Formula for calculating the net profit of an enterprise
To calculate net profit, it is necessary to make the difference between all costs and taxes of the enterprise. The formula has a single economic meaning, but can be reflected in different ways:
Net profit = Revenue – Cost of goods – Administrative and selling expenses – other expenses – taxes;
Net profit = Financial profit + Gross profit + Operating profit – Amount of taxes;
Net profit = Profit before tax – Taxes;
Net Income = Total Revenue – Total Expenses.
Net profit is also called “the bottom line” because it is reflected in the balance sheet as the last line. In the balance sheet before 2011, net profit was reflected in line 190 of Form No. 2 (Profit and Loss Statement); after 2011, the net profit indicator is reflected in line 2400.
| ★ InvestRatio program - calculation of all investment ratios in Excel in 5 minutes (calculation of Sharpe, Sortino, Treynor, Kalmar, Modiglanca beta, VaR ratios) + forecasting rate movements |
Formula for calculating net profit on balance sheet
Let us describe in more detail the formula for calculating net profit through the balance sheet lines.
Net profit (line 2400) = Revenue (line 2110) – Cost of sales (line 2120) – Selling expenses (line 2210) – Administrative expenses (line 2220) – Income from participation in other organizations (line 2310) – Interest receivable (line 2320) – Interest payable (line 2330) – Other income (line 2340) – Other expenses (line 2350) – Current income tax (line 2410)
The figure below shows part of the balance sheet of the enterprise OJSC “Surgutneftekhim” and its reporting for 5 years. As can be seen from the balance sheet in Excel, in order to obtain net profit, you must first calculate: gross profit (marginal profit), profit from sales and profit before tax.
How to calculate net profit on the balance sheet?
According to Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010, the financial results of the enterprise’s activities are recorded on this report form.
This form has a special column numbered 2400 to reflect net profit (loss) for the reporting period.
Separately, we note that one of the reliable ways to calculate the amount of net profit is a calculation based on information from the company’s statements.
To calculate this indicator, use the following formula, where the numbers indicate the line numbers in the form:
2110 – 2120 – 2210 – 2220 + 2340 − 2350 – 2410, Where:
- 2110 corresponds to gross revenue;
- 2120 – cost;
- 2210 and 2220 - production and administrative expenses;
- 2340 – other income ( 2350 – similar expenses);
- 2410 – income tax.
Therefore, you must have a completely completed balance sheet form. The necessary data is taken from it, from which net profit is calculated.
But you can calculate the state of emergency using a simpler algorithm, simply by subtracting line 2410, corresponding to income tax, from line 2300 (profit before taxes).
Or use the turnover on account 99 in correspondence with account 84.
We recommend
“Increasing enterprise profits: calculation, methods, examples” Read more
Place of net profit in the enterprise income system
Net profit occupies a key position in the enterprise's income system. In order to understand, let’s consider its relationship with other types of income. The figure below shows the types of profit and their relationship. Each type of profit allows you to evaluate efficiency. So Marginal Profit shows the efficiency of sales and product sales. (you can find out more about this type of profit in the article: “Marginal profit. Calculation formula. Analysis with an example”) Operating profit reflects the efficiency of production or other type of core activity of the enterprise Profit before tax is profit without taking into account other costs/income from non-core activities . As a result, net profit, cleared of all costs and expenses, shows the integral result of the functioning of the enterprise.
Distribution of net profit
The funds remaining after paying all taxes are subject to distribution among the business owners. Everyone is paid a portion of the profit in proportion to their contribution to the common cause. In joint stock companies this is called "earnings per share." In addition, net profit is spent on:
- Consumption. This includes the payment of dividends, bonuses or financial assistance to employees, etc.
- Accumulation. This item includes placing funds in bank accounts, purchasing valuables and other liquid assets. The accumulation fund is mainly used for business development in technical terms. These funds are spent on acquiring new technologies, financing research and development, etc.
- Investment. There are internal and external placement of investments. In the first case, finances are used to develop one’s own enterprise, and in the second, they are invested in third-party projects in order to generate income.
Net profit can be used to offset losses from previous years.
Goals and directions for using the net profit indicator
The amount of net profit characterizes the efficiency of the entire company/enterprise and is used for various purposes by various external and internal stakeholders (individuals, users).
| User/stakeholder | Purpose and directions of use |
| Investors | Goal: assessment of investment attractivenessAssessment of the size and dynamics of changes in the net profit of an enterprise to analyze its investment attractiveness. The more a company can generate net profit at the end of the reporting period, the higher its profitability. |
| Creditors | Purpose: assessment of creditworthinessAssessment of the size and dynamics of changes in net profit to analyze the solvency and creditworthiness of the enterprise. Cash is the most quickly liquid type of asset, and the more cash a business has left after paying all tax deductions, the greater its ability to pay its obligations in the short and long term. |
| Owner/Shareholders | Goal: assessing the effectiveness of activities as a whole. Analysis of net profit is an integral indicator of the activity of an enterprise/organization and characterizes the effectiveness of all management decisions for the reporting period. The larger the net profit, the more effective the management of the organization was. An increase in net profit increases the size of dividend payments and allows you to attract additional buyers/shareholders. |
| Suppliers | Goal: assessing the sustainability of operation. The net profit of an enterprise serves as an indicator of its sustainability of development. The higher the net profit for the reporting period, the higher the ability to pay suppliers and contractors on time for raw materials. |
| Top managers | Goal: assessing the sustainability of financial development The amount of net profit and the dynamics of its change serves as a guideline for developing strategies and plans to increase it at the operational level. Planning of contributions to reserve funds, wage funds and production funds. |
| ★ InvestRatio program - calculation of all investment ratios in Excel in 5 minutes (calculation of Sharpe, Sortino, Treynor, Kalmar, Modiglanca beta, VaR ratios) + forecasting rate movements |
Methods of analysis
| Way | Description |
| Factorial | The main purpose of compiling this calculation is to determine the reasons for changes in profit. A decrease in net profit indicates a possible depreciation of money or changes within the company. All factors on which the amount of net profit depends are divided into two categories: external and internal. External factors include:
The category of internal factors includes:
When conducting factor analysis, it is necessary to take into account the cost of the product itself, the amount of associated costs, additional costs and the amount of revenue received from the sale of products |
| Statistical | This method of analysis is carried out in order to study the structure and amount of profit received by an enterprise over a certain period of time. In addition, using statistical analysis you can:
|
To determine the financial condition of the enterprise and assess its profitability and payback, a profitability analysis should be performed. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that the profitability of an enterprise is not about calculating the amount of money, but about measures to obtain maximum profits with minimal costs. Using this analysis, you can determine how effectively all the resources of the enterprise are used: monetary, material, production, etc.
Methods for analyzing the net profit of an enterprise
Let's consider various methods of analyzing the net profit of an enterprise. The purpose of this analysis is to determine factors, cause-and-effect relationships between indicators that affect the formation of net profit as the final indicator of the enterprise’s performance.
The following analysis methods can be distinguished, which are most often used in practice:
- Factor analysis;
- Statistical analysis.
These types of analysis are opposite in nature. Thus, factor analysis focuses on identifying significant factors that influence the formation of the enterprise’s net profit. Statistical analysis emphasizes the use of time series forecasting methods and is based on an analysis of the pattern of changes in net income over the years (or other reporting periods).
Factor analysis of an enterprise's net profit
The main factors in the formation of net profit are presented in the formula described earlier. To assess the influence of factors, it is necessary to evaluate their relative and absolute changes for 2013-2014. This will allow us to draw the following conclusions:
- How did the factors change during the year?;
- Which factor had the greatest change in net income?
In financial analysis, these approaches are called “Horizontal” and “Vertical analysis”, respectively. Below are shown the factors that form the amount of net profit and their relative and absolute changes during the year. The analysis was made for the enterprise OJSC “Surgutneftekhim”.
As we see, during 2013-2014, other expenses and other income changed as much as possible. The figure below shows the change in the factors that form the net profit for 2013-2014 for Surgutneftekhim OJSC.
Let's consider the second method of assessing and analyzing the net profit of an enterprise.
Statistical method for analyzing the net profit of an enterprise
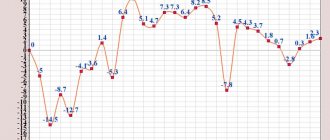
To estimate the future amount of net profit, various forecasting methods can be used: linear, exponential, logarithmic regression, neural networks, etc. The figure below shows a forecast of net profit based on an analysis of changes in the indicator over 10 years. Forecasting was carried out using linear regression, which showed a downward trend in 2011. The accuracy of forecasting economic processes using linear models has an extremely low degree of reliability, so the use of linear regression can serve more as a guide to the direction of changes in profit.
Comparison of net profit with other indicators of enterprise performance
In addition to assessing and calculating the net profit of an enterprise, it is useful to conduct a comparative analysis with other integral indicators that characterize the efficiency and effectiveness of the enterprise. These indicators include: sales revenue (minus VAT) and net assets. Net assets show the financial stability of the enterprise and its solvency, revenue reflects its production and sales performance. The figure below shows a graph of a large Russian enterprise, OJSC ALROSA, and the relationship between its three most important indicators. As you can see, there is a close relationship between them, and it can also be noted that there is a positive growth trend in the enterprise’s net assets, this indicates that funds are being directed to expand production capacity, which in the future should increase the amount of net profit received.
Current assets (section II of the balance sheet) and net profit
The influence of current assets on net profit differs from the similar influence from the assets of Section I and is characterized by one feature. If the cost of non-current assets is transferred to expenses gradually and they affect the amount of net profit over a long period, then current assets are included in expenses much faster and are reflected in net profit.
Thus, materials transferred to production and used in the current period immediately form the cost of manufactured products and affect the net profit indicator.
But we should not forget that not only expenses are involved in calculating net profit. At the same time, the net profit is also affected by the income from the sale of these products. That is, on the one hand, the cost of material written off for production reduces net profit, but revenue from the sale of products produced from these materials increases it. As a result, the net profit indicator changes.
Current assets reflected in line 1250 “Cash and cash equivalents” do not directly affect net profit, but it depends on their correct and rational use.
For example, the simultaneous absence of inventories on the balance sheet and cash in the current account or in the cash register may indicate that the company does not have money to purchase raw materials. And without MPZ it is impossible to organize the technological process of production. In this case, the company loses income from its sale. This circumstance does not contribute to the growth of net profit, and in some cases reduces it (for example, if the contract with the customer provides for penalties for late delivery).
However, the absence of any figure in line 1250 does not always indicate a lack of working capital and a negative impact on net profit. With a competent approach to spending this resource, money is in constant circulation and has a faster impact on net profit. Thus, funds sent to the supplier of materials in a timely manner will help increase the company’s net profit, since there will be no failure in production due to a shortage of materials and materials and the products will bring in sales income on time.
Is the credit rating of a company related to the amount of net profit?
In my research, I analyzed the relationship between the amount of net profit for the Rosneft OJSC enterprise and the credit rating of the international agency Standard & Poor's. There is a close relationship and correlation shown in the figure below - this proves the importance of such an indicator as net profit as a criterion of investment attractiveness not only in the national space, but also in the international arena.
Summary
Net profit is the most important indicator of the effectiveness and efficiency of an enterprise. Net profit reflects investment attractiveness for investors, solvency for creditors, sustainable development for suppliers and partners, efficiency/performance for shareholders and owners. To analyze net profit, two methods are used: factorial and statistical. Based on the factor analysis method, the absolute and relative influence of various indicators on the formation of net profit is assessed. The statistical method is based on forecasting time series of changes in net profit. The conducted study of the close relationship between the credit rating of the international rating agency Standard & Poor's proves the importance of the net profit indicator in assessing an enterprise in the international financial arena.
Author: Ph.D. Zhdanov Ivan Yurievich
What is net profit
To contents
Net profit is a criterion that indicates the effective commercial activity of an enterprise. This is the name given to the part of the balance sheet (gross) profit that an organization can dispose of after forming a salary fund, paying taxes and other mandatory payments, including loans.
How to spend these funds is decided by the owners of the company themselves. Most often, special funds are created:
- consumer (employee encouragement, social support);
- cumulative (increasing working capital, developing production, purchasing equipment, purchasing shares of other enterprises);
- reserve (reserve for a rainy day).
Also, a share of profits goes to pay dividends to shareholders.
The amount of net profit is directly dependent on the volume of revenue, commodity costs, tax deductions and other costs. An increase in this amount compared to the previous period indicates that the organization is working efficiently, a decrease indicates management errors. But identifying only this indicator is not enough to make management decisions. You also need to know how much money is in the accounts. It happens that according to reporting there is a profit, but the account is empty. Perhaps this money is “suspended” in accounts receivable or in reserves. A competent accountant, having compiled a balance sheet, will be able to calculate what caused the problem.
Net profit formulas for the Russian Federation and some CIS countries
In many CIS countries, in accounting based on the Soviet system, net profit is calculated this way:
formula in the Republic of Belarus and the Russian Federation – Pch = Pf + Pv + Pop – N, where:
- Pf – financial profit (the difference between financial income and expenses);
- Pv – gross profit;
- Pop – operating profit;
- N – the amount of taxes and obligatory payments to the budget.
The data for calculation are indicated in the report on the financial result of the enterprise. Using the formulas for calculating gross and operating profit, you can easily find all the variable values.
There is another general formula for calculating the net profit of an enterprise: Chn = B – Seb + D – R – N, where:
- B – total amount of revenue;
- Seb – full cost of products sold;
- D – other income;
- R – other expenses;
- N – the amount of taxes and obligatory payments.
If you look closely at the variable values of the formula, you can see that it is identical to the first method of calculating net profit. The only difference is that in this case, the values of gross and operating profit are replaced by the components for finding them.
Formulas for calculating operating and gross profit
Gross profit characterizes the efficiency of a business. The indicator is used to analyze any type of enterprise. Gross profit is determined by the formula: Pv = B – Seb, where:
- B – total amount of sales revenue;
- Seb – cost of sold products (works, services).
As can be seen from the formula, gross profit shows the amount of income received from sales, not including other income/expenses and income tax. The gross profit value fully reflects the results of the sales process.
Operating profit allows you to see the financial result of the enterprise. The calculation formula consists of the difference between total income and expenses, production costs, and depreciation charges. In mathematical form it looks like this: Pop = B – Seb – Rop – A, where:
- B – total amount of sales revenue;
- Seb – cost of goods sold;
- ROP – the amount of operating expenses;
- A is the amount of depreciation charges.
The operating profit indicator allows you to evaluate the production efficiency or trading activities of an organization, taking into account the need to reproduce fixed assets.
Profitability indicators and net profit margins
In financial analysis, another indicator of the enterprise’s activity is used - the net profit rate. The calculation formula consists of the values of net profit and total revenue: Np = Pch ÷ B × 100%. It is believed that if the enterprise operates efficiently, the coefficient is ≈ 0.2.
Thus, the profitability indicator of an enterprise of any direction is always the net profit rate. The balance calculation formula is based on the components of the value. Let us describe the calculation algorithm according to the lines of the balance sheet:
- Net profit is listed on line 2400, and the amount of revenue is listed on line 2110.
- Compute the result of the private string 2400 and 2110.
- Multiply the resulting number by 100%.
- The result of the actions performed is the net profit rate.
In addition to Np.h., the value of net profit margin is used in financial analysis. Profitability is an indicator of the efficiency of economic activity. In the case under consideration, it characterizes the amount of profitability of sales. The formula for calculating net profit margin or net profitability ratio looks like the ratio of net profit to the amount of revenue: Kch.r. = Pch ÷ V.
The coefficient shows how much net income is generated per ruble of work, services or goods sold. Using the balance, you can calculate the value using the ratio of lines 2400 to 2110.
Net profit: calculation formula using the algorithm
Net profit is that part of the balance sheet profit that remains at the full disposal of the company and is formed only after fulfilling obligations to the state budget. There are several ways to calculate a company's net profit. However, if you have information about the main components, net profit can be easily calculated. The calculation formula consists of several steps. Let's analyze them point by point, creating a calculation algorithm:
- Based on the data in the financial result report, identify the total amount of revenue of the enterprise.
- Subtract the amount of variable costs from the found value. The resulting value characterizes the company's marginal profit.
- Subtract the amount of fixed expenses. The result is operating profit.
- Subtract the amount of other expenses. The resulting value is the enterprise’s profit before taxes (balance sheet).
- Subtract taxes and other obligatory payments to the budget. The amount of net profit was formed.
The use of the marginal profit indicator for further analysis of financial results is most typical for small business entrepreneurs, and the operating profit indicator for large organizations.