Why do you need a business plan?
A business plan is a planning document that is developed when opening a new business, when launching a new project or product within an already operating business. It contains the necessary reports and justifications confirming the feasibility of the project, as well as a plan of operations and actions aimed at achieving the goals.
This document can be developed either directly for yourself or for third parties. The methods used and the tasks that are solved during planning largely depend on the addressee.
A business plan “for yourself” helps you decide whether it’s worth taking on a given project at all. It makes it possible to accurately calculate the required level of costs for its launch and ongoing activities, identify risks and factors that may affect your business, calculate expected profits and payback periods.
Also, a business plan for aspiring entrepreneurs actually serves as instructions, following which helps to realize their goals. Therefore, he must cover in as much detail as possible all possible factors influencing the business.
Often, a business plan is focused primarily on third parties. This third party can usually be:
- investor;
- bank;
- franchisor;
- potential partner.
Accordingly, the purpose of developing a business plan will be to convince the recipient of the advisability of cooperation with you or to allocate funds for the implementation of the project. It must confirm the economic viability of this project, justify the volume of required financing, payback periods, and other important indicators.
Regardless of who exactly the business plan is aimed at, it must be drawn up absolutely objectively, skillfully and competently. Mistakes made during planning can cause serious problems in the future.
At the same time, almost any entrepreneur can write a high-quality business plan. To do this, just use a ready-made template that matches your type of activity, the recommendations given below.
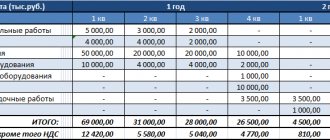
Financial plan (budget)
It is necessary to include a detailed financial plan in the business plan. It must contain the following components:
- sales volume forecast;
- profit and loss estimates;
- cash flow analysis.
The sales volume forecast should give an idea of the market share that the company (entrepreneur) expects to win with its products. For the initial production period (the first year of the project), it is a good idea to have a preliminary agreement with customers about future sales. Starting from the second year, the sales forecast is based on assumptions. It is important that they are realistic and not embellished.
The profit and loss forecast (profit and loss statement) is a document with a fairly simple structure. It includes the following indicators:
- proceeds from sales,
- production costs,
- total profit,
- general production expenses,
- net profit.
The purpose of this document is to show how the profit of the enterprise will change and be formed.
Business plan structure
It is important to create a business plan that maximally reveals the essence of your idea and answers all questions about the necessary investments and activities, expected financial results, existing risks and benefits, etc. Therefore, the document must have a clear structure.
It should be noted that there is no standard business plan structure. It may vary depending on the specifics of the area of activity, the market, the scale of the project and other factors. However, in general, the structure of a business plan should usually contain the following main sections:
- Title page of the business plan.
- Project summary.
- Disclosure of the essence and goals of the project.
- Analysis of the industry in which you intend to work.
- Detailed characteristics of the product.
- Marketing plan.
- Production plan.
- Organizational plan.
- Financial plan.
- Analysis of existing risks.
- Applications.
Business plan: section content structure
First of all, it should be said that there is no one, universal “recipe” for drawing up a business plan. As noted in our last article, depending on the nature of the final goal, there are different types of business plans. Thus, a business plan can be focused both on an “external” addressee (potential investor) and an “internal” one (company employee, founder, department).
Business plan structure
In addition, in accordance with the specifics of the functioning of each specific enterprise for which the document is being developed, the structure and sections of the business plan can vary significantly. Obviously, the structure of an innovative business plan will be fundamentally different than the structure of an organization’s business plan.
However, there are certain modern standards for drawing up business plans. And there are many of these standards. Among the most common are:
- standard of the Federal Fund for Support of Small Business (FFSMP),
- European Union standard within the framework of the program to promote the acceleration of the process of economic reforms in the Commonwealth of Independent States (TACIS),
- and etc.
International economic institutions have developed recommendations that determine what basic information the relevant sections of a business plan should contain. According to these recommendations, the typical structure of a business plan includes:
- Title page;
- Annotation;
- Confidentiality Memorandum;
- Table of contents.
Among the main sections of the business plan we should definitely mention:
- Summary;
- Object analysis;
- Analysis of the business environment of the facility;
- Marketing plan;
- Production plan;
- Financial plan;
- Risk assessment.
Title page
The title page is the “face” of the business plan. Therefore, its design should be taken as seriously as possible, so that the reader immediately gets an idea of who and what he is dealing with.
Key points on the title page of a business plan:
- name of the project being implemented;
- name of the company or full name of the individual entrepreneur implementing the project;
- location of the company or entrepreneur (country, city);
- Contact details;
- business plan developer;
- Date of preparation
The title page may contain key financial indicators that may attract the attention of potential lenders or investors - the required amount of funds raised, the expected level of income, profit level, payback period, profitability.
Additionally, a note may be made on the title page regarding the confidentiality of the information provided in the business plan. Also, the confidentiality condition may be specified in an attached document - a confidentiality memorandum. This document stipulates a ban on distributing, copying, and transferring business plan information to third parties without the consent of the compiler.
A confidentiality memorandum might look like this:
Project Summary
The summary of a business plan can be called a short summary in which its content is concentrated. Here it is necessary to reflect all the basic information from all sections of the document. In particular, the idea, economic, marketing and financial components of the business project should be briefly described here. Therefore, they fill it out at the very end, when all the calculations and conclusions have already been made, even though this section is on the first pages.
Correctly filling out the resume is of great importance, since it is this part that often forms the opinion of the entire business plan and is designed to arouse interest in the idea proposed in it. It reflects the following information:
- the main goals of the business project being implemented;
- main characteristics of the created product;
- the target audience;
- relevance and attractiveness of the product to the target audience;
- required amount of financial investments;
- list of activities necessary for the implementation of the project;
- shares of own funds and funds of investors or creditors;
- reasonable terms for return of investment or loan;
- economic and financial indicators describing the effectiveness of the project.
The volume of a resume is usually no more than 1.5-2 pages. All information here must be confirmed by calculations and conclusions made in the relevant sections of the business plan.
Disclosure of the essence and goals of the project
This section formulates the main idea of the business project and outlines the goals of its implementation . The activities that need to be carried out to achieve these goals are indicated. It is imperative to describe factors that may be an obstacle to achieving goals, and ways to overcome them are described. It is also necessary to indicate the time frame within which it is possible to achieve the goals. All data must be objective and clearly reasoned, and, if necessary, be based on calculations.
Also in this section, a SWOT analysis is usually carried out (S - strengths, W - weaknesses, O - opportunities, T - threats). It represents a comprehensive assessment of the company's internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external environmental factors (opportunities and threats). SWOT analysis allows you to formulate an effective company development strategy.
You can conduct a SWOT analysis using the following list of questions:
Industry Analysis
A detailed analysis of market developments within the industry in which the activity will be carried out is provided here. This analysis should justify the relevance of the project being implemented and its prospects.
The following data, which should be given in the section, allows us to characterize the state of affairs in the industry:
- changes in industry sales volumes of relevant products or services over recent years;
- Peculiarities of pricing in the industry, price dynamics in recent years;
- market growth rate in the industry;
- exposure of the industry to seasonal factors;
- a list of main competitors in the market, analysis of their strengths and weaknesses;
- new companies that have recently entered the market, analysis of their activities;
- analysis of consumer demand, identification of requests, requirements, capabilities of consumers;
- industry development prospects.
An assessment of the possible impact of external factors on the industry market is also provided. This includes analyzing the possibilities of the impact of changes in the economic situation in the country and region, the emergence of new scientific discoveries and technologies, social changes and much more.
Detailed product characteristics
This section provides detailed information about the goods and services that are expected to be sold. Specifications and descriptions must be provided. It is also recommended to include photos of the products.
The main points of the section may be:
- product or service name;
- purpose of the product, features of its use;
- detailed description of the main characteristics;
- listing characteristics of secondary importance;
- main competitive advantages of the product;
- information about patents and copyrights (if any);
- the need to license a product, acquire the right to produce and sell it (if necessary);
- availability of certificates confirming product quality;
- description of the product’s impact on the environment and human health;
- guarantees, principles of organizing service;
- requirements for product disposal.
Marketing plan
A marketing plan is a detailed strategy for promoting a product or service on the market, attracting buyers and clients. An important source of information is marketing market research, which is carried out using modern effective techniques.
The marketing plan provides the following data:
- expected sales volume by time period;
- description of ways to increase sales;
- pricing policy of the enterprise;
- supply and sales system;
- customer service system;
- advertising policy with a clear elaboration of all components;
- measures to organize control over the implementation of the marketing strategy.
IMPORTANT: When operating a franchise, the marketing plan must be consistent with the marketing strategy presented by the franchisor. In most cases, a significant part of it is developed directly by the franchise owner and adapted to the individual characteristics of a particular project.
Production plan
The section is devoted to measures and decisions to create production of products necessary for the implementation of the project. This part is included in the business plan if the company or entrepreneur plans to conduct production activities.
The following indicators and information must be indicated in this section:
- the required level of production capacity to achieve the goals formulated in the business plan;
- description of the technological process;
- equipment and technical means necessary for production;
- method of purchasing or leasing equipment;
- required area of production premises;
- a list of production operations that are outsourced to subcontractors and a description of these operations;
- list of subcontractors and their characteristics;
- providing production with raw materials and supplies for manufacturing products.
When starting a franchise business, production is usually organized in accordance with the requirements of the franchisor. Often, the franchise owner also provides the franchisee with equipment, supplies raw materials, or provides a supplier base for the operation. In this regard, the production plan, like the marketing plan, is usually developed in close conjunction with the franchisor.
Clothing store organizational plan example
The company "Beautiful clothes" is a limited liability company and operates in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The enterprise is a legal entity, operating in strict accordance with the adopted Charter and Memorandum of Association, has an authorized capital, production space and balance sheet.
The founders of the company are:
- Limited Liability Company "Clothing Factory";
- individual entrepreneur Ivanov A.A.;
- Limited Liability Company "Glamorous".
The authorized capital of the organization is divided into shares: Clothes Factory LLC - 60%; IP Ivanov A.A. - 20%; Glamorous LLC - 20%.
The management of the LLC is carried out by the Board of Directors, whose members are responsible for determining the main directions of development, developing and implementing plans. The profit of the enterprise is distributed among the founders in proportion to their shares.
The initiator of the creation of the store was Clothes Factory LLC. Today, the main part of the profit of this enterprise comes from the production of clothing and its sale to buyers, however, this project involves the further development of the enterprise and the opening of a branded store “Beautiful clothes”.
Management of activities is carried out by the General Director, who is appointed by the Board of Directors. His responsibilities include: resolving the main issues of the organization’s activities, signing official documents, disposing of the company’s property, hiring and firing personnel, appointing a commercial director. The director is also responsible for the accuracy of the accounting data.
The commercial director, in turn, performs the following functions: manages the organization of marketing research and advertising campaigns, as well as the sale of goods.
Accounting and the chief accountant are responsible for settlements with suppliers, accounting for turnover, incoming profits, expenses, payment of wages, and preparation of accounting reports.
The chief designer manages the designers who create new clothing collections and sew them.
Organizational structure of the enterprise "Beautiful Clothes"
Composition and number of personnel of the enterprise Table. 1.
| Speciality | Number | Required experience | Salary (monthly) |
| Gene. director | 1 | From 10 years | 80 thousand rubles. |
| Commercial Director | 1 | From 10 years | 65 thousand rubles. |
| Chief Accountant | 1 | From 10 years | 65 thousand rubles. |
| Chief designer | 1 | From 10 years | 65 thousand rubles. |
| Designers | 4 | From 5 years | 45 thousand rubles. |
| Marketers | 2 | From 5 years | 45 thousand rubles. |
| Seamstresses | 10 | From 5 years | 30 thousand rubles. |
| Cashiers | 3 | From 3 years | 25 thousand rubles. |
| Cleaners | 2 | — | 15 thousand rubles. |
| Store administrator | 1 | From 5 years | 35 thousand rubles. |
| Deputy Administrator | 1 | From 5 years | 30 thousand rubles. |
| Sales consultants | 3 | From 2 years | 25 thousand rubles. |
In total, 29 people are involved in production and in the store itself. Expanding the staff (hiring administrators, salespeople and cashiers) is possible subject to the opening of new “Beautiful clothes” stores.
Organizational plan
In organizational terms, the system and principles of company management are being worked out. For existing companies, the characteristics of the existing management system are described, as well as, if necessary, measures to improve it.
This section indicates the organizational and legal form of the company, its location, gives characteristics to managers, describes work with personnel, etc. The structure of the company, as a rule, is presented in schematic form, reflecting the relationships between individual divisions.
Business plan: organizational plan
This section provides information characterizing the organizational structure of the enterprise, information about the personnel and the personnel policy of the company.
The implementation of any plan requires human resources. This section of the business plan should show the user that the company's organizational structure allows it to achieve the goals described in the business plan.
In order to make the right decision regarding the organizational structure, the following information is required: the work that is necessary to implement the business plan; positions; duties and responsibilities of each position; who and how manages the company in the process of implementing the business plan.
To properly manage human resources, you must first answer the following questions:
- What are the requirements for performers of each type of work required to implement the business plan?
- What qualifications should each performer have?
- What should be the salary of each performer for the successful implementation of the business plan?
- How is personnel selected?
- What is being done to retain capable and highly qualified employees?
- How are performance results assessed?
The organizational plan contains the following groups of questions.
1. Organizational structure of the enterprise:
- organizational chart of enterprise management;
- composition of departments and their functions;
- organization of coordination and interaction of services and divisions of the company, etc.
2. Management personnel are characterized from the standpoint of age, education, position, experience, authority, ownership of shares in the enterprise, functional responsibilities, advantages and disadvantages.
3. Enterprise personnel not related to management:
- the need for personnel by profession;
- qualification requirements;
- form of attraction to work (permanent work, part-time work, etc.);
- working mode.
It is advisable to present this group of questions in tabular form.
4. Remuneration: regulations on remuneration (remuneration system, bonus procedure, provision of benefits, additional payments, subsidies, moral incentives, insurance, etc.).
5. Personnel policy of the enterprise:
- principles of employee selection;
- principles of recruitment;
- creation of a system for advanced training and retraining of personnel;
- development of a method and procedure for assessing the quality of employee work;
- employee promotion system.
When drawing up an organizational plan, we recommend using tables 16 and 17.
The section “Organizational plan” justifies the need for personnel to implement the project at various levels of management. It should contain the following information:
- calculating the need for specialists of various categories and justifying the level of qualifications and remuneration;
- staffing schedule;
- proposed personnel motivation system;
- recruitment, education and training plan;
- team social development plan;
- final estimate of personnel costs.
Table 16 - Plan for personnel and wage requirements
Table 17 - Consolidated plan for labor and wages
| Category of workers | Number of employees | Average monthly salary, rub. | Labor costs, rub. | Payroll accruals, rub. | Total accrued to wages, rub. | ||||||
| 1st year | 2nd year | 3rd year | 1st year | 2nd year | 3rd year | 1st year | 2nd year | 3rd year | |||
| Managers, specialists and employees | |||||||||||
| Workers | |||||||||||
| Junior service personnel and security | |||||||||||
| Total | |||||||||||
Control questions
- What aspects of staffing an enterprise must be taken into account by the organizational plan?
- qualifications of performers
- age, position and work experience of employees
- form of employment and working hours of employees
- territorial location of the enterprise relative to the nearest populated areas
- salary
- motivational stimulation of employees
- level of intellectual development of employees
- possibility of using the labor of foreign citizens
- What groups of questions does the organizational plan contain?
- organizational structure of the enterprise
- selection criteria for potential employees
- management personnel
- enterprise personnel not related to management
- optimization of labor costs
- salary
- HR policy of the enterprise
- employees responsible for personnel selection
- Should the organizational plan include a system of personnel motivation and measures for retraining and advanced training?
- Yes, definitely. It is also necessary to justify the costs of these measures.
- Yes, but not necessarily. Such events cannot be mandatory
- No. Such costs should not be included in the organizational plan.
- Can staffing needs be dynamic according to the organizational plan?
- Yes. In the case when the enterprise is newly formed, additional staffing units may be required - installers, builders and others.
- No. Even if the company is new, you should adhere to the pre-planned composition and number of employees.
- Should the organizational plan provide in advance for methods and forms for assessing the quality of employee work?
- No. An employee who performs the planned amount of work automatically confirms his qualifications.
- Yes. An employee who promptly completes the planned amount of work for some time loses interest in the work being performed and the quality of work automatically decreases.
Financial plan
This part of the business plan is one of the most important, attracting the main attention of potential investors or creditors. It is here that it is determined how interesting the project may be to them in terms of return on investment and income generation. This section characterizes the expected profitability and financial stability of the company, which is also of great importance when assessing the prospects of investing or lending.
When developing a financial plan, the entire range of costs for starting a business and carrying out current activities is taken into account. They include, among other things, the costs of making payments to the franchisor, bank interest, etc. The section must indicate sources of financing, including own funds, attracted funds from investors, bank loans, etc. If necessary, the dynamics of exchange rates should be taken into account.
Given the high importance of the section, it is not surprising that the financial plan contains the largest number of calculations. Here the main indicators are determined, on the basis of which one can draw conclusions about the viability and attractiveness of the project. The basic data that should be reflected in the calculation part include:
- a report on the current financial condition of the company;
- cash flow forecast;
- net present value;
- investment payback period;
- break even;
- profitability index;
- internal rate of return and other indicators.
To calculate indicators, generally accepted methods should be used. For example, the break-even point is calculated using the following formula:
Main functions of a business plan
There are five main functions that help the company develop harmoniously at different stages:
- Development of the main concept, strategic path. This function is of great importance during the formation of an enterprise or during a radical change in activity.
- Planning should include an assessment of existing opportunities for opening and further development of a new field of activity, as well as control of part of the processes and execution of all sections of the business plan.
- Attracting cash injections. These can be credit or loan funds.
- The investment function allows you to interest a potential investor and attract partners to work together to make a profit.
- A competent analysis of an operating business allows you to timely, that is, at an early stage, detect problems in the organization’s activities.
Analysis of existing risks
Any business is faced with a whole range of risks that can significantly worsen operating results or even lead to the closure of the company. Therefore, when drawing up a business plan, all existing risks must be carefully analyzed. These include risks of a natural, industry, social, financial nature, etc.
The analysis lists all risks and evaluates their current and potential impact on the implementation of the project. Effective measures aimed at compensating for risks or eliminating them completely (if possible) must be presented. This section also develops models for responding to situations in which risks occur.
The final conclusion of the section should be a reasoned justification that the likelihood of risks occurring and their negative impact on the business is minimal.
Organizational Plan Structure
The main task of section () is to develop activities related to the implementation of business ideas. The “Organizational Plan” shows a potential investor that you understand how to organize an enterprise and organize its work. You have an understanding of the structure of the organization and the management mechanism.
This section should contain paragraphs about:
- form of ownership with justification;
- staffing structure;
- forms, functions, tasks of departments;
- coordination, accounting, control over the work of personnel;
- circle of responsibilities of each department and manager;
- costs associated with starting a business;
- legal security of the investment project;
- BP implementation calendar schedule.
- wages, bonuses and other incentives.
This section plans the staffing and personnel policies. It is necessary to present production, supply, and sales management systems and provide economic justifications.
You can disclose information about attracting advisors, outline a plan for social development and motivational activities.
When drawing up, indicate clear numbers, required qualifications or work experience, and justify the work schedule. The team for implementing BP is the key to success. Investors do not invest in ideas, but in knowledge and experience.
According to statistics, 98% of business failures are associated with management. To avoid missing important points, develop an organizational plan according to the diagram.
Applications
In the process of drawing up a business plan, its text provides links to documents and calculations that confirm the data, indicators, and characteristics used . These documents and calculations constitute the actual material of the business plan and are necessarily attached as appendices to it.
The appendices include contracts, constituent documentation, documents for real estate and equipment, various certificates and letters, diagrams, calculation tables, photographs, reports of independent experts and much more.
You can download the examples of business plans offered by us for free in Word and Excel formats, as well as PDF
Share your business plan