What is gross profit
In the course of its activities, any organization is faced with the need to form economic indicators. They are needed to evaluate the results of its work and identify the level of profitability. One of the main performance indicators of an enterprise is gross profit.
This is the total revenue earned during an accounting period, based on the difference between sales profit and revenue, which is calculated on the cost of goods sold.
This concept combines profit from all areas of work, except production costs. The value of the indicator must be displayed on the balance sheet. It is compiled based on many indicators. All of them are divided into 2 groups. The first includes elements that depend on the leadership segment:
- Reducing the cost of production.
- Product sales performance ratio.
- Indicator of growth in production volumes.
- Carrying out activities aimed at improving product quality.
- Application of production capacities at maximum speed.
The second category includes external elements:
- Location of the enterprise.
- The regulatory framework within which production or commercial activities are carried out.
- General political and economic state of the state.
- Ecological and natural parameters.
Based on all of the above factors, the results of a business entity’s work are identified using gross profit. Unprofitable and profitable business activities are identified for subsequent analysis and the formation of profitable development paths.
What influences VP?
Gross profit changes under the influence of external circumstances, such as:
- cost of transportation services,
- natural, environmental factors,
- socio-economic environment in which the enterprise operates,
- costs of production resources,
- foreign economic contacts.
VP is also influenced by internal factors:
- income from product sales,
- other sources of income: investments, provision of services,
- cost of goods,
- demand for manufactured products, sales figures,
- cost of manufactured goods.
Gross profit is also affected by negative factors possible during the operation of the enterprise:
- overestimated or underestimated cost of products sold;
- low quality of goods;
- disciplinary violations by the company’s employees leading to losses;
- fines and sanctions.
The listed factors can affect the gross profit directly and indirectly. Factors that affect sales income have an indirect influence.
How is gross profit different from other types?
Difference with gross income.
The concept of gross receipts (income) includes all the assets that the company received from its work. These include tax and other related payments included in the cost of sold assets. This indicator is formed not only on the basis of sales volume and cost of goods, but also taking into account demand, assortment, productivity and many secondary components.
Difference from net profit.
There is also a significant difference here. When calculating gross profit, the amount of tax deductions and other similar payments is not taken into account, as when determining net income. Gross profit is calculated before taxation, after which the amount of net profit is formed.
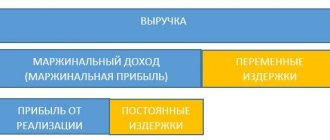
Difference with marginal profit.
Marginal income is directly related to the amount of variable costs, which are directly proportional to the production process. This includes the cost of materials, staff salaries, etc. Marginal profit is equal to the difference between the company’s income and irregular expenses.
The main difference between margins: with its help, you can develop the correct order of release of goods based on sales volume and assortment, as well as the most cost-effective way to break up the business. Gross profit reflects the profitability of the enterprise as a whole.
Difference from book profit.
Gross and book profit are quite similar indicators, however, there is a difference between them. The first coefficient is displayed on account 90, as the difference between costs and profit. The second is defined as account balance 99 - the total profit subject to taxation.
We recommend reading: What are revenue, profit and income: how they differ and what they are formed from.
Why monitor business indicators
When an entrepreneur starts a new business, it is difficult for him to assess the performance of the business. With the same revenue, a business can develop and go to bankruptcy. Business indicators will help you find out the real state of affairs and make the right decision. Here are the conclusions that can be drawn based on the numbers.
Calculate when the business will break even.
An entrepreneur rented premises for a shoe store and purchased goods for 500,000 rubles. Revenue in the first month amounted to 115,000 rubles. To determine how many months the investment will pay off, you need to calculate the net profit.
Find out which expenses to optimize.
The owner of a shoe store counted his expenses and saw that most of the money was spent on rent. To optimize costs, it is worth negotiating a discount with the owner of the premises.
Determine growth points.
The entrepreneur calculated the margin of the main product - shoes - and additional ones, such as insoles, socks, care cream. Complementary products usually have higher margins, so they should be offered more often.
What does gross profit mean?
Further planning and organization of commercial activities directly depends on its size. A negative indicator indicates that the organization is not functioning properly. With its help, you can identify problem areas when expenses exceed the planned budget.
Reducing product costs or production costs is one method of increasing gross profit from sales. It is this that provides the opportunity for the subsequent development of the organization’s activities, the use of new technologies, investment in more efficient equipment, the correct consumption of material and labor resources, etc.
What does the gross profit ratio show?
The gross profit ratio also deserves increased attention. This is its ratio to the amount of revenue, which is fixed as a percentage. A high ratio indicates a large profit, plus there is complete control over all expenses. If it is expressed in low percentages, then this indicates a lack of proper control over the cost of goods and services.
The coefficient is often used in the process of general monitoring of the state of the enterprise, comparison of past periods of activity and forecasting of future work. In addition, it can be used to obtain detailed information about the company’s performance compared to its competitors. This is a multifunctional indicator that is used in many areas of commercial activity.
Definition
Gross income expresses the amount of funds received by an enterprise during the implementation of its main activities. Its indicator characterizes the financial result based on the results of the well-coordinated work of the organization in the field of management, economics and marketing.
Gross income is generated based on the results of the commercial activity mechanism, which consists of going through the following stages:
- Release of goods or services to the market.
- Products are distributed among consumers, gain recognition and become established in a specific niche.
- Products are purchased.
- The entrepreneur receives income.
Gross income is not only of an individual nature on the scale of a particular organization, but also of national significance. At the macroeconomic level, gross national income is considered.
Its significance lies in determining the sum of the values of the total state final products at the end of a certain period. This product is distributed for the purpose of further consumption by the population of the country.
Along with commercial organizations, gross income is also formed based on the results of the work of budgetary institutions in the form of the total amount of financing.
These revenues represent donations from various companies and the public, government funding, income from authorized activities or shares.
It is important to remember that in addition to the amount of income from the main types of activity, the gross income includes the amount of some income, in particular:
- funds received from positive court decisions;
- various penalties or fines received from other persons;
- material assets received for storage under the relevant agreement;
- used or returned amounts of insurance reserves;
- charitable proceeds or gratuitous assistance;
- dividends, royalties and similar income;
- proceeds from the sale of securities;
- proceeds from insurance cases.
Gross Profit Analysis
In economics, this indicator reflects the financial result in terms of production costs. Its peculiarity is that it includes commercial and administrative costs. For example, salaries, expenses in terms of signing agreements and contracts, as well as other institutional costs. The coefficient is derived as the difference between revenue and technological cost, which reflects shop expenses, purchases of materials and wages.
Each type of indicator is divided into narrower ones. The volume of profits of managers, which are directly related to the production process, is reflected in the technological cost.
What does the calculation formula look like?
In standard form, the formula for calculating gross profit looks like this:
GP = TR - TStekhn, where
- GP—gross profit;
- TR—revenue;
- TStekhn - technological cost.
How is gross profit analysis done?
After calculating the indicator, an analysis is carried out, including a study of the sources of gross profit and its subsequent application.
The process starts with an analysis of the dynamics of the total amount through the use of constituent components (horizontal approach). Next, complex changes included in gross profit are formed (vertical approach).
A more voluminous version of the analysis contains a detailed consideration of each component of profit and the factors affecting it. All of them are divided into two groups: external and internal.
External ones include transport, economic and natural conditions, the cost of materials used and the development coefficient of foreign economic activity. Internal ones are divided into categories 1 and 2 according to the magnitude of subordination.
The first category includes income from business activities, interest payable (receipts), operating income (expenses) and non-operating income (expenses). The second category includes the amount of gross output sold, its structure, cost and retail price. In addition to them, this section includes episodes of failure to comply with economic discipline: incorrect cost formation, non-compliance with working conditions, a decrease in the quality of manufactured and sold goods, etc.
In the process of planning to increase income, other components of accounting policy are also taken into account:
- Correct debt write-off.
- Implementation of the LIFO method when analyzing inventories - the last item registered is sold first.
- Compilation of indicators for reducing intangible assets.
- Reducing taxation through the introduction of a preferential system.
- Reduced production costs.
- Using dividends for the development of the company.
- Competent approach to pricing.
Such analysis is necessary for proper management of net income. During its analysis, the structure of the application of gross profit in dynamics is examined, the impact of each individual area on the complex indicator of income and the percentage of profitability is identified.
Where to find a company's gross profit figures
The indicators are displayed in the financial statements, in account 90 “Sales”. To identify them for the selected period, loan volumes are compared with the debit indicators of this account in the direction of subaccounts. For example:
In this example, account 90/9 is closed each month by writing off the balance to account 99 “Profit and Loss”. A debit indicator for this account means that the result for the standard activities of the company is a gross loss, a credit indicator reflects gross profit during the reporting period. At the end of the year, subaccounts are written off under account 90.