Profit is the monetary expression of the main part of cash savings created by enterprises of any form of ownership. It characterizes the financial result of the enterprise's entrepreneurial activity. Profit is an indicator that most fully reflects production efficiency, the volume and quality of products produced, the state of labor productivity, and the level of costs. Profit is one of the main financial indicators of the plan and assessment of the economic activities of enterprises. Profits are used to finance activities for the scientific, technical and socio-economic development of enterprises and to increase the wage fund for their employees. It is not only a source of meeting the intra-economic needs of the enterprise, but is becoming increasingly important in the formation of budgetary resources, extra-budgetary and charitable funds.
In conditions of market relations, an enterprise must strive to obtain maximum profit, that is, to such a volume that would allow the enterprise not only to firmly maintain a sales position in the market for its products, but also to ensure the dynamic development of its production in a competitive environment.
Therefore, each enterprise, before starting production, determines what profit, what income it can receive. Hence, profit is the main goal of entrepreneurial activity, its final result.
The important task of every business entity is to get more profit at the lowest cost by observing a strict regime of economy in spending funds and using them most efficiently.
The main source of cash savings for an enterprise is revenue from sales of products, namely that part of it that remains after deduction for the production and sale of these products.
Content
- The essence and functionality that makes a profit
- What affects profit levels
- Typology
- Formation and distribution of profits
- Optimal profit distribution
- Profit distribution management
- The procedure for distributing profits at enterprises of various forms of ownership
- Distribution of profits in LLC
- Peculiarities of the procedure in a company with one founder
- Distribution of profits in a joint stock company
- Distribution of profits in a production cooperative
- Distribution of profits in a limited partnership
- Procedure for distribution of profit of a unitary enterprise (unitary enterprise)
- Distribution of profits by property
- Terms of profit distribution
- How is profit distributed under the simplified tax system?
- Conclusion
General definition
When considering the economic content, formation and distribution of enterprise profits, one should understand the essence of such a concept as financial result. Its determination occurs according to the established methodology. The result of the organization's activities is income and profit from core, investment and financial activities. On its basis, the performance of the enterprise in the period under review is assessed. The indicator is considered in dynamics, which makes it possible to determine changes and factors that influenced it.
The starting point for calculations is the amount of revenue from product sales. You also need to take into account income from transactions outside the sale of main products.
Profit is the resulting indicator. It is defined as the difference between income and resources expended. If the result of such an action is positive, this indicates effective management and organization of the production process at the proper level. If the calculation result is negative, we can say that the company was unprofitable in the reporting period. In this case, you need to look for ways to eliminate the negative impacts on the organization’s activities.
In the course of studying the economic content, formation and distribution of enterprise profits, it should be taken into account that the calculation takes into account the total amount of funds for sales at the market price. But this does not take into account excise tax and VAT. The cost is subtracted from the amount received. These are the costs incurred during the production of the product.
There are three main types of profit:
- from implementation;
- non-operating;
- from the sale of other valuables.
There are many factors that affect profit. This may be sales volume, structure and cost of production, market price of products. This indicator is indirectly affected by the quality of finished goods, the situation in the industry, inflation, etc.
The essence and functionality that makes a profit
In economic terms, profit is the difference between income and costs incurred by production. When can we say that an enterprise or company is making a profit? In order to identify the financial result, the revenue received is compared with the costs incurred for production and sales, which will take the form of cost.
If the revenue received exceeds the cost, it is concluded that a profit has been made. If costs exceed revenue, this indicates losses.
Profit performs a number of functions:
- Gives a description of the economic effect obtained by a company or manufacturing enterprise;
- Has the effect of stimulating all activities as a whole;
- Allows you to create different types of budgets;
- Summarizes the entire result of the company's activities.
The concept of the profit distribution method and its goals
The essence of the enterprise profit distribution method is to compare the actual distribution of total profit between the parties to a transaction with the distribution of profit between the parties to the transactions to be compared. In fact, these actions can be called redistribution of profits according to current market rules.
The profit involved in the distribution consists of the total profit of the enterprise from all aspects of the transaction, as well as from the residual profit from all sides of the transaction.
The main goal of the existing method of profit distribution can be called providing additional financial resources to certain areas of production in order to establish the optimal and most productive balance between funds regularly allocated for consumption and accumulation.
The profit distribution method helps to pay due attention to every aspect of the activity of an enterprise or institution, thereby finding the ideal financial balance for further functioning.
Often, the application of this method under established conditions leads to stable growth and development of the economic state of an enterprise, helps to overcome the financial crisis and improve the microeconomics of the organization.
What affects profit levels
Experts divide factors influencing profit into several groups:
- Internal factors - affect profit through output volumes, by improving the quality characteristics of products;
- External factors do not depend on the activities carried out by an enterprise or company, but they have an impact on the level of profit.
When an enterprise carries out economic activities, the entire complex of these factors is dependent and interconnected with each other.
Types of enterprise profit
The result of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise is expressed in monetary form as of the reporting date: for the month, quarter and year.
It is necessary to analyze the work done, fulfill specified indicators and pay mandatory tax payments and fees.
Types of income and profit of an enterprise are grouped depending on the content and structure of the incoming elements.
The classification of an enterprise's profit is based on the sequential exclusion of cost items (expenses) from gross income, as a result of which the result (profit) is recorded at a certain stage of calculation.
The relationship between types of income and profit can be represented in the form of a truncated pyramid, where the lower base is gross income, and the upper base is net profit.
Gross income or sales proceeds is the amount of money received per month (quarter, year) from the sale of goods (services, works).
Its value will not tell you anything without comparing the obtained indicators with the costs of production and sales of a given amount of goods (services, works).
The types of profit of an enterprise have nuances depending on the type of activity of the enterprise:
- for trading and service enterprises, sales revenue is equal to profit;
- for construction organizations, the act of acceptance of completed construction and installation work is the basis for calculating profit;
- enterprises with a long production cycle (more than a month) include the cost of work in progress in profit at the reporting date.
The concept of profit implies a positive difference between gross income and expenses.
A negative result means a loss, that is, the costs of production and sales of products turned out to be higher than the price offered for it. The starting point for economic analysis is the gross profit of the enterprise.
Typology
Profit comes in various forms. Let us briefly describe some of them.
| Profit type | Brief description of the type |
| Balance sheet | Final result for the reporting period |
| Gross | The difference between revenue and cost, excluding selling expenses |
| Clean | Which remains after deducting all expenses |
| Marginal | It turns out when revenue exceeds production costs |
| Normal | Allows you to maintain your position in this market |
| Capitalized | Used to increase assets |
| Nominal | Corresponding balance sheet reflected in financial documents |
Enterprise profit functions
In order to accurately distribute the profit of an enterprise and methods for optimizing it, it is necessary to identify the main functions that are responsible for certain processes.
In total, economists identify five main functions, the implementation of which will determine the break-even level of the enterprise and profit forecasting.
These indicators will include the following functions:
[1]. Final result. The profit of an enterprise is the result of the company's economic activity for a certain period.
This value shows how much net cash was received minus all expenses.
This function shows how effective [/anchor] is in your business or in a certain industry.
[2]. Stimulating. Profit planning at an enterprise is based on the need to increase the level of net funds. Every company is interested in this.
By optimizing the profit of the enterprise, production capacity also increases, which has a positive effect on both the general level of development and the social level, in the form of rising wages.
[3]. Fiscal. This element relates to the broader concept of profit. When forecasting profits, an enterprise seeks to improve, first of all, its economic performance.
As a result of the pursuit of big profits, income increases first. Various tax deductions are withheld from them, which depend on the regime chosen by the company.
These funds go to the budgets of the constituent entities of the federation. At their expense, various social programs for the population are formed.
[4]. Estimated. Profit from financial activities forms not only internal, but also external economic indicators.
Depending on the level of funds for each period, the total market value of the company is determined. Such an assessment of the enterprise’s profit makes it possible to determine its competitiveness.
[5]. Test. This function is important for any company. The income statement allows you to monitor economic activity.
If incoming dynamics are not properly controlled, this will ultimately lead to a decrease in incoming funds or to the complete bankruptcy of the company.
A decrease in enterprise profits is a consequence of the fact that one of the listed functions is impaired. At the same time, there will also be a decrease in production capacity and a decrease in funds allocated for development, without receiving the predicted income.
Formation and distribution of profits
There are several methods for generating profit. Let's look at each of them, analyzing the pros and cons.
- Direct counting method : in this method, profit is determined by the output of goods and the volume of products sold by the enterprise. The main advantage of this technique is its accuracy, but the disadvantage is that it is too labor-intensive and sometimes impossible to apply;
- Standard method: one of the positive aspects is the high accuracy in calculations, but at the same time it can be used only if production is stable. This method has shown its effectiveness in justifying various economic plans;
- Analytical method: used to establish the planned profit of an enterprise. The essence of the method is to analyze the influence that internal and external factors have on the results of the activities carried out by the enterprise.
The algorithm consists of the following stages : analysis of the profit received for a specific period of time, determination of production volumes, establishment of what part profit occupies in all income received, and the planned profit is determined.
There is also a combined calculation method, which combines the direct counting method and the analytical method.
As for the distribution of profits, this is the most important process, which not only ensures that the various needs of entrepreneurs are covered, but also takes part in the formation of the country’s budget.
The profit distribution system at any enterprise should be built in such a way that production efficiency increases, not decreases.
The principles of distribution are formulated as follows:
- The resulting profit must be distributed between the state and the company;
- The state receives part of the profit through taxation and fees, the size of which cannot be arbitrarily changed;
- The profit remaining with the enterprise should not have a negative impact on increasing production volumes;
- The remaining profit, first of all, goes to the savings part; the remainder can be used at the discretion of the company.
Enterprises distribute the so-called “net profit”, which remains after making all mandatory payments. Distribution of net profits is partly an area related to planning. Taking this indicator into account, expense estimates are drawn up.
The profit that remains at the disposal of the enterprise itself can be used to develop and improve its activities. The state and regulatory authorities should not interfere with the procedure for using these funds.
Along with financing production, it can be used to pay benefits, bonuses, incentives for employees who retire, and so on. These same funds can be used to finance competitions, cultural events, etc.
We also clarify that profits can be used to pay off penalties.
All profits remaining at the disposal of the enterprise or company are divided into 2 parts. The first can be considered accumulative, and the second can be used in the process of consumption. If there is profit that has not been distributed in previous years, this characterizes the enterprise as stable and financially sound.
The question naturally arises: Who makes the decision on the distribution of profits? This depends on the organizational form of the enterprise, which will be discussed further.
Optimal profit distribution
As already mentioned, net profit can be directed to a variety of expense items, or it can be capitalized, which allows you not to attract third-party assets and expand the functionality of the enterprise using your own funds.
One example of thoughtful distribution of profits is the allocation of some of it to the needs of staff. After all, the human factor, people can be called the most important asset of any enterprise.
To make a reasonable distribution, each component of the profit must be carefully analyzed. It is also important to do this in order to identify the weaknesses of the enterprise in a timely manner.
Profit distribution management
When a category such as profit is considered, not only its types are taken into account, but also the management methodology. To manage rationally, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- Before making management decisions, you need to approach them carefully and comprehensively;
- Apply different approaches to managing the enterprise as a whole;
- Respect the interests of not only the owners of the enterprise, but also the state and employees;
- Carefully analyze risks;
- Increase competitiveness.
All procedures around this indicator should be aimed at increasing positive indicators and reducing possible risks.
Chapter 3. Distribution and use of enterprise profits.
3.1 Approaches to the distribution of profits in an enterprise.
The object of distribution is the balance sheet profit of the enterprise. Its distribution means the direction of profit to the budget and by items of use in the enterprise. The distribution of profits is legally regulated in the part that goes to budgets of different levels in the form of taxes and other obligatory payments. Determining the directions for spending the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise, the structure of the items of its use is within the competence of the enterprise.
| book profit |
| net profit |
| income tax |
| taxes from net profit |
| dividends |
| consumption |
| accumulation |
Rice. 3 Distribution of balance sheet profit.
Principles of profit distribution
can be formulated as follows:
· profit received by an enterprise as a result of production, economic and financial activities is distributed between the state and the enterprise as an economic entity;
· profit for the state goes to the relevant budget in the form of taxes and fees, the rates of which cannot be arbitrarily changed. The composition and rates of taxes, the procedure for their calculation and contributions to the budget are established by law;
· the amount of profit of the enterprise remaining at its disposal after paying taxes should not reduce its interest in increasing production volumes and improving the results of production, economic and financial activities;
· the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise is primarily directed to accumulation, ensuring its further development, and only the rest - to consumption.
The distribution of profit refers to the procedure for its direction, determined by law. In a market economy, a significant part of the profit is withdrawn in the form of taxes (38-45% of gross profit), which the state uses to replenish budget revenues.
The Law of the Russian Federation “On the Profit Tax of Enterprises and Organizations” gives enterprises the right to direct part of their gross profits to finance capital investments for industrial and social purposes, as well as to repay bank loans received for these purposes. In addition, the law allows, at the expense of gross profit, to cover expenses associated with the repayment of loans from commercial banks received to finance capital investments. If an enterprise does not use these loans for their intended purpose, then the profit received from their use is subject to taxation in accordance with the general procedure. One of the directions for the distribution of profits is the repayment of a state targeted loan received from a targeted extra-budgetary fund to replenish working capital, within the terms of its repayment.
Rice. 4 Scheme of distribution and use of enterprise profits
The purpose of analyzing the distribution of profits is to establish how rationally profits are distributed and used from the standpoint of self-expansion (self-sufficiency) of capital and self-financing of a trading enterprise. At the same time, directions for using the profits remaining at the disposal of the enterprise must be explored. In foreign practice, the concept of internal capital accumulation is used at the expense of profits transferred to the reserve fund. In Russia, a reserve fund is created and replenished from profits only in joint stock companies and limited liability companies. No more than 50% of the amount of profit subject to taxation can be allocated to the reserve fund. The funds of this fund have a specific purpose - to cover unforeseen losses, compensate for risk, and other expenses arising in the process of economic activity and when distributing profits to various funds of the enterprise. The existence of a reserve fund determines the possibility of paying dividends on shares in the event of a lack of net profit. Dividends that fully reflect fluctuations in earnings are characterized by instability. If the shares of a joint stock company are listed on the stock exchange, their exchange rate becomes one of the most important limitations on the distribution of profits. Significant changes in the amount of dividends paid are immediately reflected in the stock price. Therefore, joint stock companies strive to ensure that dividends do not differ too much from the level considered normal, focusing, as a rule, on the amount of interest paid by Sberbank on household deposits.
3.2 The process of using enterprise profits.
The distribution of profit predetermines the process of its use. After paying taxes, what remains is net profit. Net profit is an important source of expanded reproduction, due to it the following is carried out:
· investment in capital construction;
· expansion and reconstruction of existing fixed assets;
· covering the need for working capital;
· creation of financial reserves.
The need for financial reserves is determined in two ways: either as a certain percentage of net profit specified in the constituent documents, or based on the need for finance in connection with the growth and expansion of the enterprise;
· repayment of long-term and medium-term bank loans and payment of interest on them;
· acquisition of loan obligations, shares and other enterprises;
· financing the activities of unions, associations and other horizontal structures of which the enterprise is a member;
· ensuring the social development of the enterprise and increasing the material interest of employees, taking into account the need for social, cultural, housing events, and their cost and others.
By directing a significant share of net profit to current needs, the enterprise reduces the rate of economic growth and, therefore, limits the possibilities of future consumption. Profits used for investment help accelerate economic growth, thereby expanding the possibilities for future consumption. Trade is the most profitable branch of capital investment, since the payback period is relatively short, and the return on invested capital ensures a quick return on investment.
In general, the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise is distributed into accumulation funds and consumption funds. These funds differ in their ownership. In a joint-stock enterprise, consumption funds are the property of the workforce, and accumulation funds are the property of shareholders and founders. Therefore, consumption funds cannot be classified as the capital of an enterprise. The difference between capital and funds is that capital is formed as a result of the accumulation of property, and accumulation funds - as a result of the distribution of net profit.
Russian legislation grants enterprises, regardless of their organizational and legal form of ownership, the right to quickly maneuver the profits coming to them after paying tax payments to the budget. The difference between the total profit for all types of activities of the enterprise and its used part for the reporting period represents retained earnings. It should be emphasized that until 1993, there was no indicator of retained earnings in the balance sheets. Since all the profit of the reporting year was distributed in the prescribed manner, and its free part was added to the authorized capital. With the development of market relations, retained earnings from previous years become a stable, long-term functioning additional part of the enterprise's equity capital.
retained earnings
– a fundamentally new indicator characterizing the economic growth of an enterprise based on its own funds. As part of retained earnings, one part characterizes the amount of accumulated profit, the second part represents free profit, that is, profit that has not received essentially any direction.
It should be noted that the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise cannot be fully attributed to equity capital.
All consumption funds, even such savings as investments in the social sphere, do not belong to equity capital. This is not the capital of the enterprise in its pure form, but essentially what the company gave to the team to improve its social needs. Social funds accumulate a significant part of the profit, registered or aimed at creating sources of financing costs for the creation of new enterprise property and social infrastructure, as well as for the needs of social development, material incentives for employees.
Social funds clearly distinguish between the funds allocated by the enterprise for production development and for consumer needs. Among these funds, formed by the enterprise at the expense of net profit, the largest share is occupied by consumption funds. Consumption funds are intended to finance expenses for social needs and material incentives for the enterprise staff. At the expense of consumption funds, employees are paid bonuses not related to production results, remuneration for long-term work, in connection with anniversaries and in other similar cases. Special and compensation payments made by the enterprise in excess of the norms established by law are also made at the expense of consumption funds. Social payments include: material assistance, payment for vouchers for workers and their children for treatment and recreation, purchase of medicines at the expense of the enterprise, etc. Social funds include the social sector fund as financial support for the development (capital investments) of the social sector. Withdrawal of economic sanctions provided for by law into the budget is carried out at the expense of the profit left at the disposal of the enterprise after tax has been calculated. These include: fines for concealing (understating) profits from taxation; penalties for late transfer of payments to the budget; economic sanctions for violation of state price discipline. The following provision is new in tax legislation: each day of delay in payment of income tax is considered as a form of lending to the enterprise by the state with mandatory payment of interest to the budget. Fines and penalties for late transfer of taxes to the budget are paid from net profit. In terms of economic content, funds are the net profit of the reporting year or previous years, distribution among funds for its intended use: for the purchase of new equipment; social events; financial incentives and other needs.
The board of founders has the right to direct funds from funds to cover losses, redistribute funds from funds between them, and direct part of the funds to increase the authorized capital and finance other activities. In any case, based on the decision of the Board of Founders, the redistribution of net profit is documented in a protocol, and after registering changes and additions in the constituent documents, the enterprise’s accounting department makes the appropriate entries. The fundless method is most often used by small businesses. Typically, they form a reserve fund, contributions to which can affect taxable income due to possible tax benefits on these contributions.
The stock method of using profit involves the distribution of net profit in accordance with the constituent documents and funds, which provide for the amount of deductions. The procedure for the formation and expenditure of funds is determined by the enterprise independently and is enshrined in the charter and order on the accounting policy of the enterprise.
Conclusion.
Profit is the monetary expression of the main part of cash savings created by an enterprise of any form of ownership.
The main purpose of profit in modern economic conditions is to reflect the efficiency of the production and marketing activities of the enterprise. This is due to the fact that the amount of profit should reflect the correspondence of the individual costs of the enterprise associated with the production and sale of its products and acting in the form of prime costs, socially necessary costs, the indirect expression of which should be the price of the product.
The main indicators of profit used to evaluate production and economic activities are: balance sheet profit, profit from sales of manufactured products, taxable profit, profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise or net profit.
As the most important category of market relations, profit performs certain functions:
· characterizes the final financial result of the enterprise’s entrepreneurial activity;
· has a stimulating function;
· is one of the sources for the formation of budgets at different levels.
Since profit is the most important indicator characterizing the financial result of an enterprise, all participants in production are interested in increasing profits.
To manage profit, it is necessary to reveal the mechanism of its formation, determine the influence and share of each factor of its growth or decline.
In order to increase the amount of profit and improve its distribution and use, the following can be proposed:
· it is necessary to create a set of measures to improve the qualifications of the enterprise’s personnel, by creating a training plan for employees both at the enterprise and with the involvement of third-party organizations (training centers, etc.);
· due to the specifics of production (production of industrial valves and parts for petroleum engineering and equipment, wholesale trade), it is possible to attract investments in the development and production of new types of products;
· to improve the financial condition (earning profit and increasing profitability), you can increase the rental of existing empty space to other organizations and firms;
· creating an attractive investment climate (it is necessary to attract the interest of additional investors);
· improve the quality of work performed, which will lead to competitiveness and interest in the choice of this enterprise by customers of work; calculate production leverage, since it can be used to control the increase in the enterprise’s profit, obtained due to an increase in production volumes due to an increase in variable costs.
· calculate financial leverage. It can be used to manage the profitability of an enterprise.
Based on the work performed, we can say that the goal of the course work has been achieved.
Bibliography.
1.
Kuksov A. Planning of enterprise activities // Economist. - 2002. - No. 6. - P. 61-67.
2.
Babich A.M. Finance: Textbook / A.M. Babich, L.N. Pavlova. - M.: ID FBK-PRESS, 2000. - P. 232 – 235
3.
Ryndin A.G., Shamaev G.A. Organization of financial management at the enterprise. - M.: Russian business literature, 2003. - P. 57 - 62.
4.
Financial management: Textbook / Ed. E.I. Shokhina. - M.: ID FBK-PRESS, 2002. - P. 115-118.
5.
V.A. Kodatsky. Costs and profits // Economist. — 2005.-№7. – pp. 23-25.
6.
Borodina E.I. Enterprise finance / E.I. Borodina, Yu.S. Golikova, N.V. Kolchina. - M.: Banks and exchanges, 2002. - P. 45-48.
7.
Stoyanova E. S. Financial management: Russian practice. - M.: Perspective, 2004. - P. 53-58.
8.
I.Glazunov, V.N. Financial analysis in enterprise income management / Glazunov, V.N. // Finance. - 2006. - No. 3. - P. 54-57.
9.
Ilyin, A.V. A new look at profit and tax / Ilyin, A.V. // IVF. — 2007.-№12.-S. 73-82.
10.
Kodatsky, V.P. Profit / Kodatsky, V.P. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2007. - P. 60-100.
11.
Nikitin, S.E. Profit: theoretical and practical approaches / Nikitin, S.E., Glazova, E.G. // MEMO. - 2007. - No. 5. - P.20-26.
12.
Novodvorsky, V.D. Enterprise profit: accounting and economic / Novodvorsky, V.D., Klestova, N.V., Shpak, A.V. // Finance. — 2006.-№4.-S. 64-69.
13.
Pavlova, L.P. Enterprise finance: Textbook for universities. - M.: Finance, UNITY, 2006. - 416 p.
14.
Balabanova I.T. Financial management: textbook. / I.T. Balabanov. M.: Finance and Statistics, 2005. - 224 p.
15.
F.G. Shamkhalov. Profit is the main indicator of a company’s performance // Finance. - 2006.- No. 6. – pp. 18-23.
The procedure for distributing profits at enterprises of various forms of ownership
As already mentioned, the distribution of profits is based on certain principles. Distribution itself includes its use in accordance with the requirements of the legislator, the goals and objectives set by the enterprise, taking into account the interests of the owners.
Distribution of profits in LLC
The procedure for distributing profits in a limited liability company is subject to taxation and is distributed in the manner prescribed for legal entities. persons In addition, the entire procedure is regulated by current legislation.
Let us immediately make a reservation that only that part of the profit that remains after all taxes have been paid and other obligations have been fulfilled (to creditors, etc.) is subject to distribution.
The distribution of net profit occurs after the accounting is compiled. reporting for a specific period of time. The decision on distribution is made through voting. If the company's participants have not made a unanimous decision, the meeting is postponed to the next date.
The constituent documents do not always reflect information about when and where payments can be sent.
The distribution of profits between the company's participants also takes into account the financial statements.
Important information: there are times when profits are not subject to distribution.
As an example, here are a few of them:
- When the amounts of the authorized capital are not paid in full;
- The company is bankrupt or has all the signs of bankruptcy.
Other cases are given in the legislation.
What part of the profit will be distributed is decided by the meeting of founders. The decision that was made is documented in the form of a protocol.
Typically, profits are distributed in proportion to the shares that participants contributed to the authorized capital. But there may also be a disproportionate distribution of profits in the LLC.
The law does not prohibit such distribution if this procedure is fixed in the Charter.
Peculiarities of the procedure in a company with one founder
This procedure has its own characteristics. It is worth saying that if a company has only one founder, he makes all decisions himself.
In this case, there is no need to hold a meeting; a written execution of the said decision, certified by the signature of the founder, is sufficient.
A sample is shown below.
Distribution of profits in a joint stock company
The distribution of profits in a joint-stock company has the most complex mechanism. Usually it is spelled out in the Charter in some detail.
A distinctive feature is the need to form a reserve, the size of which is at least 10% of the total capital. In addition, some share of profits should be used to increase the capital.
The distribution of profits among shareholders of the company also has its own nuances. Dividends on preferred shares are paid at specific rates, while on ordinary ones they are based on the decision of management, which is approved or not by the meeting of shareholders.
When planning a distribution, you need to take into account what types of shares are issued. The future development of joint stock companies largely depends on the correct distribution of profits.
If dividends are unreasonably high, this will hinder the company's development. But if they are not paid at all, this is also fraught with negative consequences for the business, since the interests of shareholders will be infringed.
Distribution of profits in a production cooperative
A production cooperative is a commercial organization in which people are united by membership, created to carry out economic or production activities jointly.
Only that part of the profit that remains after making all payments is also distributed. If members of the cooperative made a labor contribution to its activities, then the process of profit distribution will proceed in accordance with this contribution and share contributions, and if there was no labor participation, then in accordance with the contribution. The statutory documents contain all the information about the distribution procedure in this case.
Production cooperatives, as a form of doing business, are rare in Russia. This is explained by the fact that in this case, more contributions made by labor are combined, rather than cash. And the presence of liability, which is subsidiary, does not add to the popularity of this form.
Distribution of profits in a limited partnership
In a limited partnership, before distributing profits, taxes are paid, the necessary contributions to the budget are made, and only then income is paid to investors. These investors do not take any part in the daily activities of the partnership and are not responsible for the results obtained. They are only making their contributions.
Profits are divided among the partners of the partnership in accordance with the shares they contributed to the capital. And the remaining part is distributed among full comrades.
If there is no profit at all, or it is much less than planned, the following scenarios are possible:
- The members of the partnership give their share to the investors through the sale of property that belongs to the partnership;
- A decision is made not to pay shareholders their share of the profits.
Procedure for distribution of profit of a unitary enterprise (unitary enterprise)
The UE itself is characterized by the fact that it does not have ownership rights to the property that is assigned to it. The UE can dispose of property only if the owner agrees, that is, the Russian Federation itself.
Based on the developed documentation, the profit that was received by the unitary enterprise from work or services, or sold products will be directed to production, to social services. service according to standards. All standards are developed by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The remainder of the profit will be withdrawn in favor of the federal budget.
Formation of net profit of enterprises of the following forms: LLC, partnerships
What is noteworthy is that in a general partnership, profits are distributed among all participants; this process is regulated by the contents of the constituent agreement, which stipulates the size of each person’s specific share. Actually, the procedure itself depends on the factor for which the specific partnership is created. However, if a partnership is created and held according to documents for an indefinite or long period, various funds can be formed without any problems from their distributed profits.
If the notice is about a limited partnership, profits are distributed taking into account the contribution of funds for taxes and fees provided for legal entities. Only after this should funds be allocated for income for investors, as well as for the direct development of the enterprise.
In relation to LLCs, it is necessary to highlight the distribution of profits according to the principles in the general order, which is established for legal entities.
For example, net profit can be allocated to a reserve fund, which is recommended to be formed in a timely manner for the further fulfillment of obligations to the founders. At the same time, various joint-stock companies have a complex distribution mechanism, dividends in which are fixed in advance in the drafted charter. The charter is one of the defining regulatory documents for the distribution of profits. The remaining aspects are highlighted individually, according to the organizational form of the enterprise, the presence and composition of constituent documents, and operating principles.
Distribution of profits by property
Quite often questions arise as to whether it is possible to pay profits with property. Typically, these situations arise among LLC participants. The law does not limit the form of profit distribution in any way. This means that it is permissible to distribute profits in non-monetary form. This is confirmed by the presence of judicial practice on this issue.
The charter can stipulate the type of property with which profit is planned to be paid. It is clear that such a decision must be supported by the meeting of shareholders. If the general meeting does not make such a decision, then the distribution is made only in money.
Legal experts recommend making and documenting the decision of the shareholders’ meeting for each type of property, if it is planned to distribute profits using the property, so as not to have legal problems later.
Formulas for calculating enterprise profit
Due to the numerous formulas used in practice to calculate certain types of profit, we propose to give the corresponding empirical data a tabular form, solely for the sake of ease of perception...
Table 1. Formulas for calculating enterprise profit
| NAME | FORMULA |
| Formula for calculating net profit | Pchist. = Pop. - Nprib. |
| Formula for calculating revenue | B = Sed. * Kprod. |
| Formula for calculating marginal profit | Pmarj. = B - Let's stop. |
| Formula for calculating gross profit | Pvalov. = B – Prod. |
| Formula for calculating profit from sales | Prereal. = B – Full. |
| Formula for calculating balance sheet profit | Balance. = Psales – Rprot. + Other |
| Formula for calculating operating profit | Poper. = Pbalance. + PRvyp. |
The table below uses the following notation:
- Pchist. – net profit;
- Total – total profit;
- Nprib. – corporate income tax;
- Other income – other income;
- Rproc. – other expenses;
- B – revenue;
- Seed – cost per unit of production;
- Kprozh. – number of units of production;
- Pmargin – marginal profit;
- Variable – variable costs of the enterprise;
- Pvalov – gross profit;
- Production – cost of production;
- Sales – sales profit;
- Full – full cost;
- Balance – balance sheet profit;
- Psales – profit from sales;
- Operating – operating profit;
- PRpayment – interest payable.
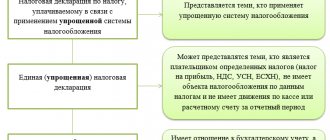
How is profit distributed under the simplified tax system?
Profit under the simplified tax system is most often distributed in order to pay dividends. Taxpayers under the simplified tax system are most often LLCs, this is already an established fact.
Let us remind you that you can distribute profits under the simplified tax system once a year, or every quarter. This requires only a decision of the meeting of shareholders or a single participant.
There are also joint-stock companies working on the simplified tax system. In this case, payments are made based on the results of the quarter, 6 months and year.
Net profit under the simplified tax system is calculated based on accounting data. accounting. This will not be difficult if all the information is reflected on time and reliably.
The amount of net profit here is the difference between the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet. At the same time, future income is not included in liabilities, but accounts payable are included in them.
If the balance sheet is not compiled, it is impossible to determine net profit and, accordingly, to pay dividends.
Operating profit of the enterprise
The operating profit of an enterprise or profit from sales of products is the difference between gross profit and the balance of operating income and expenses.
Operating expenses are the current costs of selling products and are not included in the cost of goods manufactured.
These include expenses:
- for advertising;
- storage of goods;
- transportation;
- salaries of supply and sales workers;
- salary of the administrative and managerial staff;
- payment for rent of production or warehouse premises;
- other non-production expenses.
Operating income is:
- rental income;
- interest and income on securities;
- rent payments;
- similar types of income.
At this stage, non-production costs are analyzed in comparison with previous periods.
Profit from the sale of goods and services is also operating profit for trade, transport and communications enterprises, and construction organizations.
It is calculated differently in each case:
- for trade and supply enterprises this is the difference between sales revenue and distribution costs;
- for transport and communications enterprises, revenue from services provided is reduced by the amount of operating costs;
- construction and installation organizations take into account the actual cost of completed and accepted work as profit.
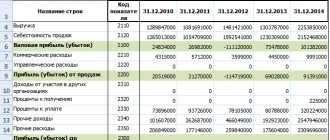
The subject of financial statements and the main financial indicator is balance sheet profit.
How is profit calculated?
The mechanism for the formation and distribution of enterprise profits is stipulated by law. This is necessary to standardize the display of the company's financial results. Their activities become more transparent, easier for third-party users to understand and evaluate. Income is the sum of all funds received by the company during the reporting period in the course of its activities. It has a certain structure.
The best way to understand the principle of calculating net profit is through financial statements. The enterprise prepares a report on financial results, which is also called Form No. 2. The formation and distribution of the enterprise’s profit begins with the preparation of this document.
According to this technique, several intermediate income values are first determined. First, the total amount of revenue from product sales is calculated. To do this, take into account the transaction data reflected in the accounting accounts at the end of the reporting period. The cost of production is subtracted from the result obtained. For the calculation, they take the revenue, from which the amount of excise taxes and VAT has already been subtracted. The resulting result is called gross profit or loss.
Commercial expenses, as well as management costs, are subtracted from the result obtained. The result obtained is called profit (loss) from sales.
During the calculations, several more steps are required. Income from sales is added to income received from participation in other companies. It can also be interest receivable and other income. Then the interest paid by the company and other expenses are taken away. The result is called profit before taxes. The amount of the corresponding payments is subtracted from it.
After carrying out the above manipulations, the net profit of the enterprise is obtained. This is the final result of the company's activities in the reporting period. After its formation and calculation, the distribution procedure occurs. But this is only possible if the company made a profit and not a loss.