Author: Ivan Ivanov
Large businesses are enterprises with a large amount of their own resources, large-scale trade turnover, a significant level of sales of services and high capitalization. Representatives are international companies operating in global markets.
Everyone, especially novice entrepreneurs, should understand the difference between a small business and a large or medium-sized one. Even at the initial stages - when defining the idea of your business and writing a business plan - you should have an idea of \u200b\u200bthe future activity.
Basic Concepts
Small business is the most common form of entrepreneurship. Such companies have a minimum number of employees (up to 100 people) and low annual income (no more than 800 million rubles). Midsize companies have extensive resources and high annual returns. According to the Federal Tax Service, small and medium-sized businesses are SMEs. Organizations that are included in the register of small and medium-sized businesses have the right to claim tax and accounting benefits. Large enterprises are a form of entrepreneurship that includes resource companies that span an entire country or more than two countries around the world and are in high demand among consumers.
Types of small businesses
There are four types of small businesses. These are production, service, wholesale and retail trade. Each of them has its own characteristics that need to be known and taken into account before starting a business.
Production
Manufacturing is the processing of raw materials into finished products or semi-finished products. There are two types of production: primary and secondary. In the first case, raw materials obtained during mining are used. For example, oil, iron, wood. In secondary production, already used products that have become unsuitable for their intended purpose are used as raw materials. For example, recycling of plastic and plastic, waste paper.
Small companies
Small businesses are not only individual entrepreneurs, but also legal entities. The average annual number of employees is no more than 100 people. The territorial activities of these companies are small. Their areas of activity include:
- the shops;
- firms with a small volume of production of goods, performance of work, provision of services;
- travel agencies;
- medical offices (dental, etc.);
- educational and training courses, etc.
For small businesses, the period for conducting inspections is reduced and is no more than 50 hours annually.
477-FZ dated December 29, 2014 indicates how the commercial activities of a small enterprise differ - newly registered individual entrepreneurs are provided with a two-year tax holiday. New entrepreneurs are not visited by the Sanitary and Epidemiological Inspectorate and the fire inspectorate, and their licensing of activities is not checked. Entrepreneurs who:
- register for the first time;
- carry out production, social or scientific activities;
- provide services to the population.
According to Part 2 of Article 10 of the Federal Law “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs in the exercise of state control (supervision) and municipal control”, when complaints are received from consumers regarding violations of the law, an audit is carried out.
Small businesses do not need status confirmation. It is necessary to adhere to restrictions on income, number of employees and share of participation in the authorized capital (Article 4 209-FZ of July 24, 2007). If you exceed the limits, you will not be immediately deprived of your SME status, but will retain it for three calendar years.
Tax benefits
Strictly speaking, the use of special tax regimes is not tied specifically to the status of a small enterprise. But the criteria for switching to special taxation options reflected in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation largely overlap with the conditions for classifying a businessman as a small business.
More precisely, the specified criteria are “between” the limits for small and micro businesses.
| Criterion | Microbusiness | PSN | UTII | simplified tax system | Small business |
| Number, people | up to 15 | up to 15 | up to 100 | up to 100 | up to 100 |
| Revenue, million rubles in year | up to 120 | up to 60 | — | up to 150 | up to 800 |
Thus, although not every small enterprise can take advantage of a special tax regime, almost every “special regime” is a small business.
An exception here is provided only for the unified agricultural tax. Agricultural enterprises can work for the Unified Agricultural Tax until they reach a staff size of 300 people, i.e. going beyond not only small but also medium-sized businesses.
Small businesses can take advantage of tax breaks at the regional level. For example, the authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to set property tax rates for organizations in the range from 0 to 2.2% depending on the category of taxpayer (Article 380 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And in many cases, it is the status of a small enterprise that is the basis for applying the benefit.
A special benefit provided only for starting individual entrepreneurs is a tax holiday . New entrepreneurs who use the simplified tax system or PSN can enjoy a preferential zero rate on these taxes until the end of 2020. To apply the benefit, it is necessary that the businessman work in the production, social, scientific spheres or provide household services to the population.
Since the widespread introduction of online cash registers primarily pursues fiscal goals, the ability to work without a cash register can also be considered a tax benefit. At the beginning of 2020, only individual entrepreneurs without employees who sell goods of their own production, carry out work, or provide benefits for the use of cash register systems have the right to accept money from individuals without a cash register will last until July 1, 2021 (Article 2 of the Law dated June 6, 2019 No. 129- Federal Law).
Medium enterprises
In Art. 4 209-FZ stipulates that it refers to medium-sized businesses: these are business entities with an average number of employees from 101 to 250 people and with an annual income of up to 2 billion rubles. Compared to small medium-sized enterprises, they include entire networks of companies working for a large consumer audience. This entrepreneurial form operates not only within one city, but sometimes even within a region. Compared to small businesses, where a large role is assigned to staff, on average the quality of goods (services) is put in the foreground. It is easy for such companies to adapt to changing market conditions. Here are examples of medium-sized businesses in Russia:
- OJSC "Udmurtnefteprodukt" - oil industry;
- JSC "Bridge Construction Unit No. 19" - construction;
- JSC "Shchekinoazot" - chemical industry;
- JSC "Murmansk Shipping Company" - sea transport;
- OJSC "Ural Pipe Plant" - ferrous metallurgy.
When a website is needed and when a small business does not need it.
When is a website not needed for a small business? The answer is simply simple - as long as you can do without a website. I could put an end to this, but I’ll add a few details.
Small businesses whose target clientele does not use the Internet to search for goods or services of these businesses do not need a website. Some very realistic types of small businesses will not need a website (or indeed the Internet in general) either currently or in the near future. For example, why do small grocery stores (or many others) that operate in a certain area and serve residents of nearby houses need a website? And there are many such shops and shops in the world. They have been predicting a near end for many years, but, strangely enough, they live.
Do gas stations and eateries need websites? I don't think they are needed. Small businesses, which can, if necessary, advertise themselves on the Internet using social networks, do not need websites. For hairdressers, household appliances, repair shops, and many other small businesses, this is quite enough.
Don't create a website for your small business without being very specific about its purpose. Not general slogans like: “websites should increase the number of clients for my business,” but specific tasks expressed in specific numbers. For example, using the site should increase the number of clients of my small business by “N%” .
By assigning a specific task to website developers, you get exactly the tool your small business needs.
Criteria
Since 2020, a unified register of SMEs has been in operation. It includes companies that have received the status of small and medium-sized enterprises. The category of economic entities is determined by a number of criteria of financial and economic activity:
- amount of income;
- average number of employees;
- share of participation of other companies in the authorized capital.
For comparison, the criteria for small medium and large businesses are in the table:
| Criterion | Small | Average | Large |
| Income | Up to 800 million rubles. | Up to 2 billion rubles. | More than 2 billion rubles |
| The number of employees | 100 employees | Average number of employees of a medium-sized business: 101–250 employees | More than 250 employees |
| Share of participation of third parties in the authorized capital | The total share of participation of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, government agencies, public, religious organizations and foundations is no more than 25%. For other legal entities (foreign and those that are not SMEs) the maximum share is 49%. If participants are SMEs, then their share is not limited. | ||
According to Article 4 of the Federal Law “On the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation”, the established limits do not apply to:
- persons holding shares in the economic high-tech sector;
- persons participating in the Skolkovo project;
- companies that practically apply the latest technologies developed by their owners from among budgetary and scientific institutions;
- companies whose founders are included in the government list of persons who provide state support for innovation activities.
If an individual entrepreneur does not have employees, his status is determined by annual income. If individual entrepreneurs and LLCs are only included in the unified register of SMEs, their status is determined by the number of employees.
A website for a small business - a necessity or a fad?
In many cases, creating your own website is a tribute to fashion. And, as strange as it may sound, the illiteracy of a businessman. “Somewhere there, someone said that without a website there is no business today” - this is roughly what their reasoning looks like. Many people have no idea how to use it or how to maintain it.
Don’t think that I deny the benefits of the Internet and my sites. For the most part, the Internet today is a powerful tool for the development and promotion of small businesses. I am against its thoughtless use. After all, the Internet can bring a lot of harm to small businesses if used incorrectly.
Many small businesses create websites for themselves without even thinking about whether it is needed or not, or whether it will be useful. And only then are they convinced of its ineffectiveness and, even, its uselessness. After all, the site requires constant attention, it needs to be maintained, updated, and all this requires considerable material and time costs. And, having made sure that the site does not recoup the costs invested in its creation and maintenance, and does not lead to an increase in the profits of the small business, the entrepreneur abandons it and the site dies.
Advantages
SMEs have certain benefits:
- they are allowed to keep any amount of money in the cash register, and they will not be fined for it;
- they have the opportunity to maintain simplified accounting and calculate depreciation once a year;
- preferences have been established for them in state and municipal procurement.
The Ministry of Industry and Trade annually compiles a list of small and medium-sized businesses and sends it to the Federal Tax Service of Russia. Tax officials make adjustments to the Unified Register.
The main advantages of small business:
- the presence of a small need for initial capital;
- low costs of doing business;
- the ability to quickly respond to changes in the market;
- high turnover of equity capital;
- trend of growth of available vacancies, involvement of the population in the work process.
Advantages of medium-sized companies:
- creation of new jobs;
- greater productivity of investment;
- relatively high profitability;
- competitiveness;
- financial mobility.
Advantages of large enterprises:
- ensuring economic stability in the country;
- changes in the external business environment;
- saving production costs;
- introduction of modern technologies into business;
- expansion in world markets, etc.
In fact, for the owner of the company it does not matter what form his LLC belongs to - it is a small or medium-sized business or even a micro-enterprise. The main thing is competitiveness, stable income and low costs.
Reasons that encourage small businesses to create their own website.
There are many reasons for small businesses to create their own website. But it is not the purpose of this article to list them. I will give only imaginary reasons that encourage you to create your own sites when they are unnecessary.
What are the main reasons that encourage entrepreneurs (especially small businesses) to create their own websites and then not know what to do with them. There are several such reasons.
Firstly , it’s a tribute to fashion, not common sense: many people already have websites, I need to start one too.
Secondly , there is a misconception about your image: how a modern businessman will look in the eyes of clients and colleagues without his website.
Thirdly , thoughtless compliance with the persistent entreaties of web studios and webmasters. Their persistent admonitions that your small business without a website is doomed to languish, but with a website it will thrive, forcing you to spend considerable sums on website creation. This money is often pulled out of the last reserves, which leads to the untimely death of the small business along with the site.
Fourthly , the banal pursuit of easy money. Today the network is replete with offers on how you can quickly earn money without investing anything, or almost nothing. I’m not talking about obvious scams here (enough has already been said about this). We are talking about real information businesses, about making money online. But, as in ordinary business, 90-95% of attempts end in failure, and in the information business (there are no exact statistics), I think the same percentage of those trying to really make money on their sites quickly become disillusioned with this idea and abandon their sites.
Cons and risks
Before starting your own business, compare all the pros and cons for different economic scales. For example, here are the main disadvantages of small businesses:
- high level of economic risk;
- dependence on larger players in the market;
- high influence of personnel on the final result;
- low professionalism of managers;
- difficulties in obtaining loans and subsidies.
The size of the initial capital also matters. The higher the savings, the greater the chances of holding out during the crisis and not going bankrupt.
Disadvantages of medium-sized businesses:
- fierce competition and the threat of takeover by large enterprises;
- difficulties in obtaining licenses and patents;
- periodic lack of funds in circulation.
Risks of owning a large company:
- excessive economic concentration;
- localization of economic relations;
- blocking horizontal commercial connections, inability to go beyond a specific enterprise.
Simplified accounting and personnel records
Small businesses are entitled to the following accounting benefits:
- The head of a small business can keep records independently. True, in operating companies this situation rarely occurs in practice: after all, even in a “micro-enterprise” the director has many other concerns. But if the company does not yet operate and does not have employees, then the manager can prepare and submit zero reports himself, without resorting to the help of “third-party” specialists.
- Small businesses can use a simplified version of accounting and submit financial statements in a shortened format. In particular, they may “cut down” the chart of accounts and not apply some accounting regulations. And “micro-enterprises” generally have the right to do without double entry and register all business transactions in one journal (recommendations approved by the protocol of the IPB of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2013 No. 4/13).
- A small business may not set a limit on the cash balance in the cash register (clause 2 of the instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 N 3210-U).
“Micro-businessmen” may not complete the full set of personnel documents required by labor legislation (Article 309.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In particular, they have the right not to draw up regulations on remuneration, internal labor regulations, etc.
But this does not mean that the relationship between the “micro-businessman” and his employee is not regulated in any way. All the main provisions that larger enterprises include in separate documents, in this case, should be reflected in the employment contract.
Differences
Here are the main differences between small, medium and large businesses:
| № | SME | Large |
| 1 | Difficulties in obtaining a loan | Simplified lending process |
| 2 | Adaptation to market changes | It is more difficult to adapt to changing market conditions |
| 3 | Up to 250 people work | More than 205 employees work |
| 4 | Annual income reaches 800 million rubles. for small ones and 2 billion rubles. from medium-sized companies | Annual income exceeds 2 billion rubles |
| 5 | Big risks during a crisis | Less risk during a crisis |
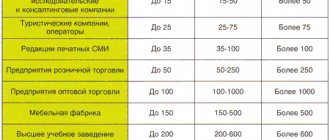
A visual diagram of how a small business differs from a medium business in terms of business processes.