When the situation of a legal entity reaches a critical point and the company is no longer able to pay off its obligations within the company and its debts to partners and counterparties, the best option for resolving debt problems is declaring bankruptcy.
The bankruptcy procedure of a legal entity means the absolute impossibility of making payments within the framework of obligations to creditors and employees. In fact, the company does not have money to carry out financial transactions.
Signs of insolvency of a legal entity
Companies with small debts and no working capital do not have the right to declare bankruptcy. To initiate an insolvency procedure, the following formal criteria must be met:
- The total amount of overdue debt obligations to creditors and government agencies is at least 300 thousand rubles. (for monopolies this value increases to 1 million rubles), the indicated amount does not include accrued penalties/fines.
- A legal entity does not have the funds to pay the required wages, benefits and other obligatory payments to its employees.
- The arrears on debt obligations exceeded 3 months.
Who can file for bankruptcy of a company?
The initiative to declare a legal entity bankrupt can come from both the management of the company and its founders, and from creditors (individual investors or other organizations), the Tax Inspectorate and extra-budgetary funds, personnel in case of significant delay in salary payments, as well as authorized civil services and the prosecutor's office . Thus, any party interested in returning the funds owed to it or solving the problem of debt obligations (not always through liquidation, but possibly through restoration of solvency) can file for bankruptcy.
For your information
For creditors and tax authorities, declaring bankruptcy of a legal entity is a right, not an obligation. They can implement it at their own discretion. Some creditors are not interested in initiating insolvency proceedings because... their chances of getting their money back will be minimal. Others deliberately begin the bankruptcy process to eliminate an unwanted competitor.
In some situations, company managers are required to file a bankruptcy claim in court. This must be done within 30 days after management becomes aware of the impossibility of ensuring payments on obligations, taking into account financial resources and intangible assets.
If the bankruptcy initiative comes from within the company’s management, then it is deprived of the opportunity to appoint its own manager.
Beginning of bankruptcy
The adoption of the relevant law “On Insolvency” was a consequence of the fact that many often use bankruptcy and declaring legal insolvency. persons in order to “escape” from fulfilling their own obligations, in order to mislead certain counterparties, to secretly curtail their affairs, with plans to evade the law.
Important: it should be remembered that fictitious bankruptcy is punishable by criminal law.
In order for the bankruptcy process of a legal entity or individual. person has entered into force, you need to file an insolvency petition submitted for consideration to the arbitration court.
Advice! Who can submit such an application? These are creditors, various bodies or direct debtors. The decision to start the trial will be made by the judge.
The main stages of bankruptcy of a legal entity are identified. or physical faces, and we will talk about them in order, noting the timing.
Purposes and types of bankruptcy
I’ll say right away that bankruptcy as a fact does not relieve you from debts.
Financial insolvency of companies and individuals is an opportunity to fulfill debt obligations in alternative ways and at least partially free themselves from pressure from creditors. As long as the debtor owns real and movable property, he will continue to pay off his debts until he pays them off in full. Another thing is that the form of debt repayment will be fundamentally different.
For businesses, the long-term goal of bankruptcy is to either close down or radically reorganize the business. Individuals initiate insolvency proceedings in order to stop the progressive growth of loan debts.
Currently, there is a massive credit default - people who at one time took out consumer and mortgage loans are experiencing difficulties paying off their debts during the crisis.
In simple terms, incomes have fallen, the cost of living has risen, and debt obligations have become difficult to meet.
Things have not improved for legal entities either: the crisis of recent years has led to the ruin of many companies, especially in the field of small and medium-sized businesses.
As an ordinary citizen, I personally observe an almost quarterly change of signs in an office building opposite the windows of my own apartment - enterprises move into new premises and within a few months wind down their activities due to bankruptcy.
There are several types of bankruptcy:
- Real bankruptcy is when companies cannot restore their solvency on their own as a result of financial losses. Enterprises simply do not have the capital to operate fully.
- Temporary bankruptcy (also conditional) - when the assets of an enterprise increase, and liabilities vice versa. This happens if, for example, the company has accumulated a surplus of unsold products.
- False bankruptcy. Intentionally declaring one's insolvency in order to mislead creditors or obtain relief and benefits from them. This type of activity is criminal and is fraught with criminal liability.
- Deliberate bankruptcy is another type of illegal act. Intentional bankruptcy is carried out by company owners for the purpose of personal gain or for the benefit of others.
This is also important to know:
What is a meeting of creditors in bankruptcy proceedings: the rights and obligations of each participant
The task of the judicial authorities is precisely to understand what type of bankruptcy they are dealing with and initiate the appropriate legal procedure.
Signs of bankruptcy
The main sign of the insolvency of a company or individual is insolvency: a person cannot pay his credit bills and has debts on loans. There is a clear lack of financial resources, and expenses exceed income. These are formal signs of bankruptcy.
There are also informal symptoms of ruin that can be noticed before the onset of real financial insolvency.
These include the following facts:
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
- there are many inaccuracies in accounting documents;
- reporting papers are submitted late;
- the external balance of the enterprise changes;
- employee wage debts are growing;
- payments to the company's investors are delayed or stopped;
- pricing policy is changing.
Persons interested in clarifying the financial condition of a company can initiate bankruptcy proceedings in court if they receive the appropriate authority to do so.
There is a separate article on the website about bankruptcy of legal entities.
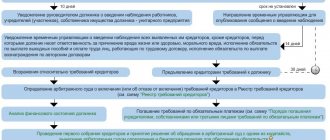
Stages of bankruptcy of a legal entity
Bankruptcy of a legal entity begins with the filing of an application by a participant in the process to the Arbitration. Here, the received claim will be assessed for legality and the existence of grounds for declaring the company bankrupt.
If the claim is satisfied and bankruptcy proceedings are initiated against the debtor, during the process the legal entity will be able to go through several stages:
- observation;
- financial recovery/external management;
- settlement agreement;
- bankruptcy proceedings.
For your information
It is worth noting that the stages listed here are not mandatory for all companies. Thus, the stages of debtor rehabilitation will be introduced only if creditors and the court have grounds to believe that the legal entity has a chance of restoring the balance of payments.
Whereas the conclusion of a settlement agreement between the parties to the bankruptcy process is very rare based on established practice.
Simplified bankruptcy procedure
The bankruptcy procedure applied at any stage can be simplified. It is carried out in similar ways as described above, but is characterized by smaller financial losses and shorter deadlines. Its features are regulated by Chapter 11 of the Law “On Insolvency”.
The distinctive factors in the bankruptcy process of individuals, companies and individual entrepreneurs are:
- insufficient number of objects on the balance sheet to fully repay obligations;
- if the activity is inappropriate, all participants in the process provide their consent to the liquidation of the organization;
- the deadline for fulfilling creditors' claims has been reduced to 1 calendar month;
- after submitting the application, the competitive description immediately begins without previous sequence periods for the legal entity;
- the absence of financial rehabilitation, a period of external management and supervision as grounds for bankruptcy of a legal entity.
This process can only be used in cases where the company is planning to be liquidated and there is no chance of stabilizing financial expenses.
The arbitration court carefully considers all evidence provided by the applicant. If the information is significant and sufficient, a decision is made on financial ruin and bankruptcy proceedings are carried out for six months.
Despite the short time frame, this process is considered complex and confusing. It involves a wide range of documentation and legal support. Therefore, it is unlikely to be possible without the services of an experienced lawyer, since the management of the enterprise is not able to cope without additional help. Today, such legal entities are most often outsourced.
If you are faced with the need to declare an organization insolvent, we advise you to contact a lawyer. Our specialists will help you prepare all the necessary documents and will represent your interests and rights in court.
Step-by-step instructions for enterprise insolvency
The bankruptcy procedure for legal entities involves going through a number of stages: 1. Filing a statement of claim to the Arbitration Court. 2. Appointment of an Arbitration Manager. 3. Drawing up a creditor register of claims. 4. Conducting the first creditors' meeting and deciding to initiate one of the bankruptcy procedures. 5. Introduction of the observation stage at the enterprise. 6. Approval at a creditors’ meeting of one of the rehabilitation procedures: reorganization or external management. 7. If none of the procedures leads to the desired result, then the legal entity is declared bankrupt and the stage of bankruptcy proceedings is assigned. 8. The manager carries out an inventory and assessment of the property, and forms the bankruptcy estate. 9. Auctions are organized and held at which all the debtor’s property is sold. 10. Settlements with creditors are carried out and current payments are repaid. 11. The bankruptcy trustee reports to the creditors' meeting and the court on the results of the bankruptcy procedure. Once his report is approved, the process is considered complete. 12. The manager submits to the Tax Inspectorate a resolution declaring the debtor bankrupt, which serves as the basis for its liquidation. 13. The company is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and is no longer considered an independent economic entity.
Courts in insolvency proceedings
The key role in the process of recognizing a company as a debtor belongs to arbitration courts.
Chapter 28 of the Arbitration Procedural Code directly regulates the conduct of proceedings in cases the subject of which is the recognition of a legal entity with certain amounts of debt as bankrupt.
This Chapter of the federal normative legal act was created for the purpose of implementing the provisions of Federal Law No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, since Part 1 of Article 6 of the latter states that the consideration of cases related to the recognition of a legal entity or individual as insolvent occurs only in arbitration courts.
Arbitration courts consider issues related to the need to accept an application to recognize a specific company as a debtor, to introduce the stages of the bankruptcy process provided for by law, to recognize creditors' claims as justified and to include them in a special register of claims, as well as to declare a company bankrupt, which entails the termination of the organization's existence , as a participant in existing legal relations.
In addition, it is the arbitration court that is considering the issue of approving a special settlement agreement, with the help of which the parties participating in the bankruptcy process can resolve existing disputes and terminate bankruptcy proceedings on the terms that will be beneficial to such parties.
Observation stage in case of bankruptcy of legal entities
The supervision stage of bankruptcy of legal entities is a preliminary stage of the insolvency process. It pursues the basic goal of ensuring the safety of the debtor’s property for further settlements with creditors. At this stage, a register of claims is compiled, the first meeting of creditors, which is most important for the bankruptcy procedure, is organized and a detailed analysis of the economic condition of the debtor is carried out.
To implement the assigned tasks at the observation stage, a temporary manager is appointed. The powers of the company's senior management are somewhat narrowed. Thus, the company’s management is obliged to provide all important information about the economic situation of the legal entity (reporting, balance sheets, etc.); during the observation period, they cannot open new production facilities, branches and subsidiaries, enter into transactions for the alienation of property in the amount of 5% of the cost, receive loans without the approval of the arbitration manager.
For your information
Bankruptcy supervision can last no more than 7 months. On its basis, the participants in the procedure make a decision on the future fate of the debtor and the introduction of a stage of rehabilitation or bankruptcy proceedings against him. Based on the results of observation, the manager must draw up a plan to satisfy creditor claims.
Observation
A procedure applied to a debtor in a bankruptcy case in order to ensure the safety of his property, conduct an analysis of the debtor's financial condition, compile a register of creditors' claims and hold the first meeting of creditors. The observation period should not exceed 7 months from the date of filing the bankruptcy petition.
The goal is to collect information about the debtor, establish the reasons for bankruptcy, and decide on the next procedure. It is introduced after the claims of the applicant (debtor) are recognized as justified and the existence of an outstanding debt to creditors.
- publish in a printed publication and post on the EFRSB website information about the introduction of surveillance;
- prepare and send requests about the availability (absence) of property from the debtor to state authorities and local governments, credit organizations and other legal entities (as a rule, these are: traffic police, Rostekhnadzor, Rosreestr, Federal Tax Service, banks in which accounts are opened to provide account statements );
- send to the debtor and the debtor's manager (at home address from the extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities) a request for copies of agreements, account statements, information about the company's assets and liabilities, accounting and tax reporting);
- participate personally (or through a representative) in court hearings to consider the claims of creditors submitted to supervision (period - 30 days), as well as in court hearings to consider the manager’s report;
- draw up a register of creditors' claims;
- conduct an analysis of the debtor’s financial condition (the manager must answer three main questions: is it possible to restore the debtor’s solvency, is there enough property to cover current expenses, including bankruptcy);
- draw a conclusion on the presence (absence) of signs of deliberate and fictitious bankruptcy;
- draw up a report of the temporary manager;
- hold the first meeting of creditors and send information to the arbitration court;
Stage of financial recovery in case of enterprise insolvency
After passing the preliminary stage of observation, a decision is made at the creditors’ meeting on the advisability of introducing rehabilitation procedures. If creditors are confident that the debtor's business can still be saved, they will set a stage of financial recovery. At its core, this is an installment plan for a legal entity to repay its obligations.
The financial recovery stage is introduced for a period of up to 2 years. It involves the development of a debt repayment schedule (debt restructuring), which is subject to approval by the arbitration court. At the same time, fines and penalties for late payments are cancelled, enforcement proceedings are suspended, and the seizure of assets is lifted.
The company's management is not removed from business, but is under the control of the administrative manager. If the company’s obligations cannot be repaid at this stage, then the stage of external management or sale of property is introduced.
Page 4 of 414.5. Judicial acts issued by the arbitration court based on the results of consideration of a bankruptcy case,
grounds and procedure for their adoption
Based on the results of consideration of the bankruptcy case, the arbitration court decides in accordance with Art. 52 Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” one of the following judicial acts:
- a decision to declare the debtor bankrupt and to open bankruptcy proceedings - if the debtor has signs of bankruptcy;
- a decision to refuse to declare the debtor bankrupt - in the absence of signs of bankruptcy, namely debt of any size;
- a determination to introduce financial rehabilitation - if it is possible to restore the debtor’s solvency based on a decision of a meeting of creditors or at the request of a third party. The procedure for resolving these issues is defined in Art. 77 Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”;
- a determination on the introduction of external management - if the debtor’s solvency can be restored through special measures;
- determination to terminate bankruptcy proceedings - in accordance with Art. 57 Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, i.e. if circumstances arise that make it impractical to carry out procedures, in particular, satisfaction of all claims of creditors included in the register of creditors’ claims;
- a determination to leave the application for declaring the debtor bankrupt without consideration - if during the consideration of the case it turns out that the debtor’s obligations to the applicant are satisfied, but there are other creditors whose claims must be considered;
- determination on approval of the settlement agreement - if there is an agreement between the creditors, it comes into force after approval by the arbitration court.
Based on the results of the bankruptcy proceedings, the arbitration court issues either a decision or a ruling.
Thus, a decision is made if the case is resolved on the merits. If the debtor has signs of insolvency and there are no grounds for introducing rehabilitation procedures, the court makes a decision to declare the debtor bankrupt and to open bankruptcy proceedings against him (Article 53 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”. If during the trial it is established that the debtor has no signs of insolvency, and also if the bankruptcy is fictitious, the court makes a decision to refuse to declare the debtor bankrupt, which is the basis for restoring his legal capacity (Articles 55, 56 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”) .
Cases when an arbitration court makes a ruling based on the results of a trial can be divided into two groups: when a rehabilitation procedure is introduced and when the proceedings are terminated (the application is left without consideration).
The law provides for two rehabilitation (another name is reorganization) procedures: external management and financial recovery. The decision to introduce them is made by the arbitration court in cases where the debtor has signs of insolvency, but it is assumed that his solvency can be restored. The ruling on the introduction of financial rehabilitation or external management is an interim judicial act: if solvency is restored based on the results of these procedures, the arbitration court terminates the proceedings (Article 57 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”), but if solvency is not restored, the arbitration court, as a rule, makes a decision to declare the debtor bankrupt and to open bankruptcy proceedings (Articles 88, 119 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”).
Termination of bankruptcy proceedings is carried out by the arbitration court in the following cases:
— restoration of the debtor’s solvency during financial recovery or external management;
— conclusion of a settlement agreement and its approval by the court;
— refusal of all creditors to declare the debtor bankrupt;
— satisfaction of all creditor claims;
— completion of bankruptcy proceedings (Article 57 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”).
All of these cases of termination of bankruptcy proceedings can be qualified as the absence of a legal need to continue the consideration of the case in view of the fulfillment of the goals of bankruptcy as an institution of substantive and procedural law.
A ruling to leave an application without consideration is made by the arbitration court mainly in cases established by Art. 148 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, in particular:
a) if the bankruptcy case of the same debtor is pending in the arbitration court, and the applicant’s demands are recognized as unfounded (clause 3 of Article 48 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”);
b) if the creditor or the authorized body did not comply with the preliminary procedure for collecting the debt: the creditor did not file a corresponding claim or demand to initiate enforcement proceedings, the authorized body filed an application to declare the debtor bankrupt, without having a decision from the tax or customs authority to foreclose on the property debtor;
c) the application is signed by an unauthorized person or is not signed.
Almost all judicial acts adopted by the arbitration court based on the results of consideration of a bankruptcy case have two features that distinguish them from judicial acts adopted by the arbitration court in cases of other categories: a) they are all subject to immediate execution;
b) information about their acceptance is subject to mandatory publication.
The decision of the arbitration court in a bankruptcy case comes into force according to the general rule, i.e. one month from the moment of their adoption or from the moment the decision was made by the appellate court (Article 180 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). But, like the definitions, it is subject to immediate execution: the debtor’s director is removed from office, his duties are transferred to the bankruptcy trustee, all previously adopted restrictions on the disposal of the debtor’s property are lifted, a special procedure is introduced for the debtor to fulfill his obligations, etc. (Article 126 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”).
Determinations that are made by an arbitration court when considering cases of insolvency (bankruptcy) and the appeal of which is provided for by the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws governing issues of insolvency (bankruptcy), separately from the judicial act that ends the consideration of the case on the merits, can be appealed to the arbitration court appellate court within ten days from the date of their issuance.
In cases of insolvency (bankruptcy), a settlement agreement can be concluded, and other conciliation procedures are also allowed.
<< First < Previous 4 Next > Last >>
External management in case of bankruptcy of legal entities
External management in case of bankruptcy of an enterprise is one of the rehabilitation procedures along with financial recovery. Its key goal is also to restore the solvency of a legal entity without its liquidation. At the optimal completion of this stage, the debtor pays off all debts to creditors and continues to exist as a market subject.
External management has one fundamental difference from recovery: during this procedure, the top management of a legal entity is removed from business. Typically, the decision to start external management is made when there is reason to believe that inept management has led to dismal financial performance.
Information
Lenders are usually interested in this stage for the reason that they have a chance of full repayment of the debt. Whereas when bankruptcy proceedings begin, the proceeds received may not be enough to cover all debts, and in 90% of bankruptcy cases this happens.
During external management, the arbitration manager develops a new company strategy and implements specific measures to restore solvency. These include: reorientation of the production line to new markets, assignment of claims, sale of unprofitable assets, additional issue of shares, closure of low-profit areas, etc. The manager also has the right to refuse contracts that are unprofitable from his point of view and challenge recent transactions on the alienation of property.
External control is introduced for a period of up to six months. But sometimes this period is extended to 1.5 years.
In order for the company to have a chance to restore its balance of payments at this stage, a ban on repaying creditor claims is introduced; the property of the legal entity cannot be seized.
Upon completion of this stage, the case may be terminated. But if the desired effect was not achieved, then bankruptcy proceedings begin in case of insolvency of the legal entity, which leads to liquidation.
Main stages of bankruptcy - goals and relationships
Each of the stages of declaring a company insolvent is closely interconnected and is carried out in order to achieve its goals. The timing of the activities, their goals and objectives are listed in Law No. 127-FZ. Let's take a closer look at all five procedures:
Stage 1. Observation
An analysis of the debtor’s current financial situation is carried out at the preliminary observation stage (Article 62—No. 127-FZ). For an independent assessment of the financial situation, a temporary manager is appointed, who publishes a notice of the introduction of supervision. This stage is also appointed to ensure the inviolability of the enterprise’s assets, notify creditors, and compile a register of claims. The company's management retains its powers, but with some (very significant) restrictions.
This is also important to know:
Consequences of termination of bankruptcy proceedings
The maximum duration of observation is 7 months. During this period, the manager conducts a full collection of information about the debtor, his financial and economic activities, the amount of assets and liabilities, and the possibility of restoring the normal functioning of the business entity.
Based on the results, the manager prepares a summary report, which, along with the minutes of the first creditors' meeting, is submitted to the arbitration court. Then the court makes a decision on the advisability of further consideration of bankruptcy or termination of the case in connection with the possibility of rehabilitating the organization in order to repay debts in full. It is also possible to sign a settlement agreement and restructure obligations.
Stage 2. Financial rehabilitation
The goal of the debtor’s recovery is to restore the financial solvency of the legal entity and, accordingly, repay the resulting debts. The procedure is carried out in accordance with legislative norms in accordance with Art. 76—Law No. 127-FZ. This stage is not assigned in all cases, but only when hidden potentials for business resuscitation are identified. The decision to apply is approved at the first creditors' meeting together with the development of a preliminary debt repayment schedule. Among the consequences of reorganization, the following steps should be highlighted:
- Cancellation of absolutely all pre-trial actions to repay debts, including already issued collection orders.
- Suspension of dividends, ban on payment of interest on shares.
- Prohibition on carrying out any transactions with obligations (barters, offsets, etc.).
- Removal of seizures from the debtor's assets, suspension of the accrual of sanctions on debt amounts.
An independent manager is appointed responsible for the implementation of the adopted financial recovery plan. The maximum duration is 2 years (calendar). If the measures taken do not bring the expected results in the form of an improvement in the financial condition of the legal entity, a transition is made to external management or immediately to bankruptcy proceedings, that is, to the sale of assets.
Stage 3. External control
In accordance with the requirements of stat. 93-123 of Law No. 127-FZ, the stage of external management is introduced following the results of reorganization if it is impossible for the debtor to return to successful life. Or it is used as the only alternative in the absence of reserves for restoring the normal financial situation of the company. The management plan is developed by an expert manager and includes:
- Closing unprofitable business areas.
- Change of activity strategy and repurposing of production projects.
- Sales of property assets of the organization.
- Collection of receivables.
- Obtaining loans from third parties, increasing the size of participant deposits.
- Additional issue of own shares for circulation on the stock market.
- Conducting an inventory of all assets, identifying internal business reserves.
The management plan may include the most radical measures necessary to rehabilitate the debtor, up to and including massive staff reductions, cessation of production, and the involvement of qualified third-party managers. The maximum period is one and a half years; as an exception, it can be extended to 2 years. If no actions bring results, debts are not repaid, the court makes a decision to introduce bankruptcy proceedings, or rather, the free sale of the legal entity’s assets.
Stage 4. Bankruptcy proceedings
The completion of recognition of the debtor's insolvency is the introduction of bankruptcy proceedings.
The procedure itself is carried out strictly in accordance with the regulations of Law No. 127-FZ (stat. 124-149) and means the inevitability of business bankruptcy. As before, at this stage the parties are allowed to enter into a settlement agreement. The main goal of the production is the fullest possible repayment of creditor claims through the sale of company assets at free auction. Management is carried out by a bankruptcy trustee appointed by the arbitration court, who is entrusted with the following functions:
- Carrying out inventory activities to determine the list of assets and their value through an independent assessment.
- Creation of a bankruptcy estate with the inclusion in a special fund of settlements with creditors of all goods and materials of the debtor, fixed assets and other types of assets identified during the inventory.
- Acceptance of creditor claims for bidding for the purpose of proportionate repayment of total liabilities.
This is also important to know:
How to file for bankruptcy: main steps
Upon completion of the bankruptcy proceedings and in the event of insufficient assets to make full payments, all outstanding debts are considered satisfied and the debtor is considered liquidated. Based on a court decision, the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate makes an entry in the unified register (Unified State Register of Legal Entities), and the activities of the legal entity are terminated.
Stage 5. Settlement agreement
Drawing up a settlement agreement by mutual mutual agreement is permitted at any stage of bankruptcy proceedings. The initial proposal may come from the debtor or creditors, but the agreement comes into force only if none of the parties to the process objects. If the initiator is creditors, the relevant decision must be unanimously approved at the meeting. Automatic signing of the consent implies a complete termination of the insolvency procedure.
What information is included in the agreement? First of all, this is the exact procedure for repaying creditors' obligations; also indicates the settlement format, including terms and interest rates. Additionally, the document may include other conditions that do not contradict legal requirements. Often, third parties are involved in concluding an agreement - investors interested in repaying debts, in whose roles both individuals and enterprises are allowed to act, incl. foreign.
Violation of the terms of the agreement by the debtor serves as a reason for resuming the bankruptcy procedure of the company.
Features of each stage
| Hidden stage | Its essence is that in the process of declaring insolvency, the nominal value of the enterprise and its property is imperceptibly reduced. As a rule, by the end of the procedure, the enterprise significantly loses its value due to unfavorable, ongoing factors (wrong decisions of the previous management, increasing debts, cessation of demand for products, expanding costs). |
| Start of the procedure |
|
| Observation |
|
| Financial recovery (rehabilitation) |
|
| External control input | If the previous stage is not effective, the governing body or person is removed from management completely - external management is introduced, the purpose of which is also financial recovery. External managers become the holders of the powers of the head of the enterprise, that is, the previous manager is completely removed. This stage can be introduced by the court both before the debtor is declared bankrupt, and after that. Its goal will be considered achieved, even if in the process the debtor is re-profiled, sold to other owners, or his property is invested in the authorized capital of another legal entity. At this stage, a moratorium is introduced on the fulfillment of the debtor’s financial obligations. The essence of such management: the enterprise operates, but under the guidance of a professional arbitration manager, who is called an “external manager” and is appointed by the court. He carries out recovery activities according to a plan approved by creditors, sometimes called a "crisis specialist." At this stage, his activities are completely managerial in nature. He manages all property, finances, securities and rights of the enterprise. The management period is 18 months, it can be extended by 6 months, but not more than 2 years. Possible activities at this stage:
Completion of the stage - a meeting of creditors to sum up the results, which decides to terminate the paperwork in connection with the payment of debts, introduce the next competitive stage or approve a settlement agreement. |
| Bankruptcy proceedings | The result of external management is a report from the manager with proposals for the further development of the bankruptcy process. It is considered by a meeting of creditors who decide to enter into a settlement agreement or apply to the court for the following measures: Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes! Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes! Call: 8 800 511-39-66 Ask a Question
The court approves the manager’s report or refuses it and determines to terminate the proceedings, extend the period of external administration, refuse to approve the report, and also decides whether to declare the debtor bankrupt and open bankruptcy proceedings. It begins if it was not possible to restore solvency or if all bankruptcy procedures are unsuccessful. If this stage has begun, it means that the debtor is officially declared bankrupt. Its main goal is to satisfy the demands of creditors. The main action in this process is the sale of the debtor’s property, and the results are as follows:
The validity period of the stage is 6 months. with a possible continuation for another 6 months. The decision on bankruptcy is subject to publication in official printed and electronic publications (Kommersant, EFRSB); an entry on the liquidation of the debtor is made in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, which completes this stage. |
| Settlement agreement |
|
The role of the court in them
The arbitration court is the central body in the bankruptcy process. If it is carried out by force, it is he who accepts the claim with a request to declare the debtor bankrupt. The procedure for recognizing insolvency begins with a judicial act issued by the arbitration court at the location of the debtor.
The court participates in every stage and is vested with the following powers:
- decides to initiate and terminate bankruptcy proceedings;
- introduces or terminates all stages, for example, terminates proceedings or external administration at the request of the administrator, and in some cases, creditors or debtor;
- approval of the manager's report or refusal;
- prolongs the duration of stages;
- declares the debtor bankrupt;
- approves the manager’s plan for the recovery of the debtor and makes a decision on recovery;
- appoints an arbitration manager who is controlled and accountable to him.
It is through the court that the special legal status of the debtor and his property is established. He introduces, controls and terminates measures carried out during the procedure.
All stages of bankruptcy as a separate procedure are carried out within the framework of the judicial stage
How does the simplified bankruptcy procedure work?
A simplified procedure is allowed - the company is liquidated as soon as possible with minimal financial losses for the owner.
Typically, this scheme is used by small enterprises with minimal assets in the form of property and cash. The expedited liquidation period is 5-7 months.
No attempts at rehabilitation or external management. After a prompt analysis of the company’s accounting and financial papers, the court makes a decision to liquidate the entity and proceeds to bankruptcy proceedings.
Receivership proceedings in company insolvency proceedings
Bankruptcy proceedings are the final bankruptcy procedure for a debtor enterprise. At this stage, the tasks of the bankruptcy trustee include the maximum satisfaction of creditor claims through the accumulation and subsequent sale of the bankruptcy estate. The decision to start bankruptcy proceedings in the event of bankruptcy of a legal entity must be published in the media. After such a message appears, creditors will have two months to submit their claims.
The deadline for bankruptcy proceedings is six months. But if the allocated time frame seemed insufficient to the manager to search for the legal entity’s assets and organize trading, then he has the right to petition the court to extend this period for another six months.
Important
All the most important functions for managing the company are transferred to the bankruptcy trustee. Its tasks include conducting an inventory, assessing property and organizing auctions. If the debtor has withdrawn his property through dubious transactions in recent years, then the manager has the right to cancel them.
The bankruptcy estate includes all the property and assets of the debtor that belonged to the legal entity at the time of the start of the bankruptcy procedure. These are real estate, industrial complexes, accounts receivable, fixed assets, etc. The need to attract a specialized appraiser to evaluate the bankruptcy estate is decided at a meeting of creditors.
In the event of insolvency, the property of an enterprise is sold through an open auction, which is conducted electronically. Trading is carried out with increasing rates, based on the market value. The most low-liquidity assets are sold at bearish prices.
All proceeds from the sale of property form the bankruptcy estate, which is then distributed among creditors in order of priority. Federal Law-127 contains three creditor levels: • 1st stage – individuals who are responsible for causing harm to life and moral damage; • 2nd stage – employees of the enterprise to whom arrears have accumulated in terms of severance pay and wages. • 3rd stage – bankruptcy creditors, budget organizations.
The principle of priority assumes that payments of each subsequent stage are made only after the previous one has been fully repaid.
Also, current payments, legal costs are repaid from the bankruptcy estate, remuneration is paid to the arbitration manager, etc. The stage of bankruptcy proceedings in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise ends with the liquidation of the company. As a result, all obligations are removed from her, even if the money was not enough to pay off all debts.
Settlement agreement in case of bankruptcy of legal entities
At any stage of the bankruptcy procedure of a legal entity, the participants in the process can enter into a settlement agreement. The initiative to conclude this agreement can come from both creditors and the debtor.
Information
The terms of the agreement are determined at the discretion of the parties. Moreover, its signing is possible only with the full consent of all participants. Sometimes a third party takes part in the settlement agreement - the guarantor of the transaction or the guarantor of the debtor.
The essential points of the settlement agreement are: terms and forms of payment, duration of the agreement and other conditions. Usually the parties have to make some concessions in the settlement agreement. For example, the creditor may write off part of the debt or accrued interest.
After signing the settlement agreement, the bankruptcy case of the enterprise is terminated. If the debtor violates its terms, the procedure is resumed.
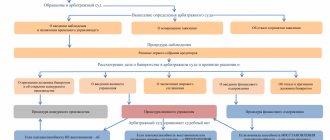
Stage diagram
So, let's look schematically at what happens after the initiation of insolvency.
Bankruptcy of individuals
from 5000 rub/month
Read more
Services of a credit lawyer
from 3000 rubles
Read more
Legal assistance to debtors
from 3000 rubles
more
Write-off of loan debts
from 5,000 rubles/month
More details
Here is a simplified scheme of the bankruptcy procedure for a legal entity.
Having examined everything clearly, it becomes clear that the stages are very closely related to each other. They are subordinated to the same ideas, although at different points in time there are different tasks. The diagram also demonstrates that in the bankruptcy procedure there are steps that change the state of affairs at any time. Like a settlement agreement. This corporate bankruptcy scheme will be an excellent cheat sheet for beginners.
Responsibility in case of insolvency of the organization
Liability under the norms of criminal and administrative legislation is applied in case of fictitious and deliberate bankruptcy of a legal entity. Deliberate insolvency implies that the company’s management deliberately created conditions for the ruin of the company: they entered into unprofitable deals, engaged in the withdrawal of assets, etc.
Fictitious bankruptcy involves creating only the appearance of financial insolvency. For example, not all assets are reflected in the balance sheet, the purchase of raw materials at an inflated cost, distortion of reporting data, etc.
Information
Managers who committed these acts can be held accountable in the form of a fine of 200-500 thousand rubles, corrective labor for up to 5 years and imprisonment for up to 6 years, depending on the scale of the damage caused.
Arbitration managers in bankruptcy of legal entities
The arbitration manager in bankruptcy proceedings is vested with a wide range of powers. The success of the procedure largely depends on the professional skills and qualities of the manager. There are external, administrative, temporary and bankruptcy trustees depending on the stage of bankruptcy. If professional skills allow this, then all functions can be performed by one person.
Information
The arbitration manager is called upon to maintain a balance of interests between creditors and the debtor legal entity. Therefore, it must be an independent figure. The manager is appointed by a court decision from among the SROs indicated by the participants in the process.
The range of tasks of a bankruptcy manager includes taking measures to return the debtor’s property, organizing tenders, monitoring the financial flows of an enterprise, assessing property, analyzing the financial and economic activities of a legal entity, developing and adjusting a business strategy, making settlements with creditors, measures to optimize staff and etc.
The complexity of the tasks assigned to the manager imposes a number of requirements on his candidacy: he must have a specialized education and undergo an internship, have no criminal record, be insured against risks, etc.
The arbitration manager takes part in the case for a certain fee. It consists of a fixed part and a bonus, which is calculated depending on the effectiveness of satisfying creditor claims. The amount of the fixed part for bankruptcy trustees is 35 thousand rubles. per month, external – 45 thousand rubles, administrative – 15 thousand rubles. The size of bonuses ranges from 2 to 7% of repaid debt obligations. The bonus part is paid based on the results of trading.
Important
If the work of the insolvency practitioner is unsatisfactory, they may be held accountable: removed from participation in the process, expelled from the SRO, ordered to compensate for losses caused to creditors, or take other measures.
Creditors in insolvency proceedings
Creditors are participants in the bankruptcy process of legal entities to which the debtor has financial obligations. Typically, several creditors simultaneously have claims against a legal entity. To avoid preferential satisfaction of claims to a certain creditor and abuse on his part, all important decisions are made at creditor meetings. Their participants are bankruptcy creditors and authorized organizations. Representatives of a legal entity, its employees, and tax authorities can also take part in meetings. But they have no say in them.
For your information
The place and time of holding a creditors' meeting in the bankruptcy of a legal entity is appointed by the arbitration manager. Usually it is carried out at the location of the debtor, but other options are allowed. In particular, the meeting may be held in absentia.
The initiative to hold a meeting may come from the committee of creditors or their largest representatives.
At the meetings, such important decisions are made as the introduction of one or another stage of bankruptcy of the enterprise, approval of the manager’s report, filing petitions for the removal of the manager, forming a creditors’ committee, concluding a settlement agreement, etc. Some decisions are made by qualified, some by an absolute majority.
Debt restructuring procedure
When is debt restructuring scheduled?
Debt restructuring is a review of all debts of an individual and the preparation of a repayment schedule that is most convenient for both parties. In this case, only the principal amount of the debt is taken into account and paid - interest, penalties and penalties for late payments are not accrued. In practice, when restructuring debts, partial debt write-off occurs - the debtor will no longer pay interest on loans, penalties and penalties for late payments, and in some cases, part of the principal amount of the loan.
Important point! Restructuring will not be prescribed if the debtor does not have a stable official source of income (salary). In practice, the court often imposes debt restructuring if the debtor has an income of 30,000 rubles or more (in Moscow and the Moscow region). In regions, the minimum income amount may be lower.
What nuances do you need to know when introducing a restructuring plan?
You should know that the restructuring plan is introduced for a maximum of 3 years. It can be drawn up both by the debtor himself and by his creditors. From the moment the debtor’s application is accepted and the financial manager is appointed, within 2 months the latter must draw up a register of creditors, where all persons in respect of whom the debtor has debt obligations will be recorded.
Next, a meeting of creditors is convened, at which the plan must be approved. Interestingly, the debtor can also be present at such a meeting, but he will not have the right to vote. The meeting is chaired by the financial manager.
Once the plan is accepted, the debtor must strictly follow it. If for some reason he cannot pay off his debts on time or his circumstances have seriously changed (dismissal from work and loss of a permanent source of income), then the plan can be canceled by the court at the request of the financial manager, creditors or the debtor himself, and then the procedure for selling property.
Consequences for physical persons in debt restructuring
During the restructuring process, the citizen will have to repay the principal amount of the debt within the period established by the plan, without taking into account interest and penalties. However, there are consequences of debt restructuring.
In particular, when applying for a loan from an organization or an individual, an individual. the person is obliged to inform about the current restructuring. Also, during the restructuring, the debtor cannot invest funds in the authorized capital, acquire shares and shares, and cannot make a gratuitous transaction or purchase and sale of securities.
Any financial claims against individuals. the person must be presented in court, and the due date for payment of monetary obligations will be considered to have occurred. Enforcement proceedings in cases of collection of collateral or property based on creditor claims are terminated.
Debtor in bankruptcy
For the debtor, the bankruptcy procedure for legal entities may result in the restoration of solvency during rehabilitation procedures or the closure of the enterprise and its liquidation. A debtor in bankruptcy is given the rights to participate in meetings of creditors, appeal the decision of the court and the manager, etc. At the same time, he cannot interfere with the activities of the manager and is obliged to provide all documents upon his request.
As for the management team, it is almost impossible to involve them in payments on debt obligations. The general director himself not only does not bear the costs associated with the bankruptcy of the enterprise, but also continues to receive wages and other payments required by law. The only thing the founders risk is their shares in the authorized capital.
Only if it can be proven in court that it was the actions of management that led to bankruptcy (i.e., the insolvency was fictitious) can the managers be held vicariously liable.
The commencement of insolvency proceedings for a legal entity has a number of important consequences for the debtor.
For your information
During bankruptcy, the debtor cannot make any significant transactions to alienate property; his property is sold at auction, information about his financial situation becomes publicly available.
Features of bankruptcy proceedings
The consideration of cases related to the bankruptcy of legal entities and individuals has a number of its own features that must be taken into account by participants at the stage of filing an application.
The main feature is the public procedure for considering cases, since in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, all information about the bankruptcy process must be publicly available, since all actual and potential participants in this process have the right to study it.
Other features of bankruptcy proceedings include:
- the use of the general procedure for judicial proceedings, which is characteristic of the arbitration process, if other options for considering a bankruptcy case are not provided for by the current legislation on declaring a legal entity or individual financially insolvent;
- the court analyzes the current situation in detail in order to decide whether a specific application for bankruptcy should be accepted for proceedings or not . There is a general rule enshrined in the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”, according to which the court accepts applications from debtors belonging to legal entities with debts of over three hundred thousand rubles, as well as from individuals and individual entrepreneurs with debts over five hundred thousand rubles. In addition, the period of existence of the debt must exceed three months. However, if, when examining the submitted application, the court establishes clear signs of the company's bankruptcy, then the application may be accepted even before the specified amounts of debt arise and the period of existence of the debt. The issue in this case is resolved individually;
- submission of an application to begin the procedure for declaring the debtor financially insolvent occurs only in writing with the attachment of all documents confirming the competence of such a process . The use of an electronic form for filing documents in this case is impossible, since the services of electronic documentary interaction with arbitration courts do not provide such an opportunity;
- the submitted application must be drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the Arbitration Procedural Code, as well as the requirements of Articles 37-41 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” (both in terms of its content and in terms of compiling a list of attached documents);
- The application can be submitted either by the debtor (Article 9 of the above law entrusts him with such an obligation if a corresponding situation is identified in the company), or by creditors (who can take advantage of the right offered to him by the same law). When submitting an application, you should remember that its signatory must be the author of the application (the head of the debtor company or creditor) or an authorized proxy (in this case, you will need to indicate the details of the document giving the signatory the appropriate powers);
- simultaneously with sending all documents to the court, the applicant is obliged to send them also to the second party involved in the case (the debtor himself, the creditor, the authorized government body, etc.);
- within five days from the day following the day of receipt of the application, the arbitration court issues a ruling on the possibility of accepting the case for consideration (in this case, copies of the ruling are sent to all persons participating in the case, to the tax authorities at the place of registration of the debtor, as well as to that self-regulatory organization arbitration managers, to which there is a link in the text of the application) or to leave the case without progress and return it to the applicant (if there are any errors in the case that prevent its acceptance for consideration);
- within a period of fifteen to thirty days from the date of acceptance of the application, the court must consider it in terms of the validity of acceptance for proceedings . There are three options for consideration in this case: the application is justified, and surveillance is imposed on the debtor; the application remains without consideration because it is unfounded or any obstacles to such a procedure have been established; consideration of the application is terminated because there are no grounds for continuation (for example, if the debt is repaid and the creditor’s claims become unfounded);
- The minimum period for conducting a bankruptcy procedure is seven months (the observation period does not cover other stages of the bankruptcy process), during which the court considers all the circumstances of the case and decides on the possibility of declaring the debtor bankrupt or on the impossibility of such recognition, and also determines the signs of fictitious bankruptcy.
Consequences of bankruptcy of legal entities
Upon completion of the bankruptcy insolvency procedure, information about the company is deleted from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Those. in fact, the legal entity ceases to exist as an independent entity and all debt associated with business activities is liquidated.
The manager must relinquish all authority and transfer the documents to the archive. All employees are pre-dismissed. The founders of a bankrupt can open new companies and implement other projects. This is not prohibited by law.