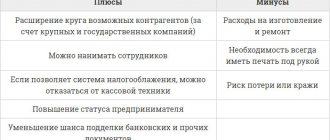
Introduction
When a businessman opens an LLC, he does not have to work in the place of opening. Without any problems, he can open a branch in another region, create a representative office or a new division thousands of kilometers from the place of registration. At the same time, the new branch is registered with the tax office exactly where it plans to conduct its activities, and, accordingly, pays taxes there.
Individual entrepreneurs can operate under different taxation schemes
When a businessman registers as a private (individual) entrepreneur, he is registered at the place of his registration. If he hires employees, he registers them again at the place of registration, drawing up the necessary applications to the Pension and Insurance Funds. Accordingly, all payments are made at the place of residence of the individual entrepreneur and his employees.
Attention:
According to the law, individual entrepreneurs cannot open representative offices and branches; this is the prerogative of the LLC. It is also impossible to sell an individual entrepreneur or appoint a manager.
Simplified
Activities that are planned as part of business expansion to a neighboring subject of the Russian Federation may be taxed under the simplified tax system if the individual entrepreneur is already a payer of the simplified tax system. In such a situation, it turns out that all your activities are subject to the simplified tax system.
There is no need to register again in another subject of the Russian Federation; the individual entrepreneur must register at his place of residence. There is only one KUDIR for the simplified tax system, one declaration is submitted - the reporting takes into account indicators regardless of the activity in which region they relate to. Tax payment is carried out in the same way as OSNO.
As for tax rates, it is important to take into account one feature. In a neighboring region, a reduced tax rate may be introduced for the simplified tax system, but since the businessman is registered with the tax office of his constituent entity of the Russian Federation, he pays the simplified tax system at the rate that is valid in his “home” region. The effect of the reduced rate of another region on individual entrepreneurs in this situation does not apply.
Do not forget that according to Art. 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if an entrepreneur buys non-residential property in another region, he will still have to register in this region - the basis for this action is the location of the specified property.
Attachment to the tax system
As we found out, an individual entrepreneur does not have the right to open representative offices or branches (which does not prevent him from opening stores or retail outlets in other places). The law does not prevent an individual entrepreneur from conducting business in any region of Russia if he has registered with the tax office at his place of residence. That is, in essence, the entrepreneur’s certificate is uniform and is valid throughout Russia: you can register in Novosibirsk and conduct business in Voronezh. But in some cases you will need to register with the tax office where you do business. It all depends on what system the individual entrepreneur uses to conduct its activities. There are currently 6 systems:
- General system.
- Simplified with a 6% income system (the rate can be reduced in the regions).
- Simplified with a system of income minus expenses of 15% (the rate can be reduced in the regions).
- Unified agricultural tax (used for agricultural producers).
- A single tax on imputed income.
- Patent system.
The entrepreneur selects a system during registration (or switches to a new one in the future). It all depends on what exactly the businessman will do, what turnover his company will have, how many employees it is planned to attract, etc. As a rule, all micro-businesses operate on a simplified system, which facilitates the reporting process and reduces the tax burden.
Attention:
If you don’t specify the taxation system during registration, then by default the tax authorities put everyone on a common system, which is not optimal. Think about which scheme is more convenient for you to work with and submit an application when registering.
Let's consider how an individual entrepreneur operates in another region, working under different taxation systems. Rules vary from system to system, so you need to understand how to conduct your business without breaking the law.
When working under PSN, patents must be issued in different regions
Can an individual entrepreneur work in another city and in another region?
Yes maybe. An individual entrepreneur can be registered at his place of residence, and can conduct activities in another city or even in another region of our huge country. The scope for the activities of an individual entrepreneur is not limited by the place of registration. Does an individual entrepreneur need to register with the tax office of another region? There are good official explanations on this issue using the following example: an individual entrepreneur is registered in Moscow, but wants to trade in the Kaluga region - is registration required with the tax office of the Kaluga region? The Tax Service explains that an individual entrepreneur is registered with the tax office at his place of residence and this registration does not depend on the place of actual activity. Therefore, if an individual entrepreneur is already registered in Moscow, then there is no need to re-register the individual entrepreneur in Kaluga. BUT there are features related to taxation. Previously, if an individual entrepreneur found himself on the territory of a subject in which UTII was operating, then he was obliged to register at the place of activity and pay the UTII introduced in this region. Since 2013, UTII has become voluntary. However, the need for accounting has not changed. In other words: if an individual entrepreneur conducts activities subject to UTII, then he will need to register at the place of business . According to Art. 335 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , you will need to register as a payer of the mineral extraction tax at the location of the subsoil plot provided to the taxpayer. If an individual entrepreneur plans to apply a patent taxation system (PTS) , then at the place of business he will also need to obtain a patent. Taxes under the simplified taxation system (simplified taxation system) or OSNO (general taxation system) will be paid at the place of registration of the individual entrepreneur; in this case, there is no need to register with the tax office of another region. And lastly: if an individual entrepreneur not only plans to conduct activities in another region, but also changes his place of residence (moves from one region to another), then registration at the new place of residence will be required. Living without registration entails a fine (Article 19.15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offences). But you do not need to notify the tax office about a change of address. In this case, the tax office itself will transfer the registration file of the individual entrepreneur to another tax office after it receives information about the change of residence from the migration service. You can read more about this innovation here.
Reason: Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offences, Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law dated 08.08.2001 No. 129-FZ “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs”, Letter of the Ministry of Taxes and Taxes of the Russian Federation dated 30.07.2004 N 09-1-02/3110 “ On registration of individual entrepreneurs."
Author:
Tatyana Reshetilova
Added:
15.04.2016
Updated:
08.04.2019
Patent system
First of all, we will analyze the simplified system with a patent. This scheme is regulated by the Tax Code, in particular Article 26.5. The entrepreneur registers with the tax authority and receives a patent. Then he moves to another region. What should he do? A patent implies a link to a specific region (where it was issued). This is regulated by Article 364 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Accordingly, if an entrepreneur has already received a patent and then decides to move, then he needs to go through the entire procedure again, submitting an application to the tax office so that he is first registered in a new location, and then submitting an application for re-registration of the patent.
Let's look at an example. An individual entrepreneur opens a store selling alcohol in Novosibirsk. This activity requires obtaining a patent. He receives a patent at the place of registration of the retail outlet. Then he decides to expand his network and opens a second store in Voronezh. In Voronezh, a second patent is required, which is registered with the local tax authorities. In this case, taxes are paid precisely at the place of registration of the entrepreneur (in our case, this is Novosibirsk). In Voronezh, he pays exclusively for the cost of the patent.
If stores are located in three or more regions, then payments for them are made to the regions (specifically for patents). Accordingly, the income declaration is submitted at the place of registration of the individual entrepreneur, and not at the place of validity of the patents. PSN involves maintaining a book of income and expenses. More precisely, there are two news at once: on simplification and on the patent system. According to the patent, only income received is entered, and in the book according to the simplified tax system both income and expenses are entered.
Taxation regime and activities
The procedure for paying taxes depends on the chosen taxation system. Operating hours differ by region of the Federation.
The legislation provides for the following tax regimes:
- OSN.
- simplified tax system (6% of total profit).
- simplified tax system (15% of profit). However, here the tax base is income minus costs.
On video: Activities of individual entrepreneurs in another city
For some types of activities the following regimes apply:
- Unified Agricultural Sciences.
- PSN.
- UTII.
The individual entrepreneur chooses the optimal mode before registering as an individual. A tax preference form is submitted along with the registration application.
On video: Leonid Furer - How to work in different regions?
Features of tax regimes:
| № | Tax regime | Registration | Filing a declaration | Payment of obligations |
| 1. | OSN | At the place of residence of the businessman (Article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). | 3-NDFL is submitted exclusively at the place of opening of the company. Expenses and income for all activities, including work in the neighboring region of Russia, are summed up. KUDIR is conducted alone. | The profit tax is transferred according to the details of the regulatory authority from the place of residence of the individual. |
| 2. | Agricultural producers + Unified agricultural tax | No re-registration is required (Article 26.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). | The declaration is submitted to the Federal Tax Service where the business is opened. KUDIR is filled in total for all expenses and income. | The Unified Agricultural Tax is credited to the account of the controlling authority at the citizen’s place of residence. |
| 3. | simplified tax system | There is no need to submit documents to register an individual entrepreneur in another region. An exception is the acquisition of property in another city (Article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). | A book of expenses and income is kept for general expenses and income. Form 3-NDFL is filled out for all transactions once a year. | Taxes are transferred according to the details of the registering authority. The amount of the rate is taken according to the place where the case was opened (Article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The reduced duty for the region of business does not apply to businessmen (Article 346.20 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Additionally, pension contributions are paid. |
| 4. | UTII + simplified tax system | The UTII-2 application must be submitted to the registration authority of the neighboring region. No more than five days should pass from the start of work in the new city (Article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). | Reporting must be provided to the inspectorate that registered the UTII payer. | Obligations are listed at the place of reporting, i.e. where another business is conducted by the individual. faces. |
| 5. | STS + UTII (transport transportation, distribution and delivery sales of goods, placement of advertising signs on cars) | It is necessary to re-register documentation in your region as a UTII payer for special types of activities. The requirement is explained by the fact that there is an indefinite place of work. The rule allows you to reduce the tax burden (Article 346.28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). | The declaration is submitted at the place of registration of the entrepreneur. | The fee is credited to the account of your tax office. |
| 6. | According to patent | It is purchased in a region where this taxation system has been introduced, regardless of the residence of the businessman. It is enough to submit a corresponding application to the Federal Tax Service of the selected region (Article 26.5, Article 346.45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). | There is no declaration. KUDIR is conducted alone. | The tax is paid to the bank account of the organization that issued permission to use the special regime. |
| 7. | USN + PSN | In another region, an application for registration and a special permit is submitted (Article 346.25.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The document is purchased separately for each type of occupation (the number is unlimited). | The simplified taxation system declaration is submitted at the place of residence. There are 2 books of accounting for expenses and income. The PSN journal reflects only profit. | The tax according to the simplified tax system is transferred to the inspectorate at the place of registration of the individual entrepreneur. The cost of a patent is paid to the organization that issued it. |
On video: HOW MANY BUSINESSES CAN BE DEVELOPED AT THE SAME TIME
Classic simplified
Next, we will consider the option of doing business according to a simplified scheme. He applies to the tax office at his place of residence and receives the appropriate certificate. If the 6% income or 15% income minus expense schemes are used, then nothing is needed other than individual entrepreneur registration. He can work throughout the Russian Federation, without submitting documents for registration in a new region.
Attention:
If an individual entrepreneur buys non-residential premises to conduct business, then he is registered in the locality where it is located. Therefore, it is easier to act through renting premises.
A businessman pays taxes exactly where he is registered, even if he operates thousands of kilometers from this place. Expenses and income are indicated in the declaration in general, that is, from all sources received, and not just those that the individual entrepreneur received at his place of registration. And there is an important nuance here. In the regions, reducing coefficients may apply, that is, not 6%, but, for example, 3%. But at the same time, for a private owner, taxes will be calculated at the rate that applies at the place of his registration, even if he does not work in this place.
Once a year, after the reporting period, the entrepreneur submits a declaration at the place of registration and pays the necessary amounts to the budget. For accounting purposes, he is required to keep a book of expenses and income, which is valid for everyone working on a simplified basis. An individual entrepreneur must have one book for all outlets. It contains data from each region and for each type of activity, according to the dates of receipt of profits and expenses.
Choose a tax scheme upon registration
What are the requirements for an individual entrepreneur?
It should be noted that this must be legal. Timely registration and payment of the required fees eliminates the possibility of fines and penalties.
Patent tax system for individual entrepreneurs - what is it and how does it work
There are no special requirements for entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system, OSNO and unified agricultural tax. Their main responsibility is to timely contribute the necessary funds to the budget of their locality.
UTII payers are required to contact the Federal Tax Service department. UTII in this department will accept transfers of material assets. In the case where such individual entrepreneurs are registered with the simplified tax system at their place of residence, tax payment data are made at the regional branch of the Federal Tax Service. In this city, the company undertakes a zero declaration.
Conditions for doing business exist for PSN payers. Applications required:
- about registration;
- to obtain a patent.
Important! A patent is valid only in the territory in which it is issued.
Imputed income
An individual entrepreneur working for UTII works according to a simplified system and is registered at his place of residence. If he plans to move, then he needs to go to the tax office and re-register in a new place as a payer of imputed income. He is given five days to do this - working without re-registration is considered a violation of the law with all the ensuing nuances. Re-registration does not take much time: you need to contact the territorial tax office at your new place of residence and submit the appropriate application.
If you conduct distribution (distribution) activities, then you need to register imputed income at your place of residence, even if you work in other regions. Moreover, if you are registered as an individual entrepreneur at your place of residence, you still need to come to the tax office and register as a payer of a single imputed income. Since 2013, the Tax Code has prescribed imputed income as optional, meaning you are not required to pay it. A simplified scheme applies by default, which simplifies accounting and reduces the burden on businessmen.
At the same time, imputed income is paid exactly where the private entrepreneur is registered as a UTII payer. If in one place the work is carried out according to imputation, and in the second according to the classic simplified tax system, then imputation is paid where the individual entrepreneur is registered as a UTII payer, and the rest of the income is paid where he is registered. Accordingly, income and expenses are recorded separately, and for this you will need different books. Declarations are also submitted separately, one for simplified income, the other for imputed income. The second one is surrendered exactly where the private entrepreneur is registered as a payer of imputed income, but if there was a peddling or delivery sale of products or services, then the declaration is submitted precisely at the place of registration.
Important:
When traveling on the road, you do not need to register at each new location. It is enough for an entrepreneur to pay the imputed tax at the place of his registration. But this rule does not apply to stand-alone stores and retail outlets.
Remember that the main declaration when working under a simplified taxation scheme is submitted precisely at the place of registration of the entrepreneur. If a businessman works on imputed income in another region (and is registered there as a payer), without carrying out any further activities under the simplified scheme, he is required to submit two declarations. One is submitted at the place of business under UTII, and the second, zero, at the place of registration of the simplified tax system.
Don't get confused about where you pay taxes, otherwise you may get fined
How it works? Procedure for paying taxes and contributions
The expansion of a business beyond the boundaries of one constituent entity of the Russian Federation is accompanied by a complete restructuring of the financial system. Opening an individual entrepreneur in another region in 2020 will require division of accounting. A clear distinction between cash flows and the movement of material assets reduces the risk of theft, negligence, and other abuses. The nature of the changes will depend on the tax regime.
- USN and OSN. The procedure for paying taxes and insurance premiums does not change. The rule has been extended to employers. Fees for hired personnel and personal income tax withheld from labor payments are transferred to the place of registration (clause 7 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Entrepreneurs can work anywhere in the country. Single tax payers keep only one accounting book, reflecting income in all areas. Reporting, including documents on employees, is submitted according to registration. The corresponding requirement is enshrined in Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- UTII. Payers transfer insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds at the place of registration. The tax is paid according to the rules of the entity in which the retail outlet or commercial facility is located. Personal income tax will have to be withheld from remuneration under employment contracts. In letter No. 03-04-05/3-47, the leadership of the Russian Ministry of Finance ordered that funds be transferred to the address of the actual location of the business. Reporting is submitted to all inspections that carried out registration.
- PSN. Calculations are made for each patent separately. Payments are made according to the details of the inspection that issued the document, that is, at the place of business. Entrepreneurs do not submit declarations. Insurance fees must be paid according to registration. Patent holders pay personal income tax for employees at the place of business. The corresponding rule is enshrined in paragraph 7 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, entrepreneurs can work, for example, in Moscow with registration in another region. At the same time, business representatives will have to take into account regional laws, the features of the chosen tax system, and think through the mechanism for accounting and reporting.
Operating hours required by law
An individual entrepreneur can carry out activities in any subject of the Federation, having registered only once at the place of residence. Depending on the area in which the individual entrepreneur plans to work, he must select one of the following administration modes:
- STS – simplified taxation system, including 15% of gross profit and 6% of gross income;
- PSN – patent system;
- UTII is a single tax levied on imputed income within certain types of activities;
- Unified Agricultural Tax is a tax system applied to individual entrepreneurs “by default” if, at the time of registration, he does not notify the tax authority of his desire to use a special regime;
- OSNO is the main taxation system, used when it is impossible to assign a special regime to the applicant.
Before starting work, an individual entrepreneur must clarify the possibility of using special tax regimes for certain types of activities within the framework of local legislation. Otherwise, the individual entrepreneur risks becoming the object of administrative prosecution.
OSNO and simplified tax system
Everything is simple here, because when working on a general or simplified system, entrepreneurs must be registered at the place of registration, submit reports there and pay taxes.
And it doesn’t matter where the business is actually conducted: in your own city or on the other side of Russia. Since 2011, businessmen have less running around: if an individual entrepreneur changes his registration address, there is no need to go to the authorities and notify the tax authorities about this. This will be done by the FMS within 10 days, when the businessman submits his passport there for registration.
The tax office, in turn, will make changes to the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs within 5 days, deregister the entrepreneur with the old Federal Tax Service and register with the new one, and also notify the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund and Rosstat about the changes, so there is no need to go there either. The entrepreneur will receive a notification by mail about registration with the new inspectorate. If an individual entrepreneur has changed his registration address within the same city or locality, then the Federal Tax Service will remain the same.
Temporary registration, if the main one is maintained, does not oblige the entrepreneur to change the Federal Tax Service. But if there is no other registration besides a temporary one, then you need to register where the temporary one was registered.