The main task of every commercial structure is to generate regular profit by doing business. Profit represents a certain portion of the funds received from the sale of commercial products or services. In order to determine the amount of profit, it is necessary to subtract from the company's income item all costs associated with production, depreciation expenses, employee salaries and other costs. Receiving regular profits allows the company to improve its financial condition, increase its equity capital and develop new market segments. In this article, we propose to consider the question of how to calculate profit from product sales.
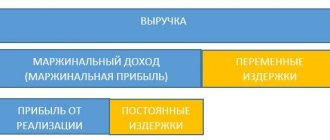
In general terms, profit is the difference between the funds received from sales and the costs of the enterprise
Profit from sales: what is it?
Profit received from the sale of commercial products is the ratio of the enterprise's income to the item of production costs . When making calculations, not only the costs of purchasing raw materials are taken into account, but also the costs of paying hired personnel, organizing the storage of finished products or sending them to the final point of sale. It is important to note that in the early stages of an enterprise’s activity, this economic indicator may be zero. In more difficult economic conditions, the profit margin may be negative. The only effective way out of this situation is to develop a strategy that can significantly reduce production costs and increase business profitability.
The concept of profit from the sale of products means the total amount of financial resources received through the sale of goods minus large expenses.
It is important to note that the concept of “income” has several meanings. In the accounting field, this term refers to funds received through business activities.
It should be noted that in the case of “accounting income”, explicit costs are deducted from this item. The economic indicator has only one fundamental difference. To determine the amount of profit, additional costs of an indirect nature are subtracted from the income item.
What you need to know when calculating net profit
Accounting
When calculating net profit, the main difficulties arise when recording income and expenses in various financial documents of the company, such as accounting, tax and management accounting. Among the main reasons for the occurrence of inconsistencies is the following:
When accounting for income:
The main problem lies in different methods of accounting for revenue. Thus, in accounting, the accrual method is mainly used, while in tax accounting, both the accrual method and the cash approach can be used.
When accounting for expenses:
While in accounting accounting absolutely all expenses are taken into account, in tax accounting certain types of expenses are not taken into account, in particular those that are covered from the personal funds of an individual entrepreneur (private entrepreneur), for example, fines and penalties paid, daily allowances for business trips.
When creating reserves:
This includes pledged payments of bonuses to employees, vacations, and unexpected debts. In tax accounting, reserves may not be taken into account at all, whereas in accounting, their accounting is mandatory.
Due to the difference in the approach to calculating income, expenses and reserves in accounting and tax accounting, the final net profit figure will be different.
Other important points to consider when calculating net profit:
- The calculation must be made “accrual” - after the goods have been shipped or the costs have been written off, regardless of whether actual payment has been received or not;
- To carry out calculations, you need to take data from profit and loss documents;
- Net profit is usually calculated once a month (usually at the end of the month);
- The calculation of net profit can be automated using special programs;
- At the end of calculating net profit, you must remember to subtract the costs of paying all taxes and fees.
??
It is also worth saying that in order to record the net profit of an enterprise, it is worth creating a separate document, for example, in Microsoft Excel, and filling it out at the end of each month.
This document can be compiled as in the example below:
Example of a document for recording net profit
It can be compiled for any of the reporting periods: month, quarter, year.
What does the indicator depend on?
There are several main factors that have a direct impact on the size of the indicator under consideration and its nature . The main factor influencing the profit margin is the amount of income the company received over a specific time period. An increase in the volume of revenue received from the sale of commercial products leads to an increase in profits. In order to determine the amount of revenue, it is necessary to multiply the cost of one product by the total number of products sold. According to experts, maximum profits can be obtained only if there is a wide range of commercial products.
Another important factor affecting profit margins is production cost . This indicator allows you to determine the amount of costs associated with the sale of manufactured products. As a rule, when calculating production costs, the following costs are taken into account:
- Purchase of raw materials.
- Employee salaries, tax payments and mandatory contributions.
- Payment of utility bills, costs of organizing storage of finished products and consumables.
- Transportation of finished products.
The main task of every entrepreneur is to reduce this item by concluding more profitable contracts with suppliers, optimizing the technological process and other factors.
From the above, we can conclude that this indicator is closely related to several key factors that must be taken into account when conducting economic analysis.
Profit from sales reflects the profit that was received after deducting all expenses that were associated with the sale
Analysis of profit and profitability of the enterprise
The goal of any commercial enterprise is to ensure that the activity is as profitable as possible, that is, all existing costs (for raw materials, labor resources, marketing and advertising, etc.) are repaid. Despite the fact that the company’s position is influenced by market conditions (presence of competitors, market factors), the financial condition must be regularly assessed to determine whether the costs incurred are bringing the expected results. You can draw conclusions about how profitable and successful a business is by considering two indicators, which include profit and profitability.
You can analyze the profit of an enterprise using various techniques.
The following types of analysis exist:
- structural,
- factorial,
- temporal,
- comparative,
- index.
Using structural analysis (analysis of the constituent elements in the profit structure), an entrepreneur can determine what share of total income is occupied by funds, the sources of which are both the main and non-core activities.
The amount of income can be calculated as follows:
Percentage of operating activities = Sales profit / Profit before tax.
Percentage from other operations = Profit from other operations / Profit before tax.
Changes in the profit structure allow us to draw conclusions about how profitable the operating activities are. If a company receives more free cash from auxiliary operations, then the existing business model is ineffective.
The factor analysis technique involves research showing how profit depends on the influence of various factors:
- cost of production per unit of production;
- the size of the wage fund;
- sales volume;
- selling price of the goods.
This method allows you to find relationships between different values of one variable. For example, find out how the gross profit of an enterprise will increase if revenue increases by 1 ruble, that is, understand how the increased sales volume will affect the final result.
You can also analyze profits from the point of view of analyzing changes in dynamics, that is, by comparing indicators in the current and past periods. For example, to track how the size of an enterprise’s revenue has changed: to calculate it, you need to divide the revenue received in 2020 by the corresponding index for 2020. We can talk about growth if the resulting result is greater than one.
The essence of comparative analysis is that the key indicators of the economic activity of an enterprise are compared with similar values of competing firms.
Index analysis of the level of profitability gives an idea of how profitable the company's activities are. This technique also involves comparing the indicators of the planned and past periods, which allows us to draw conclusions about increasing business efficiency or stagnation. Profitability shows how much profit the company receives from each ruble spent.
Calculation of profit and profitability of an enterprise:
- Total profitability ratio = Book profit / Revenue × 100%.
- Gross Margin Ratio = Gross Profit / Revenue × 100%.
A similar calculation shows how profitable assets or capital are.
You may also be interested in: How to calculate ROI: formula, examples
How to calculate profit from sales
In order to determine the amount of profit that was received by selling commercial products, you can use one of the following methods:
- Preparation of direct calculations.
- Identification of the amount of income per unit of expenditure.
- Use of analytical tools.
Below we propose to consider in more detail each technique and practical examples of compiling calculations.
Direct determination method
This method is more appropriate to use in situations where a manufacturing company produces a small product line that has a fixed cost. It is important to note that calculations are made taking into account the characteristics of each product group. Here you should take into account both the amount of production costs and the final cost of the product. In addition, the production plan is taken into account, according to which a certain number of units of commercial products are produced.
In order to better understand the procedure for making calculations, a practical example should be given. Let’s imagine an enterprise that spends fifty rubles on the production of one unit of goods. The planned final price of the product will be seventy-five rubles. The company's general production capacity allows us to produce up to 1,000 products monthly.
Having all the necessary data for making calculations, you can begin to calculate the amount of planned profit. To do this, it is necessary to subtract all production costs from the final cost of the products: “75 – 50 = 25 rubles.” The result obtained should be multiplied by the volume of commercial products produced during the month: “25 * 1000 = 25,000 rubles.” Drawing up such calculations allows us to determine that the size of the projected profit will be twenty-five thousand rubles.
Per ruble expenses
This method allows you to determine the amount of money received through the sale of marketable products per one ruble of production costs. As a rule, when making such calculations, the full volume of the product range is taken into account. This means that using this methodology to make calculations for one type of product is impractical.
To compile calculations, it is necessary to have basic information about the amount of production costs, revenue received in past periods and the planned income of the enterprise.
Profit from sales of products formula:
“Wholesale cost – cost of goods = profit.”
The entrepreneurial activity of any enterprise is always aimed at making a profit, which is designed to cover losses
The next stage of calculations is to determine the level of profitability. Profitability is the ratio of profit from sales to revenue for a certain time period. However, in our case it is necessary to calculate the ratio of profit and cost of production of one product. For this purpose, the formula is used: “(Net profit / cost) * 100% = profitability of the enterprise.” According to experts, the company's profitability level should exceed ten percent. In order to determine the amount of profit received for each ruble spent, the formula is used: “Cost / final cost of goods.”
Let's look at another practical example that explains the procedure for making calculations. Let's imagine a company that spent seventy-five kopecks per ruble in the last reporting period. In the near future, the company plans to release to the market a batch of commercial products worth a total of twenty thousand rubles. In order to reduce the cost item, a strategy was developed to reduce the cost by one ruble in the amount of ten kopecks.
In order to determine the profit per ruble of costs, it is necessary to perform a certain procedure. First of all, it is necessary to calculate the cost of production per 1 ruble: “75-10 = 65 kopecks.” From this example it is clear that for production, the cost of 1 ruble of production is sixty-five kopecks. Since the volume of the planned batch of goods implies the production of products with a total cost of twenty thousand rubles, it is necessary to perform the following calculations: “0.65 * 20,000 = 13,000 rubles.” Thanks to these calculations, it was revealed that the total cost of goods will be thirteen thousand rubles. The next step is to calculate the amount of profit that will be received after the sale of this batch: “20,000 – 13,000 = 7,000 rubles.”
Based on the above example, we can conclude that with a cost of one ruble, the company will make a profit of thirty-five kopecks. The main distinguishing feature of this calculation method is the maximum accuracy of the data obtained . The only significant drawback of the methodology is the inability to take into account various factors that influence changes in the volume of the indicator under consideration.
Profit represents the net income a company receives from its activities
Analytical
The use of analytical techniques allows you to determine not only the size of the planned profit, but also to evaluate various factors that have a direct impact on the production process and the sale of finished goods . When making such calculations, it is necessary to take into account the size of the product range, the quality of the products offered, the size of production capacity and the cost of production. Indicators such as return on sales, marginal profit and wholesale cost of goods play a significant role in such an assessment.
The use of the analytical method allows us to identify factors that have a high level of influence on the company’s profitability. Based on this analysis, various strategies are drawn up to increase the volume of sales of goods and the overall revenue of the company. It is important to note that the method under consideration allows us to determine the amount of planned income in several areas.
Before making calculations, it is necessary to obtain information about whether the selected product was manufactured according to the planned schedule. In the case where products were manufactured according to the production plan, data for previous reporting periods is used. In the event of the launch of a new product line, the parameters used for incomparable products are applied.
The essence of the concept, simple examples and calculation formulas
Net profit is the final portion of income remaining after paying taxes, wages, rent and other obligatory monthly expenses. The amount of net profit is one of the important indicators for any enterprise conducting business activities. Based on the results of calculating this indicator, one can judge the financial condition of the enterprise, its competitiveness and solvency. If there is an increase in profit margins, this indicates production efficiency. The opposite dynamics indicate unprofitability and imminent bankruptcy of the enterprise.
The formula for calculating net profit looks like this:
Revenue – Cost of sales – Administrative and commercial expenses + Other income – Other expenses – Tax
Or
Profit before tax + Extraordinary income – Extraordinary expenses – Tax
Let's give a simple example. The individual entrepreneur decided to start selling household appliances via the Internet. After three months of work, you can observe the following financial result:
- Income from the sale of goods amounted to 680,000.
- Total expenses amounted to 600,000. 350,000 were spent on the purchase of household appliances, 50,000 on the creation and maintenance of the website, 100,000 on advertising of goods, and other expenses (return of defective goods, repair of equipment, discounts, etc.) - 100,000.
- 680,000 (income) – 600,000 (expense) – tax % = Net profit
This calculation clearly demonstrates that the individual entrepreneur remains in the black and has income that he can use for personal purposes or invest it in the development of his business, in this case an online store. Unlike small businesses, calculating the net profit of large organizations is much more difficult. First, the composite income and expenses are calculated, and only then the net profit is calculated.
There are other formulas for calculating this indicator. At first glance, they seem different, but in meaning and result they are the same: all income and expenses are added up separately, then the amount of expenses is subtracted from the amount of income and the tax is subtracted from the resulting amount.
Net profit can be calculated using the basic (expanded) formula:
Sum of financial, operating and gross profit – Tax percentage
Each type of profit is calculated separately:
- Financial = Financial income – Financial expenses;
- Operating = Operating income – Operating expenses;
- Gross = Sales Income – Cost of Products.
As an example, let’s take a large company and calculate its net profit for 2020.
| Income and expenses | Sum |
| Sales of goods | 2.5 million rubles |
| Product cost | 1.5 million rubles |
| Warehouse rental | 200 thousand rubles |
| Financial investments | 15 thousand rubles |
| Income from financial investments | 300 thousand rubles |
| other expenses | 150 thousand rubles |
Based on the table data, we calculate gross, financial and operating profit, as well as taxes.
Gross = 2,500,000 – 1,500,000 = 1,000,000
Financial = 300,000 – 15,000 = 285,000
Operating room = 200,000 – 150,000 = 50,000
Taxes = (285,000 + 1,000,000)*20% = 257,000
Now let's calculate the net profit:
285 000 + 1 000 000 – 257 000 = 1 028 000
If the company has a large debt, then the calculated net profit should be considered a loss, which will show to what extent it is possible to repay existing debts to creditors.
Analysis of the obtained indicator
Factor analysis of profit allows you to determine the effectiveness of the company's financial activities. To compile such calculations, accounting reports are used, which record all financial transactions during the reporting period. When making calculations, as a rule, the amount of gross profit received through the sale of released goods is taken into account.
The size of this indicator is determined by the volume of revenue and cost of goods sold. When calculating one unit cost of a product, natural expressions (liters, pieces or tons) are taken into account. Next, a graph of changes in market demand for the model range presented by a particular company is drawn up. To calculate the volume of gross profit, the formula “Revenue – cost of goods sold” is used.
The need to compile these calculations is explained by the need to calculate the amount of tax deductions. Profits are taxed at a rate of twenty percent. Most of this amount goes to the regional budget, and the rest goes to the state treasury.
The concepts of profit and revenue cannot be considered equivalent
Balance line
Financial accounting statements are heterogeneous; they include several documents filled out separately by economists. Among them is the income statement, which, in turn, includes the balance sheet.
Important! In accordance with the provisions of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 “On Accounting”, reporting means the provision of reliable data on the results of the company’s work and cash flow.
Revenue: line 2110
The line is intended to reflect information about revenue (profit received from ordinary activities). Let us remind you that, in addition to revenues from sales of products, goods and services, this includes the following income items:
- for work performed;
- license fees, commissions and royalties;
- rent;
- proceeds related to injections into the authorized capital of other companies.
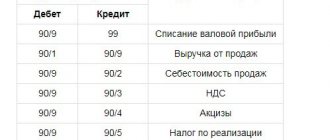
Accounting entries
Profit from sales of products - there is no line in the balance sheet reflecting this indicator. To reflect the value of this indicator, several lines are used, including “Cash,” “Sales Expenses,” “Revenue,” “Cost,” “Profit and Loss.” In order to determine the size of this indicator, you must perform the following steps:
- Line 50 (Cash) / line 90.1 (Revenue).
- Line 90.2 (Cost of sales) / line 41 (Products).
- Line 90.7 (Sales expenses) / line 44 (Sales expenses).
- Line 90.1 (Revenue) / Line 90.9 (Profit / Loss).
- Line 90.9 (Profit / Loss) / line 90.2 (Cost of sales).
- Line 90.9 (Profit / Loss) / line 90.7 (Sales expenses).
Compiling such calculations allows you to determine the size of the credit balance, which reflects the total profit obtained through the sale of marketable products.
Profit rate
The rate of profit is considered one of the basic concepts in the field of economics, expressed as a percentage and defined as the ratio of surplus value to the total capital advanced. It is calculated using the following formula:
Rate of profit = Mass of surplus value / (Constant capital + Variable capital)
The cost of goods and services produced depends on the rate of profit. The indicator itself is influenced by internal production and market factors. Intra-production factors include the amount of profit, costs incurred, scale of production, cost reduction, capital turnover. Market factors include average market value, supply and demand, competition and monopoly in the market.