Hello! In this article we will talk about the liquidation of an enterprise, the steps that need to be taken and what difficulties an entrepreneur may encounter as part of the abolition of a legal entity.
Today you will learn what liquidation is, what may be the reasons for liquidating an enterprise. How to liquidate a company if it has outstanding debts. What are the features of voluntary and forced liquidation? What payments and in what volume must be made in relation to dismissed employees.
Content
- What is liquidation
- Reasons for liquidation of the enterprise
- Grounds for voluntary liquidation of an enterprise
- Grounds for forced liquidation of an enterprise
- Liquidation of a company with debts
- Recognition of bankruptcy and liquidation of the enterprise
- Liquidation of an enterprise - step-by-step instructions
- Procedure for settlements with creditors
- False liquidation
- Features of liquidation of a representative office of a foreign company
- Features of employee dismissal
- Payments upon liquidation of an enterprise
- Procedure for calculating compensation
What is liquidation
If it were necessary to find an illustration for the common phrase “it’s easy to start, it’s hard to finish,” then the topic of liquidation of an enterprise would fit it perfectly. Indeed, in contrast to a newly created company, it has already existed for some time due to accounting entries, errors, debts to creditors and increased interest from the tax authorities. Thus, a legal entity needs to begin the long thorny path of gradual abolition of itself, where each step is strictly regulated by the legislator.
“liquidation” itself is of Latin origin, liquidus meaning “liquid, fluid.” What matters is the easily visible logic in the phrase “liquid funds” - that is, those that are easy to implement, turn into money, “soft, flowing”. With this in mind, we will regard liquidation not simply as the destruction of the company, but as an event to obtain the greatest benefit for ourselves, or at least with the least loss.
The legal definition of liquidation does not go into the etymology of the word and is as follows:
Liquidation is a set of measures taken to terminate the activities and the very existence of an enterprise without transferring responsibilities and rights under it to other persons.
Among other things, this means that those creditors who did not have time to request from the liquidated company everything owed to them in due time will subsequently be unable to present anything - because there will be no one left. Liquidation is the final stage of a company’s commercial activity, its swan song. The company as a legal entity will disappear from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities - which means it will disappear completely.
In what cases and how are enterprises liquidated?
Typically, the liquidation procedure is a difficult and lengthy process that can last more than six months and be accompanied by numerous checks. It consists of three main stages.
- ✔ Making a decision on the termination of the enterprise’s activities - by the court, founders or other bodies authorized for this purpose.
- ✔ Appointment of a liquidation commission (or liquidator) - by the court, founders or other body agreed with the administration.
- ✔ Making an entry into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities about the termination of the enterprise’s activities (made by the state registrar).
Depending on the type of organizational and legal actions, a distinction is made between voluntary liquidation (so-called self-liquidation) and forced liquidation.
Reasons for liquidation of the enterprise
Liquidation is either a voluntary decision made by the founders, or forced, in which case we are talking about a compulsory measure on the part of the judiciary. Another method stands out - liquidation of an enterprise due to being burdened with debts, where the only way to legitimately resolve the issue would be to declare bankruptcy. Let us consider all these reasons in turn.
Grounds for voluntary liquidation of an enterprise
Depending on the form of the legal entity, the decision on its liquidation is made at a general meeting of shareholders (for JSC) or at a meeting of participants (for LLC). The decision to liquidate the JSC is approved if three-quarters of the votes agree. For an LLC, liquidation will be ordered with unanimous support.
The following reasons may justify liquidation:
- Achieving the purpose for which the society was founded. For example, the completion of the construction of a facility (a society was organized to raise funds for it);
- Expiration of the period for which it was created. Let’s assume that an LLC was created to service a large-scale sporting event for the duration of the event;
- Conclusion about the unprofitability of the enterprise. For example, the closure of a ski store due to global warming in the area and melting snow;
- The owners want to end an annoying type of business in order to receive funds to start another project.
Voluntary liquidation is the only type where the founders can change their minds and not carry it out. The law does not limit them in this right even after a decision has been made, which can be canceled by submitting the appropriate document on cancellation to the tax authority. The “point of no return” will be considered the entry of data into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities - after which the company will officially cease to exist.
Grounds for forced liquidation of an enterprise
- It turned out that the legal entity initially existed illegally; an intentional or accidental violation of the law, including the provision of false information, was revealed. For example, if it becomes known that the company, instead of selling paper clips stated in the charter, distributes alcoholic products;
- Conducting activities without the required license. For example, according to the Federal Licensing Law, such a permit is needed for the production of medicines, television broadcasting, educational, security and many other types of activities;
- The company carried out activities prohibited by law or in violation of articles of the Constitution of the Russian Federation. For example, according to the Law “On Competition”, a deputy as a representative of state power cannot conduct business at the same time as his main activity;
- If it is determined that the company will not be able to achieve the goals for which it was founded, or its activities become impossible. For example, in 2020, during inspections, the Federal Air Transport Agency recognized the further activities of the air carrier Transaero as impossible.
Liquidation of a company with debts
Naturally, there is hardly at least one company that, before closing, will not have at least some debts to business partners or the state. In this case, “with debts” does not mean the fact of debt, but the inability to pay it off on your own. Sometimes the founders re-register the company with another general director, a purely nominal person, and hope that, like the cases with shell companies, the entry about their company will disappear from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
However, practice shows that the likelihood of such entrepreneurs being held accountable is very high. The tax authorities are figuring out what's what, and the threat of subsidiary liability hangs over businessmen. In the context of the issue under discussion, this means that the founders may be forced to pay for the company’s debts with personal funds and property.
The only legal way to liquidate a company with debts is to declare bankruptcy.
Types of liquidation
There are several types of liquidation:
- Voluntary liquidation is the closure of an enterprise at the request of the founders themselves. For example, they lost interest in the activities of their company, decided that their enterprise was unprofitable, or considered that the company’s activities had achieved all the goals for which it was created. However, often the reason for liquidation is the concealment of legal and accounting errors made in the course of the company's activities.
- Forced liquidation is the closure of an enterprise by the relevant authorities for violation of the law during its activities.
Causes:
- repeated or gross violation of current antimonopoly, labor or tax laws;
- company activities prohibited by law;
- activities of an organization without obtaining permits or licenses.
- Liquidation as a result of bankruptcy. It is associated with the insufficiency of property in order to fully satisfy all the claims of creditors. In this case, the initiators are creditors who submit an application to the Arbitration Court for the company to be declared bankrupt. But often, companies manage to declare bankruptcy themselves, before creditors and authorities.
- Alternative liquidation - reorganization of a company is carried out in cases where there is a need to reorganize the business or there is a change in its founders. When a legal entity is reorganized, several or one company is formed, and new founders are introduced. The company continues to be listed in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but other persons are now responsible for its activities.
The most convenient and profitable method should be chosen based on the characteristics of each specific case. Because the amount of required documentation, timing and costs depend on which form will be used for liquidation.
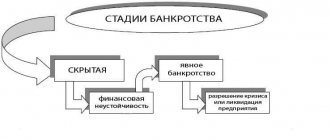
Recognition of bankruptcy and liquidation of the enterprise
A company can declare itself bankrupt either compulsorily or voluntarily. This will mean that the company has too many debts to continue its activities, and it is not possible to pay them off. There are also cases where during the liquidation process it is discovered that there are not enough assets to pay off all debts. Then the liquidation procedure must be officially re-registered as a bankruptcy procedure.
Having drawn up an interim balance sheet and discovered a debt of over one hundred thousand rubles that the company cannot repay, the liquidator must apply to the arbitration court. The debtor provides the court with a list of candidates, one of whom the court selects as an arbitration manager. During the audit, the manager decides whether to impose subsidiary liability on the founders, that is, force them to “pay out of their own pocket.”
Given the appointment of a receiver from the debtor's list, it is unlikely that he will request such a measure. In this case, the bankruptcy procedure proceeds at an accelerated pace, debts are written off, and the company is liquidated. There is also a distinction between bankruptcy based on the application of a creditor or a debtor. They can file an application with the arbitration court to declare the company bankrupt. In this case, the proceedings are in full force and there is a danger of the arrival of the tax commission and, as a result, the discovery of grounds for subsidiary liability of the founders.
Monitoring is a procedure ordered by the court to monitor the financial condition of the debtor and in order to preserve his property. It is carried out for a period of no longer than seven months.
During the supervision process, the appointed temporary manager does the following:
- Publishes an announcement about the beginning of surveillance in the Kommersant newspaper;
- Notifies creditors;
- Requests documentation on the debtor’s activities;
- Attends court hearings where the legality of creditors' claims is discussed;
- Monitors the activities of the debtor;
- Performs financial analysis and reports;
- Comes to a certain conclusion about the debtor’s solvency and notifies the court about this;
- Initiates the first meeting of creditors.
At the meeting of creditors, a majority vote makes a decision to move to the next stage after observation - bankruptcy proceedings.
Bankruptcy proceedings are a procedure that is applied to a bankrupt debtor in order to proportionately satisfy the claims of creditors.
The appointed bankruptcy trustee, in addition to the actions performed by the temporary trustee during the supervision procedure, inventories and sells the company's assets. The proceeds are used to settle accounts with creditors as far as possible.
Upon completion of the second stage, the debtor will be excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, and his obligations to third parties will be considered fulfilled.
Features of the liquidation of bankrupt enterprises
The initiators of liquidation of a bankrupt enterprise are usually authorized state bodies, creditors and third parties.
To submit an application, the debtor enterprise must have financial obligations in the amount of at least three hundred thousand rubles with a period of non-fulfillment of more than one quarter.
The debtor acts in court as a defendant.
The debtor is recommended to independently initiate the liquidation procedure in order to prevent an increase in penalties and possible seizure of property.
During the period of liquidation of a bankrupt enterprise, the rights to manage its property are transferred to the bankruptcy administrator.
Upon completion of the sale of the enterprise’s property at auction and the repayment of obligations to creditors, the court will forcibly register the liquidation of the enterprise.
The proceeds are transferred to creditors.
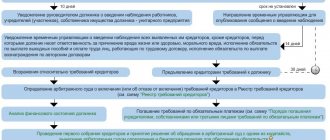
Liquidation of an enterprise - step-by-step instructions
Any liquidation has standard instructions for its implementation, where all steps are regulated in detail by the legislator.
For better clarity, let’s consider all the stages of liquidation of a legal entity in the form of a table:
| STAGE | DESCRIPTION | IMPORTANT |
| 1. Notify the tax authority | The authorized person submits the completed Form N P15001 with the decision made within 3 working days after the meeting | You cannot submit by proxy - only the management does this |
| 2. Appoint a liquidator (commission) | The founders select members of the liquidation commission (or one person), set the procedure and deadlines. The tax authority must also be notified about this. | From now on, only this body has full management powers |
| 3. Publish the news in the media | Namely, in the publication “Bulletin of State Registration” + the Commission notifies all creditors in writing | The period for creditors to apply is at least 2 months from the date of publication |
| 4. Draw up an interim balance sheet | Must contain information about the company’s property, creditors’ claims and decisions on them. From 2020, a calculation of insurance premiums for the period is also attached | Drawed up only after the expiration of claims from creditors, completion of a tax audit or legal proceedings against a legal entity |
| 5. Pay off creditors | If there is not enough money for creditors, the commission can sell off the property of the legal entity. faces. If this is not enough, the legal entity must declare itself bankrupt | Exceptions (cannot be bankrupt): political parties, government and religious institutions |
| 6. Close accounts and cancel licenses | After paying debts, the company is obliged to close bank accounts. For licenses, you must submit an application to the licensing center | The tax office, social insurance funds and pension funds are notified of the closure of accounts. |
| 7. Distribution of property of a legal entity | The property that remains after settlement of debts is distributed among the participants (or shareholders) | If there is a dispute over an item, it is sold as a commission from the auction, and the money is divided |
| 8. Sort out documents | Important documents as part of the Archive Fund of the Russian Federation and on labor personnel are transferred for storage to municipal archives | All other documents are destroyed, including the organization’s seal |
| 9. Make an entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities | Notification of the registration authority about the completion of liquidation. Possibly no earlier than 2 months after publication in the media | From 2020, liquidation is impossible until the end of the legal proceedings against the legal entity. persons, if such is carried out |
If, over time, undistributed property of an already liquidated company is discovered, the interested party can go to court. The condition is that no more than five years must pass from the final date of liquidation.
Liquidation through bankruptcy
This method of closing a business is directly related to the inability to fulfill obligations to creditors.
The bankruptcy of a company does not occur instantly. The company is given time - 3 months - to restore its financial well-being.
If the organization fails to improve its financial situation, liquidation is envisaged.
The procedure for bankruptcy of an enterprise in Russia
Liquidation through bankruptcy can be carried out in two ways:
- Voluntary. In this case, the head of the organization can begin to act under the most deplorable circumstances, and then prove that you tried to correct the violations.
- Forced. This option goes through the courts. In this case, you will not be able to solve all the errors and violations and liquidation of the organization will be the only solution.
The court may order bankruptcy proceedings when it is no longer possible to pay off creditors.
The purpose of such a measure is to search and identify the debtor’s property, liquidate the organization and satisfy the claims of creditors.
The approximate duration of bankruptcy proceedings is six months. During this time, the bankrupt company will be managed by a meeting of creditors or a manager appointed by the court.
After the reporting period, the bankruptcy trustee makes a decision to liquidate or cancel the liquidation of the enterprise. He must submit his application to the court. The judge must then either agree or reject it.
If the decision was not made in favor of the businessman, then within 5 days the tax authorities must issue the appropriate documents on the liquidation of the company through bankruptcy.
Procedure for settlements with creditors
The Civil Code requires a company to comply with the procedure for satisfying claims from creditors during the liquidation process.
After approval of the interim balance, the calculation is carried out as follows:
- If an enterprise has citizens to whom it is responsible for causing harm, then settlements with such persons are carried out first;
- In second place are all employees of the enterprise who, by law, are entitled to severance pay and compensation.
A month after the interim balance has been compiled, it is necessary to repay debts of the third and fourth degrees, namely:
- Pay taxes, fines, penalties and insurance premiums;
- In fourth place are all debts not included in the first three categories.
Let's turn to the legislation
According to clause 1, part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract can be terminated on such grounds. In this case, employment contracts are terminated with absolutely all employees, including pregnant women, single mothers, veterans and representatives of other groups enjoying additional labor guarantees. The procedure for terminating employment relations with employees in the event of liquidation of an enterprise consists of several steps, which we will consider below. That is, dismissal due to liquidation applies to absolutely every staff member of the enterprise. What are the rights of an employee during the liquidation of an organization? We will discuss this in detail below; the law establishes that employees must be warned, firstly, about the termination of the contract, and secondly, they have the right to appropriate payments and compensation.
False liquidation
Sometimes it is possible to carry out liquidation only on paper - in reality, the company will continue to exist, significantly or slightly changing its form. Let's consider these possibilities.
Transformation of a legal entity
Occurs when a company changes the address of a legal entity, founders. At the same time, the company does not merge other enterprises and does not divide itself.
Enterprise reorganization
During reorganization, one or two enterprises may cease to exist, and one or two new ones appear. Types of reorganization include acquisition, merger (liquidation by incorporation), spin-off, division and transformation of organizations. The first type is especially often discussed in the media - acquisition, when a large company buys a smaller one in order to reduce costs, increase efficiency or expand its area of operation.
For example, in the global community, Google is considered the most merciless absorber. Over the years, this “shark” has swallowed up more than a hundred companies, including Motorola, Picasa, Android, YouTube and others. If we take Russian reality, a story from 2011 comes to mind, when the American PepsiCo bought the Russian Wimm-Bill-Dann.
In the event of such an accession, the rights and obligations are transferred to the legal successor.
Features of employee dismissal
A company at the liquidation stage will soon cease to exist and, as a result, will no longer need hired labor. All employees on staff will need to be accounted for. The Labor Code establishes that dismissal during liquidation occurs at the initiative of the employer.
The process occurs in stages:
- At least three months before dismissal, you must contact the union and negotiate with it.
- At least two months in advance, lists of employees are submitted to the employment center, indicating their names, professions, and wage conditions. Still, the company does not guarantee the continued employment of its former employees.
- The employees themselves are notified two months before dismissal. All notices are given in writing and signed by employees. If an employee is absent from the workplace due to a business trip, vacation or sick leave, a notification is sent to him by registered mail.
- When the notice period expires, the company issues dismissal orders and introduces them to the employees against signature. If any of them refuses to sign the document, a corresponding mark is placed on the order.
Based on the issued orders, entries are made in work books in strict accordance with the Labor Code, and the data is entered into the employee’s personal card. On the day of dismissal, workers are handed over and a full settlement is made with those dismissed.
Payments upon liquidation of an enterprise
Payments to employees are made strictly on the last working day; delays in payments are unacceptable. The only exception is if the employee himself is absent from work that day, then the calculation will take place the next day upon his request.
Dismissed persons are entitled to payments and compensations:
- The required salary for the time worked;
- Compensation for unused vacation days;
- Compensation in the amount of two months' salary for termination of the contract;
- Severance pay in the amount of one month's salary;
- Salary for the third month if the employee was looking for a job through the employment center and could not find it within fourteen days.
All dismissed workers are entitled to compensation.
Therefore, payments must be made in respect of the following categories:
- Working pensioners . According to the Labor Code, persons who, due to age, are entitled to pension payments can simultaneously continue their working activities. Therefore, they are entitled to both severance pay and the rest of the listed payments (with the assistance of the labor exchange - even the third month’s salary in case of non-employment). According to the law, the exchange does not have the right to refuse to issue such a certificate to a pensioner;
- Part-timers . They receive only severance pay due to the fact that they have a main place of work;
- Employees are on vacation or sick leave . According to the general rules of the Labor Code, it is impossible to fire an employee who is absent from work due to illness or vacation. The exception is the liquidation of the enterprise. Here the law obliges the dismissal to be carried out on the exact date indicated in the notice. Moreover, these employees receive all compensation and payments in full, unless otherwise provided;
- Employees on maternity or child care leave . Even a liquidated company is obliged to pay everything due on sick leave. If a woman goes on maternity leave after the liquidation of an enterprise, all benefits are paid by the social security service, and in full from the salary, despite the length of service. Pregnant women and women on maternity leave with children under three years of age who were dismissed due to liquidation are entitled to additional assistance in the form of social unemployment benefits and accrual of seniority.
If the rights of employees were violated during the liquidation process, they can appeal to the prosecutor's office, court or labor inspectorate within a month from the date of dismissal.
Amendments to the second reading
As Sergei Zhigarev, head of the State Duma Committee on Economic Policy, previously emphasized, 86 amendments were received to the bill, 28 of which were recommended by the committee for adoption, and 58 for rejection.
According to him, the government’s concept, which provides for a reduction in the number of unitary enterprises, has been preserved for the second reading. At the same time, as a result of finalization of the document, the list of grounds for creating unitary enterprises has been significantly expanded, in particular, these are cases of ensuring livelihoods in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, ensuring activities for the development of culture, art and cinematography and preserving cultural values, ensuring activities outside territory of the Russian Federation of a number of federal executive authorities and the Rosatom corporation, the deputy said.
A ban has been established on the activities of unitary enterprises in commodity markets that are in a state of competition (except for the cases noted above), if the revenue of the unitary enterprise from its activities exceeds 10% of the total revenue of the unitary enterprise for the last calendar year. This restriction does not apply to unitary enterprises created on the basis of federal law, acts of the President of the Russian Federation or the Government of the Russian Federation, and to unitary enterprises operating in the field of radioactive waste management, unitary enterprises with the status of a federal nuclear organization.
At the initiative of members of the Federation Council, the law was supplemented with norms providing for the possibility of the government of the Russian Federation, upon a reasoned proposal from the head of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, to make a decision on the creation or preservation of a unitary enterprise, if this is necessary to eliminate the consequences of an emergency situation or to prevent a threat to the normal life of the population in the region.
Another innovation of the law was the mitigation of the consequences of violations of antimonopoly legislation for unitary enterprises in comparison with the version introduced by the Russian government earlier, Zhigarev said.
It is stipulated that in case of violation of antimonopoly legislation, the founders of unitary enterprises are given a warning to terminate unauthorized activities or liquidate the enterprise. At the same time, amendments were made to eliminate the need to obtain permission from the antimonopoly authority to register a unitary enterprise.