Individual entrepreneur authorized capital
When thinking about creating his own business in the form of an individual entrepreneur, the future entrepreneur is forced to solve a number of organizational issues, including: does the individual entrepreneur need authorized capital, and what should it be? The law defines the status of the need for authorized capital for individual entrepreneurs quite clearly, but there are some nuances that will have to be taken into account. So, how to organize your own individual entrepreneur, and what financial investments will be needed?
How to open an individual entrepreneur in 2020?
Opening an individual entrepreneur, compared to other forms of enterprise ownership, is significantly simplified: there is no need for lengthy legal red tape or significant capital investments. But a number of actions will still have to be done.
The procedure for registering business activities in 2017-18 includes several steps:
- A visit to the tax office, where the future entrepreneur receives an application form.
- Selecting in the OKVED directory the code of the activity you plan to engage in. It will need to be indicated in the application. It is possible to specify several codes, but only one appears as the main one.
- Choosing which tax system to work with.
- Payment of state duty.
- Filling out the application itself and a package of other necessary documents to the tax office.
- Receiving documents on registration of individual entrepreneurs.
The OKVED directory is available in the Consultant system and on other resources. For an entrepreneur planning to make, for example, kitchen furniture, the main code will be 31.02. If the product list includes mattresses, then the second code will be 31.03 - and so on. Code designations do not have to be indicated from related areas; in addition, their number for individual entrepreneurs is not officially limited.
There is a recommendation to include up to 30 items from OKVED in the application. If necessary, they can be changed in the future.
Which tax system should you choose?
The following options are available:
- simplified system or simplified tax system;
- OSNO - general, which is suitable for everyone, but for beginners in business it causes difficulties due to complex reporting;
- patent system - PSN. An individual entrepreneur buys a patent for a period of one month to a year;
- tax on imputed income, otherwise UTII.
It is worth deciding on the system in advance, even before opening an individual entrepreneur, since an application to switch to one of them is submitted immediately after registering a business. Those who do not do this will be forced to transfer to OSNO after 30 days.
The necessary step is to pay the registration fee. Today it is 800 rubles. You can pay through any bank, but it is advisable to do this at Sberbank. A receipt for payment is generated through the Federal Tax Service website. Upon payment, a check is printed and submitted to the tax office along with other papers.
From the documents you will need:
- Russian passport;
- TIN (if any);
- application for registration of individual entrepreneurs;
- a receipt confirming payment of the duty.
The papers are submitted to the tax office at the place of permanent registration. The addresses of the branches are listed on the Federal Tax Service website. It is also allowed to submit documents to the state multifunctional center. After delivery, the future individual entrepreneur receives a receipt with a list of papers, and he is assigned a date of receipt. By law, registration takes no more than 3 working days.
After them, the entrepreneur receives:
- TIN (if there was none);
- extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
An important point is the relationship with the Pension Fund and the social insurance service:
- if there are no employees, no additional actions are required, these authorities will register themselves, having received data from the Federal Tax Service;
- if you plan to hire workers (or already have them), you will need to register additionally as an employer.
It is important to remember that some activities are carried out under specific tax schemes. Therefore, all questions should be clarified before registering a business.
What about the authorized capital?
The law does not require an individual entrepreneur to have any fixed amount to start a business; entrepreneurship does not officially require initial funds. But business always involves some costs, and you will definitely have to invest. The capital of an individual entrepreneur, however, remains at his discretion. In the case of LLC, CJSC, etc., the requirements are different - they must have an authorized capital and constituent documents.
What is authorized capital?
Authorized (or authorized - both spellings are found) capital (MC) is one of the key differences between an individual entrepreneur and a legal entity. This is a certain amount of money that the founder of the company invests in order to start operations. That is, the management company is a resource necessary to launch an enterprise. The invested funds can be spent at the discretion of the legal entity - transfer salaries, pay for the services of suppliers or rent.
Different types of legal entities are required to have a capital in the amount of:
- opening an LLC will require 10 thousand rubles;
- The charter capital for an OJSC is calculated using the formula 10*minimum wage;
- The capital of a closed joint stock company must be 100 times the minimum wage.
The type and size of investments (not lower than the minimum allowable by law) is determined by the founders of the company. It is not necessary to contribute it in cash - it can be securities, material assets, trademarks, patents. The procedure for entering the Criminal Code is approved upon the creation of the company and is reflected in the Charter; for example, you can pay it one-time or monthly in equal installments. Once established, the Criminal Code is changed only by a notary. Speaking about individual entrepreneurs, we can note the advantage of this organizational form: authorized capital is not needed.
When the property of an individual entrepreneur is contributed to the authorized capital of an LLC, taxable income does not arise
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in its letter No. 03-11-11/54 dated March 16, 2010 explains whether taxable income arises for an individual entrepreneur applying the simplified tax system, transferring as a contribution to the authorized capital of an LLC, property the value of which, according to tax accounting data, is less than the cost , assessed by the evaluator when assessing the contribution.
The letter notes that, in accordance with subparagraph 4 of paragraph 3 of Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of property, if such transfer is of an investment nature (in particular, contributions to the authorized capital of business companies and partnerships, contributions under a simple partnership agreement (agreement on joint activities), share contributions into mutual funds of cooperatives) is not recognized as the sale of goods, works or services.
What is the capital of the individual entrepreneur?
Opening an individual entrepreneur, compared to other forms of enterprise ownership, is significantly simplified: there is no need for lengthy legal red tape or significant capital investments. But a number of actions will still have to be done.
The procedure for registering business activities in 2017-18 includes several steps:
- A visit to the tax office, where the future entrepreneur receives an application form.
- Selecting in the OKVED directory the code of the activity you plan to engage in. It will need to be indicated in the application. It is possible to specify several codes, but only one appears as the main one.
- Choosing which tax system to work with.
- Payment of state duty.
- Filling out the application itself and a package of other necessary documents to the tax office.
- Receiving documents on registration of individual entrepreneurs.
The OKVED directory is available in the Consultant system and on other resources. For an entrepreneur planning to make, for example, kitchen furniture, the main code will be 31.02.
If the product list includes mattresses, then the second code will be 31.03 - and so on.
Code designations do not have to be indicated from related areas; in addition, their number for individual entrepreneurs is not officially limited.
[/su_box]
There is a recommendation to include up to 30 items from OKVED in the application. If necessary, they can be changed in the future.
What is the nature of the capital of an individual entrepreneur
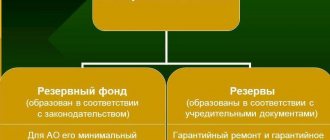
Financial reserve capital can be used only for specific needs, for example, to compensate for losses that may arise in the process of doing business or to purchase fixed assets. There is no such order by law, but every entrepreneur has the right to decide to establish his own reserve capital; in the future, such steps may allow him to work successfully even in difficult economic periods.
Individuals who are tax residents of the Russian Federation, as well as individuals receiving income from sources in the Russian Federation who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation, are recognized as payers of personal income tax (clause 1 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Authorized capital of individual entrepreneurs
Opening an individual entrepreneur, compared to other forms of enterprise ownership, is significantly simplified: there is no need for lengthy legal red tape or significant capital investments. But a number of actions will still have to be done.
The procedure for registering business activities in 2017-18 includes several steps:
- A visit to the tax office, where the future entrepreneur receives an application form.
- Selecting in the OKVED directory the code of the activity you plan to engage in. It will need to be indicated in the application. It is possible to specify several codes, but only one appears as the main one.
- Choosing which tax system to work with.
- Payment of state duty.
- Filling out the application itself and a package of other necessary documents to the tax office.
- Receiving documents on registration of individual entrepreneurs.
Is it needed for individual entrepreneurs?
When discussing whether authorized capital is needed for an individual entrepreneur, it should be borne in mind that private entrepreneurs do not have a charter. Based on this, the formulation itself in this case is somewhat incorrect.
The individual entrepreneur is the sole founder of his entrepreneur and decides for himself how to conduct business. Legislators do not impose strict requirements on private entrepreneurship. In addition, the businessman himself decides how to distribute income, but does not share profits with anyone.
When talking about an individual entrepreneur, its authorized capital often means its starting capital. The law does not oblige an entrepreneur to have one, but in practice, of course, it is often present. However, the very fact that the State does not require capital from individual entrepreneurs attracts many businessmen to register this particular form of ownership for their business.
IP finances in 2020: income, expenses, taxes, funds
Any business activity is associated with making a profit from the sale of goods, provision of services, performance of work, etc. Making a profit is the main goal of entrepreneurship. Profit, as well as interest from its use, plus other cash receipts form the finances of individual entrepreneurs.
Revenues and profits
Profit is the difference between the income received and the entrepreneur’s expenses incurred in the process of obtaining this income. This difference between income and profit is not always taken into account when creating your own business.
Back to contents
What is income
According to the law, the income of an entrepreneur means all the money he receives while carrying out business activities.
IP income includes:
- revenue from the sale of goods, works, services;
- income from the sale of own assets, as well as personal property and securities;
- non-operating income.
All income is subject to reflection in accounting documentation, as well as in tax reporting, which the entrepreneur is required to submit. Moreover, most taxation systems provide for a tax on the income of individual entrepreneurs: for example, when using the general taxation system, the tax base is income reduced by the amount of professional deductions.
In other situations, the object of taxation is conditional income, which an entrepreneur can theoretically receive when carrying out business activities under certain conditions. This income is called imputed; in the first case, an economic concept such as the gross income of an entrepreneur is used.
However, the need for correct accounting of income in business activities is important not only when calculating taxes. Thus, the maximum income of an individual entrepreneur is taken into account when assessing his ability to use the simplified taxation system. At the same time, the legislation does not contain any restrictions on the amount of income received by an entrepreneur without reference to a specific taxation system.
Back to contents
Declaration of income of individual entrepreneurs
Also very important in many situations is the question of how to confirm the income of an individual entrepreneur, for example, when he receives a loan.
In such a situation, it is necessary to submit a tax return on income, and here it is important that the data be as truthful as possible (see how to fill it out correctly).
Note that, depending on the taxation system, the income declaration of individual entrepreneurs has different forms, as well as the procedure for reflecting income in it. This feature must be taken into account when submitting a declaration to interested organizations, for example, banks.
Back to contents
What is profit
The profit of an entrepreneur, as noted above, is formed by the financial resources received as a result of the activity, minus the funds spent on this activity. As a rule, this category is not subject to taxation.
With a simplified taxation system, the object is income reduced by the amount of expenses. However, it should be remembered that for tax accounting purposes, expenses are recognized only in accordance with the list defined by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the difference between income and expenses shown by an individual entrepreneur in his tax return under the simplified tax system often does not coincide with his real profit.
Back to contents
Profit calculation
It is also important to make correct calculations of profit, since profitability is the main category showing the effectiveness of business activities. Calculating the entrepreneur’s profit is also important for investing in his activities, since the invested funds must bring certain dividends.
Profit is the main source of both the individual entrepreneur’s own funds, allocated for personal needs, and investment in business.
Distribution of profits is not difficult, but requires a thoughtful approach to this process. There is often a high risk of using all the funds received for your own needs, as a result of which the business is left without financial investments: this is extremely dangerous, especially at the very initial stage of its existence.
Back to contents
Profit on assets
The most optimal option for distributing profits is to direct most of it to fixed assets of individual entrepreneurs, which form the production capacities necessary for running and expanding the business.
Purchasing them at the expense of one’s own profit indicates a more than stable position of the entrepreneur, and also allows one to avoid additional costs of paying interest on the loan.
Fixed assets of an individual entrepreneur are in personal ownership, which allows them to be quickly managed, replaced in a timely manner, the sale of surpluses, etc. Do not forget that fixed assets can serve as an additional source of profit, for example, when selling them in cases of non-use business.
Due to the importance of fixed assets in the financial and economic activities of an entrepreneur, it is necessary to organize detailed accounting of fixed assets. It allows you to identify ineffective fixed assets that require replacement, as well as the need for new funds that are necessary to expand production or improve its efficiency.
Back to contents
Accounting for income and expenses
Any entrepreneur must keep records of income and expenses. This is often necessary due to legal requirements. For example, to correctly calculate the tax base or to ensure that the maximum turnover of individual entrepreneurs is observed, to maintain the possibility of using a simplified taxation system.
But these indicators are also important for the entrepreneur himself, as they provide a clear picture of business performance. An analysis of the financial condition of an individual entrepreneur may also be useful here. Experts advise carrying out such analysis at regular intervals. This makes it possible to timely identify an unfavorable situation, as well as carry out certain measures to resolve the current situation, and it is the analysis that often makes it possible to identify specific areas that require prompt intervention.
Taxes, income and profit of individual entrepreneurs
- acquisition of property for the purpose of subsequent profit from its use or sale;
- accounting of business transactions related to transactions;
- the interconnectedness of all transactions made by a citizen in a certain period of time;
- stable relationships with sellers, buyers, and other counterparties;
- taxpayer status at the time of the transaction, etc.
We recommend reading: Permission from guardianship to purchase an apartment with a mortgage
According to the financial and tax authorities (see letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 7, 2006 N 03-01-11/4-82, dated September 22, 2006 N 03-05-01-03/125, dated August 16, 2010 N 03-04- 05/3-462, dated 06/01/2010 N 03-04-05/3-302, letters from the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 03/30/2007 N 28-10/28916, dated 12/25/2008 N 18-14/4/ 121074, dated December 29, 2008 N 18-14/), the following facts may indicate the presence of signs of entrepreneurial activity:
Does the individual entrepreneur have an authorized capital? :
When people are going to create their own business, the second question after choosing the type of activity arises is in which form it is more profitable to exist: an individual entrepreneur, whose authorized capital is zero, or a joint-stock company (in different legal forms) - if several participants are involved in the business. We will consider these and other nuances in more detail in the article.
Individual entrepreneur
This form of business organization implies the conduct of business by one person, often in a simplified form, when the owner of the company acts as the founder, manager, and sometimes the only employee. It would seem to be a convenient and accessible form, but it is fraught with the main drawback - if the obligations of an individual entrepreneur are not fulfilled, he risks losing absolutely all his property.
The registration process is simple, usually lasts no more than five working days and costs about 800 rubles. This is explained by the fact that for individual entrepreneurs, authorized capital, constituent documents and special management bodies are not needed. When registering, you don’t even need to have a stamp or open a current account.
Although the latter will still be needed later due to the Central Bank’s ban on spending cash from the cash register (everything that does not relate to the payment of wages, payment for goods and services). In addition, cash payments by an individual entrepreneur in the amount should not exceed 100,000 rubles.
All other agreements are settled only in non-cash form.
Advantages of IP
Individual entrepreneurship is attractive from the point of view of the simplicity and speed of the paperwork procedure, which can be carried out at the applicant’s place of residence.
In addition, the initial package of documents required for registration is very small and consists of: the original passport and its notarized copy, a standard application and a receipt for payment of the state fee for registering a company.
This organizational and legal form provides for a simplified taxation system that relieves the entrepreneur from the need to pay personal income tax and property tax (in some cases).
This also includes the possibility of non-payment of VAT, but this only applies to the circulation of domestic goods.
A simplified form of accounting in the form of maintaining a book “Income and Expenses” also speaks in favor of individual entrepreneurship. And, of course, an important advantage is the ability of an entrepreneur to dispose of profits at his own discretion: for business or personal needs.
Limited Liability Company
An LLC is a form of organization in which one or more founders participate; they are engaged in joint business activities with the creation of a legal entity. The authorized capital of the company consists of shares of each of them.
The process of registering an LLC is quite complex and lengthy, with a large amount of documentation being submitted to the government agency. In addition, with this form of business, unlike an individual entrepreneur, an authorized capital is required. Since 2020, its minimum amount is 10 thousand rubles. In addition, a bank account and a company seal are required, and this leads to additional costs.
There are also a number of “inconveniences” of this organizational form:
- division of profits between LLC participants at a certain time interval (once a quarter);
- regular accounting reporting to the relevant government agency;
- larger fines for administrative violations compared to individual entrepreneurs;
- a very long and complex process of closing an organization.
Why is an individual entrepreneur not required to have an authorized capital?
As is known from economic definitions, authorized capital is necessary in order for a joint stock company to be able to pay off its obligations. That is, if it is necessary to pay accounts payable, only assets that constitute the authorized capital and are supported by the constituent documents of the limited liability company can be taken into account. The co-founders of the latter, depending on the share of contribution, have more or less influence in making decisions about the organization's activities.
An individual entrepreneur does not need authorized capital, since he is the sole owner of his business and decides for himself how to conduct business. As for obligations, today, according to the law, an individual entrepreneur risks losing all his property in case of failure.
If we assume that a bill will be created obliging it to have an authorized capital, there are two sides to this. On the one hand, the businessman’s degree of material risk is reduced only by the amount of funds deposited.
But on the other hand, the “availability” of business decreases, since not everyone has the required amount at the start.
Failure to pay a share in the authorized capital and its consequences
From the legislative side, the question of the consequences of non-payment of a share of the authorized capital has an unambiguous answer. In Art. 1.6 of the LLC Law clearly states that the unpaid share of the management company passes to the enterprise. And also in paragraph 3 of Art. 23 of this law states that if you fail to pay your share in full within the period established by law, this share passes to the company. Thus, a person deprived of his share loses the status of a participant in the enterprise.
As an example of the consequences that arise from non-payment of the authorized capital, we can consider a real case from judicial practice. The LLC was founded in February 2010. The authorized capital was not paid by any of the participants on time. However, one of the participants, who invested effort and money in the company and was more interested in development, paid his share in March of this year, that is, 2 years later in 2012, but still paid. The share of the second LLC participant has not been paid. It is planned to submit documents to the Federal Tax Service on the transfer of his unpaid share to the company.
Documents for state registration of the relevant changes must be submitted to the body carrying out state registration of legal entities within a month from the date of transfer of the share or part of the share to the company. These changes become effective for third parties from the moment of their state registration.
The body carrying out state registration of legal entities must be notified of the transfer of a share or part of a share in the authorized capital of the company to the company. This must be done no later than within a month from the date of transfer of the share or part of the share to the company by sending an application for making appropriate changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and a document confirming the grounds for transferring the share or part of the share to the company.
Documents for state registration of the changes provided for in this article, and when selling a share or part of a share, also documents confirming payment of a share or part of a share in the authorized capital of the company, must be submitted to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities within a month from the date of the decision to distribute the share or part of the share among all members of the company, about their payment by the acquirer or about repayment. These changes become effective for third parties from the moment of their state registration.
In order to take possession of the rights to assets belonging to one of the participants, unscrupulous shareholders sometimes try to prove his legal insolvency due to his failure to pay his share of the authorized capital. The fact is that often the issues of preserving documents proving the contribution of a share of the authorized capital are dealt with by hired employees or outside consultants. This leads to the loss of title and payment documents. And also such documents can simply be maliciously seized and destroyed.
In the absence of direct evidence of payment for his share in the authorized capital, a participant can achieve recognition of this fact with the help of other, indirect, evidence. Such circumstantial evidence is usually considered in court.
During the court hearing, bona fide participants of the company usually manage to prove the fact of payment for a share in the authorized capital
The most common evidence of payment of a share of the authorized capital is the court's consideration of the enterprise's balance sheets. The fact is that the balance sheet of the enterprise reflects in a separate line the debt for payment of the authorized capital and the transfer of the share from the participant to the enterprise. Thus, if the balance sheet indicates payment by a participant for his share of the management company, then in the eyes of the court this is irrefutable evidence of such payment. In this case, the courts rightly refer to Art. 68 Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
Actual non-payment of share of the authorized capital
It is interesting to study the issue of non-payment of the management company's share in the case when it was not actually paid. An article by lawyer Vitaly Basov is devoted to considering this situation. They tried to “squeeze” his enterprise out of his client, the director of a construction company, and its sole founder. Representatives came to the director and offered further cooperation subject to the sale of a 51% share in the authorized capital to them. He agreed to the deal and, as a result, they tried to bankrupt his company and expel him from the founders, promising to pay for his 49% share in the authorized capital. In fact, by that time the company was so indebted that any real payment was out of the question.
In what cases may it be necessary?
A private entrepreneur will need a charter only in one case - if he decides to change the organizational and legal form of his organization. This need, in turn, may be due to several important business factors:
- An entrepreneur wants to operate in an area that is inaccessible to individual entrepreneurs. For example, one that requires a license.
- A businessman wants to expand his business. To do this, he needs to attract investment. In this case, investors become full partners of the entrepreneur.
- The market is changing, and financial risks are increasing as a result. The businessman fears the closure of the business and the loss of personal property, so he decides to change the legal form.
These factors can apply to any area of business and overlap with each other. Thus, business expansion often involves starting activities in a new area that was previously inaccessible to a private entrepreneur. An unfavorable market situation can prompt several individual entrepreneurs to combine their efforts and assets. Relatively little competition in the areas subject to licensing provides incentives to expand and operate in these areas.
In case of a change in the form of ownership, the procedure for declaring the authorized capital will be the same as in the case of legal entities. The founders also set the percentage of shares in the business themselves.
In connection with the possible transition from an individual entrepreneur to an LLC, it is better for private owners to decide in advance how much material resources they are willing to invest in the future organization, and save it in case of force majeure circumstances in the business.
Individual entrepreneurs and LLCs are fundamentally different classes of business. Differences begin already in the constituent documents and predetermine the features of further activities. Businessmen prefer an easier path to their business. Convenient accounting, preferential taxation, favorable mortgage conditions - this is just a short list of the positive features of doing business as an individual entrepreneur. What makes it special is the lack of authorized capital: you can open your own enterprise with minimal costs and not declare the amount of your starting capital anywhere. This fact makes individual entrepreneurs a very attractive form of ownership for beginning entrepreneurs.