Management is a set of measures and actions aimed at coordinating the activities of employees in order to increase the efficiency of the organization. Any enterprise, regardless of its size and scope, wants to increase income and improve its level of competitiveness. The success of the company will directly depend on how well the manager understands management and coordinates the work of his subordinates.
What it is
The concept of “Management” came to us from the English language, and if translated literally, it means “the ability to lead.” It is curious that the word is familiar to almost every Russian, however, not everyone is able to explain what the essence of management is.
Agree that no enterprise can function without management, otherwise the work process would be chaotic. The art of management emerged as a separate science not so long ago, but the nature of the activity has been familiar to man literally since primitive times.
The need for management is inextricably linked with the division of labor, and man realized this even at the moment when his speech was not articulate. Why can’t society live without management? It’s easier to live this way and this is the only way to order and civilization. Over time, each person began to fulfill his assigned role. It is easier to hunt mammoths, run a farm, and build houses together, but taking into account that each member of the team will mind his own business.
Man developed, his perception changed, and strict social frameworks became an integral norm of society. Thus, gradually the realization arose that management is not a set of commands and settings, it is a full-fledged branch of science, which has its own specifics and varieties.
If we tie the emergence of management to a specific date, then it is worth mentioning 1911, when Frederick Taylor’s “Principles of Scientific Management” was published. More than a hundred years ago, management was isolated as a separate science, complex, but understandable for those who want to understand the psychology of management.
Management is usually called a set of actions and measures regarding the management of subordinates in an enterprise to achieve set goals.
In this case, when talking about goals, we mean increasing the company’s income, increasing the level of prestige, and increasing production volumes. A competent manager is obliged to know the basic principles of personnel management inside and out, which is why management is the base that connects the manager and subordinates.
“Management” is a rather multi-level concept, and it includes several aspects:
- Management talent. The manager must understand the direction in which the company is moving, what it is focused on, and what goals it wants to achieve. Based on these data, a personnel management plan is formed, basic approaches are developed to achieve the set objectives;
- Controlling function. It is not enough to give instructions; it is necessary to coordinate the process of completing tasks. In addition, it is necessary to apply methods to encourage employees and stimulate their activities. You can delegate your powers to a manager with experience;
- The ability to create a favorable climate in a team where every employee is valuable and irreplaceable;
- Ability to competently distribute human resources;
- Analysis of the market and the relevance of the enterprise. The ability to reorient employees and give new introductions.
A leader of the 21st century must become familiar with all the principles of management and skillfully apply them in practice. Management is often also called the art of managing people, where a manager must be able to guide an employee in any, even the most stressful, situation. In addition, management is a branch of science that allows universities to produce excellent managers, which the country needs, especially during a crisis.
Who does management and where to learn it
Theoretically, any entrepreneur or manager can engage in management. But in practice, specially trained managers are hired for these purposes.
Management is now taught in large private and public universities in the CIS and Europe. There are also various online courses that allow you to study remotely. Therefore, there are no barriers for people who want to study management.
A manager is a person who must control and coordinate certain processes in an enterprise. In other words, this is a manager, a leader who is responsible for the effective operation of a certain area of activity.
How long the enterprise will stay afloat depends on the manager’s strategy. Indicators of production efficiency and profit speak about the work of the manager and his team better than any words. If no one coordinated the activities of all links in the enterprise, then the working day would turn into chaos: lack of incentive to work and improper functioning of the elements of one structure.
From the electronic training course by Gennady Rekunovich
How management can help
Beginners who want to open their own business from scratch mistakenly believe that management is not worth studying, much less spending a lot of time on it. In fact, it doesn’t matter how many people you have under your command – two or two hundred, basic HR management skills are needed everywhere.
At first glance, it may seem that giving instructions and monitoring the work process is easy, but this is a misconception. A good leader becomes a “universal soldier” who understands any issue related to his field of activity. To give instructions, you must be able to show by example how exactly the work needs to be done.
An experienced manager always calculates the situation in advance, he anticipates possible mistakes and will try to optimize the expenditure of effort, money and time. Imagine that an organization changes its location. To make the move as painless as possible, it is necessary to highlight the main stages of the move, sort documents, things and equipment. A manager without the proper experience will not attach importance to the process of moving from one premises to another, which will only complicate the work of the team.
Management pursues the main goal - to establish a work process and achieve maximum team performance. There are often cases when a company mired in debt and routine was saved by a competent manager who completely analyzed the work process, found shortcomings in it and eliminated them. The best managers are led by example; their salaries are significantly higher than those of an ordinary employee, since they are able to lead the crowd, motivate and train.
Kinds
We propose to consider the main types of management, each of which is applicable to a specific situation that arose during the production process.
Familiarity with each of them provides the manager with access to basic methods of personnel management in a given situation.
Strategic management
Strategic planning of a company’s activities allows us to identify further guidelines and methods of development. A set of measures is being developed aimed at increasing the efficiency of the enterprise, and a detailed action plan is being prescribed, which must be implemented within a certain time frame.
The essence of strategic management is to bring additional income to the company in various ways. This can happen by increasing the number of sales, attracting new technologies, increasing the volume of products sold, rebranding, etc. A manager who wants to take a company to a new level of income must analyze all available opportunities and choose the best option to increase profits.
This is a difficult task that requires a lot of time and effort, however, it can significantly affect the future activities of the company and its position in the market. As soon as the plan is developed and approved, it is necessary to convey to each employee what range of powers he has, what tasks he needs to perform.
Financial management
This type involves working with the company’s material potential, as well as its effective distribution. Financial management usually concerns the activities of the financial director; he coordinates all processes related to the allocation of funds and the receipt of new money into the general treasury of the enterprise.
The financial director must objectively assess the company's financial capabilities, as well as develop a detailed plan for budget allocation. An expert in the field of finance must constantly pursue an anti-crisis policy, regardless of the state of affairs in the company. His responsibilities include maintaining the financial stability of the organization and preventing dangerous situations.
Information management
We live in an era of the latest technologies that allow uninterrupted access to information, so it is not surprising that information management has emerged as a separate type. If management wants to have a progressive company that leaves competitors behind, then it is necessary to provide the company’s employees with all the necessary software.
Thanks to the software, the work of employees becomes more efficient, they have the opportunity to access new information, analyze and quickly complete the tasks assigned to them. Managers focused on working in this area have a set of specific skills that significantly influence business advancement.
The manager's responsibilities include the following:
- Improving and streamlining office work at the enterprise;
- Analysis of the company's position in the market;
- Analysis of consumer requests;
- Work aimed at interacting with employees, processing information about each of them, financial issues, etc.
Production management
Perhaps one of the most popular areas in management today, focused on the production potential of the company. Knowledge of the basic principles of production management allows you to increase the number of sales, the volume of products produced, and strengthen the company’s position in relation to competitors.
It is extremely important for any commercial organization to have a competent manager who is able to properly organize the work of the enterprise, distribute responsibilities among employees, and also set the vector of activity. It is extremely important to have an understanding of all innovations in the field of management and to apply innovations in the process of building a work process, since the effective distribution of labor directly affects the level of sales and income.
What problems can production management solve?
- Exercising constant control over the work process. Ability to prevent mistakes that could negatively affect the company’s work in the future;
- Supervise working personnel in the process of performing assigned tasks. Apply a reward and incentive system to improve the company’s performance;
- Create all favorable conditions for an uninterrupted production process;
- Monitoring the operation of working machinery and equipment.
Production management is a comprehensive control over the main activities of the company, from the work of each employee individually to the complex production process.
Risk management
Every entrepreneur is aware that not a single company in the world has functioned smoothly. In any case, an “acute” moment may arise associated with both internal and external processes. In such situations, it is extremely important to have a pre-built plan for overcoming a crisis situation, which can be applied to improve all the company’s indicators. In addition, in the context of the global crisis and unstable market situation, large companies cannot do without a risk management expert.
How is this specialist different from other managers? He is constantly on alert, analyzing the state of affairs of the company and calculating all possible risks that it may encounter along the way of its functioning. The expert makes forecasts, warns management about the danger, allowing you to get out of a crisis situation with minimal losses for the company.
How does a risk manager work in practice?
- The expert is engaged in analytical activities, during which risks are identified. The degree of danger and the damage that can be caused to the organization are calculated;
- Next, ways out of the current difficult situation are developed;
- The expert creates a unique plan to overcome a crisis situation with detailed calculations, a description of the consequences and possible losses;
- The risk manager is constantly working, daily analyzing new data, which can significantly change the current state of affairs at the company.
A risk manager is one of the most important figures in a company, since he helps to avoid stressful situations for the company and even prevent bankruptcy.
Environmental management
In Russia, the field of environmental management is still rather poorly developed. Domestic enterprises are still more concerned about profitability, building a well-coordinated team, and competitive ability, but do not think about the damage that can be caused to the environment. In Europe and the USA they are more sensitive to this issue and environmental consciousness is more developed there.
The company's activities in the field of environmental management help to analyze whether the products produced have a negative impact and whether natural benefits are used rationally. Competent work of an expert allows you to identify ways to solve accumulated problems. For example, you can enter into contracts for waste disposal, improve production methods, reducing the amount of harmful substances released into the atmosphere.
Environmental management allows you to find alternative ways of operating an enterprise, thereby regulating its relationship with regulatory authorities and protecting it from penalties.
It is noteworthy that the “birth” of environmental management is usually associated with the 1992 summit in Rio de Janeiro. The heads of state agreed that in the 21st century it is necessary to be extremely careful about environmental issues and anthropogenic activities. Environmental management has become one of the fundamental directions for the further development of civilized countries.
Management as a special type of scientific and practical management: concept, meaning, definition
Management is defined as the integrative process by which professionally trained individuals create and manage organizations by setting goals and devising ways to achieve them.
“Management” (from the English management - management, leadership, administration, direction, ability to own) - development, creation (organization), maximum effective use (management) and control of socio-economic systems. “Management” is essentially an analogue of the term “management”, its synonym, but not to the fullest extent. The term “management” is much broader, since it applies to different types of human activities (for example, driving a car); to different areas of activity (management in inanimate nature, in biological systems, government management); to management bodies (divisions in state and public organizations, as well as enterprises and associations).
The similarity of the concepts of “management” and “management” is technologically manifested in the use of similar tools, in particular methods, principles, functions, organized structures, etc. However, their content and degree of use in centrally planned and market economies are different.
The simultaneous use of these concepts in business vocabulary is dictated by a number of reasons. In particular, this emphasizes the advancement of the domestic economy along the path of market relations. This is convenient when communicating with foreign partners, since “management” is an international word. Taking into account the above, it is quite legitimate to use the concept of “management” in modern conditions, bearing in mind its “market” semantic content.
Management is a concept that can be viewed from several angles. From a theoretical point of view, management is understood as the science of management; from the point of view of applied science, it is the organization of company management, including functions, methods, principles, management structures, etc.
Management is the effective use and coordination of resources such as capital (productive, financial and human) to achieve goals with maximum efficiency. In recent years, the importance of information resources in management has been growing, so the above definition can be expanded and information resources can be added to the list of resources.
With all the variety of characteristics that exist in the scientific literature, in a generalized form, management is understood as a management function, i.e., a type of professional activity for managing people in any sector of the economy (industry, agriculture, trade, construction, transport, banking, etc.). d.) and in any field of activity (production, sales, finance, etc.), if it is aimed at generating profit (business income) as the final result.
The management process involves performing the functions of planning, organizing, coordinating, motivating, and controlling, by performing which managers provide conditions for productive and effective work of employees employed in the organization and obtaining results that meet the goals. Therefore, management is also the ability to achieve set goals by directing labor, intelligence, and motives of behavior of people working in an organization. This is the basis for considering management as a process of influencing the activities of an individual employee, group and organization as a whole in order to achieve maximum results.
Management is a field of science, human knowledge that allows the management function to be carried out. It constitutes the theoretical basis for management practice and provides practical management activities with scientific recommendations. Science has proposed a management methodology by analyzing the content of work and identifying its main components.
If we consider management as a field of knowledge, as a science, then it represents the sum of knowledge accumulated over hundreds of thousands of years of practice and shown in the form of concepts, theories, principles, methods and forms of management. Management as a science directs its efforts to explaining the nature of managerial work, establishing connections between cause and effect, identifying factors and conditions under which the joint work of people is more effective and more useful.
The understanding of management as the art of management is based on the fact that organizations are complex socio-technical systems, the functioning of which is influenced by numerous and varied factors of both the external and internal environment. People working in and with organizations are the most important factor, the consideration of which requires not only the use of a scientific approach, but also the art of its application in specific situations.
The ability to set and implement goals, to know exactly what needs to be done and how to do it in the best way, is an art. This art must be possessed by a certain category of people - managers, whose job is to organize and direct the efforts of all personnel to achieve goals. As a result, management is often identified with managers, as well as with management bodies and apparatus. Management is a specific body of modern organizations, both commercial and non-profit. Without it, the organization as a holistic entity cannot exist and work effectively.
Management can also be considered as the organization of enterprise management, that is, the establishment of permanent and temporary relationships between divisions of the enterprise, the determination of the order and conditions of its functioning. To achieve final results, each organization in its activities transforms resources in the form of capital, raw materials, materials, technology, information, and living labor. To transform them, it is necessary to carry out various types of activities, i.e., perform certain functions.
Thus, management is management in a market environment, a market economy , which means:
- the organization’s orientation towards the demand and needs of the market, towards the needs of specific consumers and the production of those types of products that are in demand and can bring the company the planned profit;
- constant desire to improve production efficiency and obtain optimal results;
- economic independence, providing freedom of decision-making to those who are responsible for the final results of the activities of the company or its divisions;
- constant adjustment of goals depending on market conditions;
- identification on the market in the process of exchange of the final results of the activities of the organization or its economically independent divisions;
- the need to use a modern information base with computer technology for multivariate calculations when making informed and optimal decisions.
Let's consider management as a special type of professional activity. From this point of view, management is an independent type of professionally carried out activity aimed at achieving, in the course of any economic activity of a company operating in market conditions, certain intended goals through the rational use of material and labor resources using the principles, functions and methods of the economic management mechanism.
Did not you find what you were looking for?
Teachers rush to help
Diploma
Tests
Coursework
Abstracts
Management unites under its leadership the work of many specialists: economists-analysts, statisticians, engineers, psychologists, lawyers, accountants, etc. The object of management is the economic activity of the enterprise as a whole or its specific area (finance, sales, etc.).
Whatever the nature of economic activity, if it is aimed at generating profit or business income, then we can say that it is carried out with the help of management. Thus, management covers the activities of enterprises, banks, insurance companies, hotels and a number of other business organizations that act in the market mechanism as independent economic entities.
Features of the content of the economic activity of an enterprise are determined by the scope of its activity. But what is common to all areas is to provide the production process with the necessary resources and maintain its continuity. Management influences such activities as introducing scientific research results into production, improving the technological process, maintaining the required level of product quality, logistics, accounting and reporting, providing financial resources and personnel.
Management, although it plays a very definite role in the organization, nevertheless permeates the entire organization, affecting almost all areas of its activity. However, with all the diversity of interaction between management and the organization, it is possible to quite clearly establish the boundaries of the activities that constitute the content of management, as well as to quite clearly define the subjects of management activities - managers.
Management of an organization appears as a process of implementing a certain type of interrelated actions to form and use the organization's resources to achieve its goals. Management is not equivalent to all the activities of the organization to achieve final goals, but includes only those functions and actions that are related to the coordination and establishment of interaction within the organization, with the incentive to carry out production and other types of activities, with the target orientation of various types of activities, etc. P.
The ultimate goal of management is to ensure profitability or profitability in the activities of the enterprise through the rational organization of the production process, including production management and the development of the technical and technological base, as well as the effective use of human resources while simultaneously improving the skills, creative activity and loyalty of each employee.
Management is called upon to create conditions for the successful functioning of an organization based on the fact that profit is not the reason for the existence of the organization, but the result of its activities, which ultimately determines the market. The situation on the market, as we know, is constantly changing, there are changes in the position of competitors in the market, in the conditions and forms of financing, in the state of economic conditions in the industry or in the country as a whole, in the conditions of trade on world commodity markets. The consequence of this is the constant presence of risk. The goal of management in these conditions is to overcome risk or risk situations not only in the present, but also in the future.
Thus, the main tasks of management include the following:
- ensuring production automation and the transition to the use of highly qualified workers;
- stimulating the work of the organization’s employees by creating better working conditions for them and establishing higher wages;
- constant monitoring of the efficiency of the organization, coordination of the work of all its divisions; constant search and development of new markets.
- determination of specific goals for the development of the organization;
- identifying the priority of goals, their order and sequence of solutions;
- development of an organization development strategy - economic problems and ways to solve them;
- development of a system of measures to solve emerging problems for various temporary periods;
- identification of necessary resources and sources of their provision;
- establishing control over the implementation of assigned tasks.
Management tasks are continuously becoming more complex as the scale of production grows, requiring an ever-increasing amount of resources - material, financial, labor, etc.
Despite the huge variety of actions and processes, several groups of functional processes can be distinguished that cover the activities of any organization and are objects of management control:
- production;
- marketing;
- finance;
- work with personnel;
- accounting (accounting and analysis of economic activities);
- innovation.
Production management assumes that the relevant management services manage the process of processing raw materials, materials and semi-finished products entering the organization into a product that the organization offers to the external environment.
To achieve this, management carries out the following operations :
- product development and design management;
- selection of a technological process, placement of personnel and equipment in the process in order to optimize manufacturing costs and select methods for manufacturing the product;
- management of the purchase of raw materials, materials and semi-finished products;
- inventory management in warehouses, which includes storage management of purchased goods, self-made semi-finished products for internal use and final products;
- quality control.
Marketing management is designed, through marketing activities for the implementation of a product created by an organization, to link into a single consistent process the satisfaction of the needs of the organization’s clients and the achievement of the organization’s goals. To do this, the following processes and actions are managed:
- market research;
- advertising;
- pricing;
- creation of sales systems;
- distribution of created products.
- sales
Financial management consists in the fact that management manages the process of movement of financial resources in the organization . To do this:
- drawing up a budget and financial plan;
- formation of monetary resources;
- distribution of money between various parties that determine the life of the organization;
- assessment of the organization's financial potential.
Human resource management is concerned with using the capabilities of employees to achieve the goals of the organization. Personnel work includes the following elements:
- selection and placement of personnel;
- training and development of personnel;
- compensation for work performed;
- creating conditions in the workplace;
- maintaining relations with trade unions and resolving labor disputes.
Accounting management involves managing the process of processing and analyzing financial information about the operation of an organization in order to compare the actual activities of the organization with its capabilities, as well as with the activities of other organizations. This allows the organization to identify problems that it should pay close attention to, search for reserves and resources to improve performance and more effectively use the organization's potential, and choose the best ways to carry out its activities.
Innovation management is the organization of the process of scientific and experimental design work and development, the use of new products or services in the production, new organization of production and management.
These types and directions of management activities are implemented and manifested in its functions.
Goals
Now the time has come to understand what goals management pursues and why not a single successful enterprise today can do without basic knowledge of management. What do you personally mean by the word “goal”? Many of us think about our goals in life every day, but what is the goal of any business organization?
A goal can be considered a specific result of an enterprise's activities. This is the starting point from which the company begins its long journey of formation and advancement. The goals of management are exactly the same as the goals of any commercial organization, regardless of its type of activity and scale.
The main goal of management is to build a coherent work process created to generate the necessary profit for the company. The general goals of management can be considered detailed planning, forecasting and an algorithm for achieving set goals.
From the main goal we can conclude that the activities of managers are aimed at increasing the organization’s income and stabilizing the situation in the global market. Management allows you to orient workers towards achieving common goals. We are now talking about common goals inherent in almost all organizations specializing in sales, however, each enterprise is unique and has its own internal goals and objectives.
Goals allow the company to stay on the market for as long as possible, and their change and transformation prolongs the life of the enterprise, makes adjustments and allows you to move from one range of work to another. Management, aware of the goals set for it, provides favorable ways to achieve them, improves the climate in the team, and effectively distributes material and human resources.
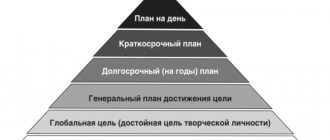
According to the time of execution, long-term, medium-term and short-term goals can be distinguished. Short-term goals are more detailed and specific, while long-term goals are more vague and abstract.
Myths and reality in the management profession
A university graduate with a degree in management is a ready-made manager . Alas, this is not true. Often, employees who work in one place for a long time and successfully cope with the same type of tasks apply for a leadership position in their department. In fact, a good specialist does not mean a good leader. The manager must not only understand the process, but also organize it correctly and monitor the progress of work.
Management and economics are one and the same . But economists are not taught strategic management, business planning, personnel management, etc. In turn, managers receive knowledge in micro- and macroeconomics, financial analysis, investment planning, and much more.
Read our article “Best Economic Universities”
“I’ll just work as a manager!” . It doesn't happen that way. To simply create a resume, you need to sign what kind of manager you want to be/are: sales manager, operations manager, online course manager, etc.
Management is a program about nothing and nothing . In fact, you will receive a wide range of universal knowledge at the university. An additional advantage of management is that a university graduate can competently conduct a market analysis and draw up a business plan for his own business. He can also write custom business plans and sell them for big money. Therefore, a person with a management degree will always find ways of self-realization.
Manager works in multitasking conditions
Tasks and functions
The goal has been set, now you need to figure out how to achieve it. Let's take a closer look at the main functions and tasks of management.
Main tasks of management:
- A set of solutions aimed at further development of the company, maintaining its status and sales volume;
- Create a favorable image for the company, presenting it as a successful partner, reliable and stable;
- Identification of new ways of development of the organization;
- Analysis of the company’s activities to ensure that the work team is provided with all the necessary benefits;
- Working with employees, creating a favorable climate in the team. An established system of incentives and bonuses that stimulate employee performance;
- Preservation and increase of capital;
- Analysis of possible risks that could lead the company to collapse;
- Comprehensive control of all areas of the company's work.
It is important to understand that the listed tasks are general in nature and each hotel organization adds several positions to this list, depending on the area and internal tasks.
A full understanding of the importance of management is impossible without familiarity with the basic functions, each of which complements our understanding of management.
Functions:
- Planning. Any enterprise sets global goals and identifies a range of main tasks that will need to be resolved within a certain period of time. Without detail and planning, it is impossible to outline the range of further actions. It is necessary to familiarize yourself in advance with the problems that await the company on the path of its formation, as well as find optimal ways to solve them. Planning disciplines, helps to optimize costs, distribute resources and production forces;
- Focus on positive results. A properly developed strategy, a strictly defined list of tasks and the presence of a single global goal greatly stimulate the work of the company. Management is entrusted with the task of conveying to each member of the work team how important the goals are and how they can be achieved;
- Competent organization of work. Chaotic behavior in the work process is destructive. It slows down the work of the company, exposing its weaknesses, so it is extremely important for the manager to competently organize the work process so that, regardless of local problems, the overall result of the team is positive;
- Coordination. The manager must be involved in the work process in order to be able to guide the employee in a timely manner, stimulate and give advice. The function is not as important as the previous ones, but it allows you to stop possible errors and shortcomings at the initial stage;
- Control. It is not enough to give instructions to workers; it is important to control all areas of the production process. Control helps in the process of analyzing the company’s activities, and also allows you to identify erroneous decisions made earlier. Control must be carried out competently and gently so that a situation does not arise when the manager hangs over the employee like a kite over the victim;
- Encouragement. Each employee is individual, he has his own views on the work process and wants to see a response to his own actions, so it is important not to ignore, but to encourage and motivate staff. To do this, it is worth thinking through the reward system in advance, allocating funds in the budget for bonuses to the best employees, and organizing joint leisure activities for employees to improve their relationships.
Knowledge of basic tasks and functions allows a manager to correctly set priorities and build a strong competitive company.
Subjects
Who can be considered subjects of management?
A management subject is a person or a team of people united by management influences, aimed at achieving the basic goals of the organization.
When we talk about the subject of management, we mean exclusively real people involved in the process of the company's work. Each of them, through assigned obligations, influences the implementation of certain tasks. In simple terms, any person is a subject of management. We manage our own lives, make decisions about moving, going to study, work, or service.
If we speak in a narrower sense of understanding the concept of “subject of management,” then we are talking directly about managers, that is, those people who manage social objects. Managers can be leaders at different levels and perform different functions, depending on the scope of their own skills.
It would be useful to mention the object of management in order to understand what the full picture looks like.
So, the object of management is everything that the management process is aimed at. The object can be a workshop, production, workers, etc. The object is hierarchical, it has a structural direction, multi-layeredness. The subject influences the object, setting in motion all the basic processes and mechanisms underlying production.
What is management in simple words + expert definitions
The concept of “management” comes from the English word “management”, which means “management” or “administration”.
You can find other translations of this word. However, the two given accurately reflect the essence of the concept by which people management should be understood. That is, management is an activity that is carried out by the heads of companies, enterprises or people among whom leadership positions are distributed.
The most precise definition of management, meaning management, was given by A. Orlov in his textbook “Management”.
“Management is a set of coordinated activities aimed at achieving set goals.”
He also cites as an example the definition of W. Siegert.
“Management is the direction of people and the use of means so as to enable the accomplishment of assigned tasks in a humane, economical, and rational manner.”
8 authoritative definitions of the concept of “management”
The authors of the definitions below mean management by management.
So management is;
- science, with the help of which you can find the best solution in a specific situation, using several options for interacting with others (V. A. Abchuk);
- organization and implementation of targeted influences (R. Buttrick);
- activities that transform an unorganized crowd into an effective productive group (P. F. Duker);
- a set of methods of interaction between elements of the production system, based on its goals and unity of functions (A. V. Karpov);
- a continuous process of influencing the control object to achieve the desired results with minimal expenditure of resources and time (W. Knorring);
- informational and purposeful process of influencing groups of people... (S. N. Knyazev);
- the process of planning, motivation and control to achieve goals (M. Albert, M. Meskon, F. Khedouri);
- a personnel administration function aimed at increasing the efficiency of the organization (A. Fayol).
Summarizing the above definitions, we can say that management is the use of various management techniques to achieve set goals and improve specific results, be it increasing the company’s profits, strengthening its position in the market or distinguishing itself from competitors.
What kind of specialist is involved in management?
We have understood the essence of the concept, touched on the main goals, objectives and functions, now it’s time to deal with the key character - the manager. Who can be called a manager, what qualities does he have, and what responsibilities are included in his work?
A manager is a person who holds a leadership position and is responsible for managing subordinates at different levels. Managers come in different levels, depending on the volume of work performed, the production segment, and the number of subordinates owned by a particular manager.
Management has its own hierarchy, where top, middle and lower level managers are represented. The top level consists of managers of large companies, while middle and lower level managers are responsible for a department, workshop, or team.
Senior managers are usually called TOP managers, and in Western countries their work is valued tens of times more than the work of an ordinary employee. In the hands of TOP managers are concentrated decisions about the development of the company, its strategic goals, as well as key issues regarding production, finance, work team, innovation and other things.
Top-level managers set the pace for the work process, while lower-level managers work to bring their goals to life. Managers communicate a lot with subordinates; this profession requires a high level of communication skills, knowledge of the basic principles of psychology, and the ability to win over and lead a crowd.
Managers can be called both managers and managers, because each of them goes towards the intended goal, but at different levels. If we talk about the practical part of the work of managers, then they form a kind of network in production or a framework through which the company functions successfully. The manager’s skills directly affect the organization’s performance, so it is extremely important today to recognize a talented manager who can minimize the company’s costs and significantly increase its income.
Examples of the best managers in the history of mankind inspire and prove how important the role of managers is and what influence they have not only on the work of the enterprise, but also on the world order. Under the leadership of TOP managers, deals are concluded with billions at stake, and the whole world, with bated breath, watches the proven decisions of famous managers.
The first one worth mentioning is the legendary Steve Jobs. One of the founders of the apple company managed to bring its profit to three thousand percent! Jobs always said that, first of all, it is necessary to have high goals and go towards them, despite all the obstacles and difficulties. In addition, according to Jobs, there are no unnecessary or trivial parts in the production process, because each of them forms an important part of a single mechanism.
An example of another legendary manager is Yun Chen Yong, who is the CEO of Samsung Electronics. Thanks to his talented leader, the company's shares soared by 1400%, and his principles of austerity and the introduction of the latest technologies are still used today. Amazon founder Jeff Bezos is considered one of the richest people on the planet, thanks to the competent promotion of his own company. Bezos claims that the reason for this was curiosity and the desire to develop, which he always teaches to his subordinates.
Each of the great TOP managers went through a difficult path to success and identified their own special “recipe” that helps them in their work. There is no consensus on what an ideal manager should be, but we have identified the main criteria inherent in an effective manager.
Main goals and objectives of management
For those who have not had experience managing at least 2-3 subordinates, it is difficult to understand what management is and why this science should be studied long and hard. It would seem that everything is extremely simple: subordinates work, and the manager observes and indicates what they should do to increase productivity and increase the company’s income.
In reality, everything is much more complicated: in order to give the right instructions, you need to clearly understand the essence of production processes. Management must be as effective as possible, otherwise it will bring losses and harm instead of benefit.
Any leader must base his work on knowledge of scientific principles and understanding of the current situation.
For example
A personnel manager in a printing house must not only skillfully manage printers and printing equipment operators, but also have a good understanding of the printing business.
One more example
You urgently need to remove the goods from the warehouse and load them into transport. A qualified manager will order the goods to be removed from the treasure in advance and distributed on the loading dock in a certain way - large and durable ones closer, fragile and small ones further away. When the vehicle arrives, movers will quickly move the items into the truck in the order in which they are located.
An inexperienced or lazy manager will not take care of the preliminary work at all, so the loaders will have to carry goods from the warehouse for a long time without any system.
The main goal of management is the harmonious and coordinated work of the organization, the effective functioning of its external and internal elements.
The specific content of management is influenced by 2 groups of factors:
- General development trends of the company;
- Territorial or national economic factors.
Local management tasks are subordinated to the main goal.
Supporting tasks include:
- development and survival of the organization, maintaining its market niche and focusing on expanding its sphere of influence;
- achieving the set results, ensuring a specific level of profit;
- creating conditions necessary for the stable existence of the organization;
- overcoming risks and predicting risky situations for the company;
- monitoring the effectiveness of the organization.
Management of the activities of a company or group of people is carried out taking into account the potential capabilities of the organization and constant correction of production processes. In large enterprises, management is divided into 3 interacting levels - higher, middle and lower.
Management structure of the production company:
How to find a good manager
A successful manager who can lead a company to success, who is he? This is a person who has not only basic theoretical knowledge about the structure of management, he is a subtle psychologist, a skilled speaker, a hardworking manager who is open to dialogue. This position should be filled by a person with a sharp mind, a desire to constantly develop and achieve their goals. It is also important to be objective and impartial.
We have compiled a list of qualities that a successful manager must have:
- Ability to inspire, guide and motivate. The manager is the face of the company, its flagship, whom every employee looks up to. There is no single rule according to which it is possible to stimulate the work of absolutely all team members, so it is important to be able to find an approach to each person, using fundamentally different methods and incentive schemes. A competent manager will be able to understand how to inspire an employee, increase the level of labor productivity and have influence and respect in the team;
- Ability to dialogue with subordinates. Many managers ignore this important point. The work team consists of people united by one goal, but each of them can see completely different ways to solve the assigned problems. It is important to be able to listen, interact, learn from experience and pay attention to constructive criticism;
- Improving your own skills. The best managers never rest on their laurels; they are constantly developing, gaining new information, and improving their personnel management skills. It is important to hone the skill of influencing others, to attend special trainings and conferences more often;
- Working time planning. Time is the most valuable resource, and a good leader differs from a bad one in that he can effectively plan not only his own working day, but also the work of his subordinates. Coordinate plans with the team, do not lose contact, start working on new projects together;
- Knowledge of the state of affairs in the team. The generalization of the manager creates a colossal barrier between him and the employees, so it is extremely important to be involved and interested in the life of the team;
- Showing creativity. Famous world-famous TOP managers broke stereotypes, allowing creativity to take precedence over a routine approach;
- Forecasting. A successful manager must see the future of the company in perspective, be aware of what work needs to be done to achieve the goals and lead the company to success;
- Belief in your own strength. All great managers were unshakable in their own strengths and capabilities. A strong-willed, self-confident manager is the driving force of any company.
When all the criteria are put together, we can say that we have before us an example of a successful modern manager who can be relied upon during a crisis. The presence of a well-coordinated management apparatus is the key to its successful functioning, therefore it is necessary to approach the process of selecting managers with all responsibility.
A good manager is worth his weight in gold; many foreign companies highly value the work of managers and are willing to pay more for it than their competitors.
The art of management is one of the most subtle and in demand, since the manager has influence on all the main processes occurring in the course of the company’s work.
Profession manager - how to become a successful leader
Who is a manager?
The dictionary definition reads:
Managers are leaders who manage subordinates. Managers can be considered foremen, heads of sections and departments, and shop supervisors. This is the middle and lower (linear) level of management. Higher echelons – heads of enterprises, companies, government bodies. They are also called “top managers”.
Top managers make the final decisions, and middle management and line managers implement these decisions. Top management is also involved in setting the goals of the organization.
Let's say the head of a company makes a decision for the enterprise to take a leading position in its industry in the current quarter. The methods by which this task will be implemented depends on middle management and line managers.
Managers are called both managers and managers - persons involved in management. Managers must have a certain number of people subordinate to them.
Today, managers are also called workers whose professional activity involves contacts with people. Such specialists often do not have subordinates, but have direct contact with the organization’s clients and partners. This type of activity is carried out, for example, by office managers and sales floor managers.
In fact, any person, excluding infants and bedridden patients, is the manager of his own affairs: he is forced to constantly plan and manage his resources.
The main resource of each of us is time. You can use it usefully, or you can waste it in vain. It follows from this that knowledge of the theory and practice of management is useful for each of us, and not just for executives.
In the modern business world, the concept of time management or “time management” is distinguished. This area of knowledge involves effective planning of your time and proper distribution.
One of the founders of this science is the popular Western author Brian Tracy. His book “Effective Time Management” is popular all over the world among managers and simply business people who want to competently organize their personal time.
Brian Tracy on time management:
In the specialized literature, the concept of “manager” is often contrasted with the term “performer”. Thus, in a narrower sense, a manager can be called someone who has at least one subordinate under his command.
In production, managers represent a kind of frame structure on which the work of the entire company rests. The company's profits, relationships within the team, and the company's development prospects directly depend on the talent of managers.
1) What a good manager should know - 7 golden tips
To become a successful manager, you must have excellent theoretical training and developed communication skills. A manager must be knowledgeable, fair, reliable and available for dialogue with subordinates.
7 golden tips:
- Build interpersonal understanding . Managers must be able to understand their subordinates and superiors. To do this, a manager must be able to communicate and be genuinely involved in the lives of his employees and colleagues. It is not for nothing that this principle comes first, because it is a healthy relationship between you and your wards that will bring the “ripe fruit” of joint activities.
- Learn to motivate those around you. It is clear that there is no incentive common to everyone, so the principles of motivating employees need to be constantly improved and changed. You must have a very clear sense of people's needs and wants. Everyone has different values, for some it is important to get an extra day of rest before their vacation, while others need material encouragement, while others simply need help solving a psychological problem.
- Keep feedback. Constantly interact with your subordinates, make communication regular: this will help you constantly stay up to date with production matters. The ability to interact and convey your ideas to the most peripheral employees of the company (including cleaners and custodians) will ensure that employees understand their tasks and goals.
- Improve your influence skills and techniques. An effective leader is not one who can force, but one who can convince subordinates that working for the benefit of the company is beneficial for themselves.
- Learn to plan. The ability to develop strategies at the stage of their creation is a necessary quality for a manager. When planning, be sure to discuss your projects with your employees - this will make your work easier, and at the same time keep your subordinates interested in the company’s affairs.
- Awareness. A good manager always knows what is happening in the organization, how its structure is structured, and what the internal culture of the corporation is. Knowledge of unofficial work methods and other “secrets of the inner kitchen” is especially useful.
- Creativity. Using imagination where an employee sees only a job description is a necessary quality of a successful leader. Sometimes an employee, when a production issue arises, does not see the problem in the future: a manager must have such a vision and be able to make non-trivial and non-standard decisions.
A successful manager never reacts to a situation, he always comprehends it (sometimes he has to do this instantly) and only after that makes a thoughtful and competent decision.
An ideal manager is a person who is interested in his work, has stress resistance, self-control, knows management theory and knows how to put his knowledge into practice.
2) Where can you learn management
Today you can learn management professionally at leading universities of the Russian Federation - in particular, at Moscow State University, the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, at the Plekhanov Economic University, the State University of Management and other educational institutions.
There are also textbooks (A. Orlov “Management”, R. Isaev “Fundamentals of Management”), schools and classes for those wishing to improve their skills, as well as video courses that can be watched for free on the World Wide Web.
Separately, it is worth highlighting the online school of Business and personal development by Alex Yanovsky (you can find many videos on YouTube). Here you can learn to think in terms of making the right decisions, learn management, entrepreneurship, and make new friends and like-minded people.
Adviсe
- A successful manager must be able to train a team and at the same time study independently; only then will he be able to keep abreast of all the latest trends and lead the company in the right direction;
- In Russia today there is a shortage of qualified managers, so the process of selecting a manager should be treated with full responsibility;
- At the moment, there are several large online business schools operating online, so you can even learn all the intricacies of management on your own;
- The manager must be aware of all the latest developments in the field of management in order to adequately represent his company on the world market;
- Read the biographies of famous TOP managers, there you can learn valuable advice that will help you build a career;
- Experts believe that management must be treated with respect, because it represents a chain of relationships in which it is important to remain human and find an approach to other people.
Universities where you can enroll in management
Currently, the vast majority of universities offer training programs in management. This suggests that management specialists are needed in any industry. Managers are trained even in sports universities, film and television institutes, etc. In such specialized universities, managers are trained in a specific field of activity, which has its own management features.
The list of the most popular universities with training programs in the field of management is quite large, we have selected the TOP 9 of them.
- Moscow State University named after M.V. Lomonosov – Moscow State University named after M.V. Lomonosov
- SPbSU – St. Petersburg State University
- National Research University Higher School of Economics - National Research University Higher School of Economics
- RUDN University - Peoples' Friendship University of Russia
- Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
- SPbGIEU – St. Petersburg State University of Engineering and Economics
- MGIMO – Moscow State Institute of International Relations (University) of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation
- REU – Russian Economic University named after G.V. Plekhanov
- RANEPA - Russian Academy of National Economy and Public Administration under the President of the Russian Federation
- VAVT – All-Russian Academy of Foreign Trade of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia
Read our article “Public service: essence, advantages, universities”
These and other universities offer the following undergraduate programs (4 years):
- Small and Medium Business Management
- Crisis management
- State and municipal administration
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management
- Marketing and management of innovative projects
- international Business
- Banking management
- Construction management
- Air transport management
- Production management
- Advertising management
- Management technologies in the digital economy
This is not a complete list of programs that you can study at universities.
Conclusion
Management is the foundation in building a business, so every manager is obliged to familiarize himself with basic knowledge and apply it in practice. The foundations of management were laid long before the registration of a direction in a separate branch of knowledge, and today without them it is impossible to increase the efficiency of the enterprise and bring it to a higher level of income. Knowledge of the basics of management allows you to “grow” competent managers, and the company to prosper and develop.
“Experts consider management one of the most popular sciences of the 21st century. Do you agree with this statement? Do you think the article helped you understand the basics of management? Write in the comments and don’t forget to rate the article!
Rate this article:
[Total: 9 Average: 5/5] (Article Rating: 5 out of 5)
Author of the article Angela Karpacheva Freelancer
Professional qualities of a leader
Among the requirements for managers dictated by the market and accumulated experience, the following can be identified:
- business planning and forecast for the development of the organization;
- identification of priority and strategic goals;
- use of traditional and innovative approaches in management;
- promoting effective methods of motivating subordinates;
- ability to exercise control.
In addition to universal management skills, a specialist in the field of organization management is obliged to ensure the effective use of the enterprise's resource base, taking into account its potential. Also not least is the ability to generate additional profit by reducing and optimizing costs.
In any case, the success of a manager’s career growth directly depends on the effectiveness of solving planned and unforeseen problems. The main thing is not to give in to frustration and stick to work schedules.