Procedure for registering a joint stock company
State JSC registration is carried out in accordance with Chapter II of Federal Law No. 208-FZ.
Company registration is carried out by the founders and consists of 4 main stages:
- determination of the main parameters of the joint-stock company - name, legal entity. address, size of the authorized capital (AC), distribution of shares between the founders, choice of OKVED and taxation system, appointment of a director and chief accountant;
- submission of documents to the Federal Tax Service;
- obtaining from the Federal Tax Service the Charter, INN, extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- initial issue of shares
All decisions on the establishment of a company are made at a general meeting by voting and documented in the form of minutes.
After the issue and distribution of securities among the founders, they must be paid within 12 months . If at the end of the established period there are unpaid shares, they, in accordance with Art. 34 of Law No. 208-FZ become the property of the joint-stock company. Such securities do not accrue dividends and do not have voting rights.
Within a year after the shares become the property of the JSC, the board of directors must make one of the following decisions:
- sell securities at a price not lower than market value
- reduce the authorized capital by the cost of unpaid securities
A special feature of the procedure for creating a joint stock company through the reorganization of existing companies is the need to determine the procedure for converting existing shares. The reorganization includes the following stages:
- holding a meeting and making a decision;
- submission of documentation on the creation of a JSC to the Federal Tax Service;
- receiving documents from the Federal Tax Service;
- registration of share issue
Legal status of the joint-stock company
The activities of Russian joint stock companies are regulated by the following legislative acts:
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation Art. 96-104
- Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ
The organizational and legal form of a joint stock company makes it possible to pool the financial resources of a wide range of people to implement large projects in various fields of activity.
Until September 2014, there were two types of joint stock companies - closed and open. But by Federal Law No. 99-FZ of 05/05/14 they were abolished. They were replaced by new types of joint stock companies - public (PJSC, former OJSC) and non-public (NAO, former CJSC).
Reorganization and liquidation of an open joint stock company
An open joint-stock company can be voluntarily reorganized in the manner provided for in the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of November 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”.
JSC can be reorganized in the form:
- transformations;
- accessions;
- mergers;
- divisions;
- discharge.
An open joint-stock company can be liquidated voluntarily and only in the manner established by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, taking into account the requirements of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies” and the company’s charter. In addition, an open joint stock company can also be liquidated through a court decision.
In accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation, if a legal entity is liquidated, then the rights and obligations cannot be transferred as succession to other persons.
According to Article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a legal entity (which is a joint-stock company) may be liquidated:
- based on the results of a decision of its founders or a body authorized by the constituent documents of the body, including after the expiration of the period for which the legal entity was created, with the achievement of the purpose for which it was created;
- by a court decision, if gross violations of the law were committed during its creation, and also if these violations are irreparable, or the activity is carried out without proper permission (license), or contradicts its statutory goals.
Legal form of joint stock company
According to Rosstat, in the Russian Federation the most common organizational and legal form for large business enterprises is the joint-stock company. First of all, this is due to the possibility of attracting funds from an unlimited number of people. If the JSC requires additional investments to expand its business, it may issue additional shares. The percentage of shares of large companies traded on the stock exchange is characterized by a free-float ratio.
JSCs issue shares of 2 types:
- ordinary - provide the opportunity to receive dividends, as well as the right to vote at the shareholder meeting;
- preferred - give the right to a fixed dividend income, the calculation procedure for which is prescribed in the company's charter, but do not allow participation in the management of the joint-stock company.
Russian second-tier joint stock companies often prefer to issue preferred shares, since their holders do not participate in business management. If ordinary shares are bought by a competing company, this may lead to a complete loss of independence of the joint-stock company. So, for example, Kamaz PJSC has a share of ordinary shares in free float of only 4%, while Pharmacy Chain 36.6 PJSC has about 6%.
In addition, in order to attract additional financing, a joint-stock company has the right to issue bonds - debt securities that do not give the owners the right to manage the company. Owners of such securities receive coupon income and redemption of the paper at the end of its circulation period. The procedure for issuing securities is regulated by Federal Law No. 39-FZ dated April 22, 1996.
Another feature of the legal form of a joint-stock company is a multi-stage enterprise management system. The main body of the board is the meeting of shareholders. It is where the main decisions on the development of the company are made. Each holder of a common share will be able to vote, and decisions are made by a majority vote.
True, with this form of government, minority owners (who have less than 25% of shares) will not be able to influence the final decision.
The disadvantages of this legal form are:
- lengthy registration procedure during creation, because in addition to registering the company itself, it is necessary to register the issue of shares;
- if one owner holds more than 50% of the shares, then he will be able to make decisions on the development of the company without taking into account the opinions of other participants;
- To make key decisions, you will have to go through a long procedure, which can sometimes take several months.
Special requirements for the charter
In addition to other requirements relating to a joint stock company, the charter of a PJSC must contain the following data:
- Full as well as abbreviated corporate name of the organization, indicating its publicity status.
- Mandatory presence of a board of directors, the procedure for its activities and powers. This is due to the fact that the company has a significant number of shareholders, whose rights may be significantly affected without the presence of an intermediate link between them and the executive body. The Board of Directors is a permanent body, which includes only individuals. The minimum composition of this body may include 5 members. If the number of voting shareholders is over 1 thousand, then the minimum size of the board of directors is 7 people, and if the number of such shareholders is over 10 thousand - 9.
- Lack of opportunity for the general meeting of shareholders to expand its competence. This is due to the fact that the management of large companies is complex, and many ordinary shareholders may not have the relevant competence. Therefore, management functions are carried out indirectly, through the board of directors and the governing body, acting under the control of an intermediate structure. The effectiveness of the latter is revealed by the reporting of PJSC.
The provisions of the charter relating to the limit of shares that can be owned by one person, as well as restrictions on their sale, are considered invalid.
If we are talking about transferring a non-public JSC into a public one, then the provisions of the charter must be adapted to the new requirements.
However, the greatest difficulties are not associated with correctly filling out all the fields of the registration application and entering the required code for the relevant inspection. Large expenses will require a significant amount of information that will have to be processed during the work of the PJSC.
Types of joint stock companies
According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, there are two types of joint stock companies:
public (PJSC)
non-public (NAO)
The main difference between a PJSC and a NJSC is the possibility of open sale of securities of a public enterprise on the exchange market, while shares of a NJSC are distributed only among the founders.
The authorized capital of a PJSC must be at least 100,000 rubles, and in a NAO it must be at least 10,000 rubles.
Joint stock companies must maintain registers of shareholders. The PJSC must enter into an agreement on maintaining the register with a specially authorized company (registrar). In the NAO, such a duty can be assigned not only to an authorized organization, but also to a notary.
If one of the shareholders of a PJSC decides to sell his shares, then the other shareholders do not have a priority right of redemption, while in a NJSC one of the shareholders must notify the other founders in writing and invite them to buy out their share. And only in case of refusal will he be able to sell the shares to third parties.
For NAO there is a limit on the number of company participants. Their number cannot exceed 50 people. Otherwise, the company is obliged to change the legal form of a joint stock company to a PJSC. For a public JSC the number of participants is not limited.
Along with the differences, there are some common features between these types of joint stock companies:
- shareholders are paid dividends
- after the liquidation of a joint stock company, shareholders have the right to claim part of the company’s assets, determined in proportion to the number of shares
- business management is carried out by the general meeting of shareholders
- the key internal document regulating activities is the Charter
PJSC governing bodies
The main body for carrying out management activities in a PJSC is the general meeting of shareholders. It is usually held once a year and is initiated by the board of directors. If such a need arises, the meeting can be held on the initiative of the audit commission, or based on the results of the audit.
There are two ways to solve this problem:
- The number of shares whose owners can participate in the meeting is limited;
- Discussions are conducted remotely, using the method of sending out questionnaires.
The meeting of shareholders makes all important decisions on the activities of the PJSC and plans events for the development of the company in the future. The rest of the time, management responsibilities are performed by the board of directors. Let us explain in more detail what kind of control body this is.
In large companies, the number of board members can reach 12 people.
Joint Stock Company Agreement
If a JSC has more than one founder, then a constituent agreement is concluded between them. It is not the main constituent document, therefore it is not required for registration of a JSC. The founding document is the Charter. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 98 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the agreement of a joint-stock company stipulates:
- the procedure for the activities of the founders;
- size of the authorized capital;
- types of securities issued;
- procedure for payment of shares by founders, etc.
The founding agreement of a joint-stock company is a type of agreement on joint activities. It is signed by all founders of the company.
The joint stock company agreement is subject to challenge in court. In this case, the invalidity of the contract, as a rule, does not entail the invalidity of the created company.
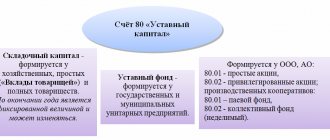
Authorized capital of PJSC
Information about the authorized capital of a PJSC is contained in the charter of this company. The size of the authorized capital of a PJSC is determined by federal legislation (Article 2 of Federal Law No. 208). The formation of the authorized capital of a PJSC occurs due to the fact that shares are issued for a certain amount of money. Also, the authorized capital of a joint-stock company is divided into a fixed number of shares, certifying the binding rights of all shareholders in relation to the company. Thus, the authorized capital of a PJSC is compiled on the basis of the par value of all its shares acquired by shareholders. The authorized capital also determines the minimum amount of company property that guarantees the interests of creditors.
The total amount of the authorized capital in the case of a PJSC is a certain value that can vary significantly, either decrease or, on the contrary, increase. Such fluctuations primarily depend directly on how the shares of a particular company are redeemed. Further, examining the differences between public and non-public joint-stock companies, the minimum amount of authorized capital for a public joint-stock company will be mentioned, which, by the way, is 100 thousand rubles.
In practice, it is clear that the control exercised by inspection bodies is much stricter than in the case of other JSCs. The explanation for this is that absolutely all statutory documents indicate that the mentioned company is as open as possible to all third parties. In other words, it should be completely obvious that the company's shares can be purchased by all interested citizens. Consequently, all supervisory authorities require maximum accessibility and transparency of all PJSC data.
Before registering a company, the founders enter into a special agreement. It takes into account the following points: types and categories of shares, the size of the authorized capital, the procedure and amount of their payment, etc. But it is worth noting that this agreement does not serve as a constituent document. Its effect remains in force until the moment specified in the agreement, until each of the shares is paid for by the shareholders. However, there are cases when a company has one founder. Then a similar list is in his decision.
JSC participants
In addition to the founders (those who created the organization), there are other persons in the JSC - participants. The participants of a joint stock company are the owners of the shares of this company - the shareholders.
The differences and similarities between the participants and founders of the company are presented in the table.
| Comparison parameter | Founder | Participant |
| Who can become | Individual or legal entity | |
| Lineup changes | Only when the share is transferred to another person | When buying/selling shares |
| Responsibility | Fully responsible with their own property | Bear risks within the limits of funds invested in shares |
| Control | Participate in business management within the limits of the number of ordinary shares | |
| Responsibilities | At the formation stage, companies carry out the necessary activities and develop documentation | Pay for the acquired shares within the period established by the decision on the issue of securities |
| Rights | Receipt of dividends and property upon liquidation | |
The founders are the first shareholders of the joint-stock company, since it is between them that the shares issued upon the creation of the company are redistributed.
Property of a joint stock company
At the stage of creating a JSC, its property is formed. It consists of contributions to the authorized capital in kind (for example, the founder transferred a building to the company to pay for the cost of shares) and the acquisition of property using money received from the redemption of shares.
All property, property rights and other assets are the property of the joint stock company . The participant owns only the securities he has acquired, which give him certain rights. Those. a participant cannot demand that the JSC return to him the money paid for the securities or the assets contributed to the authorized capital.
Subsequently, the composition of the property changes, new assets are acquired, old ones are written off. If the existing assets at some stage of operation become insufficient, the participants of the joint-stock company can transfer their own property to the joint-stock company free of charge . This possibility is provided for in Art. 32.2 of Federal Law No. 208-FZ.
The transfer is formalized by an agreement, which is subject to preliminary approval by the board of directors. In this way, the company's assets increase without changing the size of the authorized capital.
JSC participants receive rights to the company's property upon its liquidation. If the company ceases to exist, each participant will be able to receive a portion of the property in proportion to his share of the securities. The distribution takes place in accordance with Art. 23 of Federal Law No. 208-FZ.
Features of PJSC
A public joint stock company has all the features inherent in a joint stock company, regardless of its type.
These include the following characteristics:
- Authorized capital divided into shares, confirming their liability rights. The establishment of such a legal entity does not imply other methods (shares or shares).
- Participants respond with the value of their shares. The status of a shareholder implies liability only for the unpaid portion of the shares.
This type of joint stock company is characterized by its own characteristics:
- The corporate name of a public joint stock company must indicate its public status. In practice, this requires the presence of the word “public” before the words “joint stock company”. Legal regulation requires this to protect the interests of investors. It is important that they understand the applicable rules and the minimum and maximum risks before making their investments.
- They may place shares and other securities convertible into shares through public subscription, in accordance with the rules provided for by the legal regulation of financial markets.
Based on the characteristics, we can obtain the following definition. A public joint stock company should be understood as a legal entity whose authorized capital is divided into shares owned by shareholders who are liable for obligations within the value of their contribution to the authorized capital.
Its shares are distributed through open subscription, and the company name contains an indication of its public status.
PJSC is not an independent organizational form, but a separate OKOPF code is provided for it. This indicates that it stands out from other joint stock companies.
JSC liability
Like any legal entity. a person, a joint-stock company, is liable to counterparties for the obligations assumed. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 3 of Law No. 208-FZ, the company is liable to creditors with all its property, i.e. movable and immovable assets, money in accounts and on hand, securities, etc.
The company is not liable for the obligations of its participants, but shareholders may be held vicariously liable for the obligations of the joint stock company in the event of its bankruptcy.
Claims may be made against a shareholder if the JSC’s own property is insufficient to fulfill its debt obligations. Holding participants accountable is only allowed if the insolvency of the JSC was due to their fault.
A shareholder can only be held accountable in court. In this case, it is necessary to prove that the actions of the JSC participant were intentionally aimed at bringing the company to bankruptcy.
State joint stock company
If we consider JSCs according to the degree of state participation, they can be divided into two types:
- private
- state
State joint-stock companies, in turn, can be divided into 4 groups:
- 100% of the authorized capital belongs to government agencies or the Government;
- the state has a controlling stake (more than 50%);
- the state has a blocking stake (more than 25%);
- the state has less than 25% of the shares.
The owner of a controlling stake may make sole decisions on the management of the enterprise, with the exception of decisions provided for in Art. 48 of Law No. 208-FZ. Such decisions include:
- amendments to the Charter
- reorganization/liquidation of the company
- determination of the number, type and par value of shares and others
The blocking package allows you to veto a decision of the board of directors, i.e. Without the vote of the owner of the blocking package, decisions will not be valid.
State joint-stock companies, 100% owned by the Government, are created with the aim of solving the strategic problems of the country. Such a company is completely dependent on government authorities, is not subject to the influence of private investors, and is protected from information leakage.
An example of such an enterprise is JSC Russian Railways. The sole founder and shareholder is the Russian Federation. The company is managed by the Government of Russia. The company's shares have never been traded on the stock exchange.
Another example of a JSC with 100% state participation is Russian Post. According to the charter, the sole shareholder is the Russian Federation, and management powers are vested in the Federal Agency for State Property Management.
The state owns more than 50% of the shares of such companies as the Russian joint-stock company "UES of Russia", "Aeroflot", "Mosenergo", "ALROSA" and others.
The advantage of state participation in a joint-stock company is the possibility of replacing private financing with budgetary financing. If a private owner puts the primary goal of making a profit, then the state puts the development of the economy as a whole as a priority. The state can afford to invest in long-term projects that will pay off in 5-10 years. Private investors are often less patient and invest in small businesses, expecting returns in 1-3 years.
The disadvantage of state-owned companies is also clear - managers and workers expect funding regardless of results. As a result, private business (including those represented by joint stock companies) is in most cases more profitable, although it is less noticeable in the country’s monetary turnover.
Private joint stock company
As such, the concept of a private joint stock company is not enshrined in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. However, in contrast to a state joint-stock company, a private company is considered to be a company whose controlling stake is owned by private investors.
Private joint-stock companies include all non-governmental joint-stock companies created without state participation. Since the shares of such companies are not offered at public auction, the state cannot buy them and take part in the activities of the company.
PJSCs with a state share of less than 25% can also be classified as private joint-stock companies. With such a number of shares, the state will not be able to influence the final decision of the shareholders - after all, in order for the decision to be considered valid, it is necessary to receive ¾ of the votes.
Features of managing an open joint stock company
The right of a shareholder to participate in the management of the activities of an open joint-stock company is exercised through:
- providing the opportunity to participate in the General Meeting of Shareholders, which is considered the highest management body of an open joint-stock company, which identifies the main directions of the company’s activities;
- shareholders have the legal right to elect and be elected to the management bodies of an open joint stock company.
One ordinary (or also called simple) share gives its owner the right to one vote in managing the affairs of the joint-stock company. As a rule, a shareholder can use this vote only at general meetings of shareholders.
Different categories of shareholders have different interests. Therefore, it should be noted that the policy pursued by a joint-stock company will largely be determined by the preponderance of any interest of shareholders, that is, the group that has the largest stake.
A controlling stake is the maximum number of ordinary (common) shares owned by a shareholder, which now allows him to individually block or make decisions on the activities of the JSC at a general meeting of shareholders.
Signs of a joint stock company
From the regulatory legal acts regulating the activities of joint-stock companies, it is possible to identify distinctive characteristics for enterprises of this type. The characteristics of a joint stock company are:
- The authorized capital is divided into shares;
- JSC is a commercial enterprise, i.e. the main purpose of creation is to make a profit;
- can be created by one or more participants, incl. legal entities;
- The company's assets are separated from the assets of shareholders, i.e. the owner of the share is not liable with personal property for the debts of the JSC, but suffers (in the event of a deterioration in the financial situation of the company) monetary losses within the limits of the cost of the acquired shares;
- members of the company have the right to receive part of the enterprise’s profit in the form of dividends;
- JSC participants have no obligation to personally participate in the company’s activities;
- shares of a public enterprise are freely traded on the securities market, and anyone can become a shareholder
JSC is the only form of business that has the right to issue shares.
Requirements applicable to PJSC
The actual ability to attract unlimited financial resources requires special legal regulation. Special requirements accompany both the creation and activities carried out by a public joint stock company.
Creation requirements
A PJSC is created based on the decision of future shareholders. In addition to data typical for other societies, it must decide on the appointment of a registrar.
It is determined by votes, the minimum threshold of which is 75%. Future PJSC reporting will include data from the shareholder register.
Only a professional participant in the securities market has the right to carry out such activities. This is due to the fact that it is necessary to ensure maximum transparency in maintaining the register.
The agreement on the creation of a PJSC, which is concluded by the participants, determines the authorized capital, categories of shares to be placed and the procedure for their payment. This document is valid until the end of the period established for payment of shares.
The minimum authorized capital of such a JSC is 100 thousand rubles.
JSC reporting
JSC annual reporting is divided into 2 categories:
annual report
financial statements
The annual report provides information about the economic activities of the company, and the financial statements reflect the financial state of affairs at the enterprise.
The list of information disclosed in the annual report of a joint-stock company is enshrined in Chapter 70 of the Regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2014. No. 454-P.
Art. 5 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2008. No. 307-FZ provides for a mandatory audit of the financial statements of a joint-stock company . PJSC is obliged to publish annually in the public domain:
- annual report;
- financial statements;
- securities prospectus;
- information about holding a meeting of shareholders;
- other information established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation
The financial statements of PJSC are prepared in accordance with Russian and international standards. Both versions of reports are publicly available.
NAO, with more than 50 members, publishes an annual report and financial statements.
For non-disclosure of public information, administrative liability is provided in the form of a fine. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 15.19 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the guilty official will be fined in the amount of 30-50 thousand rubles, legal. person – from 700,000 to 1 million rubles.
Requirements for PJSC in the course of its activities
The documents of a public joint-stock company are carefully checked not only during the state registration process, but also throughout its entire activity. At the same time, a mandatory procedure for publishing certain materials is established.
The annual reports of a PJSC, including accounting and financial statements, as well as data on securities, are subject to disclosure. The Law “On the Securities Market” (Article 34) specifies these provisions and requires the disclosure of quarterly reports.
Based on these provisions, consolidated accounting documents for every 3 months are subject to publication.
A message about the place and time of the general meeting of shareholders, boards of directors and their decisions should be publicly available.
In addition, we are talking about the formation and termination of powers of executive bodies, approval of major transactions, approval by the issuer of internal regulations, placement and repurchase of securities, as well as the recommended amount of dividends and the procedure for their payment. This list includes more than 50 items, which are united by the fact that they reflect data on the financial well-being of the PJSC.
Compliance with these requirements should indicate the openness of the company, making it more attractive to investors.
An organization may be exempt from publishing a number of information provided it submits a reasoned application. Requirements for this include ceasing publicity status. From the site advokat-malov.ru