What the law says about tax audits of individual entrepreneurs
In Art. 88 and 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that a tax audit must be carried out for each individual entrepreneur. It can be desk-based or on-site. Their difference lies in the principle of purpose of the check and the methods of its implementation.
Tax and individual entrepreneurs
Desk is a planned procedure, which is carried out in accordance with the rules of the inspection and is carried out directly in it. Here, specific declarations are subject to consideration, which the taxpayer submits on time. Employees check the compliance of the documentation with the real state of affairs and look for errors in the preparation of declarations. This procedure applies to all individual entrepreneurs without exception and does not require any special instructions for carrying out legal actions.
For your information! Only the organization’s reporting, its literacy and compliance with the requirements are checked. The entrepreneur is not notified about the start, no matter what tax system he is on.
On the contrary, an on-site inspection is considered a forced measure that became necessary during desk inspections. It can be either planned or unplanned. In any case, it provides for the direct arrival of tax office employees at the individual entrepreneur’s registration address. Already on site, the tax officer begins to check documentation, reports and compare physical indicators with those indicated in the declaration.
Scheduled and unscheduled inspections of entrepreneurs: how often does the tax office check individual entrepreneurs?
The Federal Tax Service can check an individual entrepreneur both scheduled (according to the schedule) and unscheduled (based on an appropriate decision).
Individual entrepreneurs are included in the schedule of scheduled inspections in accordance with the category of tax risk assigned to the entrepreneur:
- the activities of individual entrepreneurs with a high level of tax risk are audited once every 3 years;
- The Federal Tax Service can check medium-risk individual entrepreneurs no more than once every 5 years;
- Individual entrepreneurs with a low level of tax risk are not included in the schedule of scheduled inspections.
You can view the schedule of scheduled audits here https://www.nalog.ru/rn77/yul/interest/control_verification/learn_audit_plan/.
Tax authorities can check an individual entrepreneur unscheduled if the entrepreneur:
- did not provide an explanation to the Federal Tax Service’s request within the prescribed period;
- did not eliminate the violations recorded during the previous inspection.
The basis for conducting an unscheduled tax audit may be other cases of violation of the current tax legislation by the individual entrepreneur. An unscheduled inspection of an individual entrepreneur is carried out only if there is a corresponding order from the head of the tax authority.
How often are desk audits carried out?
How to change the tax system for individual entrepreneurs and how often can this be done?
Desk audits of individual entrepreneurs consist of monitoring submitted tax returns. The Law on Inspections of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs establishes that the tax authorities are allocated two months for this. This period begins to last from the moment the reports are submitted to the tax authorities. Desk audits comprise the bulk of the work of all tax employees. How often the tax office checks individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system, patent or UTII is directly affected by the frequency of filing tax returns. In general, this happens four times a year.
Features of IP checks in special modes
The type of activity and the region where it is conducted, the amount of income, the number of employees and the area of the premises in which the goods are sold or the service is provided affect the right of an individual entrepreneur to use a special tax regime: simplified tax system, UTII or patent (PSN).
Employees of the Federal Tax Service check the legality of using one or another preferential treatment especially carefully. Therefore, it is better not to skimp on involving experts in filling out declarations and not to give reasons for demanding clarifications and ordering an on-site inspection. Losses due to payment of underpaid taxes, penalties and fines are not comparable with the cost of consulting services.
Checking IP on the simplified tax system
The main goal for which inspectors pay attention to individual entrepreneurs with a simplified taxation system is to identify the illegality of applying this special regime. If the tax authorities can confirm their suspicions of the illegality of using the “simplified tax”, the entrepreneur will pay all taxes that he will be charged within the framework of the general taxation system, including penalties.
The tax return form under the simplified tax system and the procedure for filling it out are regulated by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 26, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
Checking IP on UTII
To ensure that the use of UTII does not result in additional charges and fines for individual entrepreneurs, it is necessary to monthly monitor the compliance of the conditions, primarily documented, with the specified regime. And if potential risks arise, switch to the simplified taxation system or the general tax regime in a timely manner.
Important!
You can apply UTII only for those types of activities that are established on the territory of your locality. In Moscow, imputation has not been applied to any type of activity since 2012.
The form of the declaration on “imputation”, the procedure for filling it out and the presentation format is regulated by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 26, 2018 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
What documents should an entrepreneur have?
Tax and individual entrepreneurs - how to register with the Federal Tax Service and what is needed for this
A full check of an individual entrepreneur involves the consideration of a number of documents that are directly related to the activity. What documents should an individual entrepreneur have in case of an audit? The following papers are of greatest importance:
- certificate of registration of a person as an individual entrepreneur. It will help you find out at what point the individual entrepreneur began to conduct its activities and function;
- documents confirming registration with the Pension Fund and the Health Insurance Fund;
- tax returns for periods of activity;
Entrepreneur's documents
- financial statements;
- bank statement confirming the existence of a current account;
- cash reporting (for retail trade and similar activities).
These are the basic documents that every entrepreneur needs to successfully pass the audit. In some cases, documentation may be required to demonstrate eligibility for a benefit.
Important! If the activities of an individual entrepreneur require a license, then this license must also be provided to tax office employees.
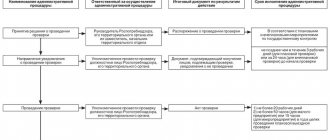
How is the check carried out?
A desk tax audit is a check of compliance with the legislation on taxes and fees on the basis of a tax return and documents that the taxpayer independently submitted to the tax office, as well as documents that the tax authority has. This check is regulated by Art. 88 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The start date of the audit is the date the taxpayer submits a declaration, calculation or information to the tax office.
Without exception, all declarations and calculations received from taxpayers are checked. Taxpayers are not notified of the start of a desk audit, and no decision is made on its appointment.
Types of checks
Unified simplified tax return - sample completion for individual entrepreneurs
All inspections are divided into scheduled and unscheduled. Each of them has its own prerequisites and implementation features.
Planned
A scheduled inspection, as the name suggests, is carried out in accordance with a pre-approved plan. This plan is approved based on many factors, some of which are truly very large-scale. For example, the state decided to increase control over medical organizations and individual entrepreneurs, and in connection with this, a number of companies were included in the list.
The planned inspection is known in advance, since lists of inspected companies are posted on the Federal Tax Service website. You can prepare for such phenomena and avoid unpleasant incidents.
Unscheduled
Unscheduled inspections pose a great danger to an entrepreneur. They are usually applied to those organizations and individual entrepreneurs that have “tarnished” their reputation in the past. Such entrepreneurs are at risk. Often inspections may occur to identify violations that have already been found or to ensure that these same violations are eliminated.
An unscheduled inspection is also a logical response to a complaint from a person about the company’s activities. In this case, tax inspectors may unexpectedly appear at the organization and request all the necessary documentation. How often can the tax office audit an individual entrepreneur? The law establishes that inspections should not be carried out more than twice a year.
What are tax audits?
Depending on the method of conducting inspections, they are divided into desk and field inspections. Let's look at them in more detail.
Desk inspection
Every time an entrepreneur submits some form of reporting, a desk audit begins in relation to it. It is carried out within the walls of the tax office without visiting the entrepreneur. The audit begins after the deadline for receiving the report and lasts a maximum of 3 months .
During a desk inspection, inspectors determine:
- whether the entrepreneur submitted the form and whether he violated the deadline for submitting it;
- whether he filled out the report correctly;
- whether the calculations were made correctly;
- whether the information provided in the documents is correct.
Such checks are carried out on a routine basis, that is, taxpayers are not informed about their conduct. And if everything is in order with the form being checked, the individual entrepreneur in most cases does not even know that a check has been carried out.
If any questions arise during the audit, inspectors may request clarification or documents from the taxpayer. Most often this happens if Federal Tax Service specialists believe that the individual entrepreneur has not paid additional taxes. But the reasons for demanding clarification may vary.
Requests from tax authorities must be responded to immediately, since the entrepreneur will have a five-day period . If there is no response or the taxpayer’s explanation does not satisfy the inspector, he will be held administratively liable. As a result, he will not only be charged arrears, but also fines and penalties.
On-site inspection
From the name it is clear that such an audit is carried out on-site to the taxpayer . However, in cases where the taxpayer cannot provide premises for inspectors, the inspection may be carried out by the Federal Tax Service. The basis for its initiation is the decision of the head of the tax inspectorate or his deputy. The decision to conduct an inspection is made based on the results of the pre-inspection analysis.
Please note that until the end of 2020 there is a moratorium on scheduled inspections of small businesses. The exception is socially significant areas - healthcare, education, social sphere, electric power industry and others.
However, an on-site inspection may be carried out outside of the plan . For example, an entrepreneur may be knocked on the door if, during a desk audit, the inspectorate identifies grounds for a more detailed analysis of his activities.
About scheduled and unscheduled inspections:
The on-site inspection covers a period of no more than the last 3 years . It is carried out in relation to one or more taxes. If a tax has already been audited, the Federal Tax Service does not have the right to reschedule it during the year.
The maximum period for conducting an on-site inspection is 2 months . Sometimes it can be increased, for example, if force majeure circumstances arose, other violations were discovered along the way, or the individual entrepreneur did not provide the requested documents on time.
During the inspection, inspectors try to study all the circumstances and find out whether the individual entrepreneur calculated the tax correctly . For this purpose, they can inspect the taxpayer’s premises, request and seize documents and items, involve experts, and interview witnesses.
As a result, the individual entrepreneur will receive an inspection report, which will list all the violations identified by the inspectors, as well as recommendations for eliminating them. If an entrepreneur does not agree with the inspectors’ conclusions, he will be able to appeal .
Grounds for checking IP
Every action of the tax authorities is supported by some reason. Depending on the type, the grounds for holding may vary. The Federal Law on inspection of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs provides for the following cases:
- increased attention of government agencies to a certain market segment due to policy changes;
- receiving a complaint about violations in business;
- completion of the period allocated by the inspection during the last inspection to eliminate violations;
- direct request of the prosecutor or other governing body.
Who checks? What are they checking?
Many citizens think that an individual entrepreneur may be subject to an inspection from any supervisory authority at any moment in order to take him by surprise, so they are in no hurry to open their own business. In fact, this is a misconception, since most inspections are carried out in accordance with a predetermined schedule, which can be found on the website of the Prosecutor General's Office.
The regulatory framework on the issues of inspections, their terms, rights and obligations of the parties is prescribed in Law No. 294-FZ of December 26, 2008 “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs in the exercise of state control (supervision) and municipal control.” In accordance with this law, the dominance of supervisory authorities has been abolished, businessmen are checked at regular intervals. In addition, there is a moratorium on inspections of small businesses in 2019, so new entrepreneurs will only be disturbed after 3 years of work. In this case, the visit of inspectors may take place much later. Government agencies practice a risk-based approach. The schedule includes businessmen whose reports or activities are questionable.
There are a lot of federal supervisory services, each area of activity has its own, but for individual entrepreneurs the most common are:
- Federal Tax Service;
- Rospotrebnadzor;
- Department of Economic Security of the Ministry of Internal Affairs;
- Ministry of Emergency Situations;
- Rostrud;
- Rostechnadzor;
- Prosecutor's Office;
- Roskomnadzor;
- Rostransnadzor;
- Roszdravnadzor;
- Rosselkhoznadzor.
If one of these services comes to an individual entrepreneur, then the first thing that will interest the employees is whether he is legally or illegally engaged in business activities, and whether he has received permits. Therefore, all primary documents, such as the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs, extracts, licenses, should always be kept at hand. What else do federal services often check?
Federal Tax Service
Control activities of the tax service are not included in the publicly available list of inspections. It is impossible to know in advance about the auditors' visit. Law 294-FZ does not apply to this type of supervision, as is directly stated in its first article. However, the appearance of inspectors can be predicted based on the order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. MM-3-06 / [email protected] dated 05.30.07.
Those businessmen who submit “zero” reports or pay wages to hired workers below the minimum wage are most often subject to individual entrepreneur tax audits. If during a desk audit, inspectors simply correspond with the taxpayer, sending requests for the presentation of certain documents, then during an on-site audit, the internal audit of activities will be checked on site and in more depth. Federal Tax Service employees will be most interested in:
- documents confirming expenses, if the individual entrepreneur is on the simplified tax system “Income-Expense” or unified agricultural tax;
- completeness of income reflection;
- documents confirming payment of duties for importing goods from abroad;
- compliance with cash discipline;
- coincidence of the average number of employees with the actual number;
- the validity of the costs taken into account when calculating obligations to the budget;
- accuracy of calculation of insurance premiums from labor payments;
- reality of transactions;
- accuracy of formation of tax registers, primary reporting, etc.
All verification activities can last from 2 to 6 months. If necessary, they can be suspended or extended. The rules are regulated by Chapter 14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Attention! The law prohibits tax officials from checking the same tax more than once during a tax period. Even a closed entrepreneur can be checked during the first 3 years after cessation of work, especially if he is in debt.
Rospotrebnadzor
The service monitors compliance with the consumer’s rights to receive quality goods, and monitors compliance with sanitary standards in places where goods and services are sold. Therefore, Rospotrebnadzor inspections are often carried out at points of sale of food products and in catering establishments. To avoid violations, the organizer of such enterprises must strictly monitor:
- so that there are no expired products on the shelves;
- for proper storage of perishable products;
- that cooks in the kitchen have sanitary certificates and special clothing;
- for the presence of all price tags on the shelves;
- so that any consumer has access to a book of complaints.
An unscheduled inspection can be triggered by gross violations, the consequence of which was, for example, mass poisoning of people. The client can also file a complaint with Rospotrebnadzor about the presence of expired products in the store, unsanitary conditions, etc. This can even be done through the official website of the department.
It is also worth remembering that in 2020 the service received the right to conduct test purchases. Inspectors can appear at the point of sale under the guise of ordinary buyers (Law 81-FZ of 04/18/18).
Ministry of Emergency Situations
In connection with the latest tragic events in the shopping center in Kemerovo, the topic of fire safety is especially relevant. A wave of inspections from the fire inspectorate is quite expected not only in crowded places, but, in general, in all institutions that people visit. It will not be surprising if after this many property owners will have to organize a fire prevention system in accordance with the law, and not pay off the authorities, as was the case before.
Control is carried out by territorial divisions of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation in accordance with the inspection schedule for 2020. The supervision procedure is established by Administrative Regulation No. 323 of June 14, 2016. Unscheduled visits by auditors are allowed in the event of complaints or information about threats appearing in the media.
You should pay special attention to the following things:
- There must be a fire extinguisher in each room, and the person in charge must be able to use it.
- Fire safety briefings for personnel should be carried out regularly.
- Information must be displayed in a visible place: telephone number of the Ministry of Emergency Situations (01, 010), instructions for detecting a fire, evacuation plan.
- There should be exit signs and stairs hanging in the premises. All emergency exits must be open.
- The fire alarm must be in working order.
- The finishing of walls, ceilings and floors of evacuation corridors should not be flammable.
Important! Under no circumstances should fire safety be neglected! It’s better to organize everything conscientiously once than to deal with dire consequences later.
What can happen to an individual entrepreneur?
If violations are discovered during a tax audit, the individual entrepreneur may face penalties. Here are a few of the most common violations:
- Tax reporting was not submitted on time. If the tax is not paid at all, the fine will be at least 1000 rubles*, plus 5% of the tax amount. If the declaration is simply not submitted, the fine is 1000 rubles;
- gross violation of the rules for accounting for income and expenses. A fine of 10 thousand rubles. depending on the results of violations;
- non-payment of taxes. A fine of 20 to 40% of the amount, plus penalties;
- violations of cash register operation. Fine from 10 thousand rubles.
Entrepreneur's responsibility
If the violation is removable, the inspection will allocate a certain time for this. After it expires, the inspection may come again. If the violation is not eliminated, more severe penalties will follow, including the seizure of accounts and a ban on business. All this can lead to the closure of the IP.
How to reduce tax risks when checking individual entrepreneurs
(basic principles of competent tax optimization using individual entrepreneurs):
- Comply with the industry average tax burden.
- Do not report losses over multiple tax periods. If this is unavoidable in your case, prepare in advance a justification for the losses incurred.
- Keep track of the growth rate of your expenses in comparison with income; the growth of expenses should not exceed the growth of income.
- Pay employees wages no lower than the average for your type of activity.
- If you are on the simplified tax system, try not to get close to the income limit that gives you the right to use the simplified tax system, especially for several tax periods in a row.
- Monitor the level of profitability of your business; it should not differ from the industry average.
- Try to avoid concluding agreements with resellers or intermediaries. Enter into contracts directly with manufacturers.
- Answer the tax authorities’ requests in a timely manner and as completely as possible and provide explanations.
- Submit your reports on time.
- Do not interfere with the audit, even if the tax office deems it necessary to inspect the property of the individual entrepreneur.
1C-WiseAdvice experts defend the interests of their clients at all stages of the relationship with the Federal Tax Service
We prepare reasoned responses to requests and demands during tax audits of individual entrepreneurs, and provide explanations. Our specialists do not refuse the opportunity to minimize the entrepreneur’s losses even in the most hopeless situations. Although those who entrusted their accounting and reporting to us do not find themselves in such situations.
Disputing the results
The results of a tax audit can be very disappointing for an entrepreneur. And this is predictable if the entrepreneur actually committed gross violations. If the entrepreneur does not agree with the results, he can file a complaint with a higher tax authority. This can be done during tax actions if they involve gross violations of current legislation. In this case, the entrepreneur draws up a special complaint and sends it to higher authorities and the prosecutor's office.
Disputing the results
Disagreement with the results can be expressed in a special act, which will be provided within a certain time from the moment of inspection. There, violations in the procedure are indicated and protests are expressed about the results. This act is sent to higher tax authorities.
Note! If the entrepreneur’s claim is found to be legal, a re-inspection will be carried out to change the decision. Otherwise, the complaint will be rejected and the results will remain the same. But even in this case, there is a chance to change the decision of the tax authorities by applying to an arbitration court.
Violations due to desk audits
When conducting a desk audit of specific declarations and/or calculations, the entire taxpayer’s reporting for that period is analyzed. The data specified in the general reporting is compared with the audited one. It is during this analysis that most violations are revealed. Data from external sources, information received from taxpayers' counterparties, and previous desk audits are analyzed.
Various violations are established:
1) simple arithmetic errors;
2) discrepancy between the tax base of VAT and income tax;
3) discrepancies between 6-NDFL and RSV data;
4) violation of the procedure for recovering VAT on advance payments paid;
5) provision of an incomplete set of documents when refunding VAT from the budget or for losses;
6) understatement of revenue;
7) overestimation of expenses;
 for UTII and PSN, there is a discrepancy between the physical indicator of the number of employees and the data of 6-NDFL and DAM;
for UTII and PSN, there is a discrepancy between the physical indicator of the number of employees and the data of 6-NDFL and DAM;
9) lack of documents confirming tax benefits;
10) calculations of property tax without taking into account the cadastral value of the property.
These are the most common violations that are detected during desk tax audits. It is impossible to describe them all. But, as statistics show, 90 percent of violations and errors are made by taxpayers due to their carelessness. This is explained by both the heavy workload of accountants and the lack of experience. But we must also understand that this inattention can be costly for the organization. Therefore, very carefully check that all reporting forms are filled out correctly, do not delay submission until the last day, compare report data, and prepare packages of documents on losses and VAT refunds in advance.
Source:
"Accountant's Time"
Heading:
Tax audits
desk audit, preparation and submission of reports, updated declaration, explanations to the reports
Checks for self-employed citizens
Verification of self-employed citizens has long been considered a sore point of the tax system. It is quite difficult to track their activities, given that they are not affiliated with any specific organization and are not individual entrepreneurs. This is both a plus and a minus for self-employed people. Tax audits for such persons are complicated by a whole list of factors. But even they can be checked by the tax authorities if there are grounds to believe that they have untaxed profits. Often such actions occur simply on a tip from third parties, which can be anyone: from offended customers to direct competitors. It is enough just to notify the Federal Tax Service that a person has a profit and does not pay taxes.
Thus, tax audit is an important tool that supports the stable functioning of the economy. The Tax Inspectorate has all the necessary powers to exercise control over the activities of individual entrepreneurs.
* Prices are as of July 2020.
Features of conducting on-site inspections of individual entrepreneurs
An entrepreneur should not forget that the powers of guests from the tax office are indicated in the decision on the audit. Any request or requirements not recorded in this document are considered an abuse of authority by the inspector.
How does an on-site tax audit work and how does it end?
If an individual entrepreneur does not have the opportunity to organize jobs for inspectors on his territory, you need to be ready to send the originals of the primary documentation to the Federal Tax Service (clause 12 of Article 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An attempt to hide or change the “primary” will lead to the forced seizure of these documents (clause 12 of article 89 and clause 8 of article 94 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
1C-WiseAdvice has developed a unique technology for rapid processing of primary documentation “Processing”, which guarantees timely preparation of documentation that meets the requirements of tax legislation. The patented 1C-WiseAdvice technology - unlike regular accounting, which is not able to provide operational control over the status of primary documents - allows you to prepare documents required as part of on-site inspections as quickly as possible.
There is no need to limit access to property and taxable objects used in business activities. This can work against you: without seeing the real picture, inspectors will assess taxes based on their own data (clause 3 of Article 91 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to behave during an on-site inspection: rules of survival in an extreme situation
In addition to requesting documents and inspection, tax authorities can organize:
- seizure of objects and documentation confirming the violation (Article 94 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- inventory, during which they will be convinced (or not convinced) of the reliability of the data provided (clause 13 of article 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- engaging an expert who, if necessary, will document his conclusions (Article 95 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- calling and questioning witnesses, and if necessary, inviting an interpreter (Articles 90 and 97 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, an on-site inspection can result not only in colossal losses, but also not the most pleasant adventure for your employees and partners, which cannot but affect the company’s reputation. It is better to identify and eliminate shortcomings that can create such problems at the stage of initial organization and maintenance of accounting and tax records.
Rostechnadzor inspection
This authority is authorized to carry out environmental, construction, industrial and technological control.
If the activities of an individual entrepreneur are related to the use of natural resources or production facilities that pose a certain danger, it is Rostechnadzor that is responsible for issuing a license.
To obtain it, the individual entrepreneur must eliminate existing violations in advance, otherwise the entrepreneur will not be able to obtain permission to carry out the desired activity. In the future, inspections are carried out regularly to monitor compliance with safety rules.
Labor inspection check
Entrepreneurs who employ foreigners or minor citizens fall under the regular supervision of this government body. In this case, the basis for conducting an inspection of the individual entrepreneur is the receipt of a complaint from a dissatisfied employee (for example, as a result of receiving a low salary or non-compliance with the working hours).
Labor inspectors check the following documents:
- vacation schedules;
- work books of employed citizens;
- correctness of execution and existence of employment contracts;
- salary payment schedules;
- staffing schedule;
- etc.
To avoid close attention from Rostrud and the labor inspectorate, an entrepreneur needs to carefully study labor legislation and not violate its provisions.
MORATORIUM ON SCHEDULED INSPECTIONS IN 2020
In 2020, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted Law No. 246 Federal Law, which established that:
from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2020, scheduled inspections are not carried out in relation to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who are small businesses, with the exception of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs carrying out types of activities, the list of which is established by the Government of the Russian Federation, in accordance with part 9 Article 9 of this Federal Law.
Federal Law No. 480-FZ of December 25, 2018 extended the moratorium on inspections until 2020 for small businesses.
However, the moratorium will not apply to those individual entrepreneurs for whom a risk-based approach has been introduced, as well as to individual entrepreneurs carrying out licensed activities.
What is a risk-based approach? Supervisory agencies collect information about the activities of individual entrepreneurs and determine the degree of risk of the individual entrepreneur committing illegal actions. If there is no such information on the individual entrepreneur, therefore, the moratorium on inspections applies to him. Supervisory agencies that collect information about illegal actions of individual entrepreneurs include the Federal Tax Service, the Ministry of Emergency Situations, the Federal Antimonopoly Service, Rosprirodnadzor, Rosalkogolregulirovaniya and Rospotrebnadzor.
The law came into force on January 5, 2020.
If a risk-based approach has not been introduced for your individual entrepreneur, but you find yourself on the list of the inspection plan, then you have the right to make a request to exclude your company from the consolidated inspection plan for 2020. To do this, you need to fill out a special application and submit it to the department that scheduled the inspection. For example, to the tax authority or labor inspectorate in the region. The application form was approved by Government Decree No. 1268 dated November 26, 2015.
Rospotrebnadzor inspection
This authority is authorized to carry out sanitary supervision and control over compliance with consumer rights. If a private entrepreneur sells any goods or offers certain services to the public, he cannot avoid inspections from Rospotrebnadzor.
As a rule, the basis for an inspector to visit an entrepreneur’s office or retail space is a complaint from a dissatisfied client or competitor.
Rospotrebnadzor is authorized to check:
- the procedure for placing goods;
- area of retail premises;
- compliance of the product with the declared quality and sanitary standards;
- temperature regime;
- availability of ventilation;
- signs and price tags;
- staff have sanitary records and appropriate uniforms;
- etc.
If violations are detected, officials are held accountable, obliging to pay a significant fine, as well as correct the detected deficiencies.
Verification from other authorities
If an entrepreneur is engaged in certain types of activities, other supervisory authorities may also visit him. For example, police officers have the right to visit the office or commercial premises of an individual entrepreneur in a situation where they have received information about the commission of a crime.
As a result of a police check, a criminal or administrative case may be initiated. Among other supervisory authorities authorized to check the activities of businessmen are:
- Rosselkhoznadzor;
- Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- housing inspection;
- Roszdravnadzor;
- Ministry of Education;
- customs control;
- etc.
How often inspections from the listed authorities can take place depends on many factors (the frequency of receiving complaints, the presence or absence of identified violations by the individual entrepreneur, the type of business activity, etc.).
Prosecutor's check
An inspection by the prosecutor's office is carried out in the event of a complaint. The prosecutor must check the information about the existence of a violation on the part of the individual entrepreneur and issue a written response to the complaint within a month. For this purpose, an appropriate check is carried out.
If the fact of violation has not been confirmed, the complaint is rejected, which is reported to the citizen who sent this appeal.
If the inspection reveals non-compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, violators will be held accountable.
It is worth noting that the prosecutor's office is authorized to carry out inspections only in cases that are beyond the control of other government agencies.