his salary. The amount of payments to compensate for the damage caused should not exceed the average monthly income of the person.
- Fourthly, this type of liability threatens only for actual property damage.
It is impossible to oblige an employee to make payments for non-compliance with plans and income not received by the company. Finally, if several employees are at fault, the amount of payments should be distributed taking into account the degree of guilt of each of them. This phenomenon is called shared liability.
If you want to know more about govt. orders and regulations, go here. Here we provide an analysis of Russian legislation on this topic. Having talked about the concept of financial responsibility, let's move on to the types.
When should you go to court?
In accordance with current legislation, the employer has the right to independently bring a subordinate to liability of a material nature only when it comes to the amount of damage that does not exceed the employee’s average monthly earnings. In addition, the employer must decide to hold the employee financially liable no later than one month from the date of final determination of the amount of damage caused. If the period for making such a decision has expired, you will have to demand compensation for damage, regardless of its size, in court (Part 2 of Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the amount of damage determined during the inspection exceeds the employee’s average monthly earnings, then in order to bring the latter to financial responsibility it is necessary to go to court. Seeking protection from the courts is also necessary in cases where the damage was caused by an already dismissed employee who is not currently in an employment relationship with the employer.
In addition, going to court to bring to financial responsibility an employee who does not agree to voluntarily compensate for the damage caused is also practically the only option.
It should also be noted that holding an employee financially liable does not prevent him from applying other sanctions provided for by law, including bringing him to criminal, administrative or disciplinary liability.
Liability of a legal entity
Legal entities that are directly related to property also have some obligations. For example, an employer who did not comply with the rules for storing and operating goods must compensate the owner for all damage caused.
So, financial responsibility is a term without which it is impossible to imagine labor law . The obligation to compensate for property damage caused may be imposed on both individuals and legal entities.
The amount of monthly payments, the procedure for penalties, and types of liability are regulated by labor legislation. Any departures are illegal.
The main purpose of this type of liability in production is compensation for harm caused. Any collection measures must be carried out either on a voluntary basis or through judicial proceedings.
On the financial responsibility of the employee to the employer
An employee’s financial liability may arise in cases where his actions (or, conversely, inaction) were the basis for causing material harm to the employer.
It is important to note that prosecution is possible only if a number of conditions are met, the main of which are:
- availability of recording and evidence of the damage that was caused;
- the presence of a cause-and-effect relationship between the damage and the actions (inaction) of the employee that led to such consequences;
- determining the amount of damage caused.
At the same time, an employee can be brought to full financial liability only in cases where an appropriate agreement has been signed with him.
For liability to occur, an inspection is also a necessary condition. This is carried out by authorized representatives of the employer or by a specially created commission appointed by order of the employer.
During the inspection period, materials are collected that help restore the picture of what happened and identify the culprit. It is important to correctly and reasonably establish the amount of damage caused. The employee has every right to familiarize himself with all materials received during the inspection, make his objections and give explanations.
After the inspection, the employee is introduced to its materials, allowing him to express his own opinion regarding the decision made by the employer and the established amount of damage. The opinion must be expressed in writing, and if the employee refuses to familiarize himself or give explanations, the employer draws up a corresponding act.
An employee’s financial liability can be of several types:
- limited;
- full;
- individual;
- collective.
We will consider each of the mentioned types in more detail below.
The principle of employee liability
Almost any organization develops a special system of incentives and criteria for assessing employee performance. Such systems are supported by the basic principle of financial responsibility. It lies in the fact that every employee who is directly related to the property is responsible for the results of their work. At enterprises, there are 2 forms of organization of this type of responsibility: individual and collective.
The most common is form 1 . It means that the employee who is responsible for the organization’s property:
- salesman,
- cashier,
- storekeeper,
- watchman,
- accountant,
- driver,
- director,
- caretaker,
- serviceman
- and positions in other areas
will have to compensate for damage caused by the shortage of certain goods. We wrote about such an agreement here. The collective form represents the responsibility not of one person, but of a group of financially responsible persons (about an agreement of this type).
As for employers, for them the principle of this type of obligation is expressed in a system of fines and penalties for non-compliance with tax legislation.
Terms of attraction
Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation assumes that the guilty employee is obliged to compensate the employer only for direct actual damage caused to him. Lost income (lost profits) cannot be recovered from the employee.
Direct actual damage includes:
- a real decrease in the employer's cash assets;
- deterioration of the condition of such property (including property of third parties owned by the employer);
- the need for the employer to incur costs or pay funds for the acquisition, restoration of property or compensation for damage to third parties.
According to the law, an employee’s financial liability is excluded in the event of damage due to force majeure, normal economic risk, extreme necessity or necessary defense, or the employer’s failure to fulfill the obligation to provide adequate conditions for storing property entrusted to the employee.
If the manager was stingy in equipping the warehouse with proper locks and did not restrict access to third parties, then it will not be possible to recover the shortage from the storekeeper.
Types of liability
To resolve the issue of bringing an employee to punishment, remember that financial liability in the Labor Code is divided into:
- full and limited;
- individual and collective.
| Limited financial liability of the employee | Full financial responsibility |
| In an amount not exceeding his average earnings (Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | In full (Articles 242 - 245 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) |
The Labor Code imperatively restricts the employer from placing full financial responsibility on personnel, protecting a conscientious employee from abuse by superiors. In this regard, it is necessary to remember:
- Bringing an employee to financial liability is a right, but not an obligation (Part 1 of Article 22, Article 240 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer has the right to refuse to recover damages in full or in part.
- The terms of the employment contract and local regulations cannot worsen labor rights in comparison with those established by current legislation. Imposing financial liability on employees by including such a clause in the text of the employment contract and job description is being challenged in court as contrary to the labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
- Bringing an employee to liability is permitted only if there are grounds established by Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, taking into account the restrictions established by Article 239 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (due to force majeure; due to normal economic risk; due to extreme necessity or necessary defense; due to lack of appropriate conditions for storage of entrusted property).
- The subordinate is obliged to compensate only for direct actual damage, that is, a real decrease in property or deterioration in the condition of property, including the property of third parties, if the employer is responsible for its safety. The concept of direct damage also includes costs that the company must incur, or excessive payments for the acquisition, restoration of property, or compensation for damage caused by the employee to third parties.
- When limited financial liability is introduced, the amount of average earnings within which the employee pays for damages is calculated from the amount that remains after withholding taxes from wages (letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated November 16, 2011 No. 22-2-4852). According to Part 2 of Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating the average salary, all types of payments provided for by the payment system that are used by the employer are taken into account, regardless of the sources of these payments. The average salary is calculated based on the salary actually accrued to him and the time actually worked by him for the 12 previous calendar months.
IMPORTANT!
As a rule, a limited liability agreement (a sample of which is developed independently in free form) is not concluded with employees, since this is not necessary. This type of liability is already provided for by the provisions of Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Recovery of damages in the absence of an administrative offense
Case No. 1
The company filed a lawsuit to recover material damage from A. in the amount of 120,000 rubles. At the court hearing, it was established that A. was hired as a driver, and an agreement on full financial responsibility was concluded with him. As a result of damage to the car caused by A., the company suffered damage in the amount of 120,000 rubles (repair cost).
By the court's decision, the claim was partially satisfied, and damages in the amount of 19,500 rubles (average monthly earnings) were recovered from A. Since the law does not provide for the conclusion of an agreement on full individual financial liability with the driver, then, in accordance with the requirements of Art. 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, A. is liable for damage caused only in an amount not exceeding his average monthly earnings. The plaintiff’s reference to the fact that the damage to the car was caused by a collision with a concrete support, which is a violation of traffic rules, was considered unfounded by the court, since the case of an administrative offense based on the fact of the accident was not initiated against A., and the corresponding resolution was not issued.
Reducing the amount of damages recovered
Case No. 3
As a result of the warehouse inventory, a shortage of inventory items was identified. The employee (warehouse manager), who entered into an individual agreement on full financial liability, refused to compensate for the damage voluntarily. The employer filed a claim for damages in full. In accordance with Article 250 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the body for the consideration of labor disputes is allowed, taking into account the degree and form of guilt, the financial situation of the employee and other circumstances, to reduce the amount of damage to be recovered from the employee. The amount of damage to be recovered from the employee is not reduced if the damage was caused by a crime committed for personal gain. When making a decision, the court took into account that the damage to the employer was caused as a result of careless accounting of property due to the inexperience of the employee; selfish motives for causing the damage were not established. From the case materials, it is clear that the employee’s age at the time of concluding the employment contract and the agreement on full financial responsibility is 22 years, the total length of service is 1 year, and there is a dependent minor child. Taking into account all the above circumstances, the court partially satisfied the employer’s claim, reducing the amount of recovery by 50%.
Case No. 4
The employer filed a lawsuit to recover from a group of employees the full amount of damage caused as a result of the electric forklift overturning. An agreement on full collective (team) financial responsibility has been concluded with the employees. The court found that such an agreement is prohibited from being concluded with the defendants, and therefore the agreement concluded with them is not the basis for holding them, as employees, to full financial responsibility. The employer did not provide any other grounds established by the Labor Code. The court partially satisfied the employer's claim - the amount of the employee's financial liability amounted to the amount of his average earnings.
How to draw up a full liability agreement
Agreements on financial liability can be individual or collective (team).
Collective - when people work together and it is impossible to know who to ask. For example, there are three people working in a warehouse. The entrepreneur carried out a monthly inventory and discovered that 5 boxes of shoes were missing. Each employee will pay a third.
Under the collective agreement there is a presumption of guilt. By default, the employee is guilty, but he can prove the opposite - Art. 245 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, he did not enter the warehouse for a whole month, and during the last inventory the shoes were still there. Then there is nothing to collect money for.
How to introduce collective responsibility:
- Issue an order.
— Ask employees to sign an agreement (standard form).
— Appoint a “brigade” leader.
Example: how liability agreements helped in court
An entrepreneur hired two salespeople for a clothing store. He drew up employment contracts and an agreement on collective financial responsibility.
One day, an entrepreneur noticed that there was too little money in the online cash register. The inventory showed that 62,880 rubles were missing. The sellers were supposed to pay the shortfall, but they refused.
Then there was a long dispute with a statement to the police, a trial and accusations of bias on the inventory commission. But in the end, the court said that clothing sellers are fully responsible for the cash register, and the inventory is in order. You will have to pay 32,483 ₽.
Case No. 33-4711/2019
Standard form of an agreement on full individual liability
Standard form of an agreement on full collective liability
The goods and money are transferred to the employee according to the act or an inventory is taken before the start of work.