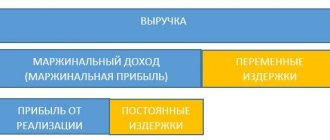
One of the factors of economic growth is the increase in the purchasing power of the country's citizens. On its basis, gross domestic product is calculated, demonstrating the economic well-being of people and the financial stability of enterprises. The indicator includes the monetary value of goods (services) that will be used by people. Changes in this indicator affect inflation. Macroeconomic research is important for the economy of any state. Based on these data, experts study the dynamics over certain periods and draw the following conclusions:
- about financial stability in the country;
- about the level of well-being of citizens.
What is a deflator?
A deflator is a statistical coefficient. It is necessary for the correct recalculation of financial indicators in monetary terms. The main task of the deflator is to bring current price indicators to specific prices of the past time period. In numerical terms, the deflator can be compared to the price increase index. That is, the deflator is an indicator demonstrating the value change in consumer and industrial goods. This is a statistical technique that smooths out the difference between the market price and the base price. The main indicators used for recalculation:
- GDP deflator (GDP);
- GNP deflator (DVNP).
GDP and its indices
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a macroeconomic indicator. It denotes the cost characteristics of goods created within the territorial boundaries of the country over a certain period of time. The GDP deflator is also called the indirect price deflator. It shows the ratio of the total price of a set of consumer goods (services) of a given year to the total cost of the same set in the base year. The indicator demonstrates how much the decrease or increase in GDP in basic prices of the year occurred due to changes in the price level in the economy.
When calculating the GDP deflator, two GDP indicators are used:
- nominal, corresponding to the current state of affairs;
- real, corresponding to the base period.
There are two ways of calculation:
- In the first, the agreed set of goods in the base prices of a particular year is taken as a basis. The numerator is equal to the cost of products produced during the base time period at current prices. The denominator is the indicator in base prices of the period. This is the Laisperes index.
- In the second case, the numerator is taken equal to the cost of goods of the current period, the denominator is the cost of products produced in the reporting time period in base prices. This is the Paasche index. It is similar to the Laisperes index, but applies to the current period.
Both indexes are imperfect. They are not able to show changes in the total price level. In this regard, the Fisher index can sometimes be used, which corrects shortcomings in the calculations and represents the geometric mean of the indices.
Therefore, the most accurate calculation of price level growth and inflation is demonstrated by the Fisher index.
- If the deflator exceeds one, then real GDP is less than nominal GDP, which means the real price level has increased, and inflation processes are observed (decrease in real incomes of the population and enterprises, depreciation of the money supply).
- If the deflator is less than one, then real GDP is greater than nominal GDP, which means the real price level has decreased, and deflationary processes are observed (increase in income).
- If the indicator is equal to one, then the process of stagnation in the economy is underway.
Procedure and features of calculations
The deflator index should show by what percentage the value will change in the future period. But no one knows the exact prices, so nominal prices are taken as a basis, that is, project prices predicted taking into account the planned inflation rates.
The formula used to calculate the deflator index looks like this: ID = NZS/TZS * 100, where ID is the deflator index itself, NZS is the nominal value of the cost (that is, planned, projected, predicted, expected), and TZS is the current value value (real).
To apply a deflator index, you need to multiply the real current cost of the service or product of interest by this coefficient. You will receive the expected price of this position taking into account inflation in the future period, that is, in 2021.
For your information! The presented formula is used to calculate deflator indices in different sectors of the economy.
The calculation of deflator indices is carried out by the authorized state body of the Russian Federation, namely the Ministry of Economic Development. Its members analyze possible changes in cost, taking into account a combination of factors influencing the pricing policy. The Ministry of Economic Development carries out calculations for several years in advance. Typically, the billing period is three years following the reporting period. That is, the data for 2021 were compiled by the ministry three years ago – in 2017.
Deflator and price index
The deflator should not be confused with the consumer price index (CPI):
- The GDP deflator is similar to the Paasche index. Data from the current period are taken as the basis for calculations.
- The CPI is calculated as the Laspeyres index. The calculation uses products of the base year.
- When calculating the CPI, only the prices of goods consumed by the country's population (consumer basket) are taken into account.
- When calculating the deflator, a collection of all goods (services) produced within the country is used. This set is modified depending on the adjustment of consumer preferences (citizens of the country). All new products used by consumers, or the appearance of completely unique new products (services) on the market, are taken into account by the deflator. It reflects the real consumer basket of the country's population, where all goods are included in a certain share of consumption at a specific market value (price).
- The cost of imported goods consumed by citizens is taken into account when calculating the CPI. When calculating the deflator, imports are not taken into account.
The difference between the deflator and the CPI is insignificant in numerical terms. The legislative authorities of many European countries, including the Russian Federation, use the price index in the annual economic planning of the country's budget (for example, calculating social benefit payments, settlements with budgetary organizations). Differences between the numerical values of GDP indicators affect budget revenues and government expenditures.
Features of CPI calculation in the USA
In English, the consumer price index is abbreviated CPI (Consumer Price Index).
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports the CPI monthly and first calculated it back in 1913. The index is based on the average for the period 1982 to 1984 (inclusive), which was set at 100. Thus, a CPI value of 100 means that inflation has been zero since 1984, while values of 175 and 225 indicate an increase in the inflation rate by 75% and 125%, respectively. The reported inflation rate is actually the change in the index compared to the previous period, whether monthly, quarterly or annually.
While the CPI does measure changes in the prices of many different goods paid by consumers, it does not include things like savings and investments, and can often exclude spending by foreign nationals from its calculation. Its calculation uses a consumer basket consisting of eight main types of goods:
- Cloth;
- Housing;
- Food and drinks;
- Health care;
- Rest;
- Education and Communication;
- Transport;
- Other goods and services.
Types of CPI
There are two main types of consumer price index in the United States:
- CPI-W
- CPI-U
The CPI-W measures the consumer price index for urban wage and white-collar workers. Between 1913 and 1977, the BLS focused on measuring this type of CPI. It was based on households whose income was more than half from clerical or salaried occupations and in which at least one of the workers had been employed for at least 37 weeks during the previous 12-month cycle. The CPI-W primarily reflects changes in the value of benefits paid to individuals on Social Security. This CPI measure is based on data from at least 28 percent of the country's population.
CPI-U is the consumer price index for urban consumers. It includes data for 88 percent of the US population and therefore covers a broader cross-section of the public. It was introduced in 1978, so the BLS improved the CPI and introduced a broader target audience into its calculations. This type of CPI is based on the expenditures of almost the entire population living in urban or metropolitan areas and includes:
- specialists;
- self-employed workers;
- those living below the poverty line;
- unemployed;
- pensioners;
- city employees;
- clerks
Despite the introduction of the CPI-U in 1978, the BLS continued to measure the traditional CPI-W score. But since 1985, the two main differences between the two indices have been the spending weights assigned to item categories and geographic areas.
Disadvantages of Indexes
The advantages of the deflator index include the fact that it takes into account:
- current prices of the current period;
- prices for imported goods consumed by the population;
- only the goods and services produced that are needed to calculate the gross product of a particular country.
The disadvantages of a deflator are as follows:
- The dynamics of real prices turns out to be too high when the deflator decreases, and when consumer prices increase, it turns out to be too low. The deflator cannot demonstrate an income effect when considering changes in consumer basket prices because it includes the Paasche index.
- It is also based on the Laisperes index, calculated on the basis of consumer prices. It does not delve into changes in the consumption basket due to price adjustments. It shows the income effect but does not take into account the substitution effect.
GDP deflator index
This is a coefficient that is used to convert economic indicators into constant prices calculated in the analyzed period of time
.
The deflator index is set for one calendar year, taking into account fluctuations in prices for goods and services for the period that precedes the one being analyzed. Its indicator is published in Russian publications. And Rosstat is counting it.
Deflator index of Gross Domestic Product
is
a set of different indices with the help of which the components of GDP are recalculated
. It is also used to analyze indicators that summarize price dynamics in the country.
Methods for calculating the indicator:
- Deflation of the price index. When calculating, the price index indicator and the cost of goods produced at the existing cost are taken into account.
- Product evaluation. For analysis, we take some categories of goods at present and their value in the base period. This analysis is applicable in manufacturing and agriculture.
- Extrapolation using physical volume indices. For calculations, you will need data on the total cost of goods and services for the analyzed period and the physical volume index, which is calculated when determining GDP.
The latter method is used to determine how much the physical volumes of products and services produced and sales affect their cost.
The most common mistakes
Calculating macroeconomic indicators is a complex, labor-intensive job, which is carried out by specialists at the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. In private calculations, there are often shortcomings and miscalculations in the calculation of one or another index.
Since the GDP deflator is calculated as a ratio of GDP of different years, there are often common errors such as:
- Calculation of the index taking into account the cost of imported goods.
- Calculation of the index taking into account the replacement of expensive goods with more inexpensive ones. The substitution effect should not be taken into account.
Deflator coefficient for 2020 for PSN
The patent tax system is used only by individual entrepreneurs. The deflator coefficient is used to calculate the maximum annual income, which determines the maximum possible value of the patent. In 2020, this coefficient will change from 1.518 to 1.592.
The basic maximum annual income on a patent is 1 million rubles. This means that, taking into account the new deflator, its size will be 1.592 million rubles. At the same time, local authorities have the right to increase the amount of potential income.
What does the deflator show?
The economic deflator is calculated by the Federal State Statistics Service. The deflator coefficient by year is subject to official publication on the website of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation in the following order. The indicator values are published along with the calculation of gross domestic product and are duplicated three times:
- advance paynemt;
- viewing and analysis data;
- final data.
The index shows the level of inflation or deflation in relation to a certain calculation period. There are several indices that measure the depreciation of money:
- deflator;
- consumer prices.
Using special indicators, you can measure the inflation level (depreciation of the money supply), gain the opportunity to control and influence changes in the level of the current price currently operating on the market and the base price. The deflator shows this. Using the calculated data of the indicator, you can monitor and evaluate changes in profit or any other economic indicators.
Scenarios and calculations
The Ministry of Economic Development is obliged to calculate and approve deflator indices by 2021. Moreover, the values are determined for each reporting period separately, and the forecasting of coefficients is carried out by officials taking into account external and internal factors. Depending on how each factor affects the overall state of the economy, several development options are determined.
In simple words, the Ministry of Economic Development approves forecast deflator indices until 2021 based on scenarios. What is it for? Let's show it with an example.
It is no secret that a number of countries have imposed restrictive sanctions against the Russian Federation. The price level for raw materials (especially oil products) has negative dynamics. The level of customs duties and fees is growing. And officials, when determining deflator indices for 2020-2021, take these factors into account. They develop three scenarios at once:
- Basic, in which all external and internal factors will retain their current values. In simple words, sanctions will remain in place, oil prices will fluctuate around $40-50 per barrel, and customs duties will be frozen at the 2018-2020 level.
- A favorable forecast, in which a positive development trend is expected. For example, sanctions will be eased or completely lifted. Prices for oil products will rise, and customs duties on Russian goods will be reduced.
- Target scenario. This type of prognosis is the most unfavorable. Provides for the most negative impacts of external and internal factors on the Russian economy. For example, sanctions will be tightened, the price of oil will drop to critical levels, customs duties will be increased significantly, the level of inflation and unemployment within the country will increase.
Consequently, the deflator indices of the Ministry of Economic Development are not only a coefficient for calculating price dynamics in the future, but also an important indicator of the development of the Russian economy as a whole, taking into account the influence of external and internal factors.
Formula
The deflator calculation formula, when dividing nominal GDP (Nominal GDP) by the indicator (GDP deflator) and multiplying the result by one hundred, shows the indicator of real GDP (Real GDP). This process is called deflation of nominal GDP into real GDP. The GDP deflator is equal to:
Nominal gross domestic product is calculated using current year prices. Real GDP involves calculation using base year prices. If the obtained value is more than one hundred percent, then this indicates inflationary processes, and if it is less than one hundred percent, then, on the contrary, it indicates deflationary processes.
Publication of the indicator
In the countries of the European Union, and even in the United States, statistics on this indicator are kept quarterly every year. This statistical method demonstrates the growth or decline of a country's gross product and signals the need for urgent government action to increase its growth.
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
| 109,1 | 105,4 | 107,5 | 108,0 | 103,2 | 105,5 |
The forecast for the deflator index according to the Federal Statistics Service of Russia in the current year 2020 is only two percent. This is a rather low indicator of the country's economic development (the lowest over the past several years of development). To speed up the process, improved relations between the public and private sectors are required through:
- project refinancing;
- trade on-lending (replacement of one debt obligation with a new, different obligation on more favorable market conditions);
- mortgage lending secured by commercial real estate of legal entities.
The financial problems of the Russian Federation lie in the lack of investment in the real economy of the country, which is the locomotive for the growth of the state's gross domestic product.
To create conditions for attracting investments, you need:
- carrying out fundamental reforms in the sphere of government of the country (reduction of the state apparatus);
- carrying out privatization of objects in the real sector of the economy;
- transition to intensive economic growth (application of new modern innovative technologies);
- improvement of the country's credit, monetary and fiscal policies (tax reduction);
- support for private business at the state level;
- increasing high-productivity jobs;
- support for the demographic program.
Let us dwell on the state program that concerns the population of the country. It is aimed at:
- maintaining economic growth;
- reducing the level of poverty of citizens (now about a third of the population is below the poverty line);
- bringing the minimum wage to the level of the population's subsistence level;
- a decrease in the number of citizens with incomes below the minimum required for living.
In general, the program should have a beneficial effect on the growth of the state’s GDP. The program will be implemented through the following activities:
- increasing consumer demand;
- increased labor activity of women with children;
- support for the industries of heavy and light engineering, metallurgy, construction (including materials production).
Measures of state support for the Russian economy
For three years, the Russian Ministry of Economic Development has declared the implementation of the following goals:
- creation of an effective management system;
- development of a reliable environment for the development of private business;
- support for the country's domestic production (including exports);
- support for the development of innovative technologies;
- quality provision of public services;
- competent, targeted spending of budget funds (strengthening budget control) and management of state property;
- support for entrepreneurship (SMEs), including the creation of a non-bank depository and credit organization;
- promoting the country's interests on the world stage;
- development of civil society institutions.
The main threats to the Russian economy in 2020 are divided into external and internal.
External ones include:
- lack of developing financial relations with European countries;
- deterioration of the situation in the countries of the Middle East.
The internal ones include:
- reduction in consumer lending;
- decrease in retail turnover;
- reduction in business investment;
- reduction in development programs.
This year, economic growth in Russia may be limited:
- high level of unemployment;
- slight increase in labor efficiency;
- reduction in investments in fixed assets of enterprises against the backdrop of declining company income;
- low financial activity on the part of Russia’s partners on the world stage;
- reduction in borrowing for companies in the non-financial sector;
- reduction of investments for capitalization of enterprises;
- a slowdown in the growth of real incomes of the population and financing of private clients, as a consequence of a decrease in the growth rate of consumer demand, which is the main engine of economic growth.
A developmental contribution to the GDP growth rate this year can be made by:
- reduction in import purchases due to decreased domestic demand while maintaining export growth rates;
- investment support and workforce development;
- creating favorable conditions for investors to invest in the development of the country’s economy;
- government support for private business (reducing the fiscal burden, tariffs, placing government orders);
- development of innovative technologies in the field of logistics and trade.
The development of the investment environment is extremely necessary. Today, according to the Russian Ministry of Economic Development, it is necessary to inject about five trillion rubles into the country’s economy for further stable GDP growth.
Investment should be through:
- expansion of domestic and foreign markets for manufactured products;
- increasing export opportunities by reducing import opportunities;
- development of labor capital (improving the quality of higher and secondary education in the country, supporting young specialists, creating jobs within the country);
- increasing labor productivity.
The CPI is required to be published annually by the Russian State Statistics Service on the official website.
| Periods | For goods and services | For food products | For non-food items | For services |
| 2013 | 106,5 | 107,3 | 104,5 | 108,0 |
| 2014 | 111,4 | 105,4 | 108,1 | 110,5 |
| 2015 | 112,9 | 114,0 | 113,7 | 110,2 |
| 2016 | 105,4 | 104,6 | 105,6 | 104,9 |
Deflator in 2020 - forecast values
The Ministry of Economic Development has not yet officially published the deflator index for 2020-2021, but forecast values in various production areas have already been presented. At the same time, the indicated values of the coefficient for future periods will still be adjusted by specialists of the ministry, taking into account recent economic changes and social reforms, such as pension (increasing the retirement age) and tax (increasing excise taxes on fuel).
Upcoming events will directly affect the deflator indices of the Ministry of Economic Development for 2020. But when developing a budget and planning procurement activities for the next year and planning periods, customer organizations can use the existing coefficient values calculated by the ministry’s specialists.
Let's present the calculated consumer price index, which characterizes the inflation rate, and deflator indices for 2020-2021 in the table.
| Industries | 2018 | 2020 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Production, transmission and distribution of electricity, gas, steam and hot water | 109,0 | 107,1 | 106,7 | 106,7 |
| Mining | 108,7 | 106,5 | 106,0 | 106,2 |
| Manufacturing industries | 106,8 | 105,4 | 105,1 | 105,0 |
| Industry | 107,6 | 105,9 | 105,3 | 105,5 |
| Construction | 106,8 | 105,9 | 105,2 | 104,9 |
| Agriculture | 105,3 | 104,2 | 103,9 | 103,8 |
| Freight transport | 107,0 | 106,0 | 105,7 | 105,6 |
| Investments in fixed assets (capital investments) | 106,9 | 105,5 | 105,! | 104,8 |
| Retail trade turnover | 104,9 | 103,9 | 103,5 | 103,7 |
| Paid services to the population | 106,9 | 106,2 | 105,6 | 105,7 |
| Inflation (CPI) average annual | 104,7 | 104,4 | 104,2 | 104,1 |
The index for consumer goods is planned at 104.2. Retail electricity prices will be indexed to 109.1.
Also on the official website of the Ministry of Economic Development there are indices that will be used in 2020 for tax purposes:
- UTII - 1.915;
- simplified tax system - 1.581;
- Personal income tax - 1,729;
- property tax for individuals - 1.518;
- patent - 1,518;
- trading fees - 1,317.
Thus, many industrial and manufacturing sectors are seeing a gradual decline in the ratio. Thus, after calculating the deflator index for 2020 (Ministry of Economic Development), construction and construction work will be calculated with a coefficient lower than in the current year, 2020.
Economic sense
The Ministry of Economic Development of the country uses the deflator as an indirect price indicator to calculate the cost characteristics of products and services of a particular state for a certain time period.
When expecting an increase in this indicator, the following occurs:
- significant increase in the exchange rate;
- a significant increase in interest rates on placement and attraction of borrowed funds.
We can say with complete confidence that the deflator index influences the domestic and foreign exchange markets of the country.