It is mandatory to pay to the treasury, but not all entrepreneurs do this and are increasingly trying to reduce taxes in various ways (individual entrepreneurs, LLCs). This is dangerous: frauds are discovered, and their participants receive large fines, are brought to administrative and even criminal liability. Sometimes accountants, whom entrepreneurs for some reason tend to trust unconditionally, push their clients onto a slippery slope.
In this article, we examined dangerous tax optimization methods that an accountant can offer. If you are recommended to use them, this is a reason to think about the competence of the specialist.
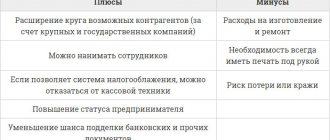
Fragmentation of a business for the purpose of applying a special regime
In this case, it is proposed to divide the business into several organizations. One company operates on the basic tax system, the second can be registered as an individual entrepreneur using a simplified system. By transferring settlements to an individual entrepreneur, the company will pay less to the budget, since the rates are lower.
According to documents, the organizations operate as two separate companies and pay a small tax. However, in reality they are one company and must pay tax according to the common system. In accordance with the definition, such activity indicates the creation of a legal entity in order to reduce the amount of tax without the purpose of conducting actual business activity.
To identify such a tax evasion scheme, inspectors conduct an audit. Typically, in separate organizations, employees perform the same work, tax and accounting records are handled by the same people, and the company supplies the company with goods from one supplier. These and other signs indicate that the business was divided formally in order to obtain a tax benefit.
Individual entrepreneur and self-employment: how to combine to avoid tax claims
Let's look at these rules in more detail. So, if you want to combine individual entrepreneurs with self-employment, then you will have to comply with a number of conditions.
Refuse other special modes
An individual has the right to be an individual entrepreneur and self-employed at the same time, but he cannot combine the professional income tax (PIT) with other special tax regimes - simplified tax system, UTII and unified agricultural tax. That is, you cannot use two tax regimes at the same time.
You need to have time to refuse special regimes within a month from the day the individual entrepreneur registered as self-employed (Part 4 of Article 15 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ). Otherwise, the registration will not be counted. To do this, it is important to send to the tax office, with which the entrepreneur is registered, a notice of refusal of the simplified tax system, UTII or Unified Agricultural Tax in the standard form, which is given in the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 2, 2012 N ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] This can be done in person, by mail, through the personal account of an individual entrepreneur.
To confirm that the notification has been sent to the tax office, you can make a copy or photograph the application with a note of acceptance.
If an individual entrepreneur applies a special regime for some type of activity that is not subject to professional income tax, he must pay personal income tax on income from this activity. In this case, self-employment for all income, including income from personal property, terminates automatically.
Please note that if an individual entrepreneur uses a patent taxation system, he will be able to register as a tax payer only after the patent expires or after he notifies the tax authority of the termination of such activities.
Monitor your income
They should not exceed the limit of 2.4 million rubles. in year. This is exactly the limit specified in Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018 for tax on professional income. If you go beyond this limit, the tax office will certainly notify you of the termination of your self-employed status.
Therefore, “it is important to monitor the level of your income and, if it exceeds it, promptly switch to other taxation regimes in order to avoid paying personal income tax of 13% and VAT of 20%,” notes lawyer and general director of SaaS Project Izabella Atlaskirova. “If a self-employed person is late in switching to the new tax regime, he will have to pay taxes under the general tax regime until the end of the year.”
To avoid this situation, you can again choose a special regime by submitting a notification to the tax office at your place of residence using a standard form within 20 days after termination of registration as a self-employed person (Part 6, Article 15 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Online accounting for new business
Details
Do not count on a decrease in income for expenses
In the “Questions to an Expert” section of Kontur.Magazine, the following questions periodically appear: how can a self-employed person deduct expenses necessary for the manufacture of products?
But if a self-employed person is engaged in the manufacture of products, then the costs of creating them do not reduce the income received from the sale of these products. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 8 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018, when citizens apply the NDP, expenses associated with conducting activities are not taken into account. Income is considered the entire amount of proceeds from sales, regardless of the amount of business development expenses and net profit. Self-employed people pay tax on this income - in the amount of 4% or 6% of revenue, depending on whether they work with individuals or legal entities.
Thus, the NAP differs from the special regime of the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses”.
The simplified tax system with the object “income” may be more profitable than self-employment
“Individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system and self-employed people cooperating with legal entities pay the same tax - 6% of income, but at the same time, for individual entrepreneurs, the tax is reduced by the amount of insurance premiums, and self-employed people pay insurance premiums in full,” notes the lawyer and general director “SAAS project” Isabella Atlaskirova.
“Accordingly, an individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system, cooperating with legal entities and other individual entrepreneurs, finds himself in a more advantageous position than a self-employed person.” In addition to the opportunity to reduce tax under the simplified tax system, you can also save your pension using insurance contributions. In addition, the simplified tax system, unlike the NAP, allows you to earn more than 2.4 million rubles. per year and still maintain the same tax rate.
Keep separate records of income and expenses
If an individual entrepreneur, in addition to entrepreneurial activities, carries out other activities as an employee, he will have to keep separate records of income and expenses.
When receiving income from ordinary individuals, a self-employed person applies a tax rate of 4% on income. In case of receiving income from individual entrepreneurs or legal entities, but deducts 6% of the income.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that when carrying out business activities as an individual entrepreneur, it is better if all cash receipts go through the individual entrepreneur’s current account. Although the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated June 20, 2018 No. ED-3-2/ [email protected] states that an individual entrepreneur has the right to use a personal bank card issued to him as an individual to receive funds from customers, unless the bank account agreement directly prohibits the use personal account in commercial activities. Accordingly, these incomes are taken into account for tax accounting purposes if they are produced for the purposes of entrepreneurial activity.
For self-employed individuals providing personal services, an individual’s personal account opened with a bank is used. At the same time, self-employed people can accept payments via payment systems or electronic wallets. To do this, an agreement is concluded with the payment system. Self-employed people do not need an online cash register.
Expect some privileges
In particular, when switching to self-employment, you can maintain your current account and individual entrepreneur status. But he won't be able to hire employees or resell goods that someone else made. But if he wants to do this, then he will have to switch back to the simplified tax system or another tax regime.
According to Art. 2 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ, individual entrepreneurs applying NAP:
- are not recognized as VAT taxpayers, with the exception of VAT payable when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation and other territories under its jurisdiction (including tax amounts payable upon completion of the customs procedure of the free customs zone on the territory of the SEZ in the Kaliningrad region);
- are not exempt from performing the duties of a tax agent;
- are not recognized as payers of insurance premiums for the period of application of the NAP of individual entrepreneurs specified in subparagraph. 2 p. 1 art. 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When is it more profitable to completely close an individual entrepreneur?
If an entrepreneur, having become self-employed, accepts payments only from individuals, he does not need a current account for entrepreneurs, as well as the individual entrepreneur status itself. In this case, he can submit a tax application to close the individual entrepreneur.
A hired employee works under an employment contract, he is also an individual entrepreneur. Can he also be self-employed?
“There are no obstacles to registering as self-employed for persons working under employment contracts and at the same time being individual entrepreneurs,” assures Isabella Atlaskirova (SaaS project). – It is important that activities as a self-employed person do not overlap with activities as an individual entrepreneur and are not carried out in the interests of the organization in which he works under an employment contract.
For example, you can simultaneously work as a manager in an organization, be the owner of a store as an individual entrepreneur, and provide accounting services as a self-employed person.
Individual entrepreneurs that do not use the labor of hired workers, are not engaged in activities prohibited for self-employed workers, and apply special tax regimes (STS, UTII or Unified Agricultural Tax), have the right to switch to paying NAP.”
Fictitious transactions through shell companies
To optimize taxes in this way, the company hires a fictitious contractor and issues false documents for the purchase of goods or provision of services. So she is trying to increase expenses, reduce the amount of income tax and get a VAT deduction or cash out the money.
As a result, the incoming documents indicate an invoice with a separate VAT, act or invoice, according to which the accountant registers the receipt of goods, accounting for incoming services or work performed. If an organization pays VAT, VAT for deduction is also registered. In response to the documents received, money was transferred to the shell company, it cashed it out, retained its reward and returned the money to the company.
Application of preferential tax rates without legal basis
To hide income, companies transfer funds to a company resident in a special economic zone. A SEZ is a part of the territory of Russia where there is a preferential regime for business activities: manufacturing, high-tech industries, tourism development, technology development and commercialization of their results, production of new types of products, health resort sector, port and transport infrastructure. While in this zone, resident companies can pay income tax at a rate of 0%.
Using a “gray” scheme, a SEZ resident company illegally accumulates money in the form of rent and withdraws it as dividends. The taxpayer then rents these assets from the resident and receives an expense to reduce the tax of the individual entrepreneur or LLC.
Such frauds are also detected. To do this, tax authorities apply the concept of tax residence of organizations and use international information exchange tools to determine who receives an unjustified tax benefit.
In accordance with
the perpetrators, additional taxes, penalties, and fines from 100 to 300 thousand rubles may be assessed, and violators may face forced labor with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions, arrest or imprisonment.
Transfer of bills and subsequent liquidation of the creditor
This method is also illegal. To better understand how to recognize it, let’s illustrate the diagram with an example described in the “GlavAccountant System”.
The company entered into a loan agreement with a friendly organization and received the money. Then the company's creditor assigned the right of claim and was liquidated, and the borrower organization secured the debt to the new creditor with promissory notes. The deadline for presenting bills is no earlier than January 1, 2020. The latter, after receiving the bills, also filed for liquidation. As a result, the borrower did not recognize income, since the bills are in circulation, the debt on them continues to operate with the liquidation of the creditor.
During a tax audit, the fraud was discovered and the auditors assessed additional income tax to the borrower. They took into account the amount of outstanding debt in the amount of 36 million rubles as part of non-operating income. The basis for additional charges is an unjustified tax benefit.
Tax officials said that this company tried to evade paying taxes because it transferred its own bills of exchange to pay for the debt. The judges of three instances agreed with the tax authorities and left the decision on additional income tax assessment in force (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Ural District dated June 20, 2017 No. F09-3440/2017).
provides two options for penalties for non-payment or incomplete payment of tax: paragraph 1 - a fine of 20% of the amount of unpaid tax, paragraph 3 - the same acts, but committed intentionally, a fine of 40%.
Restrictions, reporting and other formalities
Regional authorities will be given the right to narrow the circle of applicants for the zero rate - to reduce some indicators of individual entrepreneurs’ performance in order to apply the benefit.
Now the simplification is real only for entrepreneurs with an income of no more than 60 million rubles. per year (the indicator is indexed annually) and the number of employees up to one hundred people. The patent system is open to individual entrepreneurs with the same revenue limit and no more than 15 employees.
The reduction of precisely these quantitative indicators for the application of the benefit is left to regional legislators. Moreover, according to the “simplified” rules, the maximum annual income is allowed to be reduced by no more than 10 times, but according to patents, the authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are not limited in any way and can reduce the indicators as they wish.
Along with reporting under the simplified tax system or after 10 days after the patent expires, the individual entrepreneur must report on compliance with all requirements for the application of the zero tax rate. The report form is approved by the Federal Tax Service.
If any conditions established for the application of the 0% rate are violated, the entrepreneur loses the right to the benefit. And he must pay tax on a general basis for the entire tax period during which he went beyond the limits. There are no penalties, but such an individual entrepreneur is no longer entitled to take advantage of the zero rate.
Formal document flow with subcontractors
Using this illegal scheme, companies try to create fictitious documents with counterparties in order to obtain an unjustified VAT tax benefit and reduce the amount of income tax. In fact, all the work is performed by the taxpayer himself.
Tax inspectors identify formal paperwork by checking all subcontractor and company documents. The services prove that the counterparty did not perform the work because:
- he does not have property, funds, necessary transport or personnel;
- the company transferred money for work that was not stated in the counterparty’s activities.
For such a scheme, the taxpayer will be held accountable
. He will have to pay a fine of 20% of the unpaid tax amount, unpaid tax and interest.
Substitution of contracts
In this case, companies are trying to replace contracts in order to avoid paying VAT on the advance payment: for example, replacing a purchase and sale agreement with a loan, leasing, commission or sale of shares in the authorized capital.
Using a dummy commission agreement, the principal does not pay VAT and income tax until the commission agent sells the goods. To identify fraud, the tax service analyzes the primary documents and terms of the transaction. When the tax authorities discover that the company transferred the money before the sale of the goods, they will discover that the contract was executed by the commission agent, not the principal. And the company could face serious penalties.
In the case of a loan agreement, the parties do not stipulate an advance payment in the contract, which is why they pay VAT not on it, but at the time of shipment. After the goods are shipped, the borrowed funds are counted towards payment.
In order to avoid paying VAT, taxpayers register the sale of an object or product as the sale of a share in the authorized capital. The transaction is not subject to VAT.
If a company uses a fictitious leasing agreement, the payment is made in installments, but is designated as lease payments. As a result, the cost of the property is written off as income tax expense much faster.
Tax authorities identify such schemes quite quickly. To do this, they check the documents and discover that, for example, the leasing agreement was concluded for a shorter period than the depreciation period of the property, if the conditions in the document did not apply to the leasing agreement.
Substitution of contracts may result in various sanctions, which are provided for in the Tax and Criminal Codes.
The most severe punishment is a fine in the amount of 100,000 to 300,000 rubles, forced labor, arrest or imprisonment.
How to pay less taxes on PSN
The patent tax system is a relatively new phenomenon. The main features of PSN are prescribed in Chapter 26.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The opportunity to purchase PSN appeared only in 2013, but is available to a very limited number of entrepreneurs. The list of permitted activities for the transition to PSN is similar to the similar list for individual entrepreneurs on UTII. Among them are investors who make money by renting out real estate. They can purchase a patent if 3 conditions are met
- if they are property owners;
- if earnings per year are no more than 60 million rubles. in year;
- a corresponding law has been adopted in the region.
The calculation base will be the “basic” or potential annual income (PAI), taking into account the established coefficients. An entrepreneur must pay for a patent for a period of up to a month to a year and keep a book of income. But you don’t need to keep accounts, have a cash register and submit reports to the Federal Tax Service.
For PSN, no deductions are applied. The individual entrepreneur pays the cost of the patent and insurance premiums.
You can calculate the cost of a patent here
Plus PSN - simplicity. How profitable this is depends on the region, the amount of actual income and other characteristics. The higher the investor’s income compared to the “potentially possible” one, the more profitable the PSN is for him.
Example.
The entrepreneur received an annual income of 500,000 rubles.
The cost of a patent is 10,000 rubles
Insurance premiums – 32,385 rubles
The basic income for this type of activity does not exceed 300,000 rubles, so the entrepreneur is not required to pay additional insurance premiums in the amount of 1% on an amount exceeding 300,000 rubles.
Actual investor costs = patent + mandatory insurance premiums = 42,385 rubles per year.
In this example, for an investor, using the PSN is more profitable than the simplified taxation system Income - Expenses, but less profitable than the simplified taxation system Income or UTII. But it’s worth considering one more nuance. An entrepreneur does not need to submit reports on PSN. This means that the investor does not have to hire an accountant and pay him a salary. Taking these costs into account, it may be more profitable for an investor to choose a PSN.
If the individual entrepreneur from the example above was an individual without an individual entrepreneur and paid income tax of 13%, his expenses would be 13% of actual income (500,000 - 80,000 = 420,000 rubles)
For an individual, personal income tax = 420,000 rubles * 13% = 54,600 rubles
In the example considered, it is most profitable for an entrepreneur to become an individual entrepreneur and choose the simplified taxation system Income. In this case, with an annual income of 500,000 rubles, he is guaranteed to pay only mandatory insurance contributions to the budget in the amount of 34,385 rubles.
You can also consider the PSN or UTII tax systems. With UTII, the costs may be the same as with the simplified tax system Income, but they may be higher. With PSN, you will have to pay in addition to the mandatory insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs the cost of the patent, but you can save on the services of an accountant, purchase a cash register, and also make it easier to maintain documentation for individual entrepreneurs.
An entrepreneur can combine
the simplified tax system with UTII or PSN.
All special tax regimes (STS, UTII, PSN) are easy to account for and can reduce the tax burden. Individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system, PSN and UTII are exempt from paying the entrepreneur’s personal income tax and VAT, and also do not pay income tax. If an individual entrepreneur owns property, the tax on this property is also calculated at a special rate that differs from the property tax rate for individuals.
In what cases may it be beneficial to use different taxation systems for individual entrepreneurs:
- BASIC: if other types of taxation are not suitable for some criteria. OSNO can be beneficial at high costs.
- STS “Income”: if expenses are small.
- STS “Income – Expenses”: if expenses amount to more than 60% of the total income received.
- UTII: depends on the type of activity and region. The lessor can save on UTII if the rental cost is more than 5,400 rubles. / m2.
- PSN: entirely depends on the region and the cost of the patent.
Registration of employees as individual entrepreneurs
With this tax optimization scheme, employees are fired and registered as individual entrepreneurs in a simplified taxation system. The company then enters into contract or service agreements with them. Workers do the same work, but not for a salary, pay 6% of income and insurance premiums. According to the employment contract, the employer would have to pay insurance premiums, deducting 30% of salaries to extra-budgetary funds and 13% of income tax.
To identify this fraud, the tax service will interview employees and analyze documents and correspondence. As a result, it turns out that the employees had an employment relationship with the company and switched to individual entrepreneurs so that the employer could avoid paying personal income tax and insurance contributions.
For participation in such a scheme, organizations or individual entrepreneurs will be charged additional personal income tax, insurance premiums and fines in the amount of 100 to 300 thousand rubles, and may also be subject to criminal liability under articles
and , which means forced labor for up to two years with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions, arrest for a term of up to six months, or imprisonment for a term of up to two years.
Simplified taxation system (STS)
It's great for small businesses. The simplified tax system is actually always chosen by new entrepreneurs. According to the reason that you will pay one tax to the simplified tax system instead of three taxes of the general system and report once a year. Before switching to the simplified tax system, you should select an object - something from which you will pay tax: from profit - according to the tax rate from 1 to 6
% depending on the region, type of activity and amount of earnings received.
From the difference between earnings and expenses - at a tax rate of 5 to 15%
depending on the region, type of activity and amount of earnings received. Using the simplified tax system, you can reduce the amount of tax on insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs and employees using the profit received. Individual entrepreneurs without employees will be able to reduce the tax entirely on contributions for themselves, and LLCs and individual entrepreneurs with employees - only by fifty percent. And using the simplified tax system, you can sort out the reporting even without an accountant. And this is another way to optimize taxes.
Salaries “in envelopes”
With this scheme, the accountant can advise the employer to indicate a small part of the salary in the employment contract, and give the rest to the employee. As a result, the employer does not pay income tax and saves on insurance premiums.
The tax authorities will definitely suspect the company of fraud because:
- Employee salaries will be below the regional average for similarly qualified employees.
- The salary of ordinary workers will be higher than that of management.
- The specialist’s salary will be significantly lower than at the previous place of work.
- The employee submits documents where the amount differs from that indicated in the company’s reports (for example, to the embassy for a visa or to receive benefits).
To identify a violation, tax officials conduct an audit. If they find a document confirming the fact of double bookkeeping and payment of “gray” salaries, or receive such information from employees, the company faces a serious fine.
For using such a scheme, you will have to transfer the withheld amount of tax to the budget, in accordance with
. In addition, he faces a fine of 20% of the personal income tax amount, according to the penalty . He may also be brought to administrative and criminal liability under Art. .
How to pay less taxes on UTII
UTII, or Unified Tax on Imputed Income in accordance with Art. 346.26 of the Tax Code is paid not on real income, but on basic income, calculated by the state for certain types of activities. Among them:
- rental of residential premises and retail space, land;
- retail;
- outdoor advertising;
- catering industry;
- repair and household services to the population;
- veterinary services;
- transportation of passengers, cargo transportation and paid parking.
The tax amount is 7.5 -15% of the basic imputed income for this type of activity, established in this region.
There are a number of restrictions for landlords who want to switch to UTII. For example, when leasing commercial real estate and retail space, there is a requirement that the premises should not have trading floors. Otherwise, it will not be possible to transfer the individual entrepreneur to UTII. With UTII, you can apply deductions for paid benefits and contributions.
- for individual entrepreneurs with employees – up to 50% on paid contributions
- for individual entrepreneurs without employees - for the entire amount of paid personal insurance premiums.
Another important nuance is that UTII is introduced at the level of regional authorities. In some regions, such a tax system may not exist.
Pros of UTII:
- Tax reporting on UTII must be kept to a minimum extent.
- Possibility of applying deductions. As in the case of the simplified tax system Income, on UTII the tax burden can be reduced to zero. If the amount of tax is equal to or less than the amount of personal insurance contributions paid (in individual entrepreneurs without employees), the tax is not paid.
Cons of UTII:
- Not available in all regions.
- Restrictions for switching to UTII.
- Inability to take into account expenses. If the business turns out to be unprofitable, you will still have to pay UTII.
Example
. The amount of mandatory insurance contributions is 32,385 rubles.
Income amount is 500,000 rubles per year. But in this case, the tax service calculates the basic income for this type of activity in this region. They are not interested in actual income.
Let's assume that imputed income is set at 200,000. The tax rate is 15%. Adjustment factors may be applied. Without them, the tax amount will be 30,000 rubles..
An entrepreneur has the right to reduce the amount of tax by the amount of contributions paid. Since the amount of tax (30,000) is less than the amount of mandatory contributions (34,385), there is no need to pay tax.
Tax = 0
Actual investor costs = mandatory insurance premiums = 32,385 rubles.
Along with the simplified tax system Income is the best option for this example.
Let's sum it up
The only way to optimize taxes is to choose the right tax system and then pay taxes on time. If your accountant offers one of the following ways to reduce taxes (individual entrepreneur, LLC), remember the fines (100,000 - 300,000 rubles). You will have to pay them, and you may also face criminal liability.
What tax optimization methods should you avoid:
- fictitious transactions through shell companies,
- breaking up a business for the purpose of applying a special regime,
- application of preferential tax rates without legal grounds,
- substitution of contracts,
- tax evasion through individual entrepreneurs,
- formal document flow with subcontractors,
- concealment of proceeds,
- forgery of documents,
- salaries “in envelopes”,
- registration of employees as individual entrepreneurs.
We at Finguru help entrepreneurs optimize taxes for LLCs or individual entrepreneurs using only legal methods. Therefore, if you doubt the actions of your accountant, we suggest you check it right now. Suddenly your business is in danger.
Key words for this article: how to reduce taxes, reduce the amount of tax, reduce LLC taxes, reduce individual entrepreneur taxes, how to reduce taxes in Russia, reduce the tax amount in Russia, reduce LLC taxes in Russia, reduce individual entrepreneur taxes in Russia, reduce individual entrepreneur tax on USN, how to reduce individual entrepreneur tax
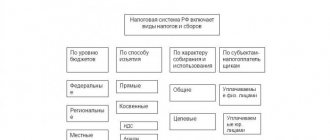
First, let's figure out what types of taxation an individual entrepreneur can use?
There are six tax systems:
- one general (OSN);
- five special ones (USN, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax, PSN, NPD (self-employed).
We won’t talk about the self-employed and the Unified Agricultural Tax today, given the limited application.
General taxation system
Using OSNO, the entrepreneur is a VAT and personal income tax payer.
The general tax system is applied by default. That is, if the individual entrepreneur has not submitted an application to switch to the simplified tax system or a patent, then the tax office will consider that the individual entrepreneur is on the general system, and therefore must pay VAT and personal income tax.
But there is a generalization of the judicial practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, which says that if an individual entrepreneur submitted returns under the simplified tax system for several tax periods, and the tax office “did not stutter” about VAT and payment of personal income tax, then it is considered that the individual entrepreneur is on the simplified tax system. Even if he did not submit a corresponding application to the inspectorate to switch to the simplified tax system.
In addition, according to Article 145 of the Tax Code, an entrepreneur may not pay VAT if his revenue for 3 consecutive months is less than 2 million rubles.
If you suddenly haven’t submitted an application to switch to the simplified tax system, then use the two life hacks above to reduce taxes and avoid paying personal income tax and VAT.
Simplified taxation system
The most common among individual entrepreneurs. There are two options for the simplified tax system:
- with taxation “income” (6% of all income);
- with taxation “income minus expenses” (15%, but not on net income, but on income reduced by the amount of expenses). More profitable are individual entrepreneurs who buy something and then sell it. Individual entrepreneurs who provide services are less profitable, because such individual entrepreneurs’ expenses are usually small.
Unified tax on imputed income (UTII)
It is not used in Moscow, that is, individual entrepreneurs from the capital cannot switch to it. This type of taxation can only be applied if an individual entrepreneur is engaged in certain types of activities. Tax is paid from units of the taxable object, for example:
- carriers pay based on the number of cars;
- sellers pay based on the area, which cannot exceed 150 square meters. m.
Patent tax system
This system is similar to UTII in that a patent can be applied by entrepreneurs who are engaged in certain types of activities. The peculiarity of the patent system is that tax calculation occurs immediately upon purchase of a patent, and a tax return on it is not submitted.
Self-employment
So far, this topic remains rather slippery. An individual entrepreneur can be self-employed and can work with self-employed people, but in the second case there is a risk that the tax authorities will reclassify contracts with self-employed people as employment contracts. And, as a result, additional insurance premiums will be charged.
So how can an entrepreneur safely reduce taxes? Our answer: first of all, you need to calculate the different types of taxation. After all, depending on what taxation regime an individual entrepreneur applies, his tax burden will be different. This also affects tax risks.