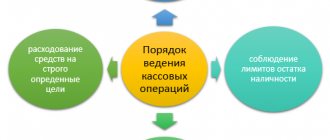
Cash control discipline involves following legally established requirements when carrying out cash receipts and expenditures. This applies not only to profit, but also to the issuance of salaries and bonuses to staff, settlements with clients, suppliers, creditors, accountable persons, delivery and receipt of cash at the bank, etc. Is it necessary to maintain a cash register for an individual entrepreneur and how to ensure cash order for a patent - we will tell you in this article.
Online cash registers for individual entrepreneurs. We will install and register in 1 day.
Leave a request and receive a consultation within 5 minutes.
Features of cash transactions for individual entrepreneurs, accounting documentation
Individual entrepreneurs have a simplified procedure for cash transactions. The entrepreneur independently determines the timing of the deposit of funds to the bank and does not approve the limit of the cash balance at the cash desk (clause 2 of Directive No. 3210-U).
Entrepreneurs are given the right not to draw up cash orders for expenses (RKO) and receipts (PKO) and, as a result, not to maintain a cash book (subclauses 4.1 and 4.6, clause 4 of Directive No. 3210-U).
Legislation allows for undocumented cash movements.
Attention! Refusal to draw up RKO and PKO increases the risk of possible abuse of official position by officials.
Refusal to maintain cash documents is justified in the absence of hired employees or business partners.
Documents that serve as confirmation of the amount of revenue in non-documentary accounting are:
- Z-reports (in case of using CCP);
- strict reporting forms.
The issuance of wages is documented in payroll form No. T-53 (OKUD code 0301011) or payroll form No. T-49 (OKUD code 0301009).
Cash discipline in 2020 for individual entrepreneurs in all other cases, except for those discussed above, is mandatory. What it consists of, read below.
Can individual entrepreneurs not keep a cash book?
In accordance with paragraphs 4.1 and 4.5 of Directive No. 3210-U, from June 1, 2014, individual entrepreneurs may not maintain a cash book and not issue cash receipts and expenditure orders. In this case, the individual entrepreneur must keep track of income, expenses, physical indicators or other objects of taxation, for example:
— Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO may not keep a cash book, since accounting is carried out on the basis of the Book of Income and Expenses and Business Operations of an individual entrepreneur;
— An individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system or unified tax system may not keep a cash book, since he keeps a book of income and expenses (clause 2 of article 54, clause 346.24 and clause 1 of article 346.53 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
— Individual entrepreneurs keep an income book using the patent taxation system.
— Individual entrepreneurs on UTII, keep records of physical indicators (clause 9 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This is in theory. Indeed, if you follow the Instructions, the individual entrepreneur may refuse to use the cash book. This makes sense if an entrepreneur works alone, he has no employees, he does not pay wages and does not issue funds on account. This situation is possible for individual entrepreneurs on UTII without hired employees. Writing out receipts and expenditure documents for yourself is a waste of time. If an entrepreneur has employees, then he must already keep records (to whom, what and on what basis he is paid). There is also a need to monitor the work of the cashier (if there is one). Here it is no longer possible to do without taking into account the inflow and outflow of cash. At least to prevent theft from happening.
In life, you should take into account judicial practice and be prepared for controversial issues. For example, according to the tax authorities, failure to maintain a cash book, PKO and RKO leads to non-receipt of cash to the cash register, respectively, to an offense provided for in Part 1 of Art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Many courts also agree that failure to record cash proceeds in the cash book on the day it was received indicates that they were not received. Sometimes courts turn a blind eye to a minor delay (1 - 2 days) in the posting of proceeds and recognize the offense as minor. Some courts go further, believing that even if entries in the cash book were not made or were made late, there is no violation called “non-receipt”, provided that the money received:
— a cash receipt order has been issued;
— the cash register check has been issued.
Responsibility for failure to maintain a cash book
We quote.
Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Violation of the procedure for working with cash and the procedure for conducting cash transactions, expressed in the implementation of cash settlements with other organizations in excess of the established amounts, non-receipt (incomplete receipt) of cash in the cash register, non-compliance with the procedure for storing free cash, as well as in the accumulation of cash in the cash register in excess of established limits - entails the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of four thousand to five thousand rubles; for legal entities - from forty thousand to fifty thousand rubles.
We remind you that the tax office considers failure to post cash as failure to maintain a cash book.
How to formalize a refusal to conduct cash transactions
If you still decide not to keep a cash book, then draw up an order that from a certain date the individual entrepreneur exercises his right not to set a cash limit (not to be confused with the cash limit), not to issue cash orders and not to keep a cash book, and indicate the reason. An example might look like this:
—
Beginning of an EXAMPLE order.
Order No. 100 dated June 1, 2014 on changes to the rules for conducting cash transactions.
In accordance with the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal entities and the simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses” I order:
1. From June 1, 2014, cancel the order establishing a limit on the cash balance in the cash register dated DATE OF THE OLD ORDER No. NUMBER OF THE OLD ORDER.
2. Starting from June 1, 2014, the NAME of an individual entrepreneur or LLC does not establish a cash limit based on paragraph 10 of clause 2 of the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014, since it applies to small businesses.
3. From June 1, 2014, cancel the maintenance of a cash book and the issuance of cash orders, since accounting is conducted FURTHER EXAMPLE 1 - on the basis of the Book of accounting of income and expenses and business transactions of an individual entrepreneur. Cash documents can be prepared for internal accounting needs or as primary documents for tax purposes in compliance with the general requirements for primary documents.
End of EXAMPLE order.
—
Do not confuse the cash book with other documents
It is important not to confuse the Cash Book, the Cashier-Operator Journal (ZhKO) and the Income and Expense Accounting Book (KUDIR). Individual entrepreneurs who use cash register systems are not exempt from keeping a cashier-operator journal. The cashier-operator's journal is a separate document that does not depend on maintaining the cash book. Everyone is required to create a cash book and it reflects the cash transactions (income and expenses) of the entrepreneur. The cashier-operator's journal confirms the movement of cash through the cash register. If you use a cash register, you are required to keep this log.
Results
Now you know that individual entrepreneurs have every right to refuse the cash book. We also learned how to formalize this decision. However, given the uncertainty in this matter, we believe it is correct to maintain a cash book. The procedure is simple, economically useful, and not labor-intensive if properly organized.
Accounting support from Firmmaker, May 2020 Anastasia Chizhova (Konatova) When using the material, a link is required
Cash
The current legislation establishes a list of purposes for spending cash received at the cash desk (clause 2 of Directive No. 3073-U dated October 7, 2013). Cash proceeds are spent on the following purposes:
- payment for goods (works, services);
- issuance of cash for personal needs of individual entrepreneurs not related to their business activities;
- payment of wages to employees;
- social payments (for example, financial assistance, benefits, etc.);
- payment of insurance compensation under insurance contracts to individuals who previously paid insurance premiums in cash;
- issuing cash to employees on account;
- refund for previously paid in cash and returned goods, work not performed, services not rendered.
Attention! Cash payments within the framework of one agreement are allowed in an amount not exceeding 100 thousand rubles (clause 6 of Directive No. 3073-U).
Application of cash register equipment
Individual entrepreneurs providing services to individuals can make calculations without using cash register systems. A detailed list of activities is presented in paragraph 2 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ. Let's note some of them:
- sale of ice cream and soft drinks on tap at kiosks;
- acceptance of glassware and waste materials from the population, with the exception of scrap metal, precious metals and precious stones;
- shoe repair and painting;
- production and repair of metal haberdashery and keys;
- and others.
CCPs are not used by entrepreneurs working in remote or inaccessible areas. The specified areas do not include cities, regional centers and urban-type settlements (Clause 3, Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ). The list of remote or hard-to-reach areas is approved by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, IP uses CCT.
From July 1, 2017, entrepreneurs are required to use a new type of cash register (online cash register).
From 07/01/2018, in the case of providing services to individuals, individual entrepreneurs will be required to issue BSOs printed on a special device - an “automated system for BSOs”. The device is a prototype of a cash register, with a fiscal recorder for transmitting data to the Federal Tax Service (Federal Law of July 3, 2016 N 290-FZ).
Changes in the mandatory list of cash documents
The updated law “On the use of cash registers...” dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ changed not only the requirements for the cash register equipment used, but also fundamentally updated the approach to the list of documents required for registration when using cash register systems.
Read about the positive and negative aspects of using online cash registers in the article “Advantages and disadvantages of online cash registers” .
This was achieved by introducing an updated art. into Law No. 54-FZ. 1, which outlines the range of legislative acts that should be followed when applying CCP. Such acts include (clause 1, article 1):
- Law No. 54-FZ itself;
- regulations adopted in accordance with this law.
Thus, the obligation to use other documents previously drawn up for transactions that required the use of cash registers has been cancelled. That is, now there is no need to use the following forms, the unified forms of which were approved in Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of December 25, 1998 No. 132:
- act on transferring cash meter readings to zero (form KM-1);
- act on taking meter readings when transferring the cash register for repairs (form KM-2);
- certificate of return of money to buyers (form KM-3);
- journal of the cashier-operator (form KM-4);
- log of meter readings (form KM-5);
- certificate-report of the cashier-operator (form KM-6);
- information on meter readings and revenue (form KM-7);
- log of calls of technical specialists (form KM-8);
- act on checking cash at the cash desk (form KM-9).
At the same time, the documents relating to transactions carried out using the operating cash desk, which take place even if there is no receipt of cash proceeds requiring the use of cash registers, remained in force. They are given in the instructions of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U:
- cash orders issued for receipts and expenses (clause 4.1);
- cash book (clause 4.6).
Thus, the need to maintain a cash book for online cash registers is preserved.
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to maintain a cash book using Form KO-4 or manually. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Individual entrepreneur fines for violation of cash discipline
Penalties for individual entrepreneurs for non-use of cash register systems range from 25 to 50% of the purchase amount, but not less than 10,000 rubles. Repeated violation of cash discipline entails disqualification for officials for a period of 1 to 2 years, as well as administrative suspension of activities for up to ninety days (clauses 2-3 of Article 14.5 of the Administrative Code).
Unified form No. KO-1 “Cash receipt order”
Unified form No. KO-2 “Cash expenditure order”
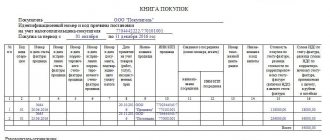
Unified form No. KO-4 “Cash book”
Unified form No. T-53 “Payroll”
Do you need a cash book for an online cash register?
This year, some changes were made to Federal Law No. 54. In accordance with them, trading companies and individual entrepreneurs do not have to use some forms of primary cash reporting. But is a cash book needed for an online cash register, or has its use also been abolished? You can find out the answer to this question from this article.
Since 2013, the use of unified forms of primary accounting documentation, which were developed and approved by the State Statistics Committee, is not mandatory. However, unified forms developed and approved by authorized bodies on the basis of other Federal Laws continue to be mandatory.
The procedure for conducting cash transactions is established by the Central Bank in Directive No. 3210-U. It says that the cash book must be used.
It is also reported that if an entrepreneur keeps records of income or income and expenses that characterize a specific type of business activity, he has the right not to maintain a cash book.
Simply put, all legal entities must maintain a cash book, and entrepreneurs can do this at their own discretion. The fact of using an online cash register in this situation does not matter.
Rules for maintaining a book
The company can choose the format for maintaining an online cash book independently - in paper or electronic form. Money is deposited into the company's main cash register based on Form Z reports, the purpose of which is to close the shift at the end of the working day.
Such a report is generated by the cashier, and at the same time the information is transmitted to the tax service. Based on the information received, a certificate and cash register are filled out, after which the information is sent to the accounting department, where the cash book is filled out.
Here are the basic principles for filling out the cash book when checking out online:
- Cash vouchers for receipts and expenses, which are drawn up on standardized forms, must be attached to the tear-off sheets of the book.
- At the end of each working day, the information is verified by the company's senior employees.
- Based on the results of a certain period (for example, a month or a year), the sheets must be stitched.
- Each correction made must be certified by the personal signature of the company manager or chief accountant. Otherwise, it will be considered invalid.
- If the book was filled out electronically, you do not need to print it. However, it must be certified with an electronic signature and stored on a magnetic storage medium.
- At the beginning of each year, you must begin filling out a new copy of the book.
- Each book must be kept in the company for at least five years from the end of its completion.
- Each sheet of the book must be numbered in order. Page skips are not allowed.
- The last page of the book should be stamped and a note should be made indicating how many stitched and numbered sheets it contains.
To summarize, the cash book must be filled out by all individual entrepreneurs and legal entities carrying out cash transactions, regardless of whether they use an online cash register or a standard cash register.