The word “balance sheet” has its roots in the Latin phrase “bis lanz”, which literally means “two scales”, that is, in essence, the balance sheet shows the state of the company’s financial balance. The balance sheet is the main component of financial statements and it reflects the success of the enterprise’s economic activities for a specified period of time.
The balance sheet is one of the main forms of accounting reporting on the state of the financial activities of an enterprise, presented in the form of a table of data characterizing all the property and debts of the organization in monetary terms for a certain period of time.
Who needs a balance sheet?
The totality of the balance sheet values literally reflects the financial appearance of the organization.
First of all, the balance sheet is necessary for the organization itself in order to have an accurate picture of the results of its core activities that were obtained for a certain period (year, quarter, month).
The balance sheet shows how steadily the company is developing, both in relation to personal activities and in relation to cooperation with other organizations, which is characterized by two total balance sheet indicators, Asset and Liability.
Moreover, the main sign that the balance sheet is drawn up correctly is the equality of the final results of the company’s Assets and Liabilities.
Also, a company's balance sheet is required for any legal entities that cooperate or intend to establish a business relationship with this company.
The balance sheet can be used to determine the financial position of the organization and whether it will be able to function properly in the near future.
The balance sheet of an enterprise is very important for banks, which will be able to assess, based on the indicators of this form, how creditworthy the future client is, and what is the maximum loan amount that can be provided to him.
Each company is forced to provide a balance sheet to shareholders, statistical authorities and tax authorities at a fixed frequency.
Temporary liabilities
Temporary liabilities , as the name suggests, are closely related to a certain period of time, moreover, they take up time from their owner. For example, you came home after school or work, and of course you were very tired. You sit down at your computer and immerse yourself in the Internet. So the computer is the most basic temporary liability. He wastes our time in various ways. But, for example, you are writing a certain work or text, especially since the text is printed faster on a computer and looks much more representative. This is why a computer becomes an asset for a while. Now it’s worth taking a closer look at power liabilities. Powerful liabilities take away both strength and ability to work. Now let’s look at the most recent type of assets and liabilities; these are precisely the power assets. For example, sleep is a strength asset. It replenishes our strength spent throughout the day. For example, the gym itself can also be considered a strength asset as it significantly increases our physical strength. In the same way, bad food that gives you indigestion is also a power liability. In a general concept, power liabilities can be defined as a set or list of things or people that take away our strength, or charge of vigor. This can be considered either a job or a person who takes away your energy in some way, time or money, or after a connection with whom you don’t want to do anything at all.
It is worth noting one specific feature. If we consider this side with a philosophical view of this concept, it turns out that philosophy, then work is a power liability, but at the same time it can be considered a monetary asset, since we receive a salary for work. And quite a lot more similar ambiguous cases can be found.
Balance Sheet Structure
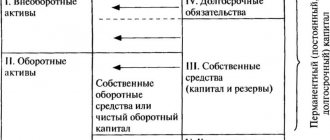
As already mentioned, the structure of the balance sheet consists of 2 main tables, one reflects the organization’s Assets, the other – Liabilities.
The balance sheet is considered to be completed correctly if the numerical results of these tables match.
Let's take a closer look at what these tables characterize.
Assets
An asset is considered to be all the property of an enterprise (real estate, financial investments, vehicles, accounts receivable, equipment, etc.), expressed in monetary form.
A balance sheet asset is the totality of everything that belongs to the enterprise and that can be converted into monetary currency
The balance sheet asset is in turn divided into several sections.
- Fixed assets. The content of the “Non-current assets” section is information about property that is used by the enterprise for a long time, or more precisely more than a year. Non-current assets include: equipment, long-term investments, buildings, etc.
- Current Assets. The final indicator of this section is the sum of all the property of the enterprise, which is consumed and requires replenishment in a relatively short period of time, or rather less than a year. Current assets are materials, cash, short-term receivables, raw materials, etc.
What is an act of completed work and rendered services]How to draw up[/anchor] a report on violation of discipline by an employee?
Passive
The liability in the balance sheet reflects the sources of formation of all the property of the enterprise, that is, its Asset.
Liabilities consist of equity capital, borrowed funds and external liabilities
The Liability side of the Balance Sheet has three main sections:
- Capital and reserves. The Liability section “Capital and reserves” summarizes all own funds that belong only to the owners of the organization.
- Long term duties. In the Liability section “Long-term liabilities”, the value of the totality of all credits, borrowings and other debts that must be paid over a long period of time exceeding one year is formed.
- Short-term liabilities. This liability component reflects the totality of debts that require immediate payment (less than a year). Short-term liabilities include: wages not paid to employees, debts to suppliers, etc.
Currently, Form No. 1 of the Balance Sheet is in force, which was approved on July 2, 2010 by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
But this form has rather a recommendatory nature of the structure of the main indicators of the organization’s performance.
The company, based on its business characteristics, can add additional lines or combine and delete existing indicators in the prescribed form.
Current assets on the balance sheet - fill line
The presence of current assets, their volumes, composition can be found out from the financial statements. It is enough to analyze the available working resources. In essence, current assets are in the balance sheet and there is data in Section II “Current assets”. This includes the following lines:
- 1210 ― the organization’s reserves available at the time of reporting;
- 1220 - the amount of non-written off “input” VAT during the reporting period;
- 1230 - the amount of accounts receivable, with the exception of debts of counterparties, which are characterized as long-term;
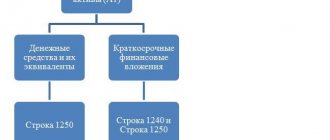
- 1240 - financial investments of an organization that are short-term in nature (loans provided to employees and other persons, shares, shares, etc.);
- 1250 - cash reserves and their equivalents owned by the enterprise;
- 1260 - other current assets, which include other settlements with counterparties, completed stages of work in progress, shortages for which no decision has been made on further write-off, amounts of excise duties and taxes that are recognized later, as well as other assets not included in the above.
How to prepare a balance sheet?
The essence of creating a balance sheet is to fill out all lines of the approved Form No. 1, the composition of which the enterprise has the right to adjust in accordance with the peculiarities of conducting business activities and the property used.
Both the Asset and Liability balance sheet consist of a sequence of lines, each of which records a certain indicator of the financial condition of the organization.
Each line has the name of an indicator and a fixed serial number, which reflects the position of the indicator in the hierarchical structure of the table.
So, for example, in the “Non-current assets” section in the Balance Sheet, the first line corresponds to number 110 (if the management of the enterprise increases the number of lines in form No. 1, the number may have a larger number) and is called “Intangible assets”.
The value of this row is usually obtained by adding the values of rows numbered 111 to 119, if such exist.
After all the rows in the Asset table are filled in, to obtain the final value, it is necessary to add up the results of the first two sections of the balance sheet, which were obtained by summing the other rows in a hierarchical sequence.
Consignment note – sample filling. How to write an explanatory note to the balance sheet?
The same principle works in the Passive table.
The first section of this table, “Capital and Reserves,” has serial number 310, since it is the third main section of the entire balance sheet and is formed by adding the rows that are in its subgroup of the hierarchy, that is, rows numbered from 311 to 319.
Filling out the balance sheet can be done starting from any table (Liability or Asset)
The main condition for the correct preparation of a balance sheet table is the exact correspondence of the value of each line and the indicator entered into it, as well as the presence of monetary values in all lines established by the enterprise.
There are exceptions when the amount for some indicator may be zero, in which case it is necessary to provide explanations for this item in the financial report.
As a rule, all indicators are displayed in numbers that mean thousands of rubles, for example, if the value of an organization’s real estate is 10,000,000 rubles, then 10,000 must be written in the balance sheet asset in the corresponding line.
Of course, if the company has a larger scale, and their cash turnover is mainly in the millions, then you can enter numbers by removing the last six digits, and indicate the numerical unit million rubles in the title of the indicator column.
The final numbers of the Asset and Liability balance sheets must coincide, since, in fact, the Asset reflects everything that the organization has, and the Liability balance sheet provides a description of where all the listed Assets were obtained from.
For a more detailed description of the preparation of the balance sheet, we will consider the principle of filling out each line of the Liability and Asset tables.
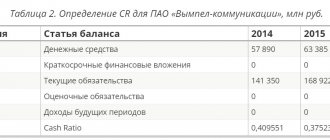
Determination of asset liquidity
Liquidity is the firm's ability to pay its obligations on time. When determining this indicator, much attention is paid to the presence of assets that have the highest rate of conversion into money. It follows that the size of current assets has a direct impact on the solvency of the company and its attractiveness for investment.
The liquidity of current assets is calculated as follows:
KTL = TA / TO.
Where:
- KTL – liquidity indicator;
- TA – size of current assets;
- TO – the amount of current liabilities.
The TO value is determined by adding lines 1510 (borrowed resources), 1520 (accounts payable) and 1550 (other current liabilities). Only short-term debts are used in the calculation.
In order to find out the value of quick liquidity, subtract the size of the MTZ from the size of the TA.
The normal value of KTL should be greater than 1. If a company has this value less than 1, this indicates its low solvency. Too high values of the indicator indicate ineffective use of funds.
Similar articles
- Grouping of assets by degree of liquidity
- Slow moving assets
- Long-term assets on the balance sheet
- Enterprise asset structure
- Assets and Liabilities
Concept and structure of assets and liabilities
Assets are the resources of an enterprise that it uses for its activities. They can represent both material objects and various rights of claim, intellectual property, etc.
What assets have in common is that a company owns them and can use them to obtain economic benefit.
Liabilities are the sources through which an enterprise acquires assets. This could be owner funds, accumulated profits, various forms of accounts payable.