The following ready-made samples of business plans with calculations are not standards, but are only examples to show the entire structure of each business. Therefore, all calculations given in these business plans can be considered indicative. These free examples provide insight into the steps to building a successful business and also serve as a template for writing your business plan with calculations. There are 175 examples in total for free use.
Each sample business plan includes calculations of costs, income, payback period and other business indicators. This selection of ready-made business plans is also suitable for students.
What issues are covered in the organizational section of the business plan?
In order to effectively and quickly draw up an organizational plan in a business plan, you will only need to prepare a list of several questions, the answers to which will be described in detail in this paragraph, and will also become the basis for the implementation of the organizational structure. Among the main ones are the following:
- What are the main links in the organizational management chart?
- What is the relationship between the individual links?
- Buy a business plan
How can you present a project for coordinating the activities of individual departments? - What kind of personnel is required for the job?
- How are the responsibilities of employees divided within a given enterprise?
These are the main issues that you will need to cover in your business plan. It is the competent answers to them that will determine the success of project management.
Advice! It is best to start working on a section by drawing up all the questions that need to be covered in as much detail as possible, this will make it easier to write.
Why Presentation Is Important to the Success of a Business Plan
Not all entrepreneurs pay due attention to preparing a presentation for a business plan. This is mistake. The information posted on the slides is what investors pay the most attention to when getting acquainted with a business idea, so their development should not be left to chance.
It is important to understand for what purpose the presentation is being created. It must be remembered that it is being developed in order to convince listeners that the business plan project for which the presentation was made will be profitable and worth investing in.
Legal form
It is necessary to select and describe the legal form of the enterprise. In accordance with the chosen organizational and legal form, the main interactions, as well as the structure of the company's hierarchy, will be determined. A responsible approach to this organizational section of the business plan will ensure a simpler and more understandable preparation of the necessary documents, and will also significantly simplify the task of managing the company. Consideration should be given to the differences between different types of legal forms regarding the structure of the company, as well as how one or another form will suit a particular enterprise.
Step-by-step instruction
To contents
Before you draw up a business plan yourself, analyze potential markets. Find out which segment of the population will use your products or services, taking into account age, geography, family, financial status, interests. Even if you have developed a universal product, you must first identify a smaller, more targeted group of customers, possible competitors. You need to clearly define what you need to get started. This applies not only to material costs, but also to the time to achieve results.
How to write a business plan - step-by-step instructions:
Step 1: Create a cover page
It contains information about the company, its owner, and contact information. The next page contains the content. If you are afraid that someone will steal your original idea, insert a non-disclosure agreement that potential investors, for example, will sign.
Using this sheet, investors will form a first impression of the project. Please format it correctly. The title page contains:
- name of the project;
- the name of the company for which the document was developed;
- the state and locality where the company will operate;
- contact information – telephone numbers, email, video communication data;
- date of creation.
To attract the attention of potential partners, indicate the payback period, time to reach the break-even point, planned profit, and volume of investment.
The next page contains the content. If there is a risk of your original idea being stolen, insert a non-disclosure agreement for potential investors to sign.
Step 2. Completing your resume
A brief overview of everything that will be described next. The section includes:
- list of goals and objectives of the company;
- available and required resources;
- potential expenses and income;
- ways to implement a business idea;
- the uniqueness of the offer, its relevance to the target audience;
- volume of investments, credit funds;
- key performance indicators;
- refund deadlines.
The data is compressed into several paragraphs.
Resumes are written when planning has already been completed. It should not exceed one or two pages in length. Based on it, investors form an opinion about the project and decide whether it is worth investing in it. Make the description vivid, but do not embellish the possibilities - business people involved in investments will immediately sense the implausibility of the information. Be based on accurate numbers and factual information.
Step 3. Formulation of commercial goals
Goals need to be presented in advance, before drawing up a business plan yourself. They must be specific and achievable. The minimum number of targets is four.
When describing what you plan to achieve, articulate the benefits that customers who choose the product or service will receive. Support the benefits with evidence. Indicate that your offer is unique. Even if you produce something ordinary, you can always find nuances that distinguish the product from its analogues. For example, low cost due to transport accessibility of raw materials or manufacturing technology that improves quality. If there are patents or copyrights, be sure to mention this, confirming the uniqueness of the product.
At the end of the page, inform about plans for scaling the business and ways to achieve global goals. This could be accelerating the production process through the introduction of new technologies, equipment, attracting suppliers, expanding the range. If you fill out this section correctly, potential partners will be convinced that the project is not a dummy, and the company will not close due to high competition.
Step 4: Mission Description
Here the intangible values of the enterprise are indicated, indicating its role in society and its differences from other market participants. The mission is not a constant value; it develops as the activity grows. Step-by-step instructions do not always include this point, but it can show the social significance of the undertaking, which will be an advantage in the eyes of investors.
Step 5. Market analysis
This part consists of two subsections: researching the scope of activity and assessing market competition. In the first case, the main thing is to find out what is sold in the chosen niche and what is not in demand. The information must be up to date. This will show what the prospects for the development of the project will be. Indicate external factors that affect the market state of the industry: sanctions, lack of trained personnel. Highlight growth potential. Investors invest in companies that will achieve significant growth within three to five years. Show them why your business can quickly capture market share.
Additionally, you can create a composite portrait of a representative of the target audience, describing the reasons why this particular person needs your product.
Evaluate the opportunities and offers of competitors. They exist even if you are promoting a unique product. Someone is sure to offer something close to the target audience. Your idea should be different. Demonstrate that you can maintain your competitive advantage. The hardest part is to articulate what you will do to maintain your position in the market when new competitive threats emerge. Proving that your product or service offering is so superior that customers have little incentive to look elsewhere will convince investors to invest in your project.
Step 6. Assess the campaign's industry capabilities
List the key success factors: what you can achieve by implementing your idea, what are the real advantages over your competitors.
Please indicate:
- legal information about the new company - time of creation, number of specialists, organizational and legal form;
- data on real estate, equipment that will be used;
- information about what is owned by the organization;
- potential or actual financial performance (in brief);
- availability of raw materials, materials necessary for processing into a finished product
Describe the types of activities of the enterprise with all the nuances: seasonality, market volatility, operating hours.
This section is especially important for startups. Here, all the points need to be worked out more carefully, indicating the prospects for the successful development of the future enterprise, so that investors assess the reliability of the investment.
Step 7: Listing Products or Services
In this section, explain what you offer to the potential client. Clearly formulate a description of the physical qualities of the product and technological criteria. Attach high-quality photographs, drawings, diagrams or advertising brochure. For those who plan to provide services, graphs and diagrams will help. If you plan to provide additional products and services after the initial launch, include those too.
Having given an accurate description of the product or service, focus on the possibilities of use and attractive aspects. This is what will show the uniqueness of the offer and draw attention to the potential. Comment on the readiness of products or services to enter the market, this will help assess the viability of the enterprise. Details regarding research and development efforts should be included as part of the production plan.
Additionally, it is worth submitting a list of experts who are familiar with the product and can give favorable feedback. The evidence itself, in the form of a letter or report, is included in the appendix.
Step 8. Drawing up a marketing strategy
Describe the tasks, goals of marketing policy, techniques for solving problems, increasing sales. Reveal the strategy for promoting goods or services - all the ways to promote your business. The section is designed as specifically as possible: tasks are outlined down to which of the staff specialists will be entrusted with which task.
You must also indicate:
- market research methods in the selected industry;
- planned volume of goods (services) sold, assortment;
- ways to improve product quality and increase its attractiveness to buyers;
- stages of the organization reaching full capacity;
- description of product packaging and price;
- procurement and sales system;
- control of marketing activities.
The advertising strategy must be clear and understandable. In addition to online marketing, consider offline methods: business cards, flyers, local media, direct mail, magazine advertising, signs. Tell us what the advertising policy will be, how much you will have to invest in promotion. Assess the risks and benefits that lead to an increase or decrease in demand. Indicate specific sales routes and techniques for increasing demand. Draw a conclusion about the effectiveness of the marketing strategy as a whole, evaluate the possibilities of implementing all of the listed tasks.
Step 9: Create a production plan
This includes everything that directly concerns the creation of the proposed product. Those entrepreneurs who plan to make money through intermediary can exclude this item. Describe here the stages of product production, relevant technological processes, and requirements for personnel qualifications. List suppliers, contractors and subcontractors, partners, and indicate the operations that will be entrusted to each of them. Describe techniques that allow, if necessary, to increase or decrease production volumes. Tell us how product quality, production process, inventory, and maintenance will be monitored. Describe in detail the equipment, necessary raw materials, cost and method of purchase or rental.
Explain how your technology works in simple and understandable terms. Don't try to impress with knowledge or assume that the reader has technical training. The main thing is for the investor to understand that using technological processes you can make money.
Step 10. Organizational planning
Here the organizational and legal form of the enterprise, the management scheme are prescribed, the owners of the company are listed, indicating their shares in project management, and personnel. This item includes a project implementation schedule with exact deadlines.
When planning a startup, you should outline how you are going to run your new venture. The owner of an operating company needs to prove to investors that the organizational structure is as efficient as possible.
Clearly describe the qualifications and payment of specialists, technologies for motivating and increasing loyalty to the enterprise, interaction between departments, and personnel policies. Imagine a scheme for supplying each department with the necessary material and technical resources. Make the investor believe in your management team. If there are past successes, indicate them: this will provide a kind of guarantee of the fruitful work of the new project. Show what skills and experience are required for development, how you assembled a team taking into account specific requirements. It is recommended to provide excerpts from the laws and regulations governing the work of the chosen field of activity in the country.
Step 11. Financial calculations
The section provides summary financial data. The calculation format largely depends on the goals of the project, scale, and market opportunities. But in most cases, calculation standards must be indicated in this paragraph:
- sources of capital formation;
- constant and current prices;
- tax payments according to the chosen regime, taking into account deadlines and interest rates;
- planning horizon – time of project implementation;
- currency dynamics;
- information about inflation in recent years.
It is necessary to draw up a reasonable forecast of income and expenses for the selected period - constant and variable, a description of financing methods, an approximate cash balance
It is important to analyze key financial indicators, for example, net present value NPV, profitability index PI, internal rate of return IRR.
Most often, a monthly calculation is created for the year. The most convenient way to organize this information is in Excel. The payback period for investments is drawn up in the form of a schedule. Additionally, an analysis is carried out to determine the break-even point.
The section includes a profit and loss forecast implemented through a cash flow table, offers of shares, and discounts. This is perhaps the most important point for investors, since it best shows the profitability of the project. It is especially necessary to clearly describe the cost estimate with the calculation of the cost of production. After all, investment costs are included there. The cost is calculated based on data on costs, wages, and overhead costs. This takes into account total production volumes and sales levels for a certain period.
Step 12. Conduct a potential risk analysis
The section includes not only a list of possible dangers, but also ways to prevent them, and strategies for getting out of difficult situations if they do arise. Here the entrepreneur is obliged to examine the project for negative factors that lead to a decrease in profitability. Risks may be:
- Commercial. Depend on external factors, for example, the actions of competitors, decreased demand.
- Financial. Associated with non-payment of accounts receivable, incorrect choice of investors.
- Organizational. Strikes, sabotage, violation of trade secrets.
- Natural. For example, crop failure due to bad weather.
Determine all possible risks as a percentage using estimates and forecasts of experts. Develop a detailed scheme for their prevention or minimization, describing a set of techniques and tools. Predict the behavior model of an enterprise in a difficult situation.
If you are counting on third-party investment in the project, indicate the barriers to entry into the market. List those points that will prevent competitors from intercepting customers during the rapid development of your enterprise. The more barriers you can name, showing how you can deter a buyer, the more interesting your proposal will be to the investor.
The step-by-step instructions end with an appendix containing information about the company that does not fit the above categories. For example, construction permits, lease agreements, equipment documentation, licenses and permits, recommendations. Step-by-step instructions do not always include this point, but sometimes it is necessary to further convince investors.
When creating a business plan yourself, keep in mind that this is not a static document. As the company grows and develops, amendments are constantly made to the planning data. This gives you the opportunity to expand your business, look back and see what has been achieved and what has not.
Organizational structure of the company
In this organizational section of the business plan, it will also be necessary to clearly and in detail disclose the issue of the organizational structure of the enterprise, the features of which greatly influence the function of adapting the company to various changes in the external environment. The better and more effective the connections between the various structural divisions of the enterprise, the more reliable the entire system will be, which means it can easily counteract many outside interventions. There are main factors that determine the choice of organizational structure, primarily:
- scope of the company;
- legal form;
- technologies that are planned to be used in the development of the company;
- The cost of a business plan,
features of the market that the company expects to enter; - company size (number of employees, cash turnover, production capacity, etc.);
- provision of resources and options for alternative suppliers;
- features of information flows within the company, as well as information relationships with the external environment.
The important point is that the more accurately these points are assessed and the more detailed the structure of the company is spelled out, the lower the various risks for the enterprise will be and the easier it will be to carry out management functions. By and large, production activities largely depend on a well-developed and thoughtful structure of the organization. It is also important to think through and consider in as much detail as possible the levels of interaction between production and people (staff, clients, etc.), between various structures of the organization, and with the external environment, taking into account both favorable and possible unfavorable events.
Personnel issues (managerial and rank and file). Schedule and mode of operation
The organizational section of the business plan must necessarily include personnel issues; this topic is very important and it is its correct planning and description that will provide the company with the necessary staff and qualified specialists who will be in the right quantity and in the right place.
Advice! It is most convenient and clear to present the management and rank and file of employees in the form of a block diagram, in which all connections will be clearly illustrated, the hierarchy, number and main functions of each employee will be visible.
It is important to work out and describe the work schedule and mode as clearly as possible. It will also be necessary to specify in detail the wages of each staff unit, both per month and per year. Since this part of the financial plan will help organize the planning of future bonuses or the possibility of hiring new employees, it is worth paying maximum attention to it. In the future, this approach will help create a sustainable production structure that will take into account the characteristics of each working link, with the possible replacement of one employee by another and partial or complete duplication of functions.
Types and classification
To contents
Planning documentation differs not only in size and detail. Business plans are classified according to their purpose:
- Starters. A document for launching a new business includes sections describing the product or service, market potential, revenue forecasts, profits, and cash flow.
- Internal. Targeted at a specific audience, such as a marketing team that needs to evaluate a project. Describe the current state of the enterprise, including operating costs, profitability, potential marketing costs, hiring specialists, technical expenses, market analysis.
- Strategic. They are among the most long-term. These include the mission, critical success factors, strategies for achieving goals, and implementation schedule.
- Technical and economic. Describe the need for a product, service, target demographic indicators, required capital, recommendations for further development.
- Operating rooms. Includes implementation markers, deadlines for achieving goals for the coming year, and employee responsibilities.
There are also growth BPs needed to scale a company. They are compiled for internal or external purposes. If growth requires investment, the BP must contain all the nuances to satisfy potential investors. If there is no need for additional injections, the emphasis is on financial forecasts of sales and expenses.
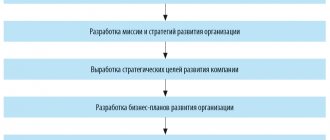
Example of an organizational plan in a business plan
When working on a business plan, theoretical postulates and advice are important, but it is best to turn to ready-made examples. It is thanks to the organizational sections included in the work and well-tested in practice that you can easily write this paragraph, reorienting it to suit yourself and the characteristics of your enterprise. This will help novice entrepreneurs avoid many mistakes and solve the problem of section design, carefully and in detail describing all the subtleties of the structure of an organization of any type.
Example of an organizational plan in a business plan.
Forms of business organization in terms of
This paragraph is intended to justify the choice of ownership form. In Russia, there are legally three types:
- individual entrepreneurship;
- limited liability company, joint stock company;
- corporation.
Sole proprietorship is the most common form, since the procedure for registering an individual entrepreneur is simple, you can get tax holidays, and the tax rate is low.
If several people are planning to open a business, then you need to choose an LLC. The form is suitable for a network of retail outlets, production, establishments selling alcoholic beverages. The classifier contains a whole list of activities that only LLCs are allowed to carry out.
Open and closed joint stock companies require the involvement of founders; the authorized capital of such an enterprise is divided by the number of shares.
If the BP is aimed at creating an LLC or JSC, you need to supplement this paragraph with the following information:
- about governing bodies;
- on the composition of the co-founders and their terms of reference;
- on the rights and obligations of each founder.
Depending on the form of business organization, the enterprise management plan may vary.