For a ship that has no course,
no wind will be favorable.
Ancient Roman philosopher
and statesman Seneca
Where to start developing a strategic plan?
What sections must be present in the strategic plan?
What methods can be used to check the correctness of the strategic development plan?
How to analyze the external and internal context of an organization?
How to formulate a mission and develop development strategies for an organization?
How to develop a business plan for the development of an organization?
How to ensure the implementation of the strategic development plan?
How to ensure the relationship between strategies, business development plans and budgets of the organization?
A company that does not have strategic development goals and specific plans to achieve them is doomed to follow current events with very vague prospects for the future. But developing a correct strategic development plan requires management to have high competencies and skills, since it involves not so much calculating business performance indicators as forecasting business dynamics, taking into account the risks and opportunities associated with both the external and internal context of the organization.
You can often come across the opinion that strategic planning is needed by large companies that have already declared themselves as leaders in their market segment and look to the future with confidence.
But, firstly, any company has a specific goal for its activities and at least an approximate business plan. And these are already elements of strategic planning.
Secondly, even novice entrepreneurs assess the size of the market in which they are going to operate, the competitive environment and their ability to enter this market. That is, they engage in strategic analysis, which is also one of the components of strategic planning.
In other words, most small and medium-sized companies in fact also use strategic planning, but, unlike large players in the market, they do it unsystematically and not in full.
And even in large companies it happens that strategic development plans developed with a lot of time and effort remain just plans. This can be caused by many external and internal factors, the most common of which are the lack of integrity in the planning methodology and disruption of the relationships between strategies, business development plans and company budgets.
We offer a methodology for developing the most effective strategic development plan and recommendations that will help avoid possible risks of erroneous forecasts, we will tell you about the sequence of forming a strategic development plan, and we will reveal the relationship between the context, goals and resources of the company, which should be reflected in the strategic development plan.
Of course, the strategic development plans of large, medium and small companies will differ due to the difference in the scale of economic activity, the specifics of the business, the complexity of the organizational structure and business processes.
But in any case, a well-developed strategic development plan is formed on the basis of sequentially implemented stages:
What is it for?
The business structure of an enterprise is designed to ensure the development of the organization as a whole. Its presence allows the responsible team to quickly make a decision, determine the area of responsibility and quickly transfer information to the required structural unit.
The organizational structure of a company's business is not something static; it can change quite often, adapting to changes in the economy. This is due to the fact that any ambitious manager strives for his company to interact with other organizations as productively as possible, and for employees to perform their duties efficiently.
Strategy Development
If you want to rule the world, you need to draw up a clear plan. Yes, the time has come. It's time for us to develop our own business strategy.
We use the approach proposed by Toyota marketers; the Japanese will not advise anything bad.
Take a blank sheet of paper and divide it in half. The present time will be on the left, the future on the right.
Each column will have three lines, which must be filled in from top to bottom. Just don’t put this off, elephants won’t sell themselves.
This is how we divide
The first line in the left column is the background, one might say the mission. It sets the general direction, so it should not be too extensive.
Briefly write down what you want to achieve. Let me remind you that we are talking about your goals in business, and not about your life goals.
The second line is the current situation. Here you can not skimp on the description; it is better to formulate everything in sufficient detail, focusing separately on the description of existing problems and shortcomings.
The third line is analysis. Try to determine why the goals were not achieved, and for what reasons the problems that currently exist in your business arose.
The first two lines will help you with this, which clearly demonstrate what you wanted to achieve and what happened.
The present
Finally, we move on to forming a strategy. I warn you right away that this process is very difficult and cannot be written in one day. You need to take into account all the risks and conduct a market analysis. So let's get started:
The first line is the goal. We take previous conclusions as a basis and formulate tasks for the future.
Just set realistic goals, otherwise it will be a shame if you still don’t get the planned billion dollars of net profit in a year.
The second line is a plan for implementing tasks. There is no need to describe everything in detail, but you should not formulate too general and global tasks. Remember the SMART rule.
Third line - what's next? Imagine, in the good sense of the word, what you will do after completing the plan outlined above.
Future
The minimum indicators that we achieve with the help of a business strategy should not be the limit of dreams. Develop yourself. Who knows, maybe elephants are just the beginning.
How the structure of an enterprise can change
The hierarchical structure is a collection of many departments, such as the sales department, production department, accounting department, the main function of which is to provide resources for activities.
The structure of a business can undergo changes if, to solve certain problems, by order of the manager, process units are created that deal with more specific issues. For example, a group of sales managers may be formed who work on individual orders. This organizational structure is called a matrix, or two-armed. It may look like this:
strategies to increase profits
Now let's look at strategies that will help you increase your company's profits, so I advise you to keep them in mind when you develop your own.
You, of course, have heard about them, and many textbooks write about them. But we are practitioners, so I will tell you without boring theory and with examples.
By the way. Do you want to double your sales and increase business efficiency? Then implement CRM quickly! I recommend Bitrix 24 and Megaplan (“Megastart” 10% discount on everything + 14 days free). Then you will say thank you.
Concentrated Growth
Here you need to focus on the product or service being produced. Refresh old ideas, or prepare something completely new for launch.
The main tools here are product policy and market research (a video on this topic is below).
A good example of this basic strategy is introducing elephants to an emerging market in another country where our direct competitor, a company that sells gray elephants, operates.
We need to invest in advertising, convincing that an elephant is much better than a rhinoceros. And also carry out various events to strengthen the idea.
Integrated Growth
This business strategy is suitable for expanding the company by building additional structures, creating additional branches, and changing the very structure of the relationship with the end consumer.
For example, you can buy a company that resells our elephants at its own markup and take their profit for yourself.
It turns out to be a pretty good option. And by the way, another unusual strategy of this type is below in the video.
Diversified Growth
Usually this strategy is resorted to when there is no other choice: the market is oversaturated with supply, competition is too high, or a new, high-tech product has appeared.
Its trick is that you share your risks. That is, you are expanding your product range or going in a completely different direction.
For example, if someone starts selling flying elephants, and the demand for our pink ones begins to fall, then our company will have to urgently either expand the line and introduce flying, talking and yellow elephants, or produce dinosaurs together with elephants. And you can also buy your competitor if you have enough money.
Reduction strategy
The constant development of technology will sooner or later lead to the fact that our product will lose its relevance. Therefore, if you notice that you are riding a dead horse, get off.
Reducing unprofitable production is a painful step, but sometimes necessary. Especially if we are still trying to sell wingless elephants.
By the way, the video below presents a pretty good strategy for this type of business.
More about matrix structures
In this type of business organization, process units lease resources from major departments in order to perform specific tasks. To implement such projects, groups of employees are created and allocated to the main departments. Workers united in such groups are subordinate to both the main manager and the process manager.
To avoid misunderstandings, an agreement is concluded between the employee and the two managers, on the basis of which the resource department is responsible for the quality of the task performed by the employee.
A business structure organized according to a matrix type has a certain advantage: the presence of clear requirements for process structural units increases the efficiency of the resource unit.
This type of organization is most widely used in project companies and where there is a high variety of business processes. This structure is also useful in that it creates market relations between departments and reduces the number of top and middle managers.
An example of a successful company that uses a project structure for various types of software products is MicroSoft.
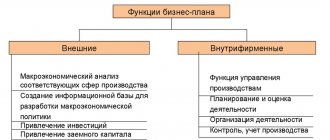
Structure and brief description of sections of the business plan
The content of a business project, as a rule, is usually compiled according to the classical structure. The total volume of text should not exceed 80 A4 pages. Additional materials can be included in appendices to the work.
Remember! The table of contents must include not only all items, but also page numbers.
The work must contain chapters, the completion of which is mandatory even for a simple, standard business plan:
- Abstract or appeal to management or investor.
- Summary, introductory information.
- Direct business plan.
SWOT analysis for a business plan is required.
In a broad sense, the document should consist of:
- A title page on which you should display information about the name of the project, the name of the company for which it was developed, the territorial location of the hero of the occasion, the date of development and the approximate date of exit from the project.
- Summary of the project, that is, conclusions about the calculations performed. As a rule, experienced businessmen or creditors carefully study only this chapter. As introductory material, you can indicate the purpose of the work, how much cash injection will be needed at one stage or another, a general description of the future brainchild, distinctive qualities and advantages over competitors.
- Organizational plan. It is necessary to describe the legislative and regulatory documents that permit the conduct of this business. It is also recommended to display the deadlines for the implementation of all points of the business plan.
- Financial plan. The success of the entire event largely depends on this section. This chapter should consist of income and expenditure parts for several years. It is also necessary to calculate the break-even point with and without investments.
- Descriptions of risks or circumstances that could have a negative impact on the results of operations. Here it is necessary to analyze possible risks and describe in detail how to solve them.
Attention! All data and decisions must be supported by numbers. No investor will invest in “far-fetched” work or “inflated” indicators.
Step-by-step calculations are required
Classification of company strategies
Business structure can also be classified depending on the level at which strategic decisions are made.
It is customary to distinguish three types of strategies:
· corporate;
· business;
· functional.
It is worth noting that to achieve success, all strategies must be closely interconnected and coordinated, and structural units must interact with each other. Next we will talk in detail about each of them.
1. Corporate strategy
This is the highest level according to this classification within the concept of “business development structure”. Corporate strategy determines the general direction of the company's development and the dynamics in its sales activities. One of the most important goals of corporate strategy is to determine the direction of activity within the company and identify where investments should be directed.
At this level the following issues are resolved:
1) on the distribution of resources between structural units;
2) about changing the structure of the organization;
3) resolving issues related to mergers with external structures.
2. Business (competitive) strategy
At this level, the organization’s business behavior is developed, aimed at creating competitive advantages for a specific product market. Within the framework of this strategy, the pricing policy is determined and it is decided how the company will gain the upper hand over its competitors. At this level, a business plan is developed. In companies with the same type of activity, corporate and competitive strategies coincide.
3. Functional strategies
Structural divisions of the company are responsible for their development. The corporate and economic strategies are necessarily taken as the basis for the functional strategy. It is designed to ensure the effective functioning of the unit within the framework of the business policy of the enterprise. Here it is appropriate to talk about the strategies of the financial department, human resources and marketing departments.
In particular, the main objective of the production department may be to increase the quantity/quality of products produced. A financial strategy can be aimed at increasing profits and reducing costs.
Examples of enterprise models
Typical process structures
Standard business process structures (Process Frameworks) were developed by the Group as a methodological basis for building models of business processes of real companies. Typical structures are provided in PDF format for reference and in XML format for use in Business Studio (available for download on the Self-Download Packages page).
Provision of services (PDF)
Project activities (PDF)
Production (PDF)
Management company (PDF)
Unique opportunity
You can diagnose your company based on typical process structures to identify the most problematic areas. Diagnostics are carried out using the online organizational diagnostic system BIZDIAGNOSTICS.
Business process models created in Business Studio
This section contains examples of business processes - educational models and models of business processes of real enterprises, created in the Business Studio system.
Models are published in HTML publication format, automatically generated by Business Studio. The HTML publication contains diagrams of the enterprise's business processes, examples of organizational structures, main regulatory documents (Process Regulations, Procedure Regulations, Division Regulations, Job Description) and management information with the ability to navigate between documents via hyperlinks.
Attention!
The document templates used in the business models are for demonstration purposes only. The format, structure and composition of information in Business Studio output documents generated when building business models can be customized to the needs of a specific company.
Manufacturing plant model
Characteristics of the enterprise
Main activities:
- Production and sale of aluminum profiles;
- Production and sale of auto components.
Number of personnel: 1200 people.
Model description
The model is a localization of the 8-process normative model of the organization's business processes. The goals of creating a model are preparation for automating business processes (creating a “as it will be” model, taking into account the use of a future information system), creating technical specifications for automation.
Model includes:
- Model of business processes and procedures;
- Organizational structure of the enterprise;
- List of documents used when performing business processes of the enterprise;
- List of functions of the future information system.
To plan automation, the model establishes a connection between processes and the functions of the information system. As a result, a technical specification for automation was automatically generated, including:
- List of business processes of the enterprise that are subject to automation;
- List of documents and reports that must be obtained using the information system;
- List of all functions of the information system;
- List of planned jobs.
Technical specifications for automation
Regulatory 8-process model of activity of a manufacturing enterprise
The model was developed personally by the leading Russian specialist in the field of organizational development of companies T.R. Kadyev. Can be used as a basis for subsequent localization at a specific enterprise.
Model includes:
- A business process model that describes the activities of an enterprise;
- The organizational structure of the enterprise, built on a process (cross-functional) principle;
- List of documents used in business processes of the enterprise.
The principle of constructing a business model is to identify the main management objects of a business system and design the processes for managing these objects: (business processes, development strategy).
| Control object | First level process |
| Business system | Development of agreed operating conditions |
| Product | Product development and modification |
| Client | Promotion and sales |
| Production cycle | Product manufacturing |
| Resources | Logistics support |
| Technology | Reproduction of means of production |
| Staff | Reproduction of labor resources |
| Finance | Financing of activities and settlement of obligations |
The result of the execution of the first level processes is the control object brought to the required state. Processes of the first level are decomposed into subprocesses necessary for the sequential transformation of the state of the control object from the initial one to the required one. For each subprocess, goals are set that must be achieved within the framework of the subprocess. The tree of goals obtained in this way provides a decomposition of the strategic goals of the enterprise down to the level of specific performers.
Model
Model of a company engaged in the design, installation and maintenance of engineering systems.
Model includes:
- Model of business processes and procedures, including goals and process indicators;
- Organizational structure of the company;
- Financial structure of the company;
- Budget structure of the company;
- Section of the QMS containing the requirements of ISO 9001:2000 and ISO/TU 16949, Quality Manual;
- The structure of the information system and the Technical Specifications for automation.
This model is contained in the demo version of the Business Studio system.
Model of production activities in accordance with ISO 9001:2000 standard
Growing competition between Western and domestic companies for the right to dominate the Russian market of goods and services forces the latter to more actively use modern management methods, in particular, the construction of a quality management system (QMS) that meets the requirements of ISO 9001:2000. This standard is a set of requirements for subsystem of quality management of manufactured products or provision of services to the organization. A functioning QMS allows us to assert that the organization is able to produce high-quality products (provide services) on a regular basis, and therefore has great advantages over competitors. However, building a QMS is not an easy task, often requiring the organization to make significant changes to its production and economic activities and to the business processes of the enterprise. To facilitate understanding of the requirements of the ISO 9001:2000 standard itself, as well as as an example of constructing a QMS, a model of the activities of an organization producing products is proposed. The model includes all standard processes, from design to product after-sales service.
IDEF0 functional modeling notation was used to describe the organization model. The top-level processes of the model correspond to the key sections of the ISO 9001:2000 standard, then they are decomposed into lower-level subprocesses directly in connection with the production and economic activities of the organization. Thus, the model represents a set of business processes of an organization with the requirements of ISO 9001:2000 integrated into them. At the same time, there are limitations in interpreting the requirements of the standard (translating them onto the activities of the organization), due to the fact that a fairly conventional organization was taken as a basis , without any industry specifics. In this regard, in practice, such a model can be used as a basis for analyzing the compliance of an enterprise’s activities (by areas of responsibility - sections of the standard) with the requirements of ISO 9001:2000, as well as as a normative model for the development and implementation of a QMS.
You can submit your suggestions and comments on business process models by email: [email protected]
Business development strategies. Kinds
At the level of corporate strategy, four approaches to company development can be distinguished. Let's look at them.
1. Limited growth. This strategy is chosen by companies with stable technology. Goals are determined depending on what has been achieved to date and undergo adjustments if external conditions change. This is the simplest and least risky method to implement.
2. Growth. It is most successfully used in rapidly developing industries where technology changes frequently. The method used here is to compare the indicators of the current period compared to the previous one.
3. Reduction. This strategy is characterized by setting targets lower than those achieved in the past period. This method of development is chosen most rarely and is typical for companies where there is a tendency to decrease profits and there are no effective solutions to change the situation.
Within this strategy there are:
1) liquidation (the company is no longer able to conduct business);
2) obtaining the maximum possible income in the short term (a business can bring significant income at minimal costs);
3) reduction (the organization parts ways with one of the business areas/structural divisions).
4. Combined strategy. It is typical for large businesses (the presence of several industries) and can be a combination of any three strategies.