Labor legislation gives the right to every organization and enterprise to pay monetary rewards to its employees for quality work done (Labor Code, Art. 191). Such incentives are an effective way to motivate the team and individual employees to further improve their work performance, improve and develop their skills.
The conditions for the provision, size, and procedure for calculating bonuses are fixed in collective agreements, internal disciplinary regulations, charters and rules of organizations. Various salary bonuses for work done, exceeding plans, length of service, and fulfillment of special tasks can be paid based on the results of the month, quarter, or year. Taxation of such financial remuneration, the amount of insurance and pension contributions from premium amounts are determined by the Tax Code and the relevant Federal laws of the Russian Federation.
Is the premium taxable?
Types of awards
The most common types of monetary rewards include:
- individual or collective incentives for completing assigned tasks and conscientiously fulfilling duties;
- rewards for exceeding plans and achieving high performance results;
- incentives for completing special tasks;
- payments when an employee reaches significant length of service;
- awards for special services;
- one-time bonuses on the occasion of an important event, for example, dedicated to professional or public holidays, the founding date of an organization, or anniversaries of company employees.
There are different types of employee benefits
Depending on the internal rules of the organization and the decisions of management, employees may be paid several different types of bonuses at once. There are one-time incentives, as well as regular ones, which are awarded based on the results of a certain period. The bonus amount may be set at a certain amount, periodically revised over time, or may be a percentage of salary.
Attention! Moreover, such incentive payments are subject to mandatory tax established by law.
How is tax on employee bonuses reflected in reporting?
The procedure for including bonus income depends on its type. The following nuances must be taken into account:
- The date of receipt of monthly incentive payments is considered to be the last day of the month for which the employee received bonuses.
- Quarterly and annual bonuses are included on the last day of the month in which the order is issued.
- Non-productive income paid on holidays, anniversaries, and professional holidays must be taken into account on the day of actual payment.
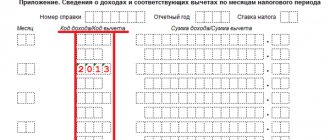
Form 2-NDFL
A certificate in form 2-NDFL contains data on the income of an individual for the reporting period. It includes the following sections:
- Agent details.
- Information about the individual.
- The amount of income for the month and the corresponding code are entered line by line. Production bonus payments are accounted for under code 2002, and non-production bonuses are recorded separately under code 2003. They are displayed for the month in which the employee received income.
- Social, standard, property, investment deductions. The appropriate fields are filled in if the individual has such grounds.
- The total amount of income paid: accrued, withheld, transferred by personal income tax (the last figures must be the same).
Help on form 6-NDFL
This type of reporting is intended to display the total amounts of income paid, withheld from them and transferred to personal income tax. Help contains topics:
- The first section contains generalized data on income (column 020), personal income tax (column 040), which are displayed on an accrual basis for the reporting period. Column 060 indicates the total number of individuals who received payments.
- The second section provides data on the amount of income paid and personal income tax withheld by date.
Monthly bonuses that the employee received along with his salary are displayed as a single block with salary income. In all other cases they are shown as a separate block. In the second section on bonus payments, fill in the following columns:
- 100 – indicates the last day of the month for which the monthly premium is accrued; the last day of the month in which the order to assign a quarterly or annual bonus was issued; date of issue of non-production cash incentives;
- 110 – date of actual payment of remuneration and withholding of personal income tax;
- 120 – date of tax transfer, the next business day after the date of receipt of payment;
- 130 – amount of incentive compensation paid;
- 140 – the amount of personal income tax withheld and transferred.
Sources of bonus payments and grounds for their taxation
Unlike wages, cash bonuses are not mandatory payments. Such incentives are paid by decision of management in accordance with the internal rules of the organizations. In cases where regular bonus payments are provided for by a collective agreement or the company's charter, refusal to provide bonuses or a reduction in the amount of remuneration must be justified and formalized in the prescribed manner.
Most employers allocate incentive amounts as a separate part of the overall compensation system developed and approved by management for their employees. This makes it possible to interest and stimulate employees to generally improve the company’s performance, and also makes it possible to optimize income tax payments.
Bonus is an optional payment, which is made by decision of management, usually for certain merits of the employee
Sources of bonus amounts can be the cost part included in the company’s budget for salaries, wages for hired personnel, as well as the net profit of the enterprise. In the first case, bonuses are directly related to work activity and achievements at the end of a certain period.
Attention! Incentives from profits are usually allocated in connection with a certain event that is not directly related to the performance of functional duties or work results.
Regardless of whether monetary incentives are regular payments from the cost part of the budget or one-time rewards from profits, all these amounts relate to employee income, which is subject to mandatory taxation by law.
Bonuses are taxed as they are employee income
Is the bonus taxable?
The Labor Code contains a mandatory requirement for employers to enter into employment contracts with all employees. The terms and conditions must specify for what and in what order the employee will be rewarded. It is possible to describe the bonus system for employees in a collective agreement, but its conclusion is not mandatory. According to the law, incentive payments are considered income, therefore they are subject to insurance premiums, and personal income tax is withheld from the accrued premium.
Taxation of insurance premiums
The law defines labor relations as a special type of contractual obligations between employers and the employees they hire. The latter undertake to carry out certain activities within the framework of their position, profession, specialty and qualifications under the guidance of the employer and in his interests. Employees must obey the rules and regulations established within the organization. In turn, the organization hiring personnel is obliged to pay workers, create working conditions that comply with the norms and requirements of labor laws.
According to Article 129 of the Labor Code, all regular, one-time monetary rewards for work performed are part of the general system of remuneration for hired personnel, developed and approved by the management of the organization. In accordance with the Tax Code, which regulates the conditions, rules of contributions to the state Pension, Medical, Social Insurance Funds, payments related to the sphere of labor relations, in addition to various benefits and compensations, are subject to corresponding insurance contributions.
Attention! This rule also applies to incentives in the form of cash bonuses.
Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The amount of insurance premiums is calculated in the same month when the reward is accrued. It does not depend on the duration of the work for which the remuneration is assigned. For example, in April, management decided to award a cash bonus to the work team for fulfilling the plan in the 1st quarter. It is in the same month that premiums will be subject to insurance fund charges, although the incentive is paid for work done in the previous three months.
Insurance contributions do not depend on the sources of incentive amounts - the salary part of the budget or the company’s net profit, with the exception of certain cases of one-time awards.
Attention! It also does not matter whether bonus payments are provided for by collective agreements and internal rules of enterprises.
Bonuses can be paid from the salary part of the budget, the net profit of the enterprise
Conditions for awarding bonuses
There are several official conditions for bonuses for employees:
- Federal Law No. 208. If one of the founders of the organization decides to award a bonus to employees, he makes this decision together with his colleagues.
- Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The procedure for calculating monetary remuneration must be specified in the employment contract.
- Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. All issues of bonuses for employees must be agreed with the trade union, if there is one at the enterprise
Add bonuses for free and automatically calculate taxes through Kontur.AccountingTry for free
Insurance-free incentives
There are types of one-time monetary awards that are not related to the direct performance of employees’ duties or success at work. They can be dedicated to professional or public holidays, the anniversary of the founding of the company, or dedicated to birthdays and anniversaries of employees. The amounts of such remuneration are usually the same for all team members, regardless of positions, duties performed, length of service, salary, or success in work. Even when these remunerations are provided for, specified in the collective agreement, the charter of the organization and called bonuses in the order, in fact they are not included in the framework of labor relations. Accordingly, insurance contributions are not deducted from such payments.
Often, tax inspectors raise claims against employers regarding the imposition of insurance contributions on one-time premiums dedicated to important dates. This is motivated by the fact that absolutely all amounts paid to hired personnel relate to the sphere of labor relations. However, according to the decision of the Arbitration Court of the North-Western District, if such incentives are paid from net profit, distributed among team members in equal shares, they are not payment for work and insurance fees should not be withheld from them.
Attention! If employees receive bonuses for a special date in different amounts, the court will consider them a reward for the performance of duties and will oblige them to accrue contributions to insurance funds.
It all depends on the type of premiums - some are still not taxed
One-time incentive payments issued as cash gifts to employees under gift agreements concluded with them should not be taxed. Article 420 of the Tax Code defines such actions as acts of civil relations that are not subject to insurance fees.
Thus, contributions to the state Insurance Funds must be withheld from almost all types of premiums. The exception is one-time incentives for important dates or events, allocated from the net profit of companies, issued to employees in equal amounts, as well as bonus amounts issued as monetary gifts under gift agreements.
If bonuses are given to employees in equal amounts and this occurs in connection with important events, they should not be taxed
Let's sum it up
- From bonuses issued to employees, it is necessary to pay personal income tax and insurance premiums to the budget.
- Personal income tax is paid on all types of premiums, regardless of their purpose and regularity of payment.
- At the moment, there is no single point of view regarding the need to charge insurance premiums for premiums issued on the occasion of a holiday, anniversary or other event.
- Gifts or material assistance in an amount not exceeding 4,000 rubles are not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions. in a year.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Income tax
The main type of tax in Russia is the collection on personal income – personal income tax. It is also called income tax. At the same time, individuals include Russian and foreign citizens living in Russia, regardless of gender and age. Profits received by individuals as a result of activities carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation are subject to personal income tax.
Attention! To determine tax payer status and tax rates, citizenship is not the main factor. The fees depend on whether the resident is an individual or not.
The following citizens are tax residents:
- over the past 12 months, living in the Russian Federation for at least 183 calendar days;
- military personnel serving abroad, regardless of length of stay in the Russian Federation;
- civil servants who are on a business trip abroad, regardless of its duration.
Tax resident – not necessarily a citizen of the Russian Federation
There are types of income of citizens that are not subject to personal income tax. Non-taxable income tax payments include the following:
- various benefits, for example, unemployment, in connection with pregnancy, childbirth, child care;
- compensation payments due for unused vacation or upon dismissal from employment;
- pension accruals;
- student and scientific scholarships;
- additional payments for donation;
- monetary awards for high achievements and special merits in science;
- various grants;
- social additional payments, financial assistance;
- compensation for losses resulting from natural disasters and emergency situations;
- various types of alimony;
- rewards for assistance in solving crimes, preventing terrorist acts, and capturing dangerous criminals.
Pensions, various benefits, scholarships, additional payments, etc. are subject to personal income tax.
Attention! Also, funds allocated for charitable activities are not subject to income tax.
What bonuses are not subject to taxes?
Employers are required to charge income tax on employee bonuses and insurance premiums, because all remuneration - labor and non-productive - is the income of individuals and is subject to taxation on a general basis. For this reason, all incentive compensation is paid to employees minus personal income tax. Article 217, paragraph seven of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for an exception. Income tax is not withheld from bonuses classified as budgetary:
- international;
- foreign;
- Russian national one.
Awarded for significant achievements in the field:
- Sciences;
- technology;
- education;
- culture;
- tourism;
- MASS MEDIA;
- literature and art.
The list of preferential bonuses is specified in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 6, 2001. Monetary rewards awarded by officials of constituent entities of the Russian Federation are not subject to income tax. At the regional level, a list of bonuses is compiled that are not subject to personal income tax.
Is the personal income tax premium in the amount of up to 4,000 rubles
The employer does not need to withhold personal income tax from the bonus if its amount is 4,000 rubles and two conditions are met:
- the entire amount is issued as a gift for the holiday;
- An agreement for donating funds to an employee has been drawn up and signed.
To avoid taxation, it is necessary to correctly display the remuneration in the reporting form 2-NDFL:
- the cash incentive paid is indicated by income code 2720 (gifts);
- code 501 (deductions from gifts) is entered next to the deduction amount, which is equal to the amount of the reward.
Tax rates
Russian tax legislation provides for various types of fees for both residents of the Russian Federation and non-residents. At the same time, the bet sizes also differ and depend on the type of income. The most common value used to calculate taxes for residents is 13% of the amount of income received from the sale of property or in the form of wages. The same rate is applied when withholding income tax on the amount of regular bonuses allocated from the cost part of the organization’s finances, as well as one-time payments from profits dedicated to an important date or special event.
Attention! The type of source of bonus funds does not matter; all cash incentives are subject to an income tax of 13%.
As a rule, personal income tax on income is 13%
For non-residents, 13% is calculated from the following income:
- profits received in the Russian Federation by citizens of other states;
- wages of foreign citizens working in the Russian Federation on the basis of patents;
- income of non-residents who move to the Russian Federation under a program promoting the voluntary resettlement of compatriots;
- income of stateless persons, as well as foreign citizens who have received asylum in the Russian Federation;
- salaries and remunerations of crew members of Russian ships who have citizenship of other states.
There are other rates that are deducted from different types of income. For example, 9% is charged on profits received from bonds, 15% on dividends transferred to individuals from organizations.
Attention! Non-residents must pay 30% of the amount received from the sale of securities to a Russian company.
Some income is subject to different tax percentages
Is personal income tax withheld from the premium?
There is a clearly regulated list containing cases when income tax is not deducted from the prize (clause 7 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), for example, for outstanding discoveries in the field of science, education, culture, etc. This list is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
In other cases, the question is whether the bonus is subject to personal income tax under clause 1 of Art. 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is not worth it, since almost any income of an individual is subject to taxation. The article “Are maternity workers subject to income tax (NDFL)?” will tell you whether personal income tax is withheld from maternity workers.
But there are payments, the grounds for which are listed in clause 28 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, if such a payment does not exceed 4,000 rubles, then it is not subject to personal income tax. These include bonuses: they must be strictly timed to coincide with some significant event and amount to no more than 4,000 rubles per year. per employee. In this case, a mandatory rule must be observed: a gift agreement is drawn up in writing (clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), then a payment under it in the amount of 4,000 rubles. for the year can be carried out as income not subject to personal income tax.
Find out whether financial assistance is subject to personal income tax in this article.
Is income tax taken on the bonus upon dismissal? Yes, it is taken in accordance with the general procedure - this is confirmed by the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia (dated September 29, 2014 No. 03-04-06/48497).
Find out how to reflect payments upon dismissal in 6-NDFL from this publication.
An example of calculation and registration of income tax on bonus payments
Let's consider, using a specific example, all aspects of paying income tax on the bonus amount - calculation, registration procedure with subsequent withholding of personal income tax.
Sergey Tokarev worked for a long time at the manufacturing enterprise Elektropribor CJSC. Now he is retired. Due to his advanced age and health reasons, Tokarev is forced every year to undergo a medical examination and a course of treatment using expensive medications. Tokarev Andrey, his son, followed in his father’s footsteps and also became an employee of the Elektropribor enterprise. At the same time, he is one of its best employees.
At the end of the year, the director of JSC Elektropribor awarded Andrey Tokarev a bonus of 10 thousand rubles for quality work done and success in production activities. At the same time, the manager, at the expense of the enterprise, decided to compensate him for the funds spent on medicine by his father. According to the sales receipts provided by A. Tokarev, this amount is 3.5 thousand. Accordingly, the total amount of bonuses issued by the director of Elektropribor for Andrey Tokarev amounted to 13.5 thousand rubles.
The manager can, at his own discretion, issue a bonus to the employee
The accounting department of the organization was faced with the problem of how to correctly draw up bonuses in order to optimize and correctly calculate the amount of income tax. The accounting department did this:
- as a gift to Andrey Tokarev for the New Year holidays, 4 thousand rubles were drawn up from the net profit of the enterprise, and a corresponding agreement was concluded for the donation of this money;
- another 4 thousand rubles were issued in the form of financial assistance;
- 3.5 thousand were allocated to compensate for the cost of medications for Tokarev’s father;
- According to the official order, Andrey Tokarev was allocated 2 thousand rubles for an annual bonus for successful work.
The task of accountants is to correctly process such payments.
All bonus payments were approved by the relevant orders, signed by the director, executed and documented in the proper manner.
In accordance with the norms of labor and tax legislation, of all amounts paid to Tokarev, only the annual bonus of 2 thousand rubles for labor success will be subject to income tax. All other payments, including financial assistance, reimbursement of the cost of medicines, holiday gifts in the form of cash, formalized by a gift agreement, are not subject to taxation.
So, 13% is deducted from 2 thousand. The income tax amount will be 260 rubles, which will be withheld from Tokarev’s annual bonus. Adding up all the other amounts, we get 13,240. This is the amount of bonuses Ivan Tokarev will receive at the end of the year. If the accounting department had issued 10 thousand rubles as a reward for successful work during the year, the income tax on this amount would have been 1300. In this case, Ivan Tokarev would have received 12200, which is 1040 rubles less.
Financial assistance is not subject to personal income tax
All bonus funds issued by the enterprise must be indicated in the 2-NDFL certificate, which is submitted to the tax authorities. Moreover, each type of payments and deductions is designated by special codes established by the Appendices to the orders of the Federal Tax Service. For example, a monetary gift corresponds to code 2720, material assistance – 2760, compensation for the cost of medicines – 2770, annual remuneration for labor achievements – 2000.
Separately, bonus amounts will be reflected in the 2-NDFL certificate in the application for deduction codes.
| Description | Code |
| Gift code in the form of cash under a gift agreement | 501 |
| Material assistance code | 503 |
| Medical reimbursement code | 504 |
Attention! It must be remembered that in order to exempt a premium from income tax, it must be formalized accordingly, confirmed by an order, agreement and other documents confirming that the payment relates to non-personal income tax items.
It must be confirmed that this or that payment relates to non-taxable personal income tax
The procedure for paying personal income tax on bonuses in 2020: how the tax is calculated, taken and deducted
Let us show with an example what the process of calculating personal income tax from a premium and subsequent deduction of this tax from the payment amounts looks like.
Example
Employee Ivanov I.M. is a former employee of Romashka LLC, is retired and undergoes annual necessary treatment with the purchase of expensive medications. His son, Ivanov R.I., is a current employee of Romashka LLC, a leader in production.
At the end of the year, the general director of Romashka LLC authorized a cash payment in the amount of 10,000 rubles. Ivanov R.I., as well as reimbursement of expenses for the documents provided for the purchase of medicines in the amount of 3,500 rubles. The accountant was faced with the question: should personal income tax be withheld from the premium and how to do this rationally?
The accountant of Romashka LLC formalized it all like this: for 4,000 rubles. a New Year's gift was issued to R.I. Ivanov, for which a financial donation agreement was signed.
In the amount of 4,000 rubles. An agreement for financial assistance was drawn up.
In the amount of 3,500 rubles. funds were issued for reimbursement of the cost of medicines.
In the amount of 2,000 rubles. An order was drawn up for a bonus to R.I. Ivanov based on the results of the year.
It turns out that in this case it is necessary to withhold personal income tax from the premium, and only from it - from the amount of 2,000 rubles. The withholding amount will be 2000 × 13% = 260 rubles, and the payout will be 1,740 rubles.
All these payments were given in the order and documented with proper documents.
As a result, R.I. Ivanov received funds before the New Year in the amount of: 4,000 + 4,000 + 3,500 + 1,740 = 13,240 rubles.
But if the accountant issued 10,000 rubles. bonuses, then from this amount it would be necessary to withhold personal income tax on the bonus in the amount of 13% (10,000 × 13% = 1300), and Ivanov R.I. would receive in his hands: 8,700 + 3,500 = 12,200 rubles.
Deadlines for paying income tax
The procedure and deadlines for transferring income tax to the state budget depend on the type of bonus. For example, if an incentive payment is tied to salary, the date of receipt of such income will be considered the last day of the month. The time of receipt of bonus funds that do not relate to labor compensation will be considered the actual date of payment.
Income tax must be withheld from the incentive amount on the day the issued money is issued to the employee. Personal income tax must be transferred to the state budget no later than the next day.
Attention! For each day of delay, a fine of 20% of the amount of unpaid income tax is assessed.
Personal income tax is withheld on the day the money is given to the employee
Reflection of the premium in 2-NDFL
Certificates in form 2-NDFL indicate the following codes of income for bonuses depending on their type (Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 22, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/633):
- production bonuses provided for by law, employment contracts and (or) collective agreements (paid not at the expense of the organization’s profits, not at the expense of special-purpose funds or targeted revenues) - code 2002;
- bonuses paid from the organization’s profits, special-purpose funds or targeted revenues - code 2003.
Payment of bonuses is reflected in 2-NDFL certificates in the month in which the date of receipt of income falls.
Bonuses in the company are made to encourage employees. Such remunerations relate to the employee’s income, therefore, according to tax law, it is necessary to pay personal income tax on the bonus. In 2020, the procedure for calculating and paying income tax has changed. Accountants need to take these changes into account to avoid penalties.
Benefits of taxation of bonus payments
According to the provisions of Articles 255, 272 of the Tax Code, all bonus payments that are paid to employees of the organization for the performance of labor duties are fully included in part of the cost of payment for work. Thanks to this, it is possible to reduce the total amount of company income tax that must be transferred to the state budget. It is advisable for organizations of the following type to use this advantage in the taxation of incentive compensation:
- companies that use a simplified tax system;
- enterprises that use a common taxation system.
To the amount of premium funds issued, organizations have the right to add all fees paid from these amounts to the Insurance Funds. Taking these contributions into account will also reduce your income tax payments.
Sometimes you can reduce your income taxes
To avoid claims from representatives of the tax service regarding tax reduction, all incentive payments to hired personnel should be carefully documented and executed accordingly. It is also advisable to include a detailed description of the provisions on the types, terms, and conditions of providing employee benefits in the internal regulations governing the company’s activities.
Attention! This will allow you to document all bonus payments as a costly part of the organization’s budget allocated to pay for the work of hired employees.
Incentive compensation clauses should be included in such documents.
- An employment agreement or contract concluded with an employee. The presence of a condition for accruing bonuses in such an agreement will allow their amount to be deducted from income tax when transferred to the budget.
- Collective agreement. This agreement must fix the possibility of providing collective and individual rewards for quality work done, labor achievements, and also indicate the amount of funds allocated for these purposes.
The collective agreement must indicate the possibility of providing individual remuneration
- A separate internal document should document the provisions on the conditions for bonus payments to employees of the organization. This local act, drawn up in accordance with all the rules and approved by the company’s management, must indicate in detail all aspects of the provision of bonuses to employees - types, conditions of remuneration, sources of payments, periods of formation and delivery, established amounts or percentage of salaries, the total amount of bonuses included in expenditure side of the budget.
All these regulations will make it possible to completely protect the enterprise from possible accusations by inspection inspectors of tax evasion and illegal reduction of taxation of the company’s profits. In the absence of mention of the terms of provision and the procedure for processing monetary rewards, the management of the enterprise will have to prove the labor orientation of such payments. Otherwise, inspectors recognize bonus amounts as unearned and unrelated to the company’s performance, which, in accordance with the decision of the Ministry of Finance, cannot lead to a reduction in income tax.
The procedure for calculating and withholding tax on personal income
When providing incentive compensation to employees, a legal entity or individual entrepreneur - agent has an obligation to calculate, withhold personal income tax from the bonus and transfer it to the budget. In 2020, there were changes in the procedure for paying income tax . There are differences in the calculation and withholding of personal income tax from labor bonuses and from non-production incentive payments.
Sources of bonus payments at the enterprise
A positive aspect of bonuses for employees is the ability to include the following as labor costs:
- the entire amount of incentive payments;
- insurance premiums accrued on remuneration.
It is not possible to reduce an organization’s profit by the amount of bonus payments and insurance contributions in accordance with the Tax Code in all cases. There are two options:
- Bonuses are given for labor achievements. The source of formation of such payments and accrued contributions is profit. It is worth taking care to document that incentive compensation is part of the remuneration system. The basis for calculation and the amount of payments must be specified in the employment contract and the Regulations on the bonus system.
- Non-production bonuses. According to the Tax Code, remuneration that is not related to the company's performance cannot increase its expenses. Payments made on grounds not prescribed in the employment contract do not reduce the profit tax base. Remunerations paid from targeted revenues or special funds cannot be included in expenses.
Tax rate
The tax rate depends on the status of the individual. For residents, the personal income tax withheld from the premium is 13%. The following options are available for non-residents:
- In the absence of special status, taxation is carried out at a rate of 30%.
- If you have a special status, the personal income tax on labor bonuses is 13%.
On a general basis - at a rate of 13%, the labor income of non-residents is taxed if they:
- carry out activities under a patent;
- are highly qualified specialists;
- are participants in the state program for resettlement in the Russian Federation;
- recognized as refugees from foreign countries;
- are members of the crews of ships that sail under the flags of the Russian Federation.
Payment deadlines
It is necessary to comply with the deadlines for paying personal income tax to the budget, because penalties will be applied in case of violation. According to the law, the withholding date is considered the day of actual payment of income, and funds must be transferred on the next business day. For non-payment or violation of the deadlines for transferring personal income tax, a fine is provided in the amount of 20 to 40% of the amount of arrears.
Are premiums subject to insurance contributions in 2020?
Accordingly, such a premium should be subject to insurance premiums (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 25, 2013 N 215/13).
If the premiums are the same for everyone, contributions must also be calculated.
If you do not pay insurance premiums from the premium for a holiday or anniversary, the tax authorities, guided by the position of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, may charge additional contributions, as well as fines and penalties under Art.
What taxes are imposed on bonuses and premiums paid at the end of the year to former employees?
The provision of this subparagraph applies to the employee’s income not exceeding 25 times the monthly calculation index established by the law on the republican budget and valid as of January 1 of the corresponding financial year.
Subparagraph 25) of paragraph 1 of Article 1 of the Tax Code establishes that for tax purposes an employee is recognized as: an individual who is in an employment relationship with an employer and directly performs work under an employment agreement (contract); state employee; a member of the board of directors or other management body of a taxpayer that is not the highest management body, with the exception of civil servants; a foreigner or stateless person assigned to work under a contract for the provision of personnel by a non-resident, whose activities do not form a permanent establishment in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 7 of Article 220 of the Tax
Calculation details
The premium is a standard income and is subject to the same payments as a salary, including income taxes and applicable insurance premiums. This rule applies to any bonuses in 2020, and applies not only to regular, but also to one-time types of payments.
An order from the manager is used as the primary documentation, according to which data is transferred to other forms of accounting reporting, in accordance with which the need to issue bonuses to any employees is determined. After this, in the month when actual payments to employees are made, the accountant must calculate and accrue both tax and required insurance payments.
Taxation of personal income tax, as well as various insurance contributions on one-time premiums can only be carried out if:
- their provision to employees is established in accordance with internal regulations;
- Only those one-time payments are taken into account that are related to the employee’s production duties, and not with any dates;
- expenses for bonus payments are indicated in the relevant accounting documentation.
Thus, regardless of whether a company pays regular or one-time premiums, in most cases it is required to withhold taxes and insurance premiums from these payments, and exceptions are provided only for a limited list of cases.
Why do you need a desk audit of your 3-NDFL declaration? Read here.
Our article indicates what 2-NDFL deductions will be in 2020.
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
That's why FREE expert consultants work for you around the clock!
- via the form (below), or via online chat
- Call the hotline:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
Is it subject to personal income tax or not?
The bonus is included in wages and is therefore taxable income. In addition, this type of payment is not included in the list of non-taxable personal income tax.
These two grounds give a clear understanding that all bonuses are subject to income tax - quarterly, annual, one-time, anniversary, monthly.
When calculating, withholding and paying personal income tax for this type of payment, it must be taken into account that the procedure for these actions depends on the type of premium.
All incentive payments can be divided into two groups:
- labor;
- unearned.
Labor or production activities include:
- additional payment for work results, plan fulfillment, percentage of sales, etc.
- payment for qualifications, professional skills, achievements in the profession;
- rationalization proposals, inventions that increase production efficiency.
A distinctive feature of production bonuses is that they can be attributed to production costs and thereby reduce the base for calculating income tax.
To do this, all types of production bonuses must be enshrined in the collective agreement, regulations on bonuses and other local regulations of the enterprise.
Non-productive payments include one-time payments dedicated to a specific date - birthday, anniversary, holiday, and so on. They do not depend on the results of labor.
Both the first and second types of premiums are subject to income tax. The difference lies in the order and timing of transferring these payments to the budget.
Do I need to pay insurance premiums on premiums?
Is the premium subject to insurance premiums in 2020?
422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Another list (payments not subject to contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation for insurance against industrial accidents) contains Art.
“On compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases”
dated July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ. A bonus is a remuneration to an employee, issued by decision of management in order to motivate work. Since the bonus is a remuneration for work, personal income tax should be withheld from it and insurance premiums should be calculated.
In Art. 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that remunerations paid within the framework of labor relations and civil contracts providing for the performance of work and the provision of services are included in the calculation of the base for calculating insurance premiums. Find out what date premium contributions should be calculated.
What taxes and contributions are levied on a bonus to an employee in Kazakhstan?
First of all, this is done both for the employee himself and for the tax office, which must be aware of all payments to the employee in order to write off taxes. All bonus payments also relate to wages, and therefore are subject to most taxes imposed. Let's take a closer look at what taxes are levied on bonuses in 2020? Most often, employees assume that they pay only one general tax.
But this is far from true. There is a tax code that displays all indexed deductions from each type of salary and bonus payments. There are 4 taxes on bonuses in Kazakhstan that employees are required to pay in 2020.
Types of taxes are presented in Table 1. Table 1. Types of taxes on bonuses in Kazakhstan in 2020 No. Name of tax payment Justification for the tax Percentage amount of wages or payments 1 IIT (individual income tax) 2 paragraphs 163 Articles
Employee bonus one-time taxation 2020 example
But even if the bonus is not included in the incentive part of the salary, if it is one-time and paid out of profit, it still remains the employee’s income. And this determines the mandatory taxation of premiums.
Read more about the document establishing the wage system in the article
“Regulations on remuneration of employees - sample - 2020 - 2020”
. Let's consider what tax is imposed on bonuses to employees, as well as what insurance contributions need to be paid to the budget.
So, what is the taxation of bonuses to employees in 2020, is income tax levied on the bonus? Since the incentive payment is part of the salary, there is no need to wonder whether bonuses are subject to income tax and insurance premiums. Of course they are taxable! A bonus is part of an employee’s income, and on it, as well as on other components of remuneration, it is necessary to accrue all insurance contributions for compulsory pension, social and medical insurance and withhold personal income tax.
Taxation of bonuses to employees with income tax is carried out taking into account the norms of Chapter.
Types of awards
Before finding out whether income tax is taken from the bonus, let’s consider what bonus payments the employer makes. Labor legislation considers a bonus as an incentive payment for remuneration for the work of personnel (Articles 129, 191 of the Labor Code). The Labor Code of the Russian Federation is talking about labor bonuses, i.e. paid for:
- achieved results in production;
- professional excellence;
- qualifications, length of service;
- introduction and implementation of progressive ideas into production, etc.
The labor bonus can be paid annually, quarterly or monthly. This issue is the prerogative of the employer, since he decides the frequency and main criteria of bonus payments, enshrining these conditions in the Regulations on bonuses for employees of the company.
In addition to labor bonuses, there is a category of bonuses, which includes payments for holidays, anniversaries, professional celebrations, etc.
All types of bonus payments are documented: for labor, the Regulations on bonuses stipulate the terms of payment, and in accordance with their frequency, an order from the manager is issued. Non-labor bonuses are issued in the same way. All bonus payments are recorded in the personal accounts of employees along with the calculation of the basic salary.
How to withhold personal income tax from quarterly and annual bonuses, according to tax authorities
A question immediately arises here. Monthly bonuses are usually calculated and paid along with your salary. That is, employees receive them after the expiration of the billing period, when income has already been accrued.
But the bonus for a longer period can be paid in the month when the order is issued. For example, company management may decide to pay an annual bonus on March 1 of the following year and actually pay it on March 10.
If in this case we are guided by the position of the tax authorities, at the time of payment of the bonus the employees had not yet received income from the point of view of calculating personal income tax. Therefore, the organization has no reason to withhold income tax on the date of issuing incentives to employees.
In unofficial explanations, Federal Tax Service specialists said that in this case the premium must be paid in full without tax withholding. In this case, the “premium” personal income tax should be withheld from the first payment of the next month - from the salary.
Thus, in the case discussed above, personal income tax on bonuses accrued to employees at the end of the year must be withheld in April, on the date of payment of salaries for March, and transferred to the budget on the day following salary.
What the Ministry of Finance thinks about this and when, in the end, it is necessary to withhold income tax from incentive payments, we will consider in the next section.
Benefit for income tax
We found out whether taxes are paid on the premium and which ones. Now about the pleasant side of the issue.
The Tax Code, on the basis of paragraph 2 of Article 255 and paragraph 4 of Article 272, allows all amounts of bonuses issued to employees for labor achievements to be attributed to labor costs. And at 100% size. And such expenses ultimately reduce the income tax payable to the budget. This approach is available to individuals:
Moreover, insurance premiums that are calculated on premiums also minus income tax along with personal income tax.
Bonuses, when there is no longer a question of whether the bonus is taxable, require careful documentation. This will allow you to remove unnecessary claims from income tax inspectors.
Ideally, the rules for issuing bonuses should be spelled out in detail in:
- labor contract;
- collective agreement;
- regulations on bonuses for personnel.
And it’s best when the contracts contain a reference to the clause on bonuses. By doing this, you will, as it were, tie bonuses to the remuneration system in the organization. It is better to make this application detailed. Even to the point of specifying in it the grounds and amounts for issuing bonuses. If this is left to the management’s orders, then it is possible that the tax authorities will have to explain the production nature of the bonuses paid.
The Ministry of Finance believes that non-labor and semi-labor bonuses do not reduce income tax! Since they have no connection with labor results (letter dated 07/09/2014 No. 03-03-06/1/33167).