Types of indicators
There are quite a lot of criteria by which different types of businesses can be compared. They differ in focus and assessment methods. To determine social and economic significance, indicators such as the number of new jobs, average wages, and the number of taxes paid to the budget are taken.
For manufacturing enterprises, an assessment of the impact on the ecology of the region is carried out. An analysis is also made of the enterprise's susceptibility to various unfavorable factors.
Financial indicators
But first you need to determine financial efficiency. It is she who will allow us to draw a conclusion about the profitability and safety of investments and ultimately decide whether the enterprise should exist or not.
Investors and budgetary organizations deciding on financing a new enterprise first look at such indicators as the ratio of equity and borrowed funds and the payback period of the project. Based on these data, an initial conclusion is made whether the enterprise is worth considering as an investment object at all.
Ideally, the project should contain a section in which such financial indicators of the business plan as break-even point, profitability, net present value and others are calculated.
Business plan assessment – why is it necessary and what problems does it solve?
Conducting an examination and obtaining an opinion is the goal of evaluating a business plan. Analysis of documents will allow:
· assess the feasibility of the project;
· attract borrowed capital by convincing the investor of the viability of the project, the profitability of the business, and the profitability of the investment;
· choose optimal investment and insurance conditions;
· draw up a well-developed investment project;
· evaluate the effectiveness of investments at different levels of profitability;
· calculate the payback period taking into account the annual budget indicators, determined taking into account mandatory wage payments, contributions to the Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, Social Insurance Fund;
· calculate the net present value (NPV) to compare the values of investment costs and the results of financial and economic activities, profit;
· calculate the internal rate of return using the IRR calculation formula (determine the interest rate at which the value of cash flows is zero).
An important stage of the assessment process is financial modeling, in which a new business project is described by drawing up tables and formulas. The basis for developing a financial model is hypotheses and estimated initial conditions (volume of products sold, technologies and production capacities used, share of manufactured goods on the market, the company’s sensitivity to changes in sales volume, etc.). Calculations are based on hypotheses when developing a plan for production, sales, investments - parameters for assessing the feasibility of the project.
Conducting a comprehensive expert assessment of plans and performance indicators ensures the reliability of forecasting, assessing the payback of the project, determining the break-even point and margin of financial strength, discounting capital and income (determining initial costs and final financial results using a special coefficient). Discounting cash flow is necessary to calculate the cost of money at a specific point in time and compare the economic efficiency of capital investments in different periods of doing business.
Evaluating a business plan helps to cope with many tasks
Input data
To calculate the economic indicators of the effectiveness of a business plan, you will need data on production costs (fixed and variable), and the estimated volume of sales revenue.
Expense items that do not depend in any way on production volumes are classified as fixed costs. For example, monthly rent for premises, equipment, mandatory loan payments, salaries for permanent employees.
Variable costs are the costs of purchasing goods, raw materials, fuel, and paying employees. When variable costs are zero, production stops.
Third stage. Analysis of the project's susceptibility to hazards
Analysis of the effectiveness of a business plan includes an assessment of various hazardous factors and the sensitivity of the project to them.
Such factors include inflation, interest rates on loans, the amount of variable and fixed costs and the amount of necessary financing. Among the factors relating to manufactured products, it should be noted their prices and sales volumes. The influence of each factor on the project is studied and calculated separately, while all the remaining ones are taken as constant values. Such large calculations are carried out by a specially developed program Project Expert. It does all the work automatically. Based on the results of its assessment, you can see the most problematic factors, as well as calculate the break-even point for them. How to write a business plan for an individual entrepreneur - instructions for writing it yourself. End-to-end link block.
| Why do you need a business plan at all? | Section No. 5: Organizational plan; |
| What parts should be in a business plan? | Section No. 6: Risk Analysis; |
| Section #1: Writing a summary for the plan; | Section No. 7: Ways to reduce risks; |
| Section No. 2: Description of the company and services; | Drawing up the financial section of the business plan; |
| Section No. 3: Drawing up a marketing plan; | Additions and annexes to the plan; |
| Section No. 4: Company production plan; | Determining the effectiveness of a business plan. |
Break even
How many products need to be produced and sold so that all costs are covered by revenue is shown by the break-even point. It is expressed in units of production or in monetary terms. When this value is exceeded, the company begins to make a profit. The lower this indicator, the more competitive the production.
To calculate the break-even point, you need to create an equation in which fixed costs equal gross profit (unit cost of production taking into account variable costs) multiplied by the required quantity of production:
C= nx(C-P),
where C – fixed costs,
n – quantity of products,
C – cost per unit of production,
P – costs per unit of production.
Obviously, the break-even point will be equal to:
n=C/C-P
Multiplying this value by the cost of a unit of production, we obtain an indicator in monetary terms. Another name for the break-even point is the profitability threshold.
Procedure for analyzing a business plan
Analysis of the investment business plan is performed in a certain order:
- The source data and quality of delivery are checked.
- The organizational scheme of the project implementation and the financing scheme are assessed.
- Marketing analysis and analysis of economic indicators are carried out.
- Finally, the possibility of achieving the goals presented in the organization’s business plan is assessed.
When checking the source data, special attention is paid to expense items and price levels. An important part of project evaluation is marketing analysis. The following parameters are assessed: market segment conditions, government participation, finished product promotion scheme, pricing scheme.
The analysis of the organizational chart consists in determining the form of participation of investors in the implementation of the project. In particular, they can be part of top management, own a block of shares or participate in the project by providing investments.
Profitability
The main indicators of a business plan include the concept of profitability. This is the most general characteristic; it shows the ratio of the profit received to the amount of money invested in the business. Expressed as a percentage, it can be calculated for an arbitrary period, usually a month, quarter and year.
The overall profitability of production is calculated using the formula:
P=P/(OF+OS)x100%
where P is profitability,
P – amount of profit,
PF and OS – the cost of working capital and fixed assets, respectively.
To see whether a certain type of product is profitable, you can calculate its profitability ratio:
Rp=(P/Sp)x100%,
where Cn is the total cost of production,
P – profit received from its sale.
Necessary components of business plan analysis
Analysis of an organization's business plan allows investors to determine whether the project meets the main indicator - the possibility of obtaining maximum profit from an investment with minimal risk. Then the economic efficiency of the proposed activity is assessed. The company's capabilities necessary to achieve the organization's goals are analyzed. For this purpose, the enterprise is assessed according to the following indicators:
- work results for 3 years;
- state of production;
- nomenclature and volume of products;
- systems for supplying raw materials and marketing finished products;
- control system;
- assessment of labor resources;
- economic situation of the enterprise.
Particular attention is paid to assessing the volume of attracted capital and production capacity that will be required to implement the project.
Net present value
Another basic indicator of the project is net present value; other values are calculated with its help. Before calculating it, we define the concepts of cash flow and discount rate.
Cash flow
Cash Flows (CF) or cash flow is the most important concept of modern financial analysis and means the amount of cash that an enterprise has at a given point in time. Can have both positive and negative meaning. To find it, you need to subtract the outflow (Cash Outflows) from the inflow of funds (Cash Inflows):
CF=CI-CO.
Discount rate
Over time, the value of money changes, often downward. Therefore, to estimate future cash flows, a variable value is used that depends on many factors - the discount rate. With its help, the investor reestimates the value of future capital at the current moment. There are several methods for calculating the discount rate: which one to choose depends on the type of problem at hand.
NPV formula
Net present value (NPV) - shows the efficiency of investing in a project, is equal to the sum of the discounted values of the payment stream reduced to today:
where NVP is the English version of the name NPV,
t=(1,…, N) – years of project life,
CFt – payment in t years,
IC – initial investment,
i – discount rate.
The higher the NPV, the more attractive the project. If the NPV is negative, the project is removed from consideration as unpromising.
Risk analysis
Analysis of an organization's business plan includes an assessment of the following types of risks: investment, market, production, financial. Investment risk depends on fluctuations in the value of investment and financial portfolios, market risk depends on price fluctuations, exchange rates, and lending rates. Production risk is associated with the possibility of failure to fulfill obligations to consumers of products, financial risk - with the possibility of failure to fulfill credit obligations.
When evaluating a business plan, the following possible problems are analyzed: a decrease in sales volume, an increase in the cost of a unit of goods, a decrease in the selling price. The result is a description of possible risks. Based on the data from the analysis of the business plan, a conclusion is drawn up, which must be presented in a form understandable to investors and partners.
The easiest way to draw up a financial plan for a project for one year or five years
- How to make a budget for the year.
Not everyone understands how much depends on the first year of a startup. During this period, factors are determined that will influence the further development and prosperity of the business. How soon you reach the break-even point, how successfully you can manage risks. At the first stage, it is important to distribute all expenses by month in order to get an idea of the amount that should reimburse them.
For successful commercial activities, it is simply necessary to develop an estimate that includes the following items.
- Tax and registration costs. When registering a company, choose the most appropriate organizational and legal form for yourself. Each of them has its own pros and cons. How big will your turnover be? Are you planning to hire staff? Include money in your budget for approval of all necessary documents and payment of taxes.
- Payments to employees. Employee salaries are a serious budget item. At the very beginning, save on staff as much as possible. Don't hire a large staff. First you need to make sure that the business you started is exactly what you were aiming for, and it can bring you real profit.
- Expenses for raw materials or goods. Many entrepreneurs purchase materials in bulk, and this is no coincidence. After all, purchasing at wholesale prices allows you to save significantly, but in the case of a project just starting, it is better to spend the minimum on production. At first, it is difficult to predict how high the demand for your products will be. It is advisable to launch only a small batch of goods, and only if customers buy it willingly can the volume of trade turnover be increased. After the first successful sale, you cannot rest on your laurels by selling the same products. Study demand, change the assortment in accordance with the interests of customers. Analyzing the dynamics of trade volume during the year will help plan the volume of acquisitions.
- Equipment costs. The initial stage of a business project involves the purchase of only the most necessary equipment. Some machines, tools and other means of producing goods can be rented. Once you have a significant net profit, you can purchase it all yourself. Equipment costs should be reflected in the financial plan.
- Transport costs. They involve payment for transportation of material to the place of production of the goods, as well as delivery of products to the buyer. The choice of a transport company with the most acceptable conditions is of great importance here. Next, decide whether the shipping cost will be included in the price of the product or whether the buyer will pay it separately.
- Rent expenses. Many businessmen start by renting premises. Some activities are initially carried out at home. One way or another, at first only the functionality of the area matters - not design or prestige. At the stage of work without loss, you can think about changing the conditions for locating production.
- Spending money on promotion. It includes not only advertising and participation in various exhibitions. This includes payment for the development of a corporate identity, and the creation of a website and packaging design, and payment for the work of a photographer, and progress in social networks, and so on. Not everyone takes this data into account in their financial plan, but it can add up to a fairly large sum.
And remember that there is always the possibility of unforeseen expenses, set aside 5-10% of your total expenses for them.
- Volume of sales. It is more difficult to determine it, the wider the range you present to the buyer. You only know the cost of the product in advance, but it is quite difficult to determine how well it will sell. It is most convenient to calculate by week. What implementation plan do you set for yourself for the week? Start from your real potential. Then multiply this figure by 4 to get your approximate monthly turnover. Considering the possibility of business development, it is a good idea to provide for an increase in trade every month by 5, or even 10%. By “raising the bar” a little, you motivate yourself to succeed and put in your best effort.
- Net profit is the remaining income minus all expenses. In the first months, you should not expect this amount to be large. It is not uncommon for a startup to have a negative net profit. This is normal and not a reason to be upset at all. Plan future expenses and investments, correct problem areas.
A financial plan will help you decide on your initial capital. When the project pays off the investment and begins to generate income, you can think about developing your business. An economic program usually contains a numerical indication of the period when profits will become positive.
- How to create a budget for five years.
Having achieved success, you never need to stop there. Owners of small or medium-sized businesses sooner or later think about increasing the scale of their brainchild, and owners of large companies think about it constantly. So after the first year of your existence, the question will arise of how to expand production, enter new markets, or simply increase recognition and popularity. You can no longer be content with reimbursement of expenses; you want a stable business that brings in a good income. At this moment, it’s time to draw up a plan for the whole five-year period, and it is advisable that it slightly overestimates your capabilities. What exactly you will develop in is up to you. You will probably hire more employees, purchase additional equipment to increase sales, change your product range, increase your customer base, expand your sales market, or maybe try to enter the international market, consider franchising. There are many options.
It is possible that the financial plan for five years will consist of the same points as the annual one. It all depends on the degree of development of the business and on the number of things that you managed to implement in the first year of existence. So, perhaps, it will again contain a clause on the proper registration of the company in accordance with all the requirements of the law. But usually organizations try to do it all at once. Approximate scheme of work:
- company registration;
- remuneration of employees;
- costs of premises (purchase or hire);
- expenses for opening new retail outlets or company branches;
- equipment costs (purchase, rental);
- marketing (spending on working with clients, which may include promotions and bonuses, gifts for regular customers, discounts and other types of loyalty programs, advertising, website promotion, master classes, corporate parties, etc.).
general information
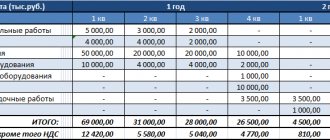
The financial section of the business plan summarizes all the information previously displayed in the document. It is expressed digitally, which allows you to assess the prospects of a future business and understand how feasible it is to implement what you have planned.
The business plan format for each project is not the same. It depends on its scale, characteristics and goals pursued. All its sections are compiled according to various schemes. The financial part of the document can be drawn up using non-identical algorithms, but it must contain the following information:
- standard values obtained by calculation taking into account regulated parameters;
- expenses for setting up a business;
- costs of supporting production activities;
- determining the cost of the result of labor;
- drawing up a financial flow diagram;
- formation of the financial balance of the project;
- calculation and analysis of basic financial indicators;
- comparison of potential profit and loss values;
- determination of methods of financing the project and their description.
What could be the financial plan for a business plan?
Any program is a sequential list of activities implemented over a certain period of time. Likewise, a financial plan is drawn up for a specific period. And the time for which it is designed can be very different. Some people prefer to draw it up as often as possible (for a month, quarter, half a year), but often enterprises plan their work for a calendar year, and some organizations prefer to draw up similar documents designed for long-term implementation (a year or more). But practice shows that it is much more convenient to evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation of plans on the basis of indicators obtained from the results of the company’s activities during the annual period.
Based on the time of execution, economic programs can be classified into medium-term, short-term and long-term.
- Short-term ones are compiled for a period of no more than a year. They are suitable for companies with a fast turnover of funds.
- Medium-term ones are developed for a year or more. But should not exceed five years. Covering such a long period is essential for organizations conducting research and long-term development.
- Long-term ones are prepared for more than five years. If the goals set by the company are characterized by duration, then it is advisable to draw up a financial plan for a long period.
A three-year project can only be called a medium-term project with a considerable degree of convention. Because if we are talking about a construction company, then the construction of a facility takes a lot of time, and three years is a fairly short time to implement an economic calculation. That is, a three-year period for this type of organization will not be medium-term, but short-term.
There are other classifications of financial programs. For example, the main ones contain figures for planned income, tax deductions, costs and other information, and the auxiliary ones serve to compile the main ones. Having written many additional ones, it will be possible to combine the data they contain into one main project. So, you can develop a side plan for revenue, cost calculation and other important indicators, and then bring everything together.
Depending on the moment of preparation and purpose, economic programs can be called:
- introductory – formed at the time of organization of the enterprise;
- current - compiled in the course of the company’s activities, otherwise called operational; the implementation period may vary;
- anti-crisis – aimed at overcoming difficult financial situations, for example, at the stage of bankruptcy;
- unifying - created during the merger of companies on the basis of the data that contains the individual financial plans of the block participants;
- dividing – necessary to forecast monetary efficiency and the feasibility of dividing the concern into separate entities;
- liquidation - contain a consistent mechanism for disposing of material resources during the liquidation of the plant.
Plans can also be static - they contain single-level information about upcoming financial events and do not imply the possibility of changing it, as well as dynamic - multi-level. They are also called flexible. They are more labor-intensive to compile, but they examine several possible development outcomes and propose solutions that must be made in a given difficult situation.
Balance Sheet Forecast
A balance sheet or statement, which is officially called a balance sheet, is a planning and reporting document of a completely different nature than a profit and loss plan (report). If the latter reflects information about the accrual of income and expenses, the formation of a financial result within the billing period, that is, it shows the dynamics of the corresponding values, then the balance sheet is a document reflecting static status. It is not for nothing that they say about the asset of the balance sheet that it demonstrates the state of funds and their placement, and about the liability - as about the state of the company’s sources of funds.
Adapted form of balance sheet. Basis: form according to OKUD 0710001 (click to enlarge)
Above is an adapted form of the balance sheet for forecasting purposes as part of the preparation of a project business plan. The purpose of the balance sheet is to show stakeholders whether the financial condition of the company (liquidity, independence, solvency) is stable or not, which intends to implement the project in a certain period of time. The company's balance sheet planning is usually carried out on December 31 of each accounting year, throughout the entire project period. This does not at all cancel the withdrawal of balances of assets and liabilities to intermediate dates. In addition, to work on the forecast, you need a starting balance if the project does not involve starting a business from scratch.
For creditors and investors assessing the possibilities of their participation, the forecast balance is no less, and sometimes even more important, than the profit and loss plan. If the enterprise is operating, I recommend planning the balance sheet, and then the movement plan of the assets according to a certain algorithm.
Step 1. Study the statistics of balances of short-term liabilities (short-term liabilities) and establish standard values of non-reducible balances for the items of the section, taking into account the planned growth of turnover. I recommend starting with the wage arrears standard, then moving on to debts to suppliers and contractors, to short-term borrowed obligations, etc. This is the first iteration of Section V.
Step 2. Plan the balances of current (current) assets. It is better to start with normalizing the level of inventory; as a guide, you should use statistics on the dynamics of the working capital turnover rate for different groups of inventory items. Extrapolating the obtained values to the growth of production volumes, develop standards for balances for all estimated dates of project implementation. Next, you need to determine the amount of investment in inventories.
Step 3. Continue planning Section II balance sheet. Perform normalization of accounts receivable balances. Calculate the value of the coefficient of diversion of current assets into accounts receivable for the last 3 years. Clarify the company's credit policy and build a loan forecast for the entire project period.
Step 4. Based on liquidity indicators, clarify the parameters of sections V and II of the balance sheet in several iterations, maneuvering through the most mobile items of these sections in order to prevent the failure of current and absolute liquidity.
Step 5. Using the investment plan, perform the first iteration of forecasting long-term liabilities, including additional equity from investors and debt capital. When building a new financial capital structure, rely on the functional financial strategy of the business.
Step 6. Having calculated the effect of financial leverage, plan the optimal amount of borrowed capital. Return to the Profit and Loss Plan and adjust the interest on the loan payable. Further steps of the algorithm are transferred to the motion planning of the DS and the dynamic modeling block.