The concept of the authorized capital of a joint-stock company
The commercial activities of any company must be carried out in accordance with current legislation. According to Art. Part 1 Art. 96 GK, JSC – a business structure whose starting capital consists of shares. The authorized capital of a company is a value that is summed up taking into account the cost of all securities purchased by the founders of the company. This category does not formally relate to property assets, but the money used to pay for the shares is included in it.
It is necessary to take into account that the authorized capital (hereinafter referred to as the authorized capital) is a conditional value that can change repeatedly over a certain period of time.
It is the main material resource of a commercial structure. This is why the actual and nominal value of a fund often differs.
Some experts believe that the authorized capital of a joint-stock company is a kind of accounting code by which they determine how much the company’s property is worth in monetary terms. Others believe that a start-up fund should be regarded as a classic form of a loan from a joint stock company to its founders, who will receive their initial investment back after the business closes.
Using the example of a joint stock company (JSC), we will consider what amount of authorized capital is needed to open a business, and why it is reduced or increased.
6.3. The procedure for forming the authorized capital of joint stock companies
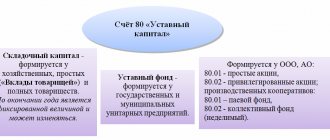
The authorized capital of a joint stock company is made up of contributions from shareholders (participants).
It reflects the own sources of formation of assets and the property of the joint-stock company as a legal entity. Time, the amount of the authorized capital reflects the collective ownership of shareholders, where the share of each is determined by the nominal value of the shares acquired by him. Accounting for the authorized capital begins on the day of registration of the enterprise in the state register of business entities and ends on the day of the company’s disposal from the state register (due to termination of activity, bankruptcy, etc.). According to the Law of Ukraine “On Business Companies,” a joint-stock company is a company that has an authorized capital divided into a certain number of shares of equal par value and is liable for obligations only with the property of the company. The authorized capital of a joint stock company cannot be less than an amount equivalent to 1,250 minimum wages at the time of the company's creation. The amount of the authorized capital reflected in financial accounting and reporting must be equal to the total par value of the issued shares specified in the constituent documents. A share is a unit of ownership in a joint stock company. The Law of Ukraine “On Securities and the Stock Exchange” defines a share as a security without a specified circulation period, which certifies equity participation in the authorized capital of a joint-stock company, confirms membership and the right to participate in its management, and gives its owner the right to receive a portion of the profit in the form dividends, as well as for participation in the distribution of property during the liquidation of a joint-stock partnership. Shares can be registered or bearer, simple or preferred. All joint stock companies must issue common shares, which will have voting rights. Preferred shares may also be issued. The amount of common shares is the residual capital of the company, because the owners of preferred shares are given priority rights in the payment of dividends and distribution of assets in the event of liquidation of the company. Owners of preferred shares do not have the right to participate in the management of a joint-stock company, unless otherwise provided by its statute. The issue of shares must be accompanied by its registration with the State Commission for Securities and the Stock Market. Forms of shares are accounted for in the off-balance sheet account “Forms of strict reporting”. The founders of a joint stock company can be legal entities and citizens. The founders of a joint-stock company enter into an agreement among themselves defining the procedure for their joint activities to create a joint-stock company, responsibility to the persons who subscribed to the shares and third parties. The founders bear joint liability for obligations that arose before the registration of the joint-stock partnership. To create a joint-stock company, the founders must make a notice of intention to create a joint-stock company, subscribe for shares, conduct a constituent meeting and state registration of the joint-stock partnership. A joint stock company has the right to issue securities in accordance with the requirements established by the State Commission on Securities and the Stock Market. In the event of an additional issue of shares without registration of the previous issue of shares, all purchase and sale agreements for shares of the additional issue are considered invalid. No later than six months after registration of the issue of shares, the joint-stock company is obliged to issue shares (share certificates) to shareholders. A closed joint stock company has the right to issue only registered shares. Shares are purchased by participants when creating a joint-stock company on the basis of an agreement with its founders, and when additional shares are issued in connection with an increase in the authorized capital of the partnership. A share can also be acquired on the basis of an agreement with its owner (holder) at a price determined by the parties, or at the price prevailing on the stock market, as well as in the order of inheritance of citizens or succession of legal entities and on other grounds provided for by law.Module. When creating a joint-stock company, shares can be distributed by open subscription to them (in open joint-stock companies) or distribution of all shares among the founders (in closed joint-stock companies). An open subscription for shares when creating a joint stock company is organized by the founders. In any case, they are obliged by the holders of shares in the amount of at least 25% of the authorized capital and for a period of at least two years. The founders of an open joint stock company (issuers) are required to publish, in accordance with the requirements of the current legislation, information on the issue of shares, the content and registration procedure of which are established by the State Commission for Securities and the Stock Market. The founders of a joint stock company publish messages about the subsequent open subscription, which indicate its corporate name, the subject, goals and terms of the company's activities, the composition of the founders, the date of the constituent meeting, the size of the authorized capital, the expected nominal value of shares, their number and types, advantages and benefits founders, location, initial and final dates for subscription to shares, composition of property contributed by the founders in kind, name of the banking institution and current account number to which initial contributions should be made. By decision of the founders, other information may be included in the message. The open subscription period cannot exceed 6 months. Persons wishing to purchase shares must deposit into the founders' account at least 10% of the value of the shares for which they have subscribed, after which the founders issue them a written undertaking to sell the corresponding number of shares. Upon expiration of the period specified in the message, the subscription is terminated. If by that time it has not been possible to cover 60% of the shares by subscription, the joint-stock company is considered unincorporated. Persons who subscribed to the shares are returned the amounts they contributed or other property no later than 30 days later. For failure to fulfill this obligation, the founders bear joint liability. If the subscription for shares exceeds the size of the authorized capital, the founders may reject the excess subscription if this is provided for by the terms of the issue. Refusal to subscribe is carried out according to the list of subscribers from the end of the list. If the founders do not reject the excess subscription, the decision to accept or reject the excess subscription is made by the constituent meetings. If the founders or the constituent meeting refuse the excess subscription, the amounts contributed will be returned in the manner prescribed by part four of this article. By the day of convening the constituent meeting, persons who subscribed to the shares must contribute, taking into account the preliminary contribution, at least 30% of the nominal value of the shares. To confirm the contribution, the founders issue temporary certificates. A joint stock company has the right to redeem the shares paid for by the shareholder only at the expense of amounts exceeding the authorized capital, for their subsequent resale, distribution among its employees or cancellation. These shares must be sold or canceled within a period of no more than one year. During this period, the distribution of profits, as well as voting and determining the quorum at the general meeting of shareholders, is carried out without taking into account the own shares acquired by the joint-stock company. The shareholder, within the terms established by the constituent meeting, but no later than one year after registration of the joint-stock company, is obliged to pay the full cost of the shares. In case of failure to pay on time, the shareholder, unless otherwise provided by the charter of the enterprise, pays 10% per annum of the amount of the overdue payment for the time of delay. If payment is not made within three months after the due date for payment, the joint stock company has the right to sell these shares in the manner established by the charter of the partnership. A joint stock company is prohibited from issuing shares to cover losses associated with its business activities. Changes to the authorized capital A joint stock company may change the size of the authorized capital in accordance with the decision of the meeting of shareholders. These changes are reflected in accounting only after state registration of the new amount of authorized capital. An increase in the authorized capital of a joint stock company by no more than 1/3 can be carried out by decision of the board, provided that the rate is provided for by the statute. Changes in the authorized capital are regulated by the Regulations on the procedure for increasing (decreasing) the size of the authorized capital of a joint-stock company, approved by decision of the State Commission for Securities and the Stock Market dated April 8, 1998 No. 44. A joint stock company has the right to increase its authorized capital if all previously issued shares are fully paid at a value not lower than their par value. An increase in the authorized capital can be carried out by issuing new shares, exchanging bonds for shares, increasing the par value of the shares. When the number of shares of the established par value increases, subscription to additionally issued shares is carried out in the same manner as for shares of the first issue, and the authorized capital is increased due to: additional contributions from participants - this will be reflected in accounting in the same way as operations for the formation of the authorized capital; indexation of fixed assets in accordance with the Regulations on the procedure for increasing the authorized capital through indexation of fixed assets, approved by the decision of the State Securities and Stock Market Committee dated February 12, 1998 No. 39; reinvestment of profits; accrued dividends - in the case when a decision is made to pay dividends in shares. When the par value of shares increases, the authorized capital can be increased through additional contributions from participants to the established level of the par value of shares or through indexation of fixed assets. We have already looked at both of these options. A decrease in the authorized capital of a joint-stock company can be carried out by reducing the par value of shares or reducing the number of shares of the existing par value by buying them back from the owners for the purpose of cancellation. Accounting with the founders is shown in the table: To register information about the issue of shares, the following documents are submitted to the registration authority: a) application for registration of information about the issue of shares; b) a notarized copy of the constituent agreement (in case of the first issue of shares); c) information on the issue of shares of an open joint-stock company. The information is submitted to the registration authority in 2 copies and must be numbered, laced and certified by the signature of the director and the seal of the issuer (in the case of the first issue of shares - by the signatures and seals of the founders or their authorized persons), as well as by the signatures and verification of the auditor (audit firm). Module. If the issuer uses the services of a securities dealer to place a given issue of shares, then the information is also certified by the signature and seal of the securities dealer; d) a copy of the payment order for payment of the state duty for registration of information on the issue of securities in the amount prescribed by law; d) the decision to issue shares is documented in minutes, which must contain information about: The number and percentage of votes of shareholders participating in the meeting; corporate name of the issuer and its location; the size of the authorized capital or the cost of the issuer's fixed and working capital; the goals and subject of its activities; instructions from the issuer's officials; name of the controlling body (audit firm), data on the placement of previously issued securities (list and results of previous issues of securities indicating registration certificates of securities issues and authorities, issued the relevant certificates (indicating for each issue the number of registered and bearer shares, common and preferred shares, interest-bearing and non-interest-bearing bonds, par value and total issue amount) purpose of issue of shares; indication of categories of shares, number of registered shares and bearer shares, number of preference shares; form of issue of shares; total issue amount and number of shares ; nominal value of shares; number and percentage of votes of shareholders making decisions on the issue of shares (if the decision is made by the general meeting of shareholders); voting procedure, procedure for paying dividends; the procedure for subscription to shares and payment for them, period for the return of funds in case of refusal to issue shares; the order of issue of shares (if they are issued in different series), the procedure for notification of the issue and the procedure for placing shares, the rights of owners of preferred shares; the procedure for exercising the preemptive right of shareholders to purchase shares that are issued additionally, in an amount proportional to their share in the authorized capital on the date of the decision to issue shares; the period for an open subscription for shareholders exercising their preemptive right, and the period for the subscription; the action of other investors and shareholders to purchase shares in a quantity that exceeds the number of shares to which the shareholder has a preemptive right e) interim financial statements for the reporting period preceding the quarter, in in which documents are submitted to register information on the issue of shares, as part of the balance sheet and the financial results statement (for banks - the profit and loss statement), certified by the signatures and seals of the issuer and the auditor (audit firm), as well as the conclusion of the auditor (audit firm) ( in case of additional issue of shares) f) balance sheet and statement of financial results (for banks - profit and loss statement), certified by the signatures and seals of the issuer and auditor (audit firm), certificate of financial condition and report of the auditor (audit firm) for the reporting year , preceding the year in which documents are submitted to register information on the issue of shares (in case of additional issue of shares); f) the conclusion of the auditor (audit firm) regarding the ability of the founders - legal entities to pay the appropriate contributions to the authorized capital (at the first issue of shares); g) a certificate certified by the signatures and seal of the registrar on the transfer of the register of owners of securities; h) copies of registration certificates of pre-issues of securities; i) a notarized copy of the company’s charter (to confirm the authority to make a decision to increase the size of the fund’s charter other than the general meeting of shareholders). Information on the issue of shares must include the following information: a) characteristics of the issuer: full and abbreviated (if any) name; location, telephone (fax, email); date of state registration of the joint stock company and the body that carried out its registration; subject and goals of activity, size of the authorized capital; number of full-time employees (for length of service, the last day of the quarter preceding the quarter in which documents are submitted) number of shareholders (as of the axis, the number of the quarter preceding the quarter in which documents are submitted) b) information about the officials of the issuer, and the chairman and members of the executive body, no members of the council (supervisory board) of the company, the audit commission and the chief accountant: also, first name and patronymic, year of birth, qualifications, length of service, length of service in this position, position held by the person at this place of work; c) information on the average salary of the executive body for the last quarter and the previous financial year preceding the filing, cops (with the consent of these members of the executive body d) a list of licenses (permits) of the issuer to conduct certain types of activities, indicating the expiration date of their validity; e) information about the issuer’s participation in holding companies, concerns, associations, etc.; f) information about legal entities in which the issuer owns more than 10% of the authorized capital of assets, including subsidiaries, and representative offices of the issuer; f) a description of the issuer's activities as of the reporting period preceding the quarter in which documents for registration are submitted informs about the issue of shares, namely data on: the volume of main types of products, services or work carried out by the issuer; sales markets and development features of gal: which the issuer operates; volumes and directions of the issuer’s investment activities; policy regarding research and development; g) possible risk factors in the issuer’s activities; c) prospects for the issuer’s activities for the current and next years; i) intermediate financial statements for the reporting period preceding the quarter, which submit documents for registration of information on the issuance of shares, as part of the balance sheet and report on financial results (for banks - reports on profits and losses);
Key Features
Having formed the authorized capital, the participants of the joint-stock company can count on significant preferences, the essence of which boils down to receiving profit in the form of dividends.
Additionally, initial investment in securities:
- fix the minimum amount of property with which the company will be liable for its obligations to shareholders;
- are the starting basis for launching a new project;
- determine the share of each shareholder when dividing profits.
Also, the authorized capital contains the list of property to which the joint-stock company will be liable in the event of failure to fulfill loan obligations to third parties.
Where to deposit and how
Information on the amount of capital (authorized) of each LLC is reflected in its Charter. It is formed from the value of the share (it is reflected as a percentage of the total size of the capital or in ruble equivalent) of each founder at the time of founding the company.
Until the moment when the founders of the organization are ready to submit an application for state registration of the LLC, they must place half of the authorized capital in a savings account.
After the founders receive the registration documentation, they must transfer the remaining part of the capital to the LLC's current account (depositing funds into the cash register is allowed).
If one of the founders has not fulfilled his obligations and has not contributed his share to the management company, then financial penalties provided for in the Charter may be applied to him.
Contributions to the authorized capital can be made by the founders at their own discretion, but within the framework of the current Federal legislation:
- funds both in cash and in the form of bank transfer;
- securities, in particular shares, bills, etc.;
- property and other assets;
- rights to any property.
Authorized capital of JSC, size
The start-up fund of a joint-stock company consists of shares, its size is determined by the number and nominal value of securities. The initial price is fixed on the share itself after it is issued. To determine it, it is necessary to divide the size of the charter capital by the number of securities that were issued by the company. The value of a share is not limited by its par value. When securities are traded on the stock exchange, they are sold at the market price.
The authorized capital is formed by ordinary and preferred shares. In the first case, their price and the scope of rights they provide to owners are the same. In the second, the cost of securities is differentiated, and the law states that the par value of preferred shares should not exceed 25% of the authorized capital.
A significant part of commercial structures tries to include as much money as possible in the start-up capital. This practice is not without meaning in the face of constant fluctuations in the financial market. In addition, clients treat companies with a large authorized capital with special confidence.
Non-public joint stock company
This is an enterprise whose participants are strictly defined, information about these persons is recorded at the time of creation of the organization. The innovation allows you to correct and make changes to the organization's charter, form management bodies, influence the board of directors and shareholders' meeting on various issues through voting. All closed joint stock companies, as well as some LLCs, will now be called non-public.
It is important to note the lower obligations in relation to the owners of securities that a non-public joint stock company bears. Responsibility to investors is less than in the case of open organizations. This is due to the fact that a non-public joint stock company has a limited number of securities owners, strictly limited by the charter documents. In simpler terms, participants are initially warned about all risks and possible losses. Often shares in such companies are not issued at all, and such enterprises are partly the result of privatization or a consequence of a unique management model with equity participation to delegate responsibility.
For non-public
In a NAO, economic activities are not advertised, and its participants cannot sell securities to third parties without the approval of the company’s supreme management body. Shares are placed by private subscription (between a certain number of participants). The minimum size of the charter capital for non-public joint stock companies is 10,000 rubles.
Some formats of joint stock companies require a higher initial investment:
insurance company - from 60 to 120 million rubles;- microfinance company – 90 million rubles;
- bookmaker's office - 100 million rubles;
- credit and financial structure (bank) – 300 million rubles. (at the time of obtaining the license).
There are certain restrictions for legal entities from the above list. In particular, a special list of property from which the authorized capital is formed has been introduced, and a maximum threshold of non-monetary assets invested in start-up capital has also been provided.
In practice, situations often occur when commercial activities become unprofitable, as a result of which the value of net assets is less than the minimum threshold of the authorized capital. This circumstance is the legal basis for initiating bankruptcy proceedings.
Stages of formation
In accordance with Federal Law No. 208 dated December 26, 1995, the authorized capital of the joint-stock company:
- is entered to register a company and subsequently carry out commercial activities;
- adjusted upward or downward until the company is liquidated.
The following can be used as a source of replenishment of the starting fund:
- securities;
- real estate, land, vehicles;
- financial assets;
- some types of intellectual property (literary works, paintings, inventions, etc.).
If a contribution to the initial capital of a joint-stock company is made not with money, but with property, then its owner must obtain consent to this investment format from the other founders.
Video about the minimum size of the authorized capital:
Public joint stock company
This is the name given to those enterprises whose shares are publicly traded in accordance with securities laws. This could be an entry to the stock exchange, an issue for the purpose of generating income, etc. Also, the publicity of a particular joint stock company is determined by the fact that the charter documents state that the organization is open in one form or another. Control of such companies is more stringent due to the fact that they may affect the interests of third parties, because citizens can purchase shares of these organizations. For example, a supervisory board of five people must be present as a supervisory body. It should also be noted that all United Joint Stock Companies (JSC), based on the new legislation, are becoming public. Moreover, new changes in legislation provide for openness and transparency of data related to the owners of securities issued by PJSC. They also have a number of additional nuances and innovations, for example, a society will be considered public provided that the number of its participants exceeds five hundred. More detailed information is provided in the first paragraph of Article 66.3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Reducing the start-up fund of a joint-stock company
In the process of carrying out entrepreneurial activities, participants in a joint stock company can use “corporate” tools to obtain additional profit. One of them is the reduction of the authorized capital on a voluntary basis.
This procedure is implemented through:
- purchase of own securities and their cancellation (such a prerogative must be recorded in the Charter);
- reduction of the nominal price of shares (the initiative must be approved by the highest management body of the company).
In both the first and second cases, the JSC participant has the right to count on profit. Moreover, the majority owners of securities can, through this procedure, redistribute the volume of corporate rights.
There are conditions under which the reduction of the criminal capital is imperative (by force of law). These include:
- the fact that there was no transaction for the alienation of shares transferred to the disposal of the JSC for 1 year;
- the fact that the JSC has securities that have not been fully paid for by the participants;
- the fact that the size of the authorized capital exceeds net assets (after 2 years of commercial activity of the enterprise).
In practice, this procedure is implemented by minimizing the total quantity of each type of securities, reducing their par value and redeeming shares that were previously acquired.
It is also necessary to comply with certain legal formalities, namely: convene a general meeting, which must approve the initiative of the company's participants; register changes in the Charter (with the Tax Inspectorate).
It is important to note that the size of the criminal capital after adjustment should not be lower than the limit established by Article 26 of Federal Law No. 208 of December 26, 1995.
Reduction of capital (option 1)
The need to reduce the par value arises when all the shares of an organization are sold out, but the actual size of the authorized capital does not correspond to the documented indicators.
Such cases occur infrequently and may be the result of mismanagement of the organization or fraud by the board of directors.
However, in accordance with Article 101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, if an organization does not have the funds specified in the organization’s charter as the amount of authorized capital, it is necessary to reduce it.
Before submitting documents to the branch of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, you must notify all shareholders about the upcoming changes.
back to menu ↑
Decision to reduce
Convening the supreme management body of a joint-stock company and including on the agenda issues related to the procedure for reducing the authorized capital is a mandatory process. The General Meeting of Shareholders must determine:
- to what amount and in what way the capital will be minimized;
- what will be the nominal value of the securities after the decision is implemented in practice;
- how many shares and what types are planned for redemption;
- how long it will take to reduce capital.
In order to make a positive decision on a specific method of reducing the par value of dividend securities, it is necessary to obtain the support of 3/4 of the votes of the highest management body of the company. The proposed format for reducing the total number of shares must be approved by more than 50% of the JSC participants present at the meeting.
When the decision to carry out the procedure is agreed upon with the highest management body of the company, it is necessary to notify the Federal Tax Service about it and make appropriate adjustments to the Charter.
Capital increase (option 2)
Compared to the previous method of increasing the authorized capital, the additional issue of new shares is a much more popular method, since it allows one to attract new shareholders and, accordingly, new deposits.
Frequent increases in the authorized capital through additional issuance of securities are typical for successful open joint-stock organizations.
Before submitting a proposal for an additional issue of shares to the meeting of shareholders, members of the board of directors must predict as accurately as possible whether they will be able to sell the newly issued securities within one calendar year.
Indeed, in case of failure, the size of the authorized capital will have to be reduced again to its actual value, which will entail the need for additional preparation of documents, contacting the Central Bank of Russia, etc.
However, purchasing shares has always been one of the great ways to generate passive income, so usually securities can be sold on the market.
If the board of directors is confident in the market demand for the shares of their company and the need to increase the authorized capital, it is necessary to convene a meeting of shareholders, at which a decision on an additional issue must be approved by a majority vote.
After the relevant decision has been made, the owner of the organization must again follow the algorithm that he used to create the primary authorized capital: approval of changes in the branch of the Central Bank, announcement of the presence of unredeemed shares and sale of shares.
Important: when counting the majority of votes of members of a joint-stock company, it should be understood that the owner of one share of the company has one vote. If one individual or legal entity owns more than one number of shares, it will have a number of votes equal to the number of shares acquired.
back to menu ↑
Notice of reduction
When reducing the par value of securities and reducing their total quantity, it is important to respect the interests of creditors. The decision adopted at the general meeting of shareholders must be published in the press (“State Registration Bulletin”). Companies to which the joint-stock company has debts must be properly notified that their partner intends to reduce the size of the fund. Publication should be submitted to the journal twice with a 1 month interval.
The notification contains the following information:
- full details of the legal entity;
- a method for reducing the capital and its size after implementing the procedure in practice;
- the procedure for filing claims and claims against the JSC by creditors.
Distortion/submission of inaccurate information to the State Registration Bulletin, as well as failure to comply with deadlines when submitting a notification, will seriously slow down the implementation of the initiative, which was initially agreed upon with the highest management body of the company.
Increase in JSC fund
The company's starting capital consists of several types of shares that have a differentiated par value. In the process of entrepreneurial activity, the joint-stock company has the right to increase its size. Often, this procedure simplifies the process of obtaining a bank loan and expands the circle of reliable partners. The company's authorized capital is increased due to:
- additional placement of securities giving the right to receive dividends;
- changes in the par value of shares upward.
The decision to change the start-up capital is included in the agenda of the supreme management body of the joint-stock company. It defines:
- the cost of the shares being placed and their quantity;
- method of placement of dividend securities;
- payment format for assets placed through subscription.
But if the decision is approved, the legal entity cannot yet place an additional package of dividend securities on the market (issue). The supreme management body of the joint-stock company must initially approve the decision to issue documents that certify the right to receive dividends. Then the documents (listed in clause 2.5.2 of the Issue Standards) are transferred to the Central Bank, which carries out state registration of additional assets. At the next stage, dividend securities are placed through their conversion, and data on new shares is recorded in the register. Next, reporting on the results of the issue of issue-grade assets is registered, after which adjustments associated with the growth of the capital are made to the Charter and entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
Charter document of the NAO
When creating a non-public JSC, you must have various papers and completed forms with you. The charter of a non-public joint stock company is a key document. It contains all the information about the organization, it tells about its property, participants and their rights, about the activities of the enterprise being formed, etc. In case of problems and disputes, the Charter will be a supporting document in legal proceedings. Therefore, it must be written in such a way that it does not contain loopholes and flaws that could be used in court against the organization. When drawing up the Charter, it is recommended to study in detail all legislative acts that are in one way or another related to the activities of the organization, or contact lawyers who have experience in this area or specialize in the development of such documents.
Formation of management companies during reorganization
When carrying out this procedure, the property assigned to the balance sheet of the joint-stock company, which decided on one or another transformation format, is used. The amount of capital of the new company may be more or less than that of the predecessor business entity.
Each succession model allows you to use your own funds (reserve assets, retained earnings, etc.) as a source of capital formation.
During reorganization, the size of the fund should not be lower than what was approved by the general meeting of shareholders when deciding on the specific format of future succession. Also, the successor company must take into account the minimum threshold of the charter capital, which is fixed in Article 26 of Federal Law No. 208 dated December 26, 1995. Moreover, the par value of preferred shares should not exceed 25% of the total mass of dividend securities.
The nuances of forming a fund for various reorganization formats are determined by the decision of the highest administrative body of the joint-stock company.
management company with money
All funds contributed by the founders to the authorized capital of the LLC must be placed immediately into a savings account, and after receiving registration documentation into a current account (in the future they can be spent on the needs of the company).
Statutory contributions can be made both in Russian rubles and in the currencies of other states.
The founder's contribution to the current account must be documented. Usually an announcement for cash deposits is drawn up, consisting of several parts: a receipt order, a receipt and an announcement.
The following may be considered as proof of deposit of funds:
- cash receipt order;
- current account statement;
- copies of bills and receipts;
- a provision of the company's charter, which states that payment of the minimum amount of authorized capital has been made in full.
Accounting of operations
The financial statements of the company must record the amount of the capital, as well as the debts of the participants to pay it (accounts 75, 80). Moreover, it allows you to find out what types of dividend securities have been placed and how many outstanding shares remain.
The “Placed Shares” column records data on assets that can only be sold within the JSC, and the “Authorized Shares” account contains information about assets that can be sold to third parties. The reason for this differentiation in financial reporting is that Federal Law No. 208 dated December 26, 1995 contains a mandatory rule on the full repayment by shareholders of debts associated with the formation of the management company (upon registration of the company).
The personal accounts of the company's participants reflect information about how much profit its owner received from the company's turnover. Information about the value of securities owned by the shareholder is also entered there. The data that appears in personal accounts makes it possible to record in accounting documents exact figures regarding the cost of the start-up fund.
No company can successfully do business without start-up capital. Initial investments in the project form the basis of the management company, which determines the company’s reputation and the prospects for cooperation with major business partners. Moreover, tangible assets from the start-up fund can be used for business development. But the money embedded in it should be spent rationally in order to ultimately avoid the risk of bankruptcy.
Top
Write your question in the form below